How much does a human heart weigh?
The average weight of a male heart is 332 grams, and a female heart is 253 grams.
Usually the size of a human heart is compared to the size of his fist, which is approximately true - the heart is the same size as a clenched human palm. An athlete has a larger heart; constant physical activity leads to the growth of all muscle groups, which include the heart muscle. The weight of an adult human heart is equal to the weight of two to three medium apples. The average weight of a male heart is 332 grams, and a female heart is 253 grams.
The heart is a powerful and uninterrupted engine in the human body, the main function of which is to pump blood from the venous vessels to the arterial ones. This is probably the only organ whose work a person feels and hears. When we are worried, the heart beats frightfully fast, when we are happy, it is exciting, and when a bright feeling settles in it - love, it just begins to sing!
This is interesting!
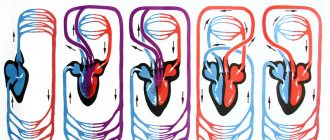
Despite its small size (the length of the muscular organ is from 10 to 15 cm, the width is 8-11 cm), the heart copes with a colossal load. It pumps about 7,000 liters of blood per day. If you place this amount of liquid medium in standard 200-liter barrels, you get 35 containers, and in one minute of operation a powerful heart pump can completely fill a bath with blood. The principle of the heart is the rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle. The heart cavity is divided into two atria and two ventricles. The right part refers to the “arterial” heart, the left is venous. Venous vessels deliver “waste” blood to the heart, and oxygen-enriched blood moves through the arteries. Veins have a thinner wall and the pressure in them is much less than in the arteries. This feature helps to distinguish the type of bleeding if they rupture: dark blood flows out of the vein in a continuous stream, while in arterial bleeding bright red, scarlet blood is ejected with pulsating movements.
When measuring blood pressure, two indicators are recorded: upper and lower. The upper pressure is called systolic, at this moment the heart muscle contracts. The second indicator is diastolic pressure; the heart is in a relaxed state during this period. Normal blood pressure readings are 120/80 mm Hg. , a deviation to a greater extent can cause a disease called hypertension, to a lesser extent - hypotension.
Stomach, intestines
Human gastric juice contains 0.4% hydrochloric acid (HCl).
For one square millimeter of the gastric mucosa there are about one hundred glands that secrete digestive juice.
The small intestine, where digested food is absorbed into the blood, has about 5 million villi on its inner surface - the finest hair-like outgrowths through which nutrients are absorbed.
During life, the human small intestine is about 2.5 meters long. After his death, when the muscles of the intestinal wall relax, its length reaches 6 meters.
How the heart works
The formation of cardiac tissue begins in the embryonic stage of fetal development.
The child receives nutrition through the mother's placenta, but in order for its own organs to begin to grow and develop, nutrients must be delivered to every cell of the body. Therefore, the heart is the very first functional organ that begins to grow and form in a tiny organism. By the 22nd day of pregnancy, the embryo has its first heartbeat; by the 26th day, its own blood circulation is formed in the growing body. At birth, the baby's heart is no larger than a strawberry. The baby's heart becomes similar to the heart of an adult by the tenth week of development: at this moment, septa and heart valves appear in it.
After the tiny “motor” begins its responsible work, the heart rate is almost the same as that of an adult: 75-80 beats per minute. By the seventh week of development, the heart “accelerates” to 165-185 beats and during a CTG study, the expectant mother hears its rapid beating. At birth, the pulse “calms down” to normal at 120-170 beats per minute.
The entire work cycle of the heart muscle consists of two phases: systole and diastole. At the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle, the atria and partly the ventricles are filled with blood. Then the atria contract and the liquid medium is pushed into the ventricles, while the veins at the mouth are compressed, which prevents blood from flowing into them. After this, the atria relax, the ventricles contract and blood is pushed into the aorta through the left ventricle and into the pulmonary artery through the right. The mitral and tricuspid valves at this moment block the return of blood to the atrium. After this, the cycle repeats again and so on throughout a person’s life.
Cardiac ri of the sympathetic nervous system. The release of adrenaline produced by the adrenal glands into the blood increases the strength and number of heart contractions, and the production of acetycholine has the opposite effect.
Listening to heart sounds is done using a stethoscope, invented by the French doctor Rene Laennec (the aesculapian was guided by the fact that it is quite difficult to hear the heart of ladies with a magnificent bust, simply by pressing the ear to the chest). Another invention is related to the human heart - this is the second hand on a watch, the patent belongs to the English doctor John Flower, he introduced an innovation to make it convenient to count a person’s pulse.
The heart rate in women is higher than in men, with an average of 78 beats per minute. In men it is 74-75 beats per minute. Although it is believed that the heart beats continuously, this is not entirely true. The period when the heart works is the contraction of the heart muscle; in a relaxed state, the heart begins a period of rest.
This explains the efficiency of the human motor; nature has arranged its activity in such a way that the heart has the opportunity to take a break from its hard and constant work.
It is known that no engine will work without fuel. For the heart, oxygen is such a “fuel”. In order to work for a day, the heart muscle will need 130 liters of pure oxygen, its average consumption per minute is 2.5 liters. One heartbeat is equal to the amount of energy it takes to lift an object weighing 200 grams to a height of one meter. The energy generated by a human engine in a day would be enough for a passenger car to travel 32 kilometers, and in a month the heart can produce such an amount of energy that if used, a person of average weight can easily be lifted to the top of the highest mountain - Chomolungmas. In a lifetime, a person could travel to the moon and back, using the resources of his own heart!
