Biochemical analysis: albumin
Maintaining optimal levels of this protein is extremely important for the functioning of the body as a whole. The volume of blood circulating in the body depends on this. In addition, the protein is responsible for regulating osmotic pressure. This indicator changes under the influence of many factors (for example, after eating salty foods). Therefore, its regulation is a very important process. Albumin is also responsible for the transport and storage of many biological compounds and amino acids. When examining your health status, the ALB level is one of the key indicators.
Basic information
Albumin is synthesized in liver cells (up to 15 g per day). For the body, it is the main reserve protein (a source of amino acids), i.e., during periods of prolonged fasting, it is consumed first.
Albumin maintains circulating blood volume. It determines oncotic (colloid-osmotic) pressure by 80%, since due to the small size of its molecules it is contained in fairly large quantities in the serum. Albumin ensures the transport of important chemical compounds: bilirubin, urobilin, cholesterol, calcium, bile salts, fatty acids, exogenous substances (penicillin, sulfonamides, hormones, mercury and some drugs).
In addition to the oncotic and transport functions, albumin has a wide range of other important physiological functions, such as immunocorrection, endothelial stabilization, and antioxidant effects.
Important! One “taxi molecule” of albumin is capable of binding and transporting up to 25-50 molecules of bilirubin, for example. Therefore, hypoalbuminemia increases the concentration of free (unbound) biologically active components. This fact must be taken into account when selecting the dosage of drugs, because against the background of low albumin concentrations, the activity of drugs, and, accordingly, their therapeutic effect, can change, even becoming toxic.
In young children, pregnant women (especially in the 3rd trimester) and lactating women, as well as smokers, the content of albumin in the blood serum is slightly lower than in other groups of patients.
Deviation from normal levels of albumin in the blood occurs under the influence of both internal and external factors. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, additional studies are prescribed to help determine the onset of the pathological process and its cause, as well as take all necessary measures to eliminate the disease.
Who needs to get tested
Blood test for albumin
used in conjunction with data from other studies in the diagnosis of many diseases. Most often, the analysis is prescribed for suspected pathologies of the kidneys and liver. Its results are also used to assess the health status of patients with cancer diagnoses, major injuries or burns. The test is prescribed independently or in combination with other tests. The composition of the examination required in a particular case is determined by the doctor based on the patient’s complaints, examination results, and medical history.
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Interpretation of results
Albumin is synthesized in the liver. Normally, approximately 15 grams of protein are produced per day. It remains in the body and performs its functions for several weeks. The main purpose of this test is to assess the protein-synthetic function of the liver. An increase in indicators indicates dehydration of the body. The causes of dehydration can be different (for example, serious burns). Also, a high level of ALB may indicate the presence of infection and a number of other diseases. For their accurate diagnosis, additional examination is mandatory.
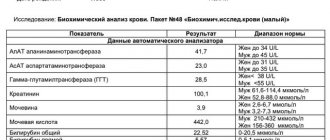
A lack of protein in most cases indicates kidney pathologies. It can also be observed in the presence of an inflammatory process. A decrease in indicators during pregnancy is normal. Reference values depend on the patient's age. For adults, the norm ranges from 35-52 g/l. Based on the test results, one can judge the severity of a number of diseases.
Total protein
To assess the total amount of albumin and globulins, total protein is determined. For newborns, its norm is 46–68 g/l, for babies under one year of age – from 48 to 76, for older ones – no higher than 80. The norm for adults ranges from 65 to 85 g/l. This test is usually performed by examining serum. An absolute increase in concentration is rare and is a sign of myeloma, polyarthritis, cirrhosis or hepatitis.
A biochemical blood test shows that a relative increase in protein is observed with burns, vomiting, diarrhea, nephritis, and peritonitis. A decrease indicates starvation, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, deterioration in the formation of proteins (including congenital disorders) or an increase in their breakdown. A physiological decrease in protein is recorded in women in the final trimester of pregnancy, with insufficient nutrition during breastfeeding.
conclusions
The amount of ALB is required to diagnose a number of diseases and select the optimal treatment tactics. It characterizes metabolism and overall health. In case of severe symptoms of kidney problems, this test is prescribed first. It can also be carried out as part of a comprehensive examination or after it, if deviations are identified and it is necessary to clarify their nature and cause. Interpretation of the results can only be carried out by a doctor; the test is not intended for self-diagnosis
. In some cases, deviations from the norm are possible in the absence of diseases.
