September 15, 2011
A heart attack is often confused with angina. There is also a “silent heart attack”, which is not accompanied by pain at all. How to recognize and - most importantly - prevent a heart attack?
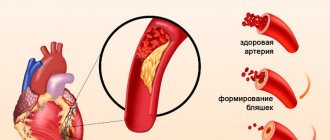
A heart attack is the death of part of the heart muscle due to insufficient blood flow to it. This disease has other names: heart attack or coronary thrombosis. Most often, a heart attack develops in those who eat poorly, move little and cannot cope with stress. A heart attack usually occurs when one of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle becomes blocked by a blood clot. If the clot is large enough, it can completely deprive the heart of blood supply. Also, a heart attack can be caused by a spasm of the artery that supplies the myocardium - the heart muscle. Most often, this spasm occurs under the influence of stress.
What causes a heart attack?
— Age
is considered the main risk factor for heart attack.
It most often occurs in men over 45 years of age and women over 55 years of age. — A heart attack is one of the signs of the development of coronary heart disease. As a rule, it is preceded by attacks of angina pectoris. - Angina pectoris
- lack of nutrition of the heart muscle - increases the risk of a heart attack.
Heart attack and angina are often confused because their symptoms are very similar: chest pain and shortness of breath are observed in both cases. But the symptoms of angina pectoris are relieved by taking special medications within 15-30 minutes, but the symptoms of a heart attack are not. — Increased blood cholesterol or atherosclerosis. With these diseases, the risk of blood clots forming and blocking blood flow in the vessels of the heart is increased. In addition, risk factors
for heart attack include: - Diabetes - Hypertension - High-fat diet - Obesity - Smoking - Lack of physical activity - Stress - Genetic predisposition. Those whose relatives have suffered from heart attacks are at increased risk of developing this disease.
What to do if you suspect a heart attack?
Call an ambulance immediately and try to calm down: you don’t need extra stress. Find a comfortable position and slowly chew one 300 mg aspirin tablet. (if there are no contraindications). Aspirin helps minimize the risk of developing a dangerous blood clot. It reduces the “stickiness” of platelets, minimizing the likelihood of them sticking together and blocking blood vessels.
Important! Don't forget to leave the door open so doctors can get to you at any time, or better yet, call a neighbor, friend or relative so you don't have to be alone. Try not to eat or drink anything until the doctors arrive.
Heart Attack Symptoms
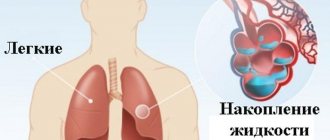
- Unpleasant sensations in the chest - Cough - Stitching pain in the chest - Dizziness - Shortness of breath - Pale with a grayish tint - Feelings of fear, panic - Nausea - Anxiety - Cold sweat on the face - Vomiting A person who is having a heart attack, first of all feels pain in the chest. Then the discomfort spreads to the neck, face and arms, and sometimes even to the back and stomach. The pain may last from a few minutes to several hours. Usually a person feels a little better if he changes his body position or lies down.
Announcement: Women often ignore dangerous symptoms that indicate an approaching heart attack. Knowing these signs could one day save a life.
For some reason, it is generally accepted that men suffer from heart attacks more often than women. In fact, women over 50 have the same heart attack rate as men of the same age. Another thing is that not everyone is equally attentive to their health and rushes to see a doctor when dangerous signs appear. It is important to consider that the pre-infarction condition in men and women is manifested by different symptoms. The following 8 typical signs most often indicate an approaching heart attack in women. 1. Numbness in the hands It appears suddenly and does not last long, so most often this symptom is ignored. Women believe that they simply went to bed in an uncomfortable position or overworked their hand. Numbness, weakness, pain in the left arm predicts an approaching heart attack. It is important to get a cardiogram as soon as possible. 2. Toothache Usually the pain is aching in nature, spreading to the entire jaw. In fact, the source of the problem may not be tooth decay, but heart problems. If there are no obvious reasons for tooth pain, it is worth undergoing cardiac diagnostics. 3. Nausea and vomiting Two out of three volunteers who took part in a scientific study after a heart attack reported feeling stomach pain before the attack, and experienced nausea and even vomiting for several days. Men mention such previous symptoms in half of the cases. 4. Difficulty breathing With poor blood circulation, the body experiences a lack of oxygen, which manifests itself in the appearance of shortness of breath. A heart attack causes blood to stop circulating properly, causing fluid to accumulate in the lungs. Lack of air is a dangerous symptom, whatever its causes. It is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the dangerous condition. 5. Severe weakness If no changes occur in the rhythm of life, and fatigue becomes stronger every day, this indicates overwork or an approaching heart attack. Many women who have had a heart attack report that in the days leading up to it, they were unable to shower, move, or carry out daily activities as easily as before. 6. Back pain Usually this symptom appears immediately before an attack and is the only one. Acute pain in the area between the shoulder blades without any previous injuries, falls or other causes indicates problems with the heart. You should urgently contact a cardiologist. 7. Strange feeling in the chest Tightness, some unclear, but unfamiliar and unpleasant sensations in the chest may indicate that something bad is happening to the blood vessels. For example, a blockage has occurred, or the heart muscle has lost the ability to push blood through at the same rhythm. Together with the above symptoms, this is a very alarming sign that should not be ignored. 8. Flu symptoms Over the age of 55, you should be very attentive to flu-like symptoms when there is reason to suspect heart problems. A common cold can provoke an exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases. During the examination, you should definitely visit a cardiologist and perform a cardiogram.
