What can affect the result?
The indicator should be assessed no earlier than 14 days after exacerbations of chronic pathologies and their acute stages. If the concentration of C-reactive protein is significantly increased, additional diagnostics must be carried out to determine the causes of inflammation.
Important! The interpretation of the analysis is carried out only by a doctor. If necessary, the patient is referred for other examinations (including instrumental and functional).
We recommend that you consult your doctor and get a check-up.
Indications
A blood test for CRP is prescribed for children when:
- suspected infectious or inflammatory disease;
- carrying out antibacterial therapy and monitoring its effectiveness;
- there is a risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies;
- recovery and complications in the postoperative period;
- transplant operations and complications such as rejection;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- control and treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Analysis result
The indicator varies from 0 to 1000 mg/l.
There is no C-reactive protein in the blood serum of a healthy person.
An increased protein content may indicate:
- About acute infections
- About exacerbation of inflammatory processes
- About serious tissue damage
- About malignant neoplasms
- About the appearance of metastases
The indicator can also increase with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, excess body weight, hormonal imbalance, and smoking.
Possible localization of inflammation
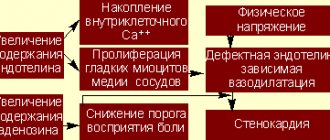
In intestinal and urogenital forms of reactive arthritis, the joints of the lower extremities are most often affected. In the nasopharyngeal form - the joints of the upper extremities and the temporomandibular joint.
Arthritis of the lower extremities
Affection of the lower extremities predominantly begins with the big toes and moves upward (staircase sign), affecting the overlying joints asymmetrically. In reactive arthritis, one to five joints become inflamed:
- interphalangeal toes; Most often the first toe is affected, it swells and turns red - the “sausage toe” symptom;
- ankles with damage to surrounding tissues; Particularly characteristic is damage to the tendons and ligaments in the heel area with the formation of loose heel spurs, which causes constant pain that intensifies when walking and stepping on the heel;
- knee – this location is characterized by the formation of a large amount of exudate (inflammatory fluid in the joint), which leads to the formation of popliteal cysts; rupture of cysts leads to the development of thrombophlebitis and impaired venous circulation;
- hip – rarely affected, occurs in the form of moderate joint pain.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Arthritis of the upper extremities
Localization of reactive arthritis in the joints of the upper extremities is much less common. This mainly occurs in diseases of the nasopharynx and dental infectious and inflammatory processes.
The most common joints affected by ReA are:
- elbow - the elbow swells, turns red, becomes painful, the arm has difficulty bending and unbending;
- wrist with damage to the ligaments and tendons of the hand - pain in the joint is transmitted to the hand; severe pain does not allow you to squeeze and unclench your hand or hold objects in it;
- shoulder – rarely affected, characterized by swelling and pain.
Temporomandibular arthritis
Reactive arthritis affects the joints of the lower and upper extremities, temporomandibular joints
Triggers include infections of the nasopharynx, ear and mouth. Characterized by slight swelling, redness and swelling in the area of development of reactive arthritis. When opening the mouth, there is a slight asymmetry; the chewing process may be disrupted and become painful. The disease occurs acutely or subacutely, is well treated, and the prognosis is favorable.
MEDSI cares about its patients
- Experienced specialists.
They professionally take blood and examine it, which guarantees diagnostic accuracy - Modern laboratory equipment.
It corresponds to a high European and global level. The laboratory uses equipment from leading manufacturers such as Beckman Coulter, Siemens, Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Thermo Fisher, Sysmex, BD - Comfortable conditions for testing for C-reactive protein.
You can complete the study throughout the day. The results will be available in your personal account - Opportunity to undergo a comprehensive examination.
If necessary, you can take all the necessary tests - Regular maintenance of equipment and automation of research processes.
All analytical installations are serviced and meet quality standards. All processes are fully automated and built in accordance with LEAN management - Automation of the process of sorting biomaterials.
Preliminary identification of the biomaterial is carried out in front of the patient. Eliminates the possibility of losing the test tube - The shortest processing time for materials.
They are provided with modern equipment and experienced specialists
To take a test for C-reactive protein and clarify its cost, as well as to make an appointment with a doctor to interpret the result, call +7 (495) 7-800-500. A MEDSI specialist will answer all questions and suggest the optimal time to visit the clinic. Recording is also possible through the SmartMed application.
C-reactive protein test: what is it for?
What is C-reactive protein? What can a test result for this substance tell a doctor? What is the normal level of C-reactive protein in the blood? Nikita Valerievich Vorobyov, a neurologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk, answers these and other questions.
— Nikita Valerievich, before we talk about the analysis for C-reactive protein, please tell us what kind of substance this is? Is it present in the body normally or does it appear only during certain diseases? And what is the significance of the C-reactive protein test?
