Sodium in food: main sources in the diet
Sodium enters the body with food and, in much smaller quantities, with water. Many foods rich in sodium do not contain sodium. The main source of sodium in the diet is table salt (also known as sodium chloride or NaCl), which is added to foods during the cooking phase to enhance the flavor of meats, vegetables, or soups and sauces. It also acts as a natural preservative to protect foods from spoilage.
Sodium is also found in highly processed foods:
- fast food;
- sauces and dry soups;
- ready-made dishes (not only salty, but also sweet);
- processed meats (cold cuts, sausages, sausages, salami, wild boar, pate and canned meats).
The sodium content in 100 grams is up to half the daily value of this ingredient for an adult!
sodium in food
Sodium is also found in large quantities in the following foods:
- bread and buns;
- salty snacks: sticks, crackers, chips, vegetable juices, canned goods (for example, canned beans);
- bouillon cubes;
- universal seasoning with dried vegetables for dishes;
- pickled vegetables: olives, capers, peppers, onions, pickles (pickled cucumbers, sauerkraut, beetroot starter);
- smoked and salted fish, canned fish;
- rennet cheeses, that is, yellow ones (for example, Parmesan, Roquepol, feta, Camembert);
- some dairy products: grain cheese, Turkish drink “Ayran”.
Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium)
Sodium, potassium and chlorine are the body's main electrolytes.
Electrolytes are mineral compounds that are capable of conducting electrical charge. Being in tissues and blood in the form of salt solutions, they help move nutrients into cells and remove metabolic products from cells, maintain water balance and the required level of acidity in them.
Research method
Ion selective electrodes.
Units
mmol/l (millimoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet for 24 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Electrolytes are mineral compounds that have an electrical charge. They are found in body tissues and in the blood in the form of salt solutions. Electrolytes contribute to the movement of nutrients into the body's cells and the removal of metabolic products from them, maintaining the water balance of cells and stabilizing acidity (pH).
The main electrolytes in the human body are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+) and chlorine (Cl-).
Most of the sodium is found in intercellular fluids. Potassium is found primarily inside cells, but small but vital amounts are found in plasma, the liquid part of the blood.
Monitoring potassium levels is very important. Even minor changes can affect the heart rate and the heart's ability to contract. Chlorides migrate through the membrane either inside or outside the cell and thereby maintain its electrical neutrality. Chloride levels usually correspond to sodium levels.
Sodium, potassium and chlorides enter the body with food, while the kidneys are involved in removing them from the body. The balance of these chemical elements is an important indicator of human health, particularly how the kidneys and heart function.
Measuring the levels of sodium, potassium and chloride together allows you to determine the anion “window” - the difference in the content of anions and cations in the blood. Its abnormal value is not a specific indicator, but suggests the presence of toxic substances in the body or the likelihood of metabolic abnormalities caused by fasting or diabetes.
Ionized calcium is a cation that circulates freely in the blood and makes up 46-50% of all blood calcium. Its level increases when blood pH decreases and decreases when alkalization occurs. For every 0.1 unit decrease in pH, ionized calcium responds with an increase of 1.5-2.5%.
Because electrolyte and acid-base imbalances are associated with a wide range of acute and chronic diseases, electrolyte testing can be ordered for both hospitalized patients and those newly presenting to emergency departments.
What is the research used for?
- For electrolyte screening and acid-base imbalance testing.
- To monitor the effectiveness of treatment for imbalances affecting the functioning of certain organs.
- The total blood calcium level is often sufficient for a preliminary assessment of calcium metabolism. It usually reflects the amount of free calcium in the blood, since often the balance between bound and free calcium is a stable and fairly predictable value. However, in some people this ratio is disrupted, so the level of total calcium is not a criterion for assessing overall calcium metabolism. In such cases, checking the ionized calcium becomes necessary.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Electrolyte | Reference values |
| Potassium | 3.5 - 5.1 mmol/l |
| Sodium | 136 - 146 mmol/l |
| Chlorine | 98 – 106 mmol/l |
| Calcium | 1.16 - 1.32 mmol/l |
Levels of potassium, sodium and chlorine depend on their dietary intake, body water content and the amount of electrolytes excreted by the kidneys. In addition, it is influenced by natriuretic proteins, which promote the excretion of sodium by the kidneys, as well as the hormone aldosterone, which maintains sodium concentration at a constant level and increases the body's loss of potassium.
Among all electrolytes, the most important indicators for a person are potassium and sodium levels. When kidney function is impaired, the body can sometimes retain excess fluid to dilute sodium and chloride so that its concentration drops below normal.
With severe fluid loss, the concentration of potassium, sodium and chlorides can increase sharply. Some forms of heart disease, muscle problems, nervous system problems, and diabetes also cause abnormal levels of one or more electrolytes.
To determine the cause of electrolyte disturbance and prescribe the correct treatment, it is important to find out which electrolyte balance is disturbed. If such abnormalities are not treated, the patient faces dizziness, seizures, irregular heartbeat and even death.
Reasons for increasing the level of ionized calcium:
- acidosis,
- excess vitamin D,
- malignant neoplasms,
- primary hyperparathyroidism,
- benign parathyroid adenomas,
- metastatic bone lesions.
- alkalosis,
- magnesium deficiency,
- pancreatitis,
- postoperative period,
- sepsis,
- injury,
- lack of vitamin D.
- Reasons for decreased ionized calcium levels:
Daily sodium requirement
The level of sodium in the blood in women and men depends on:
- age;
- gender;
- level of physical activity.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends:
- adults – consume no more than 5 grams of salt per day from all sources (1 level teaspoon)
- children – no more than 3 g (about 2/3 flat teaspoons).
5 grams of salt contains about 2.4 grams of sodium. The normal sodium content in body fluids for an adult is from 136 to 145 mmol per liter of blood.
Sodium and health
Hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, affects 29% of US adults, and reducing excess sodium intake can lower blood pressure. 89% of adults and more than 90% of children exceed 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
(see above) regarding sodium intake. 86% of American adults with hypertension consume more than the recommended 2,300 mg of sodium per day. For 75% of individuals consuming more than 2300 mg per day, the potential risk of death from stroke and coronary heart disease increases. The main sources of sodium for American adults include bread and baked goods, deli meats, pizza, poultry, soups, sandwiches, cheese, pasta, processed meats such as meatloaf with tomato sauce, and savory snacks. Sodium intake is higher in individuals whose daily diet contains higher-calorie foods. To reduce sodium intake, it is recommended to reduce the calorie content of the daily diet and increase the proportion of fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy products. 1) At the same time, according to the results of the prospective epidemiological study PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology), it was found that the relationship between sodium intake and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases was observed only in countries in which the average intake exceeded 5 g/day. The authors of this study believe that interventions to reduce sodium intake are appropriate only in these countries, but not in other countries. 2)
Sources. 1) Jackson SL et al. Prevalence of Excess Sodium Intake in the United States - NHANES, 2009–2012 / MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016;64:1393-7. 2) Mente A, O'Donnell M, Rangarajan S, et al. Urinary sodium excretion, blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and mortality: a community-level prospective epidemiological cohort study. Lancet 2018; 392:496–506; doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31376-X.
