Norm
The norm in this situation is considered to be 120-140 g/l. Numbers may vary, it all depends on the physical and mental state. A long decrease or increase in comparison with normal data indicates problems in the body.
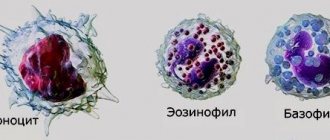
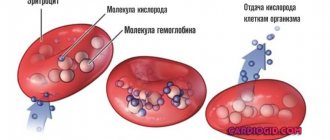
In women, an increased rate is rarely observed. It is possible for hemoglobin to increase by 10-20 units; if the values are even higher, then you definitely need to go to the doctor and get tested. The reasons may be different: blood disease, congenital heart pathologies, oncology, cardiopulmonary pathology. This plasma substance is present in red blood cells, which are produced by the bone marrow. These scarlet bloody cells transport air to various organs. Therefore, with an increase in hemoglobin, there is probably an air deficiency in some area of the body. Because of it, the bone marrow forms a lot of red blood cells, and plasma coagulability increases.
| Floor | Age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l |
| Children | 0 – 14 days | 135-200 |
| Up to 1 month | 100-170 | |
| 1-2 months | 95-130 | |
| 2-4 months | 100-140 | |
| 4-6 months | 110-140 | |
| 6-9 months | 100-150 | |
| 9-12 months | 115-145 | |
| 1-5 years | 110-150 | |
| 5-10 years | 115-145 | |
| 10-12 years | 120-160 | |
| Man | 12-15 years | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-170 | |
| 18-45 years old | 130-170 | |
| 45-60 years | 140-175 | |
| Over 60 years old | 120-175 | |
| Woman | 12-15 years | 110-150 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-155 | |
| 18-45 years old | 115-160 | |
| 45-60 years | 120-160 | |
| Over 60 years old | 110-170 |
Reduced hemoglobin
Low hemoglobin levels are often observed at different ages - both young and old.
Causes and symptoms
A lack of hemoglobin occurs when the body loses a large amount of it or receives little.
The main causes of low hemoglobin in older people:
• Monotonous food. Hemoglobin synthesis occurs thanks to foods containing iron, B vitamins, amino acids and food acids. If the diet lacks these substances, a person's hemoglobin level is reduced. A poor diet leads to a lack of this protein. For the same reason, low hemoglobin occurs in vegetarians. • Internal bleeding can cause hemoglobin deficiency. Women may experience gynecological bleeding. In men, various internal bleeding is possible: stomach, intestinal, kidney, nasal. Frequent blood loss leads to a lack of hemoglobin. • Severe infection • Chronic enteritis • Long-term use of IV drips • Excessive drinking
A reduced level of hemoglobin is associated with various disorders and internal problems in the human body.
If the level of this protein decreases without obvious reasons, examination by specialists is necessary. Low hemoglobin levels are a symptom of such problems, so the root cause needs to be identified and addressed. If you increase hemoglobin without finding out the root cause, it will return to normal only for a certain time.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin are the same for people of any age:
• dry skin • loss of strength and weakness • fatigue • dizziness • shortness of breath • palpitations
Anemia is a pathological condition that develops when hemoglobin decreases to less than 110 g per 1 liter. It occurs in almost half of people over 60 years of age. The development of anemia has nothing to do with age-related changes in the body: in a healthy pensioner, the blood functions in the same way as in a middle-aged person.
The appearance of anemia is influenced by diseases: frequent tumors, infections, diseases of the heart, autoimmune or endocrine systems, chronic illnesses. Such problems cause a decrease in hemoglobin levels, and its deficiency further aggravates the situation.
At the very beginning of the development of anemia, tests may be normal, but anemia already manifests itself in the first signs. Look out for these common symptoms of anemia:
• Dryness and paleness of the skin • The appearance of painful cracks in the corners of the mouth • Brittle and pale nails • Burning sensation and pain in the tongue • Brittleness and hair loss
Other additional signs of anemia subsequently develop:
• Fatigue, lethargy • Rapid breathing and pulse • Tinnitus • Frequent dizziness • Muscle weakness • Spots in the eyes • Difficulty concentrating • Fever • Irritability
At the beginning, there may be no symptoms or only dizziness and lethargy. With a further decrease in hemoglobin, these symptoms become more pronounced. With a large lack of hemoglobin, a person’s thoughts become confused and fainting is possible.
