The human brain is a unique organ. He manages all functional systems in the human body. Proper brain function depends on good blood supply. Insufficient blood flow leads to necrotization of neurons and causes focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature, or discirculatory encephalopathy.
Nature of the pathology
The entire brain is penetrated by an extensive blood supply system. It consists of four main arteries, from which small vessels diverge, penetrating into all structures of the brain. Impaired blood flow (dyscirculation) in some areas of the brain leads to oxygen starvation and rapid focal degradation of neurons and brain cells.
There are two types of pathology:
- Ischemic
(of a residual nature). As a result of blockage or narrowing of arteries and vessels, diffuse damage to the structural tissues of the brain occurs. Ischemia of the circulatory system supplying the brain can be caused by atherosclerotic disease or thrombosis. Post-ischemic disorders are dangerous due to their sudden rapid development. One of the manifestations of this type of pathology is Binswanger's disease. - Multi-infarction
(vascular origin). Changes in blood pressure provoke a sharp narrowing and expansion of blood vessels. This causes small vascular infarctions (micro-strokes), the consequence of which is an irreversible change in the brain matter in a small area. The culprit of this condition is arterial hypertension and atrial fibrillation.
Risk group
Previously, discirculatory encephalopathy was a disease characteristic of older people. Now the disease has become much younger, from 50 to 30 years
. It can develop in people who lead an inactive lifestyle and have harmful addictions (smoking, alcohol, drugs, overeating).
Persons suffering from diabetes mellitus type I and II, hypercholesterolemia or having a genetic predisposition are also at risk of focal destructive changes in the structural tissues of the brain.
In men, more often than in women, the disease can appear against a background of constant stress or psycho-emotional overstrain.
Diseases of vascular origin
Here it should be clarified: vascular genesis is an indication of the origin of the disease, and not the disease itself. When talking about brain diseases of vascular origin, we mean changes associated with circulatory disorders - in venules, arteries, veins, and so on.
These types of violations are divided into several main groups.
- Transient cerebral circulatory disorders are distinguished between general cerebral and focal. The first are characterized by headache, nausea, vomiting; focal ones are responsible for short-term disturbances in motor functions and sensitivity of certain parts of the body. A distinctive feature of this vascular disorder is reversibility . Treatment promises complete restoration of function.
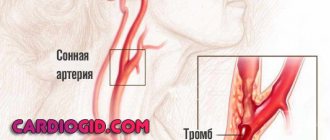
- Blockage of the arteries - narrowing of the working channel in any case leads to deterioration of nutrition, which significantly affects the functionality of the served areas of the brain, and can cause changes of an ischemic nature. Here treatment may even include surgery.
- Rupture of a cerebral aneurysm, cerebral hemorrhage – in fact, a stroke of ischemic or hemorrhagic origin.
Stages and symptoms of disease development
The disease is progressive. It is characterized by a paroxysmal course, with sharp rapid deterioration. Discirculatory focal changes have several stages of development.
Initial
Minor processes of tissue change begin in small areas of the brain. Their occurrence is facilitated by mild dysfunction of the vascular circulatory system.
Symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- recurrent headaches;
- easy absent-mindedness;
- increased emotional sensitivity (irritability and tearfulness);
- noise in the head, frequent dizziness;
- partial loss of non-professional memory;
- concentration on performing one type of activity;
- mild ataxia.
Average
The blood supply to the brain deteriorates significantly. Blockage of blood vessels provokes necrotization of cells in the superficial structures of the brain (gray matter).
The symptoms of the initial stage worsen, the following signs are added:
- Sleep disturbances. The patient sleeps more often during the day, and sleep lasts longer than at night.
- Interest in new knowledge disappears, intelligence becomes dull.
- Behavior becomes aggressive, character becomes self-centered.
- There is a lack of coordination of movements (staggering gait, uncertain hand movements).
- There is a progressive loss of memory and professional skills.
Heavy
Due to the development of chronic dyscirculatory encephalopathy in the lesion, most of the cells of not only gray matter, but also white matter die. This causes disturbances in brain function.
At this stage, neurological changes reach their peak. The clinical picture is disappointing. All previous symptoms become irreversible, which entails consequences such as:
- complete loss of ability to work and self-care;
- loss of memory and skills, development of dementia (dementia);
- loss of control over motor and speech functions.
Early diagnosis of the disease is difficult because at its initial stage there are no pronounced symptoms. Delayed diagnosis makes treatment more difficult.
If the blood flow per minute slows down to 10 ml/100 g and below
, the process of instant destruction of brain tissue, which is irreversible, starts.
Symptoms
Clinically, focal brain damage can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- high blood pressure;
- epilepsy attacks;
- mental disorders;
- dizziness;
- congestion in the vascular bed of the fundus;
- frequent headaches;
- sudden muscle contractions;
- paralysis.
The main stages in the progression of cerebral vascular disorders can be identified:
- At the initial stage, the person and the people around him practically do not notice any deviations. Only attacks of headaches are possible, which are usually associated with overload and fatigue. Some patients develop apathy. At this time, the lesions are just emerging, without leading to serious problems of nervous regulation.
- At the second stage, deviations in the psyche and movements become more and more noticeable, and pain becomes more frequent. People around you may notice outbursts of emotion in the patient.
- The third stage is characterized by massive death of neurons, loss of control of the nervous system over movements. Such pathologies are already irreversible; they greatly change the patient’s lifestyle and personality. Treatment can no longer restore lost functions.