See also: Vasilenko V.V. A little about salt.
World Health Organization recommendations
Most people consume too much sodium in the form of salt (equivalent to an average of 9-12 grams of salt per day) and not enough potassium.
High salt intake and insufficient potassium intake (less than 3.5 g) contribute to high blood pressure, which in turn increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. 1.7 million deaths could be prevented each year if salt intake was reduced to the recommended level of less than 5g per day. People often have no idea how much salt they consume per day. In many countries, most salt comes from processed foods (eg, ready meals, processed meats such as bacon, ham and salami, cheese and salty snack foods) or foods consumed in large quantities (eg, bread) . Salt is also added to food during cooking (eg, broth, bouillon cubes) or at the table (eg, table salt, soy sauce, and fish sauce). Salt intake can be reduced:
- not adding salt, soy sauce or fish sauce during cooking
- without putting salt on the table
- limiting consumption of salty snack foods
- by choosing foods that are lower in sodium.
Some food manufacturers are making reformulations to reduce the salt content of their products, and it's a good idea to read food labels to check how much sodium they contain.
Source. WHO Information Bulletin N°394. September 2015
Ways to reduce sodium in food. Recommendations from the Healthy Eating Guidelines for Americans
In 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture released a new version of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. It makes the following recommendations regarding reducing sodium intake:
- Cook your own food. Restaurant meals tend to be higher in sodium compared to home-cooked foods. As a general approach to reducing your sodium intake, try cooking and eating at home more often.
- Explore new flavors. The more often a person eats salty food, the more he begins to like it. You can train yourself to eat less salty foods - try alternative additions such as fresh herbs or garlic.
- Compare and make changes. Try to shop for low-sodium foods as an alternative to saltier ones. Check the nutrition label; if it says more than 150 mg sodium per serving, look for a lower sodium option. This also applies to canned foods such as soups, beans and vegetables, and processed meats such as bacon.
- Reduce the amount of bread, chips and crackers you consume. Although they may not taste too salty, store-bought breads, chips and crackers, as well as pre-made sandwiches and pizza, add a significant amount of sodium to your diet. Some breads contain 230 mg of sodium per serving—10% of your daily value in just 1 slice. Check nutrition labels to choose breads with less than 150 mg of sodium per slice, and be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Buy groceries around the perimeter of the store. The foods that contain the highest amounts of added sodium are typically displayed in the interior aisles of the grocery store. Shop around the perimeter of the store, where the healthiest foods are usually stocked—vegetables and fruits in particular.
Source. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020. Eighth edition. Translation by Univadis.
Mineral water and sodium
Natural mineral water can be a source of sodium.
The sodium content of different waters varies significantly. GOST R 54316-2011 “Natural mineral drinking waters. General Technical Conditions" does not classify water depending only on the sodium content in it and does not classify sodium as biologically active components, however, the sodium content in various types of water is fixed by Appendix B (mandatory) to GOST R 54316-2011 "Requirements for chemical indicators groups, hydrochemical types of mineral waters and their medicinal use.” The main (but not the only) parameter by which mineral water is classified as medicinal, medicinal-table or table water is its mineralization. Considering that the average modern person consumes more sodium than required and that excess sodium can have a negative impact on health, it is not recommended to drink large amounts of medicinal or medicinal table mineral water without studying the mineral composition and without consulting a specialist. It should be borne in mind that water manufacturers are not required to indicate the sodium content of this water. It is sufficient to indicate on the label the total content of sodium and potassium cations Na++K+. Below is a list of mineral waters indicating their content of sodium cations Na+ or the total content of sodium and potassium cations Na++K+ (depending on what information is provided by the mineral water manufacturer).
| Mineral water | Na+ content , mg/l | Na++K+ content , mg/l |
| Essentuki No. 17 | 2700–4000 | |
| Lysogorskaya | 2800–4500 | |
| Donat Mg | 1565 | 1582 |
| Essentuki No. 4 | 2000–3000 | |
| Growled-Su | 1200–1450 | |
| Borjomi | 1000–2000 | |
| Nabeglavi | 915–1250 | |
| Novoterskaya healing | 800–1100 | |
| Smirnovskaya | 600–800 | |
| Slavyanovskaya | 600–800 | |
| Kashinskaya | 250–400 | |
| Narzan | 50–250 | |
| Mattoni | 70–120 | |
| MagnesiA | 6-20 | |
| Valser | 0,3-10,5 | 0,5-12 |
The first three lines in the above table are occupied by medicinal mineral waters (Essentuki No. 17, Lysogorskaya and Donat Mg), the rest are medicinal table waters.
Appendix 1. Sodium compounds in the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification (ATC)
Sodium compounds are used in the treatment of a wide variety of diseases; they are presented in a variety of sections of ATC:
Section A. Drugs affecting the digestive tract and metabolism
Code A01. Dental preparations A01AA Preparations for the prevention of caries A01AA01 Sodium fluoride A01AA02 Sodium monofluorophosphate A01AA51 Sodium fluoride in combinations with other drugs A01AB Antimicrobial drugs for local treatment of diseases of the oral cavity A01AB19 Sodium perborate Code A02. Preparations for the treatment of diseases associated with acidity disorders Code A02A. Antacids A02AB04 Dihydroxyaluminum sodium carbonate (Carbaldrate) A02AH Antacids in combination with sodium bicarbonate Code A06. Laxatives A06AA Emollients A06AA02 Sodium docusate A06AB Contact laxatives A06AB08 Sodium picosulfate A06AB58 Sodium picosulfate in combination with other drugs A06AD Osmotic laxatives A06AD13 Sodium sulfate A06AD17 Sodium phosphate A06AD21 Sodium tartrate A06AG Laxatives in enemas A0 6AG01 Sodium phosphate A06AG10 Sodium docusate, including in combination with other drugs Code A12. Mineral additives A12CA Sodium preparations A12CA01 Sodium chloride A12CA02 Sodium sulfate A12CD Fluoride preparations A12CD01 Sodium fluoride A12CE Selenium preparations A12CE01 Sodium selenate A12CE02 Sodium selenite Code A16A. Other drugs for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic disorders A16AX03 Sodium phenyl fibrate
Section B. Drugs affecting hematopoiesis and blood
Code B01. Anticoagulants B01AB12 Bemiparin sodium B01AX05 Fondaparinux sodium Code B03. Antianemic drugs B03AB01 Sodium iron citrate B03AB03 Sodium ferdelate Code B05. Plasma replacement and perfusion solutions B05CB01, B05XA03 Sodium chloride B05CB02 Sodium citrate B05CB04, B05XA02 Sodium bicarbonate B05XA08 Sodium acetate B05XA09 Sodium phosphate B05XA14 Sodium glycerophosphate
Section C. Drugs for the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system
Code C02. Antihypertensive drugs C02DD01 Sodium nitroprusside Code C05. Angioprotectors C05BA02 Sodium apolate C05BA03 Sodium heparin C05BA04 Pentosan sodium polysulfate C05BB04 Sodium tetradecyl sulfate
Section D. Preparations for the treatment of skin diseases
Code D03.