If a person discovers signs of anemia, he needs to go to the doctor for diagnosis and subsequent treatment. Treatment for anemia depends on its type. There are several types of disease. Let's look at them in order.
Types of Anemia
There are different types of anemia. In older people, four types are more common, which we discuss below.
• Anemia of chronic diseases (ACD)
It occurs due to many diseases: infections, autoimmune diseases, tumors and others. Anemia is not severe and is a symptom of an underlying chronic illness. Treatment is carried out by resolving the underlying problem. Iron supplements will not help with ACD.
• Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
The most popular type. Occurs due to a lack of iron due to poor nutrition or blood loss due to internal bleeding. Characterized by a drop in iron levels and a less saturated color of the blood.
Bleeding is caused by internal diseases: gastric or duodenal ulcers, gastritis, intestinal angiodysplasia, diverticulosis, cancer. The development of IDA is also affected by chronic bleeding of the genitourinary system, bleeding disorders, stomach ulcers, colitis, Crohn's disease, tumors and others.
Iron-containing preparations are used in treatment. The main means for increasing hemoglobin are ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate. The medications are taken 3-4 times a day.
For better absorption of iron, vitamin C is recommended. Calcium, coffee, tea and wine interfere with the absorption of iron, so they should not be mixed in the same meal with medications and foods containing iron.
• Anemia caused by lack of folic acid
Folic acid deficiency is usually associated with poor diet. To replenish its reserves, appropriate medications and healthy nutrition are prescribed.
• Anemia due to lack of vitamin B12
Neurological signs appear before the symptoms of anemia: decreased sensitivity, muscle weakness, hyporeflexia. Then spasms and ataxia may develop.
The cause of this anemia is a decrease in intestinal absorption of vitamin B12. B12 deficiency can be observed in the following cases: gastric resection, diseases of the small intestine, vegetarianism. Vitamin B12 deficiency is treated by replacing it with medications.
Anemia in older people can be cured if treatment is started on time and all medical recommendations are followed.
Anemia is dangerous for older people and can lead to complications and serious consequences. Due to a lack of hemoglobin, immunity decreases, so a person becomes vulnerable to various viruses and infections.
If anemia is started, a severe lack of hemoglobin may develop, which will lead to health problems. At the third, severe stage of anemia, a person develops tachycardia, bradycardia, blood pressure increases, muscle atony, and fainting occur. Lack of hemoglobin leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which can cause the development of Alzheimer's disease.
Anemia must be treated immediately, since in older people it quickly turns into chronic anemia. Women may develop tumors of the reproductive system, and men may develop dementia praecox. Anemia is three times more common in older men than in women. All retirees are advised to have regular blood tests to check and detect problems early on.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of anemia appear, a blood test should be done. This informative method helps the specialist determine the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin level, and the degree of anemia.
Anemia caused by a lack of folic acid or vitamin B12 is diagnosed in a differential manner.
They investigate the root cause of anemia and pay attention to chronic diseases. After a detailed diagnosis, suitable treatment is prescribed.
Treatment
Therapy is based on the following plan:
• Getting rid of the cause of anemia • Maintaining a healthy daily routine and maintaining a complete harmonious diet • Regular intake of iron supplements • Monitoring blood counts to prevent the risks of iron deficiency anemia
Treatment for low hemoglobin depends on the type of anemia.
With iron deficiency anemia, the amount of ferritin and serum iron in the blood decreases, and the iron-binding capacity of the blood increases. With IDA, the number of red blood cells in the blood decreases.
To get rid of anemia, you need to treat the root cause. For auxiliary treatment, iron-containing drugs are prescribed.
To raise iron levels to normal levels per day, a dosage of 150-300 mg of an iron-containing product is required 1-2 times a day. Typically, medications based on ferrous sulfate or fumarate are prescribed. It is better to take the product with food for better absorption.