— C-reactive protein is a kind of indicator of various diseases, the most sensitive marker of the inflammatory process. With its help, the doctor can determine the severity of inflammation in the body. This substance is synthesized by liver cells in response to inflammatory processes in the body: during tissue damage, cell necrosis, during an infectious process, during exacerbation of chronic diseases, for example, rheumatological ones, including ankylosing spondylitis.
Being in the body within normal concentrations, C-reactive protein has a protective function: it initiates immune processes, stimulates phagocytosis (a process in which special blood cells and body tissues - phagocytes - capture and absorb various foreign structures, such as destroyed cells, bacteria, antigen-antibody complexes, etc.).
When the content of C-reactive protein in the blood begins to exceed the norm, this indicates some kind of inflammatory process, the nature of which the doctor will have to find out. Moreover, during acute inflammation, the content of C-reactive protein increases very quickly, literally in 6 hours. Much faster than, for example, ESR changes - the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
When the treatment itself has already begun, an analysis for C-reactive protein helps the doctor understand what phase the pathology is in: is the acute period still ongoing or the disease has declined.
— What is the normal level of C-reactive protein in the blood?
- Depending on the laboratory, the norm of C-reactive protein varies from 0 to 1 milligram per liter and from 0 to 5 milligrams per liter. There is no lower limit of normal; this protein is detected in the blood only in response to acute inflammation. Within acceptable limits, the level of C-reactive protein can fluctuate during physical activity (for example, after playing sports), smoking, or eating fatty foods.
- Then, it turns out, there is no point in asking under what circumstances C-reactive protein can be lowered? Is this question not valid?
- Right. There are two options: either the protein is normal, or its content is increased. There can be no reduction.
— Why can C-reactive protein be elevated?
— I have already partially answered this question: its content increases with the appearance of inflammatory processes in the body. The reasons for the increase in C-reactive protein may be:
- previous trauma, burn;
- rheumatological disease;
- presence of infection;
- transplant rejection reaction.
The content of this protein also increases during myocardial infarction, after undergoing severe operations.
An analysis for C-reactive protein - I repeat, as an auxiliary study - is used if there is a risk of developing cardiovascular complications, in particular, when diagnosing atherosclerosis: with inflammation of the vascular walls, the concentration of this protein also increases.
— Tell me, how does C-reactive protein behave during pregnancy?
— Since pregnant women have a higher immune system tension than non-pregnant women and, even more so, than men, the content of C-reactive protein during this period may be increased. If the woman is healthy and gestation is normal, this indicator increases from the 16th to the 28th week of pregnancy, then gradually begins to decrease. Then it may increase immediately before childbirth. A high concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood may indicate a risk of developing late toxicosis.
— Which doctor and under what circumstances prescribes a test for C-reactive protein? What might be the reason for this research?
— A general practitioner, therapist, or neurologist can refer a patient for this analysis. But, since this type of research is primarily used in the diagnosis of rheumatological diseases, most often this direction is issued by a rheumatologist.
An analysis for C-reactive protein is carried out, for example, if ankylosing spondylitis is suspected. When making a diagnosis, this study plays an auxiliary role; it is used in conjunction with other markers. When ankylosing spondylitis has already been detected, the doctor can determine by the concentration of C-reactive protein what phase the disease is in - in the stage of exacerbation or remission (the period of weakening or disappearance of the symptoms of the disease).
This test is also prescribed for joint pain, increased body temperature, and infectious processes.
Neurologists use this type of analysis to understand the nature of a patient's back pain.
— Do you always need a referral from a doctor to get tested for C-reactive protein? And if not, what is more correct: to take it as directed or on your own initiative?
— Having a referral for such an analysis is not a prerequisite. But it is still better to do any research after consulting a doctor.
— Does the patient need to somehow prepare for the C-reactive protein test?
— The procedure is a simple blood draw from a vein. No special preparation is required from the patient. The generally accepted rules in such cases apply. The test is taken on an empty stomach, after a 12-14 hour fast (usually this is done in the morning). The day before, 24 hours before the test, you need to avoid drinking alcohol and intense physical activity. It may be necessary to temporarily stop taking certain medications, but only after consultation with your doctor.
1-2 hours before the test, you need to refrain from smoking, tea, coffee, and juices. You can drink still water. Running and quick climbing of stairs should be avoided. It is not recommended to do the study after emotional stress or severe anxiety.
— How long should I wait for the test result?
- Usually no more than one day.