Preparations for the treatment of wounds and ulcers D03AX11 Sodium chlorite Code D08. Antiseptics and disinfectants D08AX04 Sodium tosylchloramide D08AX07 Sodium hypochlorite Section G. Preparations for the treatment of diseases of the urogenital organs and sex hormones
Code G04. Preparations for the treatment of urological diseases G04BX15 Sodium pentosan polysulfate
Section H. Hormonal preparations for systemic use
Code H03. Preparations for the treatment of thyroid diseases H03AA01 Levothyroxine sodium H03AA02 Liothyronine sodium
Section J. Antimicrobials for systemic use
Code J04. Drugs active against mycobacteria J04A Antituberculosis drugs J04AA02 Sodium aminosalicylate J04B Antileprosy drugs J04BA03 Sodium aldesulfone
Section L. Antineoplastic drugs and immunomodulators
L01XD Sensitizing drugs used for photodynamic/radiotherapy L01XD01 Sodium porfimer
Section M. Drugs for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
M01C Basic antirheumatic drugs M01CB01 Sodium aurothiomalate M01CB02 Sodium aurothiosulfate
Section N. Drugs for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system
Code N01. Anesthetics N01AF03 Sodium thiopental N01AX11 Sodium oxybate Code N02. Analgesics N02BA04 Sodium salicylate N02BB02 Metamizole sodium N02BB52 Metamizole sodium in combination with other drugs, excluding psycholeptics N02BB72 Metamizole sodium in combination with psycholeptics Code N07. Other drugs for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system N07XX04 Sodium oxybate
Section P. Antiparasitic drugs, insecticides and repellents
P01C Preparations for the treatment of leishmaniasis and trypanosomiasis P01CB02 Sodium stibogluconate P01CX02 Sodium suramin
Section R. Drugs for the treatment of diseases of the respiratory system
Code R03. Preparations for the treatment of obstructive diseases of the respiratory tract R03AK04 Salbutamol and sodium cromoglycate R03AK05 Reproterol and sodium cromoglycate
Section S. Drugs for the treatment of diseases of the sensory organs
Code S01. Preparations for the treatment of eye diseases S01AX07 Sodium borate S01AX10 Sodium propionate S01XA03 Sodium chloride hypertonic solution S01XA05 Sodium edetate Back to section
Causes and consequences of sodium deficiency in the body - hyponatremia
Sodium requirements depend on many factors, including physical activity. Causes of sodium deficiency include:
- insufficient sodium intake (low sodium diet);
- overhydration of the body - increased excretion of sodium in urine or sweat (for example, with regular exercise, dehydration on a hot day);
- food poisoning with diarrhea and vomiting;
- use of laxatives or dehydrating substances;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hypothyroidism,
- kidney, heart, liver failure;
- Bartter's syndrome (also known as inappropriate vasopressin release syndrome).
Lack of sodium in the human body, that is, hyponatremia , is very dangerous, as it can lead to dehydration, disruption of the functioning of many organs, and if the level of sodium in the body is less than 110 mmol/l, even death. Fortunately, this condition is very rare.
Hyponatremia can be mild, chronic, or acute. Main symptoms of sodium deficiency:
- headache and dizziness;
- lack of appetite;
- gastric symptoms: diarrhea, constipation, vomiting;
- trembling of the muscles of the arms and legs;
- low blood pressure;
- drowsiness and weakness;
- confusion and difficulty concentrating;
- difficulty remembering;
- dry mucous membranes and skin.
normal sodium level in blood
Detailed description of the study
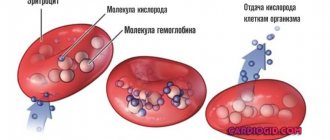
Sodium (Na) is the most important trace element in the human body. Most of it is found outside cells: in plasma, lymph, and digestive juice. Sodium is involved in mineral metabolism, maintains a certain charge in cell membranes for the transport of substances and osmotic pressure, and also participates in the transmission of neuromuscular excitation.
Nerve cells transmit impulses to the muscles. An impulse is an electrical current that is generated on the membranes of neurons. It occurs due to the movement of ions - potassium (K), sodium, calcium (Ca), chlorine (Cl) - into and out of the cell. There is a lot of K inside neurons, and Na and Cl outside. Changing the permeability of the membrane to different ions creates an electrical impulse that causes muscle contraction.
The biological effects of Na are associated with the exchange of other ions. Sodium, together with hydrogen ions, helps reduce acidosis - increased acidity - of the blood. This is important for maintaining acid-base balance in the body. Sodium and calcium increase the contractility of muscle cells. The work of the potassium-sodium pump located in the cell membrane is of great importance for the body. It begins to work when the concentration of Na inside the cell or K outside the cell increases. With the help of the pump, osmotic pressure is maintained, amino acids, sugars are transported, and carbohydrates are metabolized.
Water molecules enter from the outside through the gastrointestinal tract and are then absorbed in the intestines into the blood. The movement of water from the extracellular to the intracellular space is associated with the work of electrolytes; Na is an important regulator of this process. Its high concentration outside cells is capable of retaining water in the intercellular space. Another regulatory mechanism is to ensure the operation of the sodium-potassium pump.
Sodium enters the body with food, its main source is table salt. Smoked foods, cheese, meat, and olives are also rich in microelements. The daily norm is 2-3 g, but with increased sweating - fever, physical activity - the need for sodium increases. Na is absorbed in the small intestine and excreted in the urine. Hormones and biological substances regulate sodium levels in the blood. Thus, aldosterone (adrenal hormone) and angiotensin II help increase the concentration of the trace element in the plasma by enhancing its reabsorption into the blood (reabsorption) from the kidneys.