It is necessary to carefully observe the dosage of medications, since drugs with iron can lead to side effects: disruption of the healthy functioning of the stomach, nausea and vomiting, constipation, vascular inflammation, allergies, hypotension, and chest pain. You cannot prescribe medications for yourself - the medications are prescribed by your treating specialist.
Means for increasing hemoglobin in the elderly must meet certain criteria:
• Contain sufficient amounts of ferrous iron. • Iron must be well absorbed - for this purpose special components are added to medications. • Dosages and use of drugs should be convenient for pensioners. • Funds must be affordable.
Iron levels can be increased through appropriate nutrition. You need to include foods rich in iron in your diet and combine them with medications.
Anemia due to deficiency of folic acid and B12 is characterized by a more saturated shade of blood. Red blood cells increase in size. There is a decrease in leukocytes and platelets, and the amount of iron in the blood serum increases. A person experiences neurological and mental disorders.
The causes of this anemia are:
• Gastritis, stomach cancer • Pancreatitis, diverticulosis • Inflammation of the small intestine • Dysbacteriosis • Chronic hepatitis
Anemia can be caused by improper use of medications or a lack of important substances in the body.
Bone marrow analysis is used in diagnosis. The person is also checked through research: a course of vitamin B12 is prescribed and the patient’s blood condition is monitored. If a person gets better and his blood counts return to normal, it means he has anemia due to a lack of B12.
Treatment is carried out with vitamins. Vitamin injections are given daily until blood counts return to normal. Next, to consolidate the result, vitamins are administered 1-2 times a month.
Anemia due to a lack of folic acid occurs less frequently for the following reasons:
• Frequent alcohol intoxication • Destruction of red blood cells, oncology, dermatitis, enteritis • Nutritional deficiency • Taking certain medications
In treatment, you need to pay attention to the root cause of anemia. If it cannot be eliminated, the person is treated with vitamins. The patient is prescribed folic acid injections or tablets at a dosage of 5 mg per day.
To quickly increase hemoglobin in an elderly person, suitable medications are prescribed. The medications prescribed vary depending on the type of anemia, concomitant diseases, and the condition of the elderly. For example, Hemobin is often prescribed. This remedy is well suited for older people, and its only contraindication is individual intolerance.
Elderly people are prescribed medications in tablet and liquid form for easier and better absorption.
Nutrition and traditional medicine for low hemoglobin
Hemoglobin in the body of an elderly person is produced thanks to foods rich in vitamin B, iron, amino acids and other food acids.
A suitable diet must be combined with medication. In the future, after recovery, you should adhere to a healthy diet to maintain normal hemoglobin. Folk recipes also provide nutritional recommendations for anemia and offer healthy herbal recipes.
Nutrition rules:
• Small meals 5-6 times a day. The last meal is at least 3 hours before going to bed. • Replace coffee and tea with herbal teas, vegetable and fruit juices. • Walk in the fresh air more often to normalize oxygen balance and stimulate hemoglobin renewal.
To increase hemoglobin levels, you need to introduce iron-rich foods into your diet. These include:
• Meat, meat by-products, fish • Egg yolks • Food made from whole grain flour • Nuts and seeds • Porcini mushrooms • Buckwheat, lentils, beans • Wheat germs and sprouts • Beets, carrots, cabbage, seaweed, greens (parsley, spinach, fennel) • Prunes, apricots, dates, figs, black currants • Strawberries, currants, pomegranate, yellow and orange fruits • Herbs, seasonings • Decoction of nettles and rose hips • Dried fruits, chocolate, halva, natural dark honey
Folk recipes and useful nutritional recommendations:
• There are soups made from rye and wheat bran. • Drink juice from pickled beets - 200 ml per day. • Nettle decoction or tincture – take 20-25 g before bed. • It is useful to eat carrots, apples and parsley. • Dried apricots are an excellent dried fruit for increasing hemoglobin. You should eat seedless in small quantities every day. • Drink whole milk.
Several recipes to increase hemoglobin:
• Decoction of meadow clover. Pour clover heads (10 g) with a glass of water and brew, strain after 45 minutes. Take 3 times a day, two tbsp. l. • Rosehip infusion. Pour one tbsp. l. rosehip berries with one glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for several hours. You can drink it instead of tea three times a day. • Vegetable juice. Peel and wash the beets, carrots and black radishes. Finely grate and squeeze the juice from each vegetable. Mix in equal parts and place in the oven for 3 hours. Then take the product one tbsp. l. in a day.