Lowering values
In European practice, it is customary to distinguish the following conditions in which albumin values can be reduced:
- Ascites;
- Extensive burns and injuries;
- Glomerulonephritis;
- Liver diseases, hepatitis,
- cirrhosis,
- carcinoma,
- hepatic encephalopathy;
- starvation;
In Russian laboratories (Invitro and Helix), the interpretation of low albumin includes, in addition to the above conditions, the following:
- The presence of exudates and transudates (edematous fluid of an inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature, respectively);
- Condition after blood transfusion and severe bleeding;
- Increased catabolism (energy metabolism) of proteins: febrile syndrome;
- infections, sepsis (blood poisoning);
- endocrine disorders (thyrotoxicosis);
- some cancers;
- rheumatic lesions;
- increase in circulating blood volume (hyperhydration);
- analbuminemia (hereditary pathology characterized by a critical decrease in the amount of albumin in the blood);
- heart failure with congestion;
- treatment with hormonal drugs, amiodarone, taking high doses of steroid hormones, growth hormone, insulin;
- pregnancy.
Albumin price, where to buy
You can buy Albumin in Moscow in many pharmacies. The price of Albumin 10% 100 ml ranges from 1317-1590 rubles, and the drug 20% 100 ml from 3099-4042 rubles. Egg albumin, used in the food industry, is produced in bags of 5-20 kg, and is also sold by weight in specialized stores.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Albumin human solution for inf.
20% fl. 50mlBaxter AG RUB 2,276 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Albumin (flask 20% 50ml)Baxter Oncology
RUB 2,139 order
- Albumin (flask 20% 50ml)Baxter AG
RUB 2,217 order
- Albumin (flask 20% 100ml) Microgen Perm (Biomed)
RUR 3,789 order
- Albumin (vial 20% 100ml) Microgen Ufa (Immunopreparation)
RUR 3,718 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Hematovit with albumin and dried apricots 40 g TOV Vitapak, Dnipropetrovsk
9 UAH order - Albumin-Biopharma 20% 50 ml solution TOV "Biopharma Plasma" , Ukraine
981 UAH order
- Hematovit with albumin and coconut flakes 40g TOV Vitapak, Dnipropetrovsk
9 UAH order
- Albumin-Biopharma 10% 100ml solution for infusion TOV "Biopharma Plasma" , Ukraine
1044 UAH order
- Hematogenium classic with albumin 50g TOV "RIF", Ukraine
7 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 20% 100ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1810 UAH order
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 20% 50ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1245 UAH. order
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 10% 100ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1013 UAH. order
show more
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Albumin is a plasma replacement drug that is obtained by fractionating blood, plasma and serum of donors. Its administration replenishes the lack of plasma albumin (a source of protein), maintains oncotic pressure, increases plasma volume (in some patients this effect lasts for several hours) and blood pressure, and has detoxification properties. Available in the form of 5%, 10% and 20% solutions. After filling, the vials are pasteurized at 600 C for 10 hours to avoid transmission of serum hepatitis. A 5% solution is iso-oncotic plasma, and a 20% solution is hyper-oncotic.
Pharmacokinetics
T1/2 is 19 days. Elimination by intracellular pathway involving lysosomal proteases . In healthy individuals, 10% of the administered solution is removed from the bloodstream in the first 2 hours. Severely ill patients lose significant amounts of protein, so the rate of release is difficult to predict.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Perftoran
Gelofusin
Poliglyukin
Stabizol
Ceruloplasmin
Refortan
Gemodez-N
Reopoliglyukin
Plasbumin 20 , Albumin 20% , Alburex , Zenalb-20 , Postab solution .
Indications for use
- burns;
- shock;
- hypoalbuminemia against the background of nutritional dystrophy, glomerulonephritis , liver cirrhosis , purulent processes, ulcerative colitis and gastrointestinal tumors ;
- therapeutic plasmapheresis ;
- replenishment of bcc ;
- cerebral edema;
- during operations under artificial circulation;
- preoperative hemodilution .