Electrocardiography is included in the list of recommended studies for most patients, both adults and children. Therefore, its competent removal is an important skill for a medical specialist. The procedure involves sequentially performing the necessary steps and taking into account some features and nuances, which we will look into today.
Stages of the ECG procedure
Electrocardiography is a research method in which the electrical fields of the heart are recorded, provoked by contractions of the heart muscle. As a result, the specialist receives a cardiogram - an image of curve graphs. They can be displayed on a monitor or recorded on a special paper tape. To carry out this type of diagnosis, you need professional medical equipment - a cardiograph. This device consists of three required elements.
- An input device including electrodes, lead cables and their switches.
- Signal amplifier - allows you to amplify them to the value necessary for analysis.
- Recording unit for direct recording of a cardiogram.
When conducting an ECG, a specialist works sequentially with all these blocks, following a clear algorithm. It, in turn, is divided into several stages:
- preparing the room, equipment and patient for ECG;
- application of electrodes and connection of leads according to a specific scheme;
- adjusting the gain to correctly display the signal on the cardiogram;
- direct recording of the electrocardiogram.
For informative and reliable research results, it is necessary to avoid errors at each of these stages. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at their algorithms and features.
Carrying out an ECG using Neb
To carry out Neb diagnostics, it is first necessary to correctly position the electrodes. There are three of them in total, painted in different colors. To improve the contact properties between the electrode and the patient’s skin, a special paste with a slightly thick consistency, made from baby soap and plain water, is used. To avoid staining the sheet that is placed under the body of the subject, you need to use oilcloth.
The connection occurs as follows:
- The first to attach is the electrode, which is active and yellow in color. Using a special flat electrode plate, it is installed under the left shoulder blade in its lower corner. Installation in the V7 position is allowed - it was noticed that in this position the result is more accurate. In addition, this method greatly facilitates the diagnosis of bedridden patients.
- The next one is a red electrode, which, unlike yellow, is passive. It is attached using a pear-shaped suction cup. The location of this electrode is the second intercostal space on the right side of the chest.
- The last electrode is painted green and is attached to the body, like the red one, using a suction cup. Unfortunately, it is often the green conductor that is not fixed where it is needed. Its correct location is at the apex of the heart. The correct place can be determined by palpation - apical impulses are felt in the right place. Often the location is determined incorrectly and the electrode is installed in the fifth intercostal space, on the left side of the clavicular line.
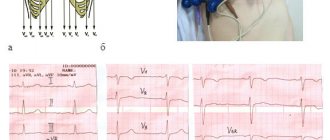
After connecting all the electrodes, you can determine the triangle with the heart inside. The ECG procedure occurs by switching a toggle switch to connect various axes in series:
- the first axis is formed from the red and yellow electrodes. This lead is parallel to the back of the heart. This standard position is written with the letter “D” and is considered the most accurate indicator for determining the presence of cardiac pathologies, and more precisely, for myocardial infarction associated with the left ventricle;
- the second position is indicated by the letter "A". The axis, which is formed when the toggle switch is switched for the second time, is located on the side of the front wall of the organ. The data that needs to be taken at this stage does not greatly affect the originally obtained values;
- the third switch remains similar to axes V2 and V3, the only difference is the location of the heart organ in the chest. The results of the third switch are written with the letter “I”, but they also do not greatly affect the data obtained during the first switch.
So, we can draw the following conclusion - the most accurate and important data in diagnostics is obtained when the toggle switch is first switched and the axis with the letter “D” is formed.
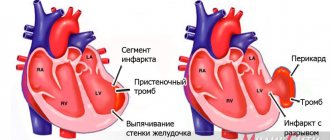
The ECG showed distinctive signs, which consisted of the ST line. It can be raised and have a hump-shaped shape, which directly indicates myocardial infarction, or it can be lowered and imply hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart. When analyzing the results, it is also important to pay attention to the shape of the tooth - it can be negative symmetrical and negative asymmetrical.
Installation of electrodes
Both reusable and disposable electrodes can be used to take an ECG. The first option is used more often in medical institutions, because is more economical. Kit includes:
- electrodes for limbs: 4 pieces;
- electrodes placed on the chest (one or 6);
- pears with suction cups.
Each electrode must be connected to a cable that matches its color. The designations must be memorized, because Most often there is confusion with them.
- A red cable is connected to the electrode on the right hand.
- On the left is yellow.