When choosing a traditional recipe, consult your doctor. You need to eat harmoniously and fully, be sure to have breakfast, lunch and dinner. The diet should be higher in calories in the first half of the day, and it is better to have a light dinner. Along with meals, you can use suitable folk remedies, for example, teas or decoctions.
Natural juices are very useful for increasing hemoglobin and are well absorbed. The following juices are suitable for anemia:
• Pomegranate. It is diluted a little with boiled water. Consume three times a day half an hour before meals every day for 2-3 months. • Birch. You can drink in large quantities - up to 4 glasses a day. It will protect against fatigue. • Beetroot. It is recommended to drink 100 ml of fresh juice daily for a month. • Carrot-spinach mixture. It is recommended to drink 100 ml three times a day. • Juice from dandelion leaves. Drink 50 grams once a day for a long time.
If you have anemia, you should not starve, overeat, or take long breaks between meals. Portions should be hearty and moderate.
In old age, you should not get carried away with interesting nutritional systems and varied diets - it is better to eat a nutritious diet and follow healthy recommendations.
If a person has lost teeth or they are in poor condition, this must be taken into account when preparing food. Food should be prepared soft so that it is easy to chew, and liquid dishes should be used. You can use a blender or grater to grind food.
With the help of suitable nutrition, anemia can be eliminated at an early stage of development. By combining nutrition and traditional medicine over a long period of time, it is possible to normalize hemoglobin levels in a short time. After a month, it is recommended to take a blood test to check. If hemoglobin is not yet normal, treatment is continued.
How to raise hemoglobin levels: useful tips
You need to lead a healthy lifestyle. Healthy recommendations include:
• High-quality nutrition - several times a day. A varied healthy diet, including all useful vitamins and substances. • Give up vegetarianism and bad habits. • Treat diseases in a timely manner, maintain normal condition in case of chronic illnesses.
In old age, you need to be prepared for long-term treatment due to the health status of the elderly person. With a competent approach, the symptoms of anemia gradually go away, and the person begins to feel better.
Causes of high hemoglobin
Increased level of hemoglobin in the blood in women, what is it? If this indicator changes, it means that there is a problem with a specific organ and system. Although sometimes high hemoglobin is the norm - for example, in people who live in the mountains or in elevated areas. The main reasons why high hemoglobin occurs in women are as follows:
- Hemoglobin often increases in those who smoke, as well as in those who have recently been in a fire. The fact is that hemoglobin easily transports air or carbon dioxide, replacing them with each other.
- A high level of water deficiency raises blood counts, resulting in an increase in the amount of circulating plasma.
- Congenital heart disease caused by high pressure in the pulmonary artery blood flow. In this situation, the skin color changes from infancy and has a blue tint. The child coughs frequently and has shortness of breath. Ultrasound of the heart allows you to determine an accurate diagnosis. Treatment of such pathologies with severe symptoms is only surgical.
- Pulmonary diseases.
- Excessive amounts of vitamins B6 and B12 in the human body.
- Cancerous neoplasms.
However, a high level of hemoglobin in the blood can not only indicate various diseases, but also signal that you lead a different lifestyle and live in an unfavorable place.
increased hemoglobin in women
Etiology
The concentration of the main element of red blood cells is one of the most important blood indicators. The norm for a healthy adult woman can range from 115 to 140 g/l. When the level increases to 150–170 g/l, urgent medical attention is required.
As for women during pregnancy, normal values will be 110–120 g/l. In such situations, the level of hemoglobin increases extremely rarely; a decrease is often observed.
The causes of increased hemoglobin in women are very diverse; they are usually divided into several large groups. The first category of provocateurs includes diseases and pathological conditions, including:
- extensive burns;
- malignant tumors;
- diabetes;
- cardiovascular failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- dysbacteriosis and hypovitaminosis;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pulmonary and respiratory failure;
- volvulus;
- kidney pathologies;
- hypertonic disease;
- congenital cardiac anomalies;
- chronic oxygen deficiency - hypoxia;
- intestinal obstruction;
- pathologies of an autoimmune nature;
- Vaquez's disease.