High blood pressure
55. High blood pressure is the most common risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
56. High blood pressure – above 140/90 mmHg. Art.
57. A persistent increase in blood pressure is called hypertension.
58. The highest blood pressure is early in the morning (around 5:00–6:00).
59. If left untreated, high blood pressure can cause a stroke or heart attack.
60. To lower blood pressure, lifestyle changes are often not enough - you need to take medications throughout your life.
61. Blood pressure should be measured at rest 2–3 times in a row to obtain an accurate reading.
Anatomy and physiology of the human heart
Our body is a complex structure consisting of individual components (organs and systems), the full functioning of which requires constant supply of nutrition and disposal of decay products. This work is performed by the circulatory system, consisting of a central organ (the heart pump) and blood vessels located throughout the body. Thanks to the constant work of the human heart, blood continuously circulates through the vascular bed, providing all cells with oxygen and nutrition. The living pump of our body makes at least a hundred thousand contractions every day. How the human heart works, what its operating principle is, what the numbers of the main indicators indicate - these questions are of interest to many people who care about their health.
general information
Knowledge about the structure and function of the human heart accumulated gradually.
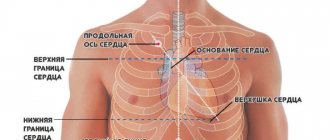
The beginning of cardiology as a science is considered to be 1628, when the English physician and naturalist Harvey discovered the basic laws of blood circulation. Subsequently, all the basic information was obtained about the anatomy of the heart and blood vessels, the human circulatory system, which is still used today. The living “perpetual motion machine” is well protected from damage due to its favorable location in the human body. Every child knows where a person’s heart is – in the chest on the left, but this is not entirely true. Anatomically, it occupies the middle part of the anterior mediastinum - this is a closed space in the chest between the lungs, surrounded by the ribs and sternum. The lower part of the heart (its apex) is slightly shifted to the left side, the remaining parts are in the center. In rare cases, there is an abnormal location of the heart in a person with a displacement to the right side (dextrocardia), which is often combined with a mirror placement of all unpaired organs in the body (liver, spleen, pancreas, etc.).
Everyone has their own ideas about what a person’s heart looks like; usually they differ from reality. Externally, this organ resembles an egg, slightly flattened on top and pointed at the bottom, with large vessels adjacent on all sides. The shape and size may vary depending on the gender, age, body type and health status of the man or woman.
People say that the size of the heart can be approximately determined by the size of your own fist - medicine does not argue with this. Many people are interested in knowing how much a human heart weighs? This indicator depends on age and gender.
The weight of an adult's heart reaches an average of 300 g, and in women it may be slightly less than in men.
There are pathologies in which deviations of this value are possible, for example, with myocardial growth or expansion of the heart chamber. In newborn children, its weight is about 25 g, the most significant growth rates are observed during the first 24 months of life and at 14-15 years, and after 16 years the indicators reach adult values. The ratio of the mass of an adult’s heart to the total body mass in men is 1:170, in women 1:180.
Ear, hearing
There are about 25,000 cells in the inner ear that respond to sound. The range of frequencies perceived by hearing lies between 16 and 20,000 hertz. It decreases with age, especially due to decreased sensitivity to high-pitched sounds. By the age of 35, the upper limit of hearing drops to 15,000 hertz.
The ear is most sensitive to the range of 2000-2300 hertz. The best ear for music (the ability to distinguish pitch) is in the region of 80-600 hertz. Here our ear is able to distinguish, for example, two sounds with a frequency of 100 hertz and 100.1 hertz. In total, a person distinguishes between 3-4 thousand sounds of different pitches.
We become aware of sound 35-175 milliseconds after it reaches the ear. It takes another 180-500 milliseconds for the ear to “tune in” to receive a given sound and achieve the best sensitivity.
Anatomical and physiological features
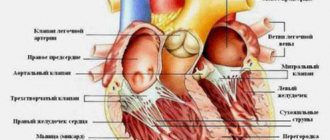
To understand the structure of the human heart, let's first look at it from the outside. We see a cone-shaped hollow muscular organ, to which branches of large vessels of the human circulatory system approach from all sides, like tubes or hoses to a pump. This is the living pump of our body, consisting of several functional sections (chambers), separated from each other by partitions and valves. Every eighth grade student knows how many chambers there are in the human heart. For those who missed biology classes, we repeat - there are four of them (2 on each side). What are these heart chambers and what is their role in the circulatory system:
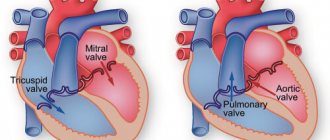
- The cavity of the right atrium receives two vena cava (inferior and superior), carrying oxygen-free blood collected from all over the body, which then enters the lower section (right ventricle), bypassing the tricuspid (or tricuspid) heart valve. Its valves open only during compression of the right atrium, then close again, preventing blood from flowing in a retrograde direction.
- The right heart ventricle pumps blood into the common pulmonary trunk, which then divides into two arteries that carry oxygen-free blood to both lungs. In the human body, these are the only arteries through which venous rather than arterial blood flows. In the lungs, the process of oxygenation of blood takes place, after which it is delivered to the left atrium through two pulmonary veins (again, an interesting exception - the veins carry oxygen-rich blood).
- In the cavity of the left atrium there are pulmonary veins that deliver arterial blood here, which is then pumped into the left ventricle through the cusps of the mitral valve. In the heart of a healthy person, this valve opens only in the direction of direct blood flow. In some cases, its valves can bend in the opposite direction and allow part of the blood from the ventricle to pass back into the atrium (this is mitral valve prolapse).
- The left ventricle plays a leading role; it pumps blood from the pulmonary (lesser) circulation to the systemic circle through the aorta (the most powerful vessel in the human