When do you need to take a General blood test without leukocyte formula (venous blood)?
- To assess general health (routine medical examinations, screening examinations, etc.);
- For diagnostics at the first stage of a wide range of diseases that may manifest themselves as changes in the characteristics of peripheral blood;
- Diagnosis of anemia, polycythemia along with the study of hemoglobin and hematocrit;
- Monitoring ongoing drug treatment for patients suffering from bleeding or chronic anemia;
- Determination of the activity of erythrocyte formation processes in the bone marrow.
Ways to increase neutrophil levels
The most important thing is that you work with your doctor to learn about the reasons for your low neutrophil levels. And get a prescription from your doctor to treat the underlying cause or disease. Treatment for neutropenia will depend on the causes of the disorder.
Medical treatments that help reduce the impact of neutropenia:
Granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (g-CSF): This is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce neutrophils and other granulocytes to release into the bloodstream. The most commonly used version of g-CSF is a drug called filgrastim.
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): A naturally produced glycoprotein that has a similar role in stimulating neutrophil production. Factors are used to restore the number of neutrophils after chemotherapy.
Antibiotics : These medications may be prescribed prophylactically to reduce the chance of infection in neutropenic patients. They are often taken at a time when the neutrophil count is at its lowest.
Talk to your doctor about additional lifestyle changes listed below. None of these strategies should ever replace what your doctor recommends or prescribes.
Lifestyle changes to increase neutrophil counts:
Exercise , eat a healthy diet , quit smoking and avoid drinking alcohol .
It is important to have a balanced diet containing sufficient amounts of vitamins B12 and folate, which are necessary for the formation of white blood cells, including neutrophils. (, )
Regular moderate exercise can help improve neutrophil function and activity. ()
When your neutrophil count is low, you may be more vulnerable to infections. Proper hygiene can reduce the risk of these infections. ()
Detailed description of the study
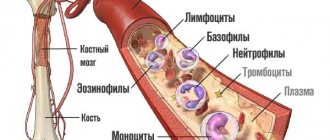
Blood is a multicomponent structure that is part of the internal environment of the body. It consists of plasma, which contains a suspension of formed elements - red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes and some others. This study is carried out to assess quantitative blood parameters. During a general blood test, the number of blood cells and cells of different types is determined, which gives an idea of their functioning, and, accordingly, the state of the body.
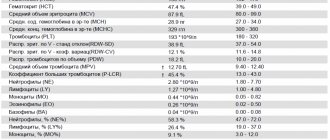
During a general blood test (CBC) without a leukocyte formula, the following parameters are assessed:
- number of leukocytes (white blood cells, WBC);
- number of red blood cells (RBC);
- hemoglobin level (hemoglobin content, Hb);
- hematocrit (hematocrit, Hct);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- average hemoglobin content in erythrocytes (MCH);
- mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC);
- platelets (platelet count, PC).
The main indicators that are included in the table of results of a general blood test:
Leukocytes (WBC, White Blood Cells)
Leukocytes, also called white blood cells or white blood cells, are a population of diverse but keyly similar immune system cells that are produced in the bone marrow. They are capable of active movement, capture and absorption of foreign particles and cells of their own body. In the first case, leukocytes provide protection from microbes and other foreign particles, in the second - maintaining the constancy of the internal environment of the body, ensuring the timely destruction of old or defective cells of the body's own.
Their number increases in the presence of inflammation - the degree of increase in the number of leukocytes indicates the severity of the infectious process. CBC allows you to estimate only the total number of leukocytes. In order to assess the population composition, structure and structure of leukocytes, it is necessary to additionally undergo a leukocyte formula analysis. If a general blood test shows abnormalities, the doctor may prescribe a more detailed option.
You can also take a blood test with leukocyte formula and ESR at the Hemotest Laboratory.
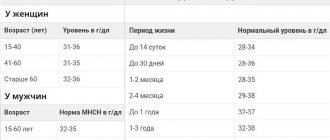
Hemoglobin (Hb, Hemoglobin)
Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. Its main function is to transport oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide from them. The normal limits for it are well known, which vary somewhat depending on gender and age: in men, its content is, on average, higher than in women, and in children of the first year of life, a slight decrease in its content in the blood is normal. The combination of iron in hemoglobin with oxygen gives the blood a bright scarlet hue.
A decrease in hemoglobin levels beyond normal values is one of the types of anemia. This disease is also called “anemia”. There are several types of anemia depending on the causes, but with any of them the amount of hemoglobin per unit volume of blood will be reduced.
The most common cause of anemia is iron deficiency in the diet. In addition, anemia can occur due to blood loss and impaired absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract. The cause may also be too intense destruction of erythrocytes (red blood cells) or disruption of their formation. To clarify the diagnosis, additional tests will be required. A complete blood count can be a starting point in the diagnosis and treatment of anemia.