There are often situations when changes in the blood vessels of the brain are detected completely by chance, during a diagnosis prescribed for another reason. Some areas of tissue die asymptomatically, without significant disruptions in nervous regulation.
Causes
The duration of development of each stage of the disease depends both on the reasons that caused it and on the age of the patient. Foci of damage can be either single, dystrophic, or multiple. The following causes of dyscirculatory encephalopathy are known:
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- hormonal disorders;
- infectious and inflammatory processes of the brain;
- oncology;
- ischemic blood flow disorders;
- head and cervical spine injuries.
If you have a history of such diseases accompanied by atypical symptoms, regular monitoring by a neurologist is required. This will allow you to identify possible pathology before it becomes irreversible.
Dystrophic damage
In addition to damage caused by vascular origin, other types of the disease are distinguished. These are focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. This type of disease occurs due to a lack of nutrients. Let's consider the main causes of the disease: too low blood pressure, osteochondrosis, oncology, skull injuries.
Dystrophic brain damage is detected due to the lack of useful substances. Patients exhibit the following symptoms: brain activity deteriorates, dementia, migraines appear, muscle tissue is weakened, some muscle groups are paralyzed, and dizziness.
Diagnostics
Since dyscirculatory focal changes for a long time are similar to chronic fatigue syndrome, the disease requires accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis is established after a thorough examination, as well as six-month observation by a neurologist. The basis for a medical opinion about the nature of the pathology is the constant presence of the main symptoms.
When contacting the doctor, he prescribes a comprehensive examination, which consists of the following methods:
- Laboratory research. They check the composition of the blood, determining the presence of negative factors. This requires general and biochemical blood tests and a coagulogram. Cholesterol and sugar levels are also determined.
- Continuous blood pressure monitoring.
- ECG and EchoCG.
- Echogram and electroencephalography of the brain.
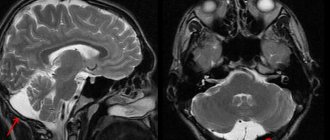
- MRI.
- Fundus examination.
Advantages of MRI diagnostics
As a result of pathological dyscirculatory changes in the structural tissues of the brain, characteristic morphological signs appear. They are diagnosed using magnetic resonance examination methods: nuclear MRI, magnetic resonance imaging and angiography.
An MRI examination allows you to identify foci of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, localize their exact location and determine the cause of pathological changes in the brain.
- Diffuse transformations of the cerebral cortex. The provoking factor is congenital or acquired pathology of the cerebral or spinal arteries (intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine, arterial thrombosis or narrowing of the lumen).
- Multiple focal tissue damage. This pathology precedes the development of stroke. This condition is characteristic of senile or pathogenetic vascular atrophy accompanying dementia, epilepsy, and ataxia.
- Age-related microfocal changes. Their appearance is typical for brain tissue after 55 years, since with age structural tissues are increasingly susceptible to endogenous changes. MRI diagnoses only those microdamages that arise as a result of negative external influences.
- Discirculatory foci in the white structural matter of the parietal or frontal lobes. The cause of such changes is hypertension from the acute stage, or this tissue structure is due to its formation during the period of prenatal development (congenital).
The presence of focal changes in the brain is the basis for periodic preventive examinations at least once every three months.
At-risk groups
If there are no signs of the disease, it is preferable to find out about risk groups. According to statistics, focal disease more often manifests itself in the following disorders: atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, VSD, diabetes, heart muscle disease, regular stressful situations, work without movement, abuse of alcohol, tobacco, drugs, obesity.
As a result of age-related changes, brain damage occurs. After reaching 60 years of age, minor lesions of the disorder appear.
Therapy
Treatment of discirculatory focal lesions depends on the stage of the disease and the reasons that provoked its appearance. To achieve a positive effect, it must be timely and under the supervision of the attending physician.
Therapy for pathology in arterial hypertension can stop the spread of the disease and reduce the likelihood of developing a stroke by 45–50%. Drug treatment is designed to stabilize blood pressure and ensure uniform blood flow in the vessels of the brain. The following drugs are used:
- ACE inhibitors;
- beta blockers;
- antiplatelet agents;
- anticoagulants;
- vitamin complexes.
If the cause of the disease is atherosclerosis, statins (cholesterol-lowering drugs) and diet are added to standard hypertension treatment. It is administered to normalize cholesterol levels and prevent the formation of atherosclerotic blood clots.
To prevent discirculatory focal changes, medications that stimulate brain nutrition are prescribed. Physiotherapy, massage, and reflexology can be prescribed as rehabilitation therapy.
Severe disorders of the cerebral blood supply may require surgical intervention.
The stable functioning of the body depends entirely on the brain. To prevent the occurrence of pathologies and the irreversible changes associated with them, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular preventive examinations.
Doctors' recommendations
Quit tobacco products or get rid of addiction. Do not drink alcohol or drugs. Move more, do exercises. The permissible intensity of physical activity is determined only by a doctor. Sleep 7-8 hours a day. Doctors advise increasing sleep duration when diagnosing such disorders.
You need to eat a balanced diet; it is preferable to develop a diet together with your doctor in order to take into account all the nutritional components that help with destructive processes in the brain. Neurons need to be nourished with useful substances.
Review other bad habits. It is better to get rid of regular stressful situations. It is better to change your job if it is a little stressful. Relax more often, choose the most suitable ways for this. Visit the doctor for examinations at the specified frequency in order to timely record changes in pathological processes and timely apply therapeutic techniques.
Nervous tissues are characterized by increased vulnerability. Neurons die when there is a lack of oxygen, so you need to treat your body with special attention.