A test to determine the concentration of sodium in the blood is used to diagnose a lack of sodium (hyponatremia) or excess (hypernatremia) in the body.
Hyponatremia occurs when there is insufficient intake of a microelement from food, with diarrhea or vomiting, if a person drinks a lot of liquid with a low sodium ion content, excessive fluid retention in the body due to diseases of the heart, kidneys, liver, overdose of diuretics, etc. Clinical symptoms of hyponatremia include weakness, increased heart rate, and decreased urine output.
The causes of hypernatremia are an increase in sodium intake from food, renal failure, vomiting and/or diarrhea (if it is not possible to take an adequate amount of fluid), hyperaldosteronism, and diabetes insipidus. Hypernatremia is clinically manifested by shortness of breath, edema of various locations, increased blood pressure, dry mouth and thirst.
Blood sodium level testing is a basic test that is performed for many diseases and reflects metabolic changes in the body.
Causes and consequences of excess sodium in the body - hypernatremia
Excess sodium, or hypernatremia , is most often caused by poor diet - excessive consumption of foods containing sodium. Inadequate fluid intake, fever, and increased metabolism (common, for example, with thyroid hormone disorders) can also contribute to elevated blood sodium levels.
Too much sodium is also dangerous because it causes too much water to be retained in the cells and tissues of the body. This may lead to:
- increased blood pressure;
- narrowing of blood vessels;
- development of high blood pressure.
The consequences of excess sodium are swelling of the legs and body, water cellulite.
Chronic excess sodium can lead to:
- renal failure;
- nephrolithiasis;
- cardiovascular diseases.
This increases the risk of stroke, aneurysms and heart attack. More often than not, excess sodium causes hypertension and worsens the disease in people who have already been diagnosed (although this is not a rule because not all patients experience increased blood pressure after eating salt).
High salt intake (the most common cause of excess sodium in the body):
- increases the risk of developing stomach cancer;
- increases the excretion of calcium from the body, which negatively affects the mineralization of bones and teeth.
Physiological role of main ions in the child’s body
Sodium. Major extracellular cation
The body of an adult contains 70-100 g of sodium, while in children its content is lower.
It is found in all tissues in the form of sodium cations. The sodium content in the blood plasma is 130-150 mmol/l (biochemical blood test for a child, Markushka children's clinic). Sodium is the main extracellular cation: it accounts for more than 90% of all plasma cations. About 85% of sodium ions are present in free form and approximately 15% of it is retained by proteins.
Sodium creates and maintains osmotic pressure of body fluids (mainly extracellular), retains water in the body, participates in absorption in the intestines and reabsorption of glucose and amino acids in the kidneys. Sodium is involved in the regulation of the acid-base state of the body, is an alkaline reserve of the blood, and an activator of certain enzymes. The sodium content in the cellular microenvironment determines the magnitude of the membrane potential and, accordingly, the excitability of cells. Together with potassium ions, sodium stimulates the ATPase activity of cell membrane fractions, stabilizes the sympathetic part of the nervous system, and takes part in the regulation of vascular tone.
The main amount of sodium enters the body with table salt; a child consumes a small amount in the form of sodium bicarbonate, citrate, sulfate and monosodium glutamate, which are found as additives in food products. A child's daily need for sodium is on average 1.5-2.0 mmol/l.
The main amount of sodium (about 95%) is excreted by the kidneys in the urine in the form of sodium salts of phosphoric, sulfuric, carbonic and other acids. Sodium is also excreted through sweat and through the intestines. A deficiency or excess of sodium causes serious changes in a child's body.
Potassium. Intracellular cation
Unlike sodium, it is an intracellular cation . In adults, the potassium content is approximately 53 mmol/l and 95% of it is exchanged. The level of potassium in the child's body is lower. The main amount of potassium (90%) is found inside cells in the form of fragile compounds with proteins, carbohydrates and phosphorus. Part of the potassium is contained in cells in ionized form and provides membrane potential.
A child’s daily need for potassium is 1.5-2.0 mmol/l. The main dietary sources of potassium are products of plant origin. Potassium is excreted from the body primarily by the kidneys (80-90%), and to a lesser extent by the digestive tract and sweat glands. The main regulator of its excretion in urine is aldosterone.
Potassium is involved in a number of vital physiological processes: together with sodium, it creates and maintains the osmotic pressure of body fluids (mainly intracellular), and participates in the regulation of the acid-base state of the body. Potassium is an activator of a number of enzymes; together with the sodium cation, it forms an electrochemical potential in cell membranes. The level of potassium in cells and the extracellular environment plays a critical role in the activity of the cardiovascular, muscular and nervous systems, in the secretory and motor functions of the digestive tract, and the excretory function of the kidneys. Typically, the release of potassium from cells depends on an increase in their biological activity, the breakdown of protein and glycogen, and a lack of oxygen. Potassium deficiency and excess cause serious changes in the child’s body.
Calcium. Intracellular and in bone tissue
It is found intracellularly in various tissues and almost exclusively in the form of soluble protein complexes. Only in bone tissue , which includes up to 97% of all calcium in the body, is it found mainly in the form of insoluble extracellular inclusions of hydroxyapatite.
The calcium content in the body in children is about 200 mmol/l, in adults - 475 mmol/l. The calcium content in the blood is maintained at normal levels in the range of 2.5-2.8 mmol/l.
The main source of calcium is food: milk and dairy products, eggs, legumes, dried fruits, etc. For infants, the main source of calcium is milk. An adult maintains a zero calcium balance , and a positive one for children.
Calcium participates in physiological processes only in ionized form. Calcium is a necessary participant in the process of muscle contraction, an essential component of the blood coagulation system (conversion of prothrombin into thrombin, fibrinogen into fibrin, promotes platelet aggregation), as a cofactor or activator, it is involved in the work of many enzymes. Calcium is part of bones and cartilage in the form of apatites, is a stabilizer of cell membranes, and regulates the excitability of nerves and muscles. Calcium is an intracellular mediator in the action of some hormones on the cell, a universal trigger for many secretory processes. Calcium ionization depends on blood pH. With acidosis, the content of ionized calcium increases, and with alkalosis it decreases. Alkalosis and decreased calcium levels lead to a sharp increase in neuromuscular excitability.
Magnesium. Intracellular and in bone tissue
Like potassium, it is the main intracellular cation (its concentration in cells is much higher than in the extracellular environment). The total amount of magnesium in the body in children is 11 mmol/l, in adults - 14 mmol/l. Half of all magnesium is found in bones (1/3 of this amount is freely exchanged), 49% is in soft tissue cells; it plays a significant role in many enzymatic reactions, including the activation of ATPase. The level of magnesium in the blood is 0.75-0.9 mmol/l, while more than 60% of the cation is in ionized form.