- The green wire is connected to the electrode on the left leg.
- On the right there will be a black, grounding cable that does not take readings.
Features of the event
- The patient exposes his body and lies down on the sofa. In this case, it is necessary to behave completely calmly;
- The health worker degreases the places where the electrodes will be attached with alcohol;
- A special gel is applied to the electrode plates, which conducts current well, as can be seen in the photo;
- The algorithm for applying electrodes is simple: electrodes are attached in the chest area, on the hands and ankles. In this case, the plates are fixed either with adhesive tape or with special suction cups;
- The algorithm for taking an ECG is as follows: the electrodes receive electrical impulses from the heart and transmit them through wires to the device itself, which processes them;
- Then the specialist turns on the device and begins recording ECG data. The device produces a long tape with a graph in the form of teeth of different heights. The monitoring data is deciphered by a doctor who will determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
At the ProfMedPomoshch clinic you can get an ECG with interpretation and learn everything about the work of your heart.
Fixation of electrodes on the limbs
On the legs, a pair of electrodes are fixed on the inside of the lower leg at the very bottom. It must be remembered that a grounding sensor is attached to the right leg. On the hands, electrodes are attached to the forearms.
With standard leads, indicators are taken as follows:
- left and right hands - first position;
- right arm and left leg - second position;
- left leg and arm - third position.
Thus, an Einthoven triangle is obtained, each side of which corresponds to one and possible leads.
Enhanced leads involve collecting a signal using one electrode, which records the potential difference between the area where it is applied and the conventional electrical zero. They have the following designations:
- right hand - aVR;
- left hand - aVL;
- left leg - aVF.
How does it work
Electrodes placed on the patient's body receive weak electrical currents that originate in the heart. As they become stronger, they are recorded using a galvanometer. Any changes in ripple are transmitted to a special device, which produces data in the form of a broken line on a paper tape.
The next important stage of the examination is the decoding of the data that the doctor deals with. The fact is that the teeth on the tape are sized according to special standards. If there are any deviations from the norm, then there is a health problem. And only a specialist can correctly decipher the cardiogram and establish an accurate diagnosis.
In order for the results of an ECG to be reliable, there is no special preparation, but some rules must be followed.
Fixation of electrodes in chest leads
If a single-channel study is carried out, then only one electrode is used. But in modern ECGs, for more accurate diagnosis, in most cases, 6 are used. They are designated by the Latin letter V and are superimposed at the following points:
- V1 - at the right edge of the sternum in the 4th intercostal space, the red wire is connected;
- V2 - also in the 4th intercostal space, but on the left edge of the sternum, wire color - yellow;
- V3 - in the middle between the 4th and 5th intercostal spaces along the left line, connect the green cable;
- V4 - along the midclavicular line in the 5th intercostal space, wire color - brown;
- V5 - along the anterior axillary line in the 5th intercostal space, connected to a black cable;
- V6 - in the middle of the axillary line at the same level with V450m, the wire color is blue (possibly purple).
Defibrillation Introduction Guide
Health care professionals must have knowledge and practical skills in the use of manual and automatic external defibrillators to effectively provide resuscitation.
What is defibrillation
Defibrillation is a method of applying an electrical current to the myocardium. The technique involves emitting an electrical impulse to restore muscle activity in the heart. A correctly performed procedure allows you to resume the interrupted blood circulation process and prevent death.
Automated external defibrillators (AEDs) are used by emergency physicians and critical care physicians to improve survival rates for people experiencing sudden cardiac arrest.
Rice. 1 Automatic external defibrillator
The most effective procedures are those carried out immediately after a circulatory disorder. The more time passes since the cessation of healthy myocardial activity, the lower the likelihood of saving the patient’s life. Every minute of delay increases the risk of death by 10%.
Preparing for defibrillation
Automatic devices for cardiac rehabilitation (automatic defibrillators) are equipped with voice and visual instructions. When providing emergency medical assistance, rescuers must:
- free the victim’s chest from clothing, clean it from dirt and moisture;
- attach electrodes to the victim’s skin;
- connect the electrodes to the defibrillator.
Application of electrodes
The resuscitation team should reduce the level of transthoracic resistance to improve electrical conduction. Shaving the patient's chest will help to increase the productivity of rescue efforts.