The deviation does not always have a pathological basis; it is not uncommon for it to develop in a completely healthy person. Physiological causes of high hemoglobin:
- engaging in strenuous sports;
- consumption of insufficient amount of liquid per day - the daily norm is at least 2 liters;
- the period of bearing a child, especially in the 2nd and 3rd trimester;
- irrational use of drugs, for example, diuretics and immunoglobulins, glucocorticosteroids and immunosuppressants;
- hormonal imbalance;
- long-term physical activity;
- chronic stressful situations;
- living or prolonged stay in high mountain areas;
- hot climate;
- abuse of bad habits, in particular smoking;
- secretion of a large amount of sweat.
Clinicians believe that genetic predisposition may act as a predisposing factor. Knowing this, women should regularly donate blood for subsequent laboratory tests.
Women need to remember that the possibility of a false increase in the concentration of iron-containing protein cannot be ruled out - the result of a laboratory test may be affected by the time of day when the blood was taken. In the morning, hemoglobin levels are higher than in the afternoon.
Hematologists involved in deciphering the results note that the causes of increased hemoglobin may be liver damage or drug overdose.
High hemoglobin
Signs and consequences of increased hemoglobin
With a high level of hemoglobin in the blood, women may have no symptoms at all, but with a long and high value along with other diseases, the patient may have vague symptoms:
- constant fatigue
- desire to sleep,
- lethargy,
- loss of appetite,
- sleep problems,
- aches in joints and bones,
- high blood pressure,
- itching of the skin, particularly after showering and bathing,
- stomach ache,
- instant bruising and easy bruising.
All these symptoms disappear externally. But the most serious of them take place inside the body. There is an increase in the coagulability of the blood space, an increase in its concentration and a reduction in the speed of movement in the body. Because of this, the internal organs do not receive proper nutrition. If this condition is neglected, blood clots and plaques can form, which cause heart attacks and strokes.
How to reduce hemoglobin in the blood?
If what causes hemoglobin to rise has nothing to do with serious illnesses, then you can influence it with a specific diet or medications. Among the pharmaceutical medications that can be easily purchased at the pharmacy, there are those that are aimed at thinning the blood: Trental, Cardiomagnyl, Curantil, Aspirin. Only a doctor should prescribe them! To reduce hemoglobin at home, you need to adjust your diet:
- Drink plenty of fluids per day. To do this you need to drink warm water. If you cannot do this, then saline drips are used.
- Reduce fats, sweets, eggs, as they increase cholesterol and so in a viscous environment.
- You should not take multivitamins or products that contain copper and iron.
- It is better to choose shrimp, fish, white meat, nuts, legumes, and vegetables.
- Also limit your intake of foods that increase hemoglobin. This is food enriched with protein and iron - red meat, red fruits and vegetables, offal, fish roe, butter, buckwheat, sweets.
Now you know why increased hemoglobin appears in a woman .
Treatment
To lower the level of hemoglobin in the blood, it is necessary to eliminate the pathological etiological factor. Treatment can be conservative, surgical or complex.
To quickly thin the blood, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- "Courantil";
- "Aspirin";
- "Trental";
- "Cardiomagnyl";
- salicylic acid.
It is important to consider that drug therapy for pregnant women is carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician and obstetrician-gynecologist.
The basis of treatment is a diet for high hemoglobin, which involves complete avoidance of the following foods:
- red meat;
- alcohol;
- cereals and coffee;
- vegetables, fruits and red berries;
- confectionery;
- carbonated drinks;
- butter and margarine.
You should limit your consumption of fatty meats and fish, sugar and sweets, fried, salty and spicy foods.
A diet with high hemoglobin does not prohibit eating the following foods:
- dietary types of meat and fish;
- milk products;
- cottage cheese and hard cheese;
- seafood;
- green tea;
- wheat bread;
- potato;
- citrus.
An increase in hemoglobin is corrected using the following methods:
- folk remedies;
- hirudotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- bloodletting;
- taking mumiyo.