Hematocrit (Ht, Hematocrit)
Hematocrit is a numerical indicator of the ratio of the volume of blood cells, 99% of which are red blood cells, to the total blood volume. However, the statement is true only in cases where the size of red blood cells is normal. If the number of normal-sized red blood cells increases, the hematocrit also increases. In cases of large or small red blood cells, this is not always the case. For example, with iron deficiency, red blood cells decrease and the hematocrit will be reduced, but the number of red blood cells per unit of blood may be normal or even slightly higher.
Hematocrit increases with dehydration, lung and heart diseases, and while in high mountains. On the contrary, a decrease in hematocrit is observed with anemia of various origins, with liver diseases, with the consumption of large amounts of fluid or the administration of large volumes of fluid intravenously.
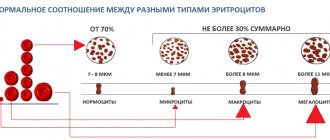
Red blood cells (RBC, Red Blood Cells)
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) are the formed elements of blood, not entirely correctly called “cells”. They are indeed formed from precursor cells, but upon maturation they lose their nucleus - one of the key features of a living cell. In this way, they provide themselves with the opportunity to implement a highly specialized function: transporting oxygen to the cells of the body and removing carbon dioxide from them. These are the most numerous formed elements of blood, which have the shape of a biconcave disc. Their entire volume is occupied by hemoglobin in order to effectively transport oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide and metabolic products from them.
The number of red blood cells is a very important indicator of health. CBC allows you to identify deviations from the norm and prescribe additional studies to clarify the diagnosis and identify the causes of changes in the number of red blood cells, including:
Erythropoietin is a hormone that is synthesized in the kidneys and stimulates the formation and maturation of red blood cells. With a lack of oxygen - hypoxia, it is synthesized more intensely. The number of red blood cells may decrease due to a lack of this hormone.
Vitamin B12, folic acid and sufficient iron are necessary components for adequate hemoglobin synthesis and red blood cell formation.
Red blood cells live in the bloodstream for 120 days, after which they are destroyed in the spleen. Excessive destruction of red blood cells can also lead to a decrease in their number. Determining the number of red blood cells, together with assessing the hemoglobin content, establishing hematocrit and characterizing red blood cells, makes it possible to diagnose the type of anemia and its causes with a high degree of probability. Based on this data, it is possible to select the most effective treatment.
Color Index (CPU)
The numerical indicator of hemoglobin saturation of red blood cells indicates the amount of hemoglobin per red blood cell.
MCH (Mean Cell Hemoglobin, average hemoglobin content in red blood cells)
Numerical expression of the average hemoglobin content in one red blood cell. Together with MCV it is used for the differential diagnosis of anemia.
MCV (Mean Cell volume, average volume of red blood cells)
Numerical indicator of the average volume of red blood cells. Normally it has no diagnostic significance, but is necessary for the differential diagnosis of anemia in combination with MCH.
If the range of red blood cell volumes is large, or there are many red blood cells of a changed shape, then averaging the indicator will not be so informative, but differences in the size and structure of red blood cells indicate the need to pay close attention to this: this is not the norm.
MCHC (Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration, mean hemoglobin concentration in red blood cells)
An indicator that shows the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells. A sensitive indicator of changes in hemoglobin synthesis processes - a possible cause of iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, and some hemoglobinopathies.
Platelets (PLT, Platelets)
Platelets are the formed elements of blood. Like red blood cells, they are formed from precursor cells, but they are not cells: they do not have a nucleus or other important intracellular structures, so their lifespan is only about a week.
The loss of cellular characteristics is due to the high specialization of these formed elements: almost their entire volume is filled with granules, which contain substances involved in the processes of blood coagulation and platelet aggregation. With the help of special receptors, platelets detect a violation of the integrity of blood vessels, form a clot there and stimulate local blood clotting to stop bleeding.
An increase in the number of platelets can occur as a result of taking certain medications, indirectly indicating malignant neoplasms, some inflammatory and infectious diseases. Some types of cancer, malaria and bronchial asthma can reduce their levels. Their levels may also be reduced as a result of disruption of their formation from progenitor cells in the bone marrow or due to increased consumption during wound healing.
The main symptom of a low platelet level is bleeding, up to life-threatening conditions: from the appearance of bruises even with light pressure and bleeding gums, to internal hemorrhages.
Segmented neutrophils are reduced - possible reasons
A decrease in the number of neutrophils in the blood most often indicates a protracted course of some disease of viral etiology. These cells do not stay in the bloodstream for long. As they mature, they transform from rod-nuclear to segmented, and within 2-3 hours they leave the bloodstream, concentrating in inflamed tissues.
If the human body has not been subjected to any complex or immune-suppressing procedures, then we can assume:
- severe viral infection, such as measles or rubella.