The electrodes must be pressed firmly against the surface of the skin. To increase current conductivity and prevent burns, you can use an additional conductor (conductive gel between the electrodes and the place where they are applied). The location of the electrodes depends on the nature of fibrillation (ECG monitoring will show atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation, etc.). If the defibrillator does not have an ECG function, the electrodes are often placed on the patient's chest in the most standard manner - on the sides of the chest, one on the right, the other on the left (axillary). It is important to apply the electrodes so that the electrical discharge between them passes through the fibrillating myocardium.
If emergency care is provided to a person with an implanted pacemaker, the lead should be positioned as far away from the implanted device as possible to minimize the risk of pacemaker failure.
Low effectiveness of the defibrillation procedure for women is observed when electrodes are placed on the mammary glands.
Improved contact
To increase the conductivity of an electrical discharge, physicians should use specialized gels or pastes that are applied to the surface of reusable electrodes. When using disposable (adhesive) electrodes, additional improvement in conductivity in the form of a gel is not necessary, since the electrodes are soft and have good contact over their entire area with the patient’s skin, repeating the shape of the chest. It is important not to allow any liquid to flow between the two electrodes, as this may cause sparks or even prevent the discharge from passing directly through the myocardium. During the procedure, it is prohibited to use ultrasound gel as it has insufficient conductivity.
Which electrodes should you choose?
Adhesive electrodes are the most convenient. They are soft, have low transthoracic resistance, and therefore are characterized by maximum efficiency during resuscitation measures. In addition, doctors do not need to constantly hold them in their hands, lubricate them with conductive gel and apply them again for the next shock.
Soft and hard electrodes have the same speed of first defibrillation. At the same time, flexible models allow for optimal restoration of heart rhythm. Conductive gels are used in conjunction with rigid electrodes.
Features of the use of AEDs
Defibrillation success can be predicted by analyzing the fibrillation waveform. During resuscitation, the doctor may administer a single shock or a series of electrical impulses.
Studies show that mortality increases with short interruptions of chest compressions for mechanical ventilation. To improve the efficiency of emergency care, clinicians are advised to administer a single shock and resume resuscitation, followed by a second shock 2 minutes later.
First category
The effectiveness of the first discharge of an AED is 65%-90% depending on the current power and the patient's condition. Clinicians should set an initial energy level.
Otherwise, there is a high risk of myocardial damage. In general, the use of high energy levels during the first shock does not reduce survival in patients discharged from hospital.
The optimal power is 200 J. Doctors do not associate the efficiency of the device with the shape of the discharge, which can be linear or exponentially truncated.
Second and subsequent categories
The shock should be repeated at 360 J. The clinician may maintain a constant or increasing power protocol.
If the emergency technician observes a return to heart rhythm, a subsequent shock is given without increasing the energy level.
Gurevich lead
The electrode from the right hand (red) is moved to the second intercostal space on the left at the edge of the sternum. From the left hand (yellow) - in the 5th intercostal space along the posterior axillary line on the left. Green (left leg) in the 5th intercostal space along the midclavicular line.
The lead switch is alternately placed in the following positions: I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF. The leads are marked accordingly: DM - posterior sections, AM - anterior and IM - inferior. CKR – lateral and partially anterior, CKL – posterior wall and CKF – anterior wall of the left ventricle.
Continue reading: Analysis of defects resulting from an ECG examination
ECG
New materials
- Normal electrocardiogram. Special part of the methodological manual - 12/16/2010 03:58
- Analysis of defects when taking an ECG (continued) - 12/15/2010 11:54
- Analysis of defects made during ECG examination - 12/15/2010 11:28
Do you need preparation for an ECG?
No specific preparation is required for an ECG, but in order to obtain the most correct results of the study, several aspects should be taken into account. The day before the diagnosis, experts recommend:
- sleep well;
- try to eliminate excessive emotional experiences;
- intra-nutritive electrocardiography is performed exclusively on an empty stomach;
- a few hours before the test, it is recommended to reduce fluid and food intake;
- During the diagnosis, you need to take off your clothes, relax, and not be nervous.
The day before the procedure, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
During the ECG procedure, the patient is advised to relax and breathe evenly.
You should not engage in sports or heavy physical work. If you need to take certain medications, this must be discussed with your doctor. In addition, it is not recommended to visit a sauna, steam bath, or perform other procedures associated with the effects of heat on the body.
Important! No special preparation is required before performing an electrocardiogram, but following the above tips will help you obtain the most accurate data from any type of ECG.