The daily requirement for magnesium for an adult is about 300 mg. Green leafy vegetables and fruits, legumes and grains, and meat are the main food sources of magnesium. A significant amount of endogenous magnesium enters the digestive tract with digestive secretions. The main regulator of magnesium content in the body is the kidneys. If there is a lack of it in the body, it is completely reabsorbed by the kidneys.
Magnesium is a structural element of bone tissue. It stabilizes biological membranes, reducing their fluidity and permeability. By forming chelates with nucleic acids, it stabilizes DNA structures, associations of ribosomal subunits connected by transport RNAs to the ribosome. Magnesium is part of more than 300 different enzyme complexes, ensuring their activity. Magnesium cation reduces the excitability of the neuromuscular system, the contractility of the myocardium and vascular smooth muscles, and has a depressive effect on mental functions.
With magnesium deficiency, the excitability of the central nervous system increases, which is manifested by weakness and mental disorder (confusion, anxiety and aggressiveness), and the occurrence of seizures.
An increase in plasma magnesium levels (more than 1.5 mmol/l) causes nausea and vomiting. High concentrations of magnesium may cause hypotension.
Chlorine. Major anion of extracellular fluid
The main anion of the extracellular fluid is chlorine ; in the body it is predominantly in an ionized state (chloride anion) in the form of salts of sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, etc. The total amount of chlorine in the body is 33 mmol/kg. The distribution of chlorides in body fluids is determined by the distribution of sodium ions. In the blood, chlorides are found mainly in the form of sodium chloride. The concentration of chlorine in blood plasma normally ranges from 90 to 105 mmol/l; 90% of the chlorine is found in the extracellular fluid. The daily requirement of chlorine (2-4 g) is completely covered by table salt.
Chlorides are involved in creating and maintaining the osmotic pressure of body fluids and in the synthesis of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Chlorides are also involved in the generation of an electrochemical gradient on the plasma membranes of cells and are activators of a number of enzymes.
A change in the concentration of chlorine in the blood leads to a corresponding change in the concentration of sodium. However, sometimes a change in chlorine concentration is not accompanied by an equivalent change in sodium concentration. Excess chlorine leads to acidosis.
Phosphorus. Exceptionally great biological significance for a growing organism
About 70% of phosphorus is concentrated in bone tissue; it is part of the intercellular fluid and active biochemical compounds of every cell of the body. Phosphates are the main anions in the intracellular fluid, where their concentration is 40 times higher than in the extracellular environment. The content of inorganic phosphorus in the blood is 0.94-1.60 mmol/l, in children of the first year of life - 1.26-2.26 mmol/l.
The phosphate requirement of an adult is about 1200 mg/day. Phosphorus is present in sufficient quantities in the diet, as it is found in almost all food products and is absorbed (about 50%) in the form of inorganic phosphates.
Phosphates are a necessary component of cell membranes and play a key role in metabolic processes, being part of many coenzymes, nucleic acids and phosphoproteins.
Phosphate is a structural component of bones and teeth in the form of apatites, participates in the regulation of the concentration of hydrogen ions (phosphate buffer system), the most important component of organophosphorus compounds of the body: nucleotides, nucleic acids and phosphoproteins, phospholipids, etc. Organic phosphorus compounds (ATP, ADP) form the basis energy metabolism.
Excess phosphorus in the body is rare and is observed in cases of impaired renal function or hypofunction of the parathyroid glands. This leads to hypocalcemia and impaired bone metabolism. Manifestations of phosphorus deficiency are bone fragility, impaired dissociation of oxyhemoglobin, weakness, myopathy, cardiomyopathy.
Sulfates, bicarbonates
Sulfates are found in larger quantities in the intracellular space and are part of many biologically active substances. Sulfates are necessary to neutralize toxic compounds in the liver.
The bicarbonate ion is found in greatest quantity in the extracellular fluid. The bicarbonate ion is in dynamic equilibrium with carbonic acid and is a component of the body's main buffer system.
How to reduce your sodium intake?
European society far exceeds salt intake recommendations, resulting in elevated sodium levels in the body. To prevent hypernatremia and reduce the risk of hypertension, doctors recommend eating a low-sodium diet, called the DASH diet.
This is the healthiest diet that suits everyone. You can stick to it without worrying about your health or nutritional deficiencies. It prevents violations such as:
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes.
Avoid over-salting foods and limit your intake of foods that are extremely rich in this element (particularly fast food and salty snacks). It is also recommended to increase your intake of foods rich in magnesium (whole grains, cocoa, nuts) and potassium (vegetables and fruits).
You can replace salt in food with many spices, such as basil, oregano or marjoram. Low amounts of sodium can be found in vegetables, fruits and unsmoked meats, so these foods should form the basis of the DASH diet.
People have long had a difficult relationship with salt. The most popular seasoning all over the world is not just that, but also vitally necessary for humans. According to L. Dahl, perhaps salt is the most important nutritional factor affecting the control of blood pressure (BP) [1]. Moreover, the consumption of table salt is such an important component of nutrition that eliminating salt from the diet can lead to an irreversible catastrophe, namely death. After all, without salt, or rather without sodium chloride (NaCl), our body simply would not be able to perform its functions normally. It is sodium, which is mainly found in salt, that will be discussed. For your information, 100 g of salt contains 38.183 mg of sodium.
The main physiological functions of sodium are as follows:
— ensures the penetration of amino acids and carbohydrates into cells;
— stimulates the activity of digestive enzymes;
- participates in the passage of impulses along the nerve fiber along with potassium;
- accumulates fluid in the body.
The most important property of sodium from a physiological point of view is its ability to bind water. Thus, 1 g of salt is able to retain up to 100 ml of water in the body. When tissues and blood vessels are oversaturated with salt, an excess of water occurs in the body, which leads to an overload of the activity of all organs involved in a particular process. For example, the heart is forced to work harder, and the kidneys are forced to remove excess amounts of both water and salt from the body.
Currently, in many countries, salt intake ranges from 9 to 15 g per day [2]. Women consume slightly less salt than men. In our country, according to data collected in Moscow, they consume an average of 12 g of salt per day [3]. However, this amount of salt, according to modern researchers, is excessively high and harmful to health, since the human body needs and only needs 2-3 g of sodium per day, and in the case of increased sweating and significant loss of water - a little more. For a healthy person, 5-7 g of table salt per day does not pose any risk. However, continually exceeding this limit has consequences. For those suffering from arterial hypertension (AH) or prone to this disease, salt can be harmful. Why did salt receive such an unattractive status?