What is a “silent heart attack”?
In people over 75 years of age and with diabetes, a “silent heart attack” may occur, which is not accompanied by pain at all.
Experts estimate that approximately one fifth of such heart attacks are not diagnosed. Damage to the heart muscle in survivors of a “silent heart attack” progresses because it is not detected and treated. Abdominal fat destroys the heart
The maximum permissible waist circumference for women is 94 centimeters, for men – 102 centimeters. Exceeding these values increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Find out more about the dangers of visceral (intra-abdominal) fat and how to get rid of it.
What will happen if you are taken to the hospital?
Firstly, they will connect you to all the necessary devices and monitors and conduct an ECG test. It will help measure the heart's electrical impulses and detect any abnormal heart rhythms or other abnormalities that indicate a heart attack. Nurses will take the necessary tests, checking your blood to measure the level of an enzyme called troponin. It is released into the bloodstream if the heart muscle is damaged or dies.
Depending on your condition, doctors may keep you in the hospital until you feel better.
Provoking factors
There are a number of factors that can provoke the development of a heart attack in young people. “In addition to those factors that can influence the development of atherosclerosis, it is important to talk about conditions that are not associated with the growth of plaque in the vessels of the heart, but can provoke heart problems in young people. These are factors that reduce the supply of oxygen to the heart. For example, iron deficiency anemia or dysfunction of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism),” says Galina Lazarenko.
In addition, she also calls the development of inflammation in blood vessels after viral diseases a provocateur. The list also includes:
- The presence of bad habits: smoking and alcohol can be provoking factors for sudden blood clots, drugs can provoke spasm of the heart vessels and lead to a heart attack.
- The use of oral contraceptives by a woman, which can cause sudden thrombosis in blood vessels, including the heart, with a certain predisposition to increased thrombosis.
Clinic of myocardial infarction in young patients
Overall, the mortality rate for young people from myocardial infarction is low, even with 5- to 10-year survival rates. However, the rate of recurrent heart attacks in young people is alarmingly high. If we consider the clinical situation of a 35-year-old patient with atherosclerosis who underwent catheterization and angioplasty of the coronary vessels, we can say with confidence that he has a very high chance of undergoing cardiac surgery or other interventions in the future. He also has a significantly higher risk of having another heart attack. The reasons lie in the more aggressive course of atherosclerosis in young people compared to the elderly. In addition, smoking clearly leads to recurrent heart attacks in young people.
Can high temperature cause complications on the heart: a cardiologist's view
Numerous microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi and other protozoa - can have a direct damaging effect on the heart muscle. However, in most cases, myocardial damage is observed as a secondary phenomenon, a complication of viral and bacterial diseases.
The effect of hyperemia on the functioning of the body
The penetration of infectious agents into the human body causes a natural response of the immune system aimed at suppressing their vital functions. The essence of the process comes down to the following: microbes, having penetrated the tissues of the body, release toxic substances, which are protein compounds. The presence of foreign elements initiates a series of biochemical reactions for the active synthesis of specific antibodies. The thermoregulation center of the brain is activated, which leads to a rise in temperature - hyperthermia, the companion of which is a feverish state.
High temperature is a factor that forces the heart to work in an “emergency” mode due to disruptions in metabolic metabolism, changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the blood, and rapid disruption of the water-salt balance. Hyperemia is manifested by an increase in the frequency of myocardial contractions, a rise in blood pressure, and centralization of blood flow. Poor blood circulation is the cause:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- seizures;
- fainting states.
Complications
Detailed diagnostic methods that cardiology in Nizhny Novgorod has in its arsenal show: in cardiac patients with hyperemia, sinus arrhythmia is recorded. Patients with fever are at risk of dangerous conditions: acute heart failure, persistent increase in the number of red blood cells - polycythemia. Hyperemia poses a threat of chronic insufficiency of cerebral blood flow and the development of a critical condition - DIC syndrome: acquired disorders of the coagulation capabilities of the circulatory system. At the same time, a sharp drop in temperature caused by taking powerful antipyretic drugs can provoke a decrease in blood pressure to critical values, which poses a threat of collapse.
One of the common ailments that is accompanied by hyperemia is tonsillitis - an inflammatory process that affects the palatine tonsils. Often, after suffering from a sore throat, especially with inadequate and not comprehensive therapy, severe complications of the disease from the cardiovascular system occur. Among the dangerous consequences of tonsillitis is acute rheumatic fever, which destroys the myocardium, endocardium, and pericardium. Chronic rheumatic heart disease may develop, the frequent outcome of which is an acquired defect, a malfunction of the valve system.
Another unfavorable outcome of angina is myocarditis - an inflammatory lesion of the heart muscle, causing disruption of all functions of the organ. Tonsillogenic cardiopathy also includes myocardial dystrophy. A dangerous consequence of streptococcal infections is acute septic endocarditis.
Therefore, at the first signs of viral or infectious diseases and an increase in temperature, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help for differential diagnosis and choice of treatment strategy.