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
Want to learn more about other tests? Read articles in our “Laboratory Tests” section If you need to get tested for C-reactive protein or other tests, you can sign up here You can make an appointment with specialists here ATTENTION: services are not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Pain with rheumatoid arthritis: how to help the patient? Are you worried about pain in your lower back? We're talking about sacroiliitis Are you crunchy? What will an MRI of joints tell you?
For reference:
Vorobiev Nikita Valerievich
Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of Kursk State Medical University in 2021. In 2021, he completed his residency at Kursk State Medical University in the direction of Neurology. Advanced training: interventional methods of treatment in neurology, First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova, 2021. Advanced training: local therapy of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and compression-neural syndromes, Kursk State Medical University, 2021. Currently, a neurologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk. Receives at the address: st. Karl Liebknecht, 7.
General clinical recommendations
In the acute and subacute course of ReA, after a course of treatment, the patient should be under the supervision of a rheumatologist for six months with clinical and laboratory monitoring every 3 months.
In the chronic course of the disease, dispensary observation is longer with the prescription of courses of anti-relapse therapy until a state of stable remission appears.
After an illness, it is recommended to avoid heavy physical activity and strength sports. Swimming is a good way to restore joint function.
Persons with a genetic predisposition (presence of the HLA-B27 antigen) to reactive arthritis are recommended to have one proven sexual partner.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
FAQ
Is reactive arthritis contagious?
No. But the urogenital infection that caused it can persist for a long time and be contagious.
Are there any peculiarities of the course, diagnosis, treatment in children?
In children, ReA is more acute and rarely becomes chronic.
What prognosis do doctors usually give?
The prognosis for reactive arthritis is favorable; in most cases, complete recovery occurs. But if left untreated, it becomes chronic with a long course and constant pain in the joints.
Reactive arthritis is a complex, incompletely studied infectious-allergic disease that mainly affects genetically predisposed people and requires timely and adequate treatment. It's not worth running.
But if you were unable to seek medical help in time, do not despair, modern technologies make it possible to provide assistance and relieve pain at any stage of the disease. The Paramita clinic (Moscow) will always help you.
Literature:
- Agababova ER, Bunchuk NV, Shubin SV, etc. Criteria for the diagnosis of reactive arthritis (draft). Scientific and Practical Rheumatology 2003;(3):82–3.
- Kovalev YN, Ilyin NI. Reiter's disease. Chelyabinsk: Option-book; 1993. 240 p.
- Zeidler H, Hudson AP. New insights into Chlamydia and arthritis. Promise of a cure? Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:637–44. doi:1136/annrheumdis-2013-204110.
- Ford D.K. Natural history of arthritis following venereal urethritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1953;12(3):177–97. doi: 10.1136/ard.12.3.177.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 10/13/2020 Date of update: 12/14/2020
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (2)
No. 3. CRP to determine the need for urgent kidney drainage
It is highly doubtful that the decision about the need for kidney drainage should be based on the level of CRP. But Angulo JC made such an attempt and published the results of his study in the journal Urology in 2010. The study involved 110 patients with renal colic, 29 of whom underwent emergency kidney drainage. The mean CRP level in patients who required drainage was 140 mg/L. The average level of CRP in patients who did not require drainage was significantly lower – 15 mg/l. The cut-off point was 28 mg/l. The authors conclude that determination of CRP levels in patients with renal colic is an objective and useful tool for deciding whether to place a ureteral stent, even more valuable than leukocyte expression or serum creatinine levels.
Complexes with this research
Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening 6,870 ₽ Composition
Rheumatoid arthritis Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and assessing the prognosis of the disease 2,610 ₽ Composition
Women's anti-aging diagnostics Monitoring of basic blood parameters in women aged 40+ 7,380 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUB 2,590
- Inflammation of joints 460 ₽
- Men's check-up No. 1 RUB 11,280
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 20,420
- Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 20,100
No. 1. CRP to determine the likelihood of spontaneous passage of a ureteral stone.
Small stones of the distal ureter pass on their own, so it is very important to divide patients into those in whom the stone will pass on its own, and those for whom it is better to operate without waiting a month. A 2021 article published by Jain A. in the journal Urolithiasis analyzed the management of 185 patients with renal colic caused by a 4 to 10 mm distal ureteral stone. During 4 weeks of observation, stones passed in 122 patients. The probability of spontaneous stone passage decreased with stone size greater than 6.7 mm and CRP level greater than 4.1 mg/L.
The prognostic value of CRP level in determining the likelihood of stone passage is explained by the relationship between the concentration of CRP and the thickening of the ureteral wall at the site of the stone. A 2016 article published by Sarica K. in the journal Urolithiasis analyzed the case histories of 80 patients with stones already in the proximal ureter. 42 patients had normal CRP levels, and 38 patients had elevated levels. At the same time, elevated levels of CRP closely correlated with the thickness of the ureteral wall according to CT results