Salt intake and hypertension
Although salt is highly regarded by many people as a versatile seasoning, its intake has long been associated with elevated blood pressure and, more recently, with other health indicators [1–3].
Mechanisms linking salt intake and increased blood pressure include increased extracellular volume and peripheral vascular resistance due in part to increased sympathetic nervous system activity.
The results of epidemiological studies show that the development of hypertension is associated with salt consumption, there is a close relationship between sodium intake and the incidence of hypertension, and in addition, limiting sodium intake contributes to a significant reduction in blood pressure [4]. The authors of a meta-analysis of several randomized trials lasting from 1 month showed that a moderate reduction in salt intake caused a significant decrease in blood pressure in both individuals with and without hypertension: a reduction in salt to 6 g per day led to a decrease in blood pressure by 7/4 mmHg. in hypertensive patients and by 4/2 mm Hg. in normotensive patients [5]. One well-controlled, double-blind, crossover study examined three levels of salt intake in 20 participants with untreated hypertension in whom salt was reduced from 11.2 to 6.4 and 2.9 g per day. Before the study, blood pressure was 163/100 mmHg, salt intake was 11.2 g/day; when salt intake was reduced to 6.4 g/day, blood pressure decreased by 8/5 mmHg. and reached 155/95 mm Hg. With a further reduction to 2.9 g/day, blood pressure decreased by 8/4 mmHg. - up to 147/91 mm Hg. 19 out of 20 participants were observed for 1 year, their blood pressure did not exceed 145/90 mm Hg. at the lowest salt intake (up to 3 g/day).
According to H. Blackburn, who devoted his population-based work to the study of hypertension: “...a decrease in blood pressure among the population by 1-3 mm Hg. will have the same effect as all antihypertensive drugs taken together that are currently prescribed to patients with hypertension” [6]. And according to S. McMahon, expressed on the basis of an analysis of the results of numerous population studies, “...a decrease in diastolic blood pressure by 2 mm Hg. reduces the risk of death from stroke by 13%, and by 6 mm Hg. - by as much as 43%" [7].
The relationship between salt intake and hypertension has changed several times. The idea of the dangers of excess salt consumption was expressed in ancient Egypt. And in 1948, W. Kempner hypothesized that excess salt can increase blood pressure and proposed a rice-fruit-sugar diet with a limited amount of salt (less than 0.5 g per day) [8]. This diet helped reduce blood pressure in 64% of patients with hypertension and normalize blood pressure in 25% of patients with heart failure. More recent work proves that the main reason for the decrease in blood pressure when following the Kempner diet was precisely the sharp restriction of salt intake [9].
In 2007, the normal daily sodium intake for humans was determined to be from 2.6 to 4.8 g per day [10]. These figures, according to the study's authors, have remained unchanged in 45 countries for 50 years.
Salt consumption peaked in the 1870s, and after the invention of the refrigerator and freezers, the importance of salt as a preservative declined, but recently there has been a resurgence in salt consumption with more salty or processed foods [2].
However, not all people with regular high salt intake develop A.G. The whole point, as it turned out, is individual “sensitivity” to salt. The concept of salt sensitivity was originally proposed in the late 1970s, but the phenomenon is the subject of modern research that supports this theory. Some people may have increased sensitivity to salt, and when they consume it in excess, they develop hypertension. In others who are not sensitive, blood pressure remains normal even when consuming foods high in sodium. Salt sensitivity, as the author further notes, is a common biological phenomenon in human society. Depending on the method of determination and measurement, increased sensitivity to salt was noted in 25-50% of people with normal blood pressure and in 40-75% of patients with hypertension [11].
Active study of salt intake and its relationship with health began in the 1960s, when L. Dahl published the results of cross-population studies in the form of a now well-known graph (Fig. 1),
Rice. 1. Linear relationship between salt intake and blood pressure in different populations. which represents the entire spectrum of salt consumption around the world. The graph shows the influence or direct dependence of the spread of elevated blood pressure on the amount of salt consumed, which makes an important contribution to the salt hypothesis of increased blood pressure. The presented data leave no doubt that high blood pressure does not occur or is extremely rare in those regions where the population consumes small amounts of sodium throughout their lives (for example, Eskimos), and is often observed in areas where they consume a lot of salt (more than 20 g/day), as, for example, in the North of Japan, where elevated blood pressure is observed in 40% of the population. Differences in the prevalence of hypertension in countries or regions with high salt consumption were proven in more recent studies, which confirmed the assumption that it is the sodium content in food that is the main factor determining the incidence of hypertension in the population. It is possible, as the authors of more recent studies note, that other factors, such as obesity, race, constitutional characteristics, and dietary patterns, also affect blood pressure levels, as well as the amount of sodium consumed [12]. The results of a prospective 3-year study conducted in Russia showed that when salt intake was reduced from an average of 12 to 6 g per day, a statistically significant decrease in blood pressure in women with high normal blood pressure over 3 years was 3.27 mmHg. for systolic blood pressure (SBP) and 2.09 mm Hg. for diastolic blood pressure (DBP) [3]. In men, a more modest decrease in blood pressure was noted: SBP decreased by 1.92 mm Hg, and DBP by 1.91 mm Hg. With an increase in salt intake, blood pressure, on the contrary, increases. The Intersalt study estimated that salt intake greater than 6 g/day over 30 years would increase SBP by 9 mmHg. [13].
How much salt does the body need?
In the Stone Age, people consumed a minimal amount of salt; their diet consisted of natural, fresh foods. Currently, in North America there are surviving tribes of Indians leading a primitive way of life. Their daily sodium intake turned out to be 20 times less than that of people living in developed countries and eating mainly processed, refined foods. It is noteworthy that the blood pressure in Indians averaged 96/60 mmHg. and did not increase with age, which is not typical for modern civilizations.
The results of epidemiological studies around the world show that the optimal daily requirement for salt is 6-7 g, the so-called. approximately half of the amount consumed in modern society [13].
It is extremely difficult to accurately estimate the amount of sodium consumed daily, since even 24-hour urinary sodium excretion (the method considered the gold standard for determining daily salt intake) varies widely among individuals. M. Alderman [14] believes that there is no evidence that reducing salt intake to 3.5 g per day will improve health outcomes. And in 2013, the Institute of Medicine recognized sodium intake of up to 1.5 g per day as adequate [15].