- allergic reaction;
- infection after a bite, for example, malaria;
- presence of helminths;
- hereditary pathology.
In addition, neutrophils in the blood decrease as a result of:
- radioactive exposure;
- taking a certain group of medications;
- undergoing chemotherapy;
- exposure to exotoxins, poisons and certain chemicals on the body.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary not only to donate blood for analysis, but also to obtain a conclusion from the doctor conducting the examination. The presence of helminths is easily determined using laboratory tests, and infection with malaria should be preceded by a trip to an exotic country and a local insect bite. Therefore, the results of a blood test are not a diagnosis, but a reason to undergo a more in-depth examination to identify or refute a low neutrophil count.
However, with the help of a blood test, it is easier for the doctor to determine the etiology of the disease if the patient comes with complaints about the severity of any symptoms. For example, if the transcript indicates that segmented neutrophils are lower and lymphocytes are higher than normal, this will indicate that the patient has contracted a viral infection and does not need antibacterial therapy.
Negative effects of elevated neutrophil levels
Too much neutrophil activity can increase the release of agents toxic to cells (cytotoxic) and over-activate parts of the immune system. Under normal circumstances, this helps protect your body from infection or injury. However, prolonged and unregulated release of these compounds can cause damage to body tissue. (, )
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Research shows that neutrophils increase inflammation in plaque in hardened arteries (atherosclerosis). ()
After a heart attack, neutrophils clear away dead cells and debris around the damaged area in the heart. After the neutrophils die, macrophages release growth factors that cause inflammation and tissue formation, which creates scarring in the heart (cardiac fibrosis). ()
A high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a predictor of cardiovascular disease. It is associated with an increased risk of developing irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) and death in patients undergoing treatment for cardiovascular disease (percutaneous coronary intervention) [,].
A study of 4,625 people found that higher neutrophil counts were associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. () Similar results were obtained in another study with 4,860 men. ()
Another study of 18,558 people found that high levels of neutrophils increased the risk of cardiovascular disease such as ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction. ()
Cancer
In general, neutrophils may play a role in the initiation of cancer , tumor formation , and the spread of metastases to other sites in the body. ()
Neutrophils promote inflammation by releasing reactive oxygen species (ROS). Research shows that they also suppress the antitumor immune response (by stimulating TGF-β to release iNOS or ARG1, which suppresses cytotoxic CD8+ T cells that fight cancer cells). ()
Neutrophils contribute to the development of cancer. (source)
The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio ( NLR = neutrophil/lymphocyte) is a blood marker that scientists have used to try to predict the outcomes of various types of cancer (colon, lung, head, neck, ovarian, etc.). Numerous studies have shown that elevated NLR values are associated with poor prognosis in colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, and lung cancer . (, , , )
In a review of more than 100 studies and 40,000 patients, an NLR value greater than 4 was associated with worse overall cancer survival rates. ()
Interpretation of the NLR depends on the clinical context. However, we can roughly imagine how this indicator can be assessed:
- Normal NLR level is in the range of 1-3
- An NLR of 6-9 suggests mild inflammatory stress (eg, in a patient with uncomplicated appendicitis)
- Severely ill patients often have an NLR of ~9 or higher (sometimes reaching values close to 100)
NEU formation and typing
Neutrophil formation begins in the red bone marrow. The particles then penetrate the plasma, where they are divided into segments for further maturation. NEU typification is determined by their maturation:
- Rods. This name was given by its external feature – the shape of the sticks. They are immature (young) blood cells and do not have a segmented nucleus. When their number goes beyond normal limits, the leukocyte formula has a “shift to the left,” otherwise cell rejuvenation. In most cases, such an analysis result requires checking the patient for the presence of oncology. And also an increased content of stabs is a clinical sign of a diabetic crisis.
- Segmented. Fully mature blood cells, with a pronounced nucleus at the base. Exceeding their number shifts the leukogram formula to the right (cellular aging). This may be a sign of depletion of bone marrow reserves, chronic renal failure (CRF). A non-pathological shift to the right is a recent blood transfusion (blood transfusion).
The average lifespan of a mature neutrophil in tissues is three (sometimes four) days. To timely replenish the antimicrobial “army,” the red brain is forced to produce them in large quantities. After eradication (destruction) of pathogenic microorganisms, NEU die and, together with other organic decay products, form purulent masses.
This type of programmed cell death is called netosis. There are certain types of bacterial microorganisms that NEUT cannot resist, and then the infectious-inflammatory process becomes chronic and protracted.
The overall high concentration of granulocytes of this type is designated as neutrophilia or neutrophilic leukocytosis (absolute or relative). A decrease in their number in the blood is called neutropenia. The neutrophil response to bacterial and infectious invasions is primary in acute inflammation. In relation to chronic pathological processes, NEU do not show much activity.