The mechanism by which blood pressure increases with excess sodium intake remains unclear. It has been shown that in hypertension the flow of sodium and potassium through the erythrocyte membrane is disrupted. Due to disturbances of the potassium-sodium pump in hypertension, the sodium content in the intercellular space of smooth muscle tissue increases. This leads to increased excitability of the latter, which can cause an increase in blood pressure [16].
In the introduction to their work, L. Dahl et al. [1] state that salt is harmful and that the need for salt is less than the actual consumption. It's right. Most people eat more salt than necessary.
How to reduce salt intake?
For several million years, the ancestors of modern humans, like all mammals, ate foods low in salt. In table 1 presented
Table 1. Average salt content per 100 g of product, salt content in basic foods. From the data in table. 1 shows that the least amount of salt (and therefore sodium) is found in fresh vegetables and fruits.
In 2003, WHO recommended limiting salt intake in adults to 5 g per day (or 2 g sodium per day) [17]. Since then, these figures have been repeated in all the recommendations that we use to this day, including for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases [18].
Patients with hypertension are advised to sharply limit salt intake. This is achieved by following several rules proposed in 2000 and thanks to which you can reduce your daily salt intake by almost 2 times [14]:
- reduce the addition of salt when cooking by 50%,
- replace canned food with natural products,
- do not add salt to food while eating,
- reduce consumption of pickles,
- use unsalted seasonings,
- Avoid taking antacids due to the sodium they contain.
It seems so easy to reduce your salt intake by following these simple rules, but our contemporaries continue to eat more salt than is recommended by the medical community.
Why do we eat a lot of salt?
Although WHO recommended reducing salt intake for all adults back in 2003, actually reducing salt intake is difficult to achieve. Here's why: Due to sodium deficiency over a long period, from the Stone Age to the present day, people have developed a powerful salt appetite. This innate desire for salty foods makes it difficult in practice to reduce salt in the diet. However, when salt consumption is reduced (particularly in older people), due to a sharp change in taste habits, a person may lose his appetite altogether.
Humanity uses salt as needed to preserve food to avoid food poisoning, as salt is known to be a natural, effective and safe preservative. The fact is that 80% of salt consumed (Fig. 2)
Rice. 2. “Hidden salt” in food. Adapted from F. He and G. MacGregor, 2009 accounts for the so-called “hidden” salt that is found in all industrially processed foods where salt is added for longer storage. The review authors blame manufacturers for adding too much salt to make a profit [19]. When salt is added to meat products, their weight increases, since salt is capable of retaining water, and as a result, manufacturers make a profit without special costs. It is estimated that the mass of a product can be increased by 20% completely free of charge using salt and water. The amount of salt in industrially processed foods is mainly due to the fact that it makes cheap, unpretentious food edible at no cost. Heavily salted foods are in high demand due to the salty taste habit - and this also increases the profits of producers. With the constant consumption of salty food, thirst arises, which contributes to the consumption of soft drinks and mineral water, which also cause thirst, i.e., a vicious circle arises for buyers and increased profits for producers. Food manufacturers attribute the addition of too much salt to consumer preference and report that if the salt content is reduced, consumers will avoid purchasing. However, this does not take into account a very important factor: only 1-2 months pass from a change in the sensitivity of taste buds in the oral cavity to a decrease in salt concentration [20]. This means that a lower concentration of salt will still be perceived as salty. There is evidence that if salt intake is reduced, people will prefer foods with less salt and may be able to avoid the highly salty foods they previously ate [21]. In the experience of UK consumers, reducing the salt in a particular brand's staple products did not reduce sales and there were no complaints from customers regarding taste. Therefore, it is unlikely that reducing the salt concentration in food products will lead to abstinence from purchases. But salt is a major contributor to thirst, and any reduction in salt intake will reduce fluid intake with a consequent reduction in sales of soft drinks and mineral water, and some of the world's largest salty snack companies are part of soft drink companies.
Less is better?
Do I still need to reduce my salt intake? The main focus of the study of salt intake has been on its beneficial effects on blood pressure. Currently, there is growing evidence of another, negative effect of reducing salt on health, which is in no way related to blood pressure. By 2013, the results of studies on the impact of salt reduction on health indicators and the idea of an additional reduction of salt in the diet of all adults, including those who do not suffer from or are at risk of developing hypertension, were published. In the same year, a special committee of the Institute of Medicine, after analyzing the research results, published a report in which it expressed its opinion on this matter [15].
1. There is no evidence of an effect of modest reductions in blood pressure with reduced salt intake on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
2. The benefits of reducing salt for the entire population have not been proven.
3. There is a safe range (just a range, not a 5 g point) for salt intake.
4. The benefits or harms of sodium intake less than 2300 mg/day (5 g salt) have not been established, but there are concerns about sodium intake below 1.5 g/day (3 g salt).
Before changing recommendations to an even lower salt intake due to proven effective lowering of blood pressure, it is necessary to understand that a person may suffer not only from increased blood pressure, but also from other diseases, metabolic disorders, or, finally, just be healthy [7]. Thus, in a study involving patients with heart failure (HF), a deterioration in the course of the disease was noted in the group with salt restriction to 1-1.7 g per day: re-hospitalization was more often required and an increase in mortality was observed within 6 months from the start of the study compared with group consuming 2-4.7 g per day. Therapy S.N. was the same in both groups. A deterioration in the course of diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2 was also noted [22]. A recently published review demonstrated a decrease in blood pressure by 1% in normotensive patients and by 3.5% in patients with hypertension, while at the same time a significant increase in plasma hormones (Table 2):
Table 2. Increase in hormone levels with decreased salt intake (adapted from N. Graudal et al., 2012) Note. Here and in the table. 4: *p<0.05 – statistically significant values. renin, aldosterone, adrenaline, norepinephrine. The demonstrated increase in adrenaline and norepinephrine is statistically insignificant, since, as can be seen from the data in table. 2, there was an insufficient number of participants and the studies themselves. From the data in table. 3 is visible
Table 3. Increase in lipid levels with decreased salt intake (adapted from N. Graudal et al., 2012) that the increase in cholesterol by 2.5%, plasma triglycerides by 7% is significant (
p
< 0.05), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low (LDL) - statistically unreliable for the same reason (insufficient participants and studies to detect statistical significance) [23]. Moreover, as noted by F. He et al. [5], the adverse effects on lipids, especially triglyceride levels, are not simply an acute effect on salt reduction, as previously thought, but are persistent and long-term.
How does the ancient health science of Ayurveda evaluate salt? The salty taste will help drive away melancholy and allow you to feel the joy of life, no matter what it is.
In this regard, we can note a study on the effect of salt reduction on psychological status. In 2015, Japanese scientists published the results of a study in which 1,014 adult men reduced their salt intake from 10.8 g per day (4.3 g sodium) to 7 g salt, or 2.8 g sodium, per day, which caused development of depression [24].
Reducing dietary salt intake leads to a decrease in blood pressure, but the possibility of a negative effect of low salt intake on health cannot be ignored, excluding A.G. To recommend salt restriction for all healthy adults below 3 g of sodium (i.e., less than 6 g of salt or less than 1 teaspoon) requires a comprehensive weighing of the benefits and risks of this measure, which requires studies involving large populations. Although there are doubts about the benefits of reducing salt intake for all people, reducing salt intake is now an adjunct to drug treatment of hypertension and contributes to improved BP control, which reduces the need for medications. In table 4 indicated
Table 4. Contents of daily salt intake in food products (for persons from 19 to 65 years old) a list of products that cover the daily salt requirement.
It is necessary to consider the impact of reducing salt in the diet (in addition to lowering blood pressure) on other health indicators. So, in Fig. 3 shown
Rice.
3. Salt intake and mortality from stroke, heart attack and hospitalization for HF. U
-shaped curve that shows that both high and low salt intake increases cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality rates, stroke, myocardial infarction, and hospitalizations for congestive heart failure.
Results from several (but not all) observational studies have shown an increase in mortality not only at “higher levels” but also at levels below 2300 mg, indicating a U
-shaped relationship between sodium intake and mortality [25].
Randomized studies, carefully selected for statistical analysis, have shown the effect of sodium reduction on blood pressure not only in patients with hypertension, but also in healthy people with normal blood pressure (about 1 mm Hg) [25]. The immediate question is whether this effect is beneficial for the population as a whole in terms of morbidity, CVD prevention and mortality, and whether it is possible that these unproven assumptions about the benefits of salt restriction should lead to recommendations for reducing sodium intake in the entire population. The answer to this question can be found in the Institute of Medicine report cited above, one of the main points of which is to warn against further reduction of salt, i.e. below 3 g or below 1.5 g of sodium. The authors of several reviews are sincerely disappointed that the negative consequences of reducing salt intake in healthy people for the prevention of CVD, more precisely the deterioration of lipid and hormonal profiles, were ignored, and that recommendations for reducing salt in the diet remained the same [25–28]. To address the issue of reducing salt intake below 5 g per day, it would be advisable to conduct a large-scale, long-term, randomized clinical trial to determine whether such restrictions provide health benefits or not, and how this restriction affects survival and quality of life. Until the results of such a study are received, it is premature to talk about further reduction of salt in the diet. Many doubt whether it is even worth talking about reducing salt in the diet if the results of lowering blood pressure are so modest [9].
In most countries, more than ½ salt comes from industrially processed foods, including processed foods and sauces. In this regard, gradual, sustainable reduction of salt in processed foods is one of the easiest dietary changes to implement, as it does not require consumers to change their diet and still allows them to achieve the recommended 5 g per day [20].
In z
In conclusion, it should be noted that dietary recommendations for reducing salt must reflect the full variety of health consequences of this measure, including the impact on quality and life expectancy, and since we do not yet have such knowledge, no dietary recommendations can be scientifically justified [26 ]. There is no common point of view on additional reduction of salt in the diet of the population. Discussions are ongoing; the issue of reducing salt intake in order to prevent CVD for the entire population, including healthy people, has not yet been reached.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions:
Concept – O.M.
Collection and analysis of material - O.M., A.B.
Editing - O.M., A.B., E.P.
Sodium is normal in blood serum. Checking your body's sodium levels
Sodium is an element that is present in bones, inside cells, and in blood and other fluids. Most of it is in the blood serum, so to determine the level of sodium in the human body, a test is performed to measure the concentration of electrolytes in the blood (ionogram). This test involves taking a blood sample and then measuring the patient's electrolyte levels:
- sodium;
- potassium;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- phosphate ions;
- chlorine ions.
You don't have to order everyone to be tested, just your sodium level can be tested.
Testing your electrolyte levels is most often ordered when your doctor suspects dehydration or illnesses related to sodium imbalances in the body. Recommended for cardiac patients taking medications that increase urine production and excretion, as well as for chronic diseases with symptoms such as irregular blood pressure or heart problems. Measuring serum sodium does not require special preparation. It is best to go for the test in the morning (7:00 - 10:00), since the examination is carried out on an empty stomach or at least 8 hours after the last meal.
If your sodium ionogram is less than 136 mmol per liter of blood, it means you have low sodium levels in your body. On the other hand, a situation where the sodium concentration clearly exceeds 145 mmol in 1 liter of blood suggests its excess. Electroionogram interpretation should always be performed by a physician. Only he can correctly assess whether a given result is truly associated with abnormal amounts of sodium and other electrolytes in the body.
Basic electrolytes
Potassium
- an important component of most cells. Together with other electrolytes, potassium ions are responsible for the functioning of muscles and nerves, normal acid-base balance, and water metabolism. The blood contains only a small amount of the macronutrient; even minor fluctuations in its level lead to serious consequences. Significant deviations from the norm can lead to life-threatening conditions (shock, cardiac dysfunction, respiratory failure, etc.). Normal potassium concentration is 3.5-5.1 mmol/liter.
Magnesium
participates in energy production, enzyme synthesis, muscle contraction and other vital processes. It is absorbed from food into the gastrointestinal tract and excreted by the kidneys. A deficiency of this electrolyte can be caused by poor nutrition, problems with its absorption, or excessive loss in urine. Elevated levels may indicate kidney pathologies. Significant electrolyte deficiency leads to symptoms such as weakness, confusion, loss of appetite, and muscle spasms. Its excess manifests itself in a similar way. Heart rhythm disturbances and nausea may also be added to the symptoms.
Sodium
present in all tissues and fluids of the body. It is necessary for muscle contraction and maintaining water-salt balance. The macroelement is absorbed in the intestines from ordinary table salt. Deviations of its normal level are associated with a violation of one of the mechanisms of its maintenance. For example, normal sodium concentrations are disrupted if antidiuretic hormone, which prevents fluid loss through urine, is produced in abnormal amounts. A violation of the amount of this electrolyte leads to the appearance of edema or dehydration, as the amount of fluid in the tissues changes. Sodium testing is used in the diagnosis of many diseases (for example, pathologies of the kidneys, lungs, brain).
Chlorine
It is part of many biologically active substances and performs a number of physiological functions. Its level is normally relatively stable (a slight decrease in levels is observed after eating). A test for the amount of chlorine is often prescribed in conjunction with other studies to identify various pathologies. Its results are also used to determine the cause of weakness, prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, and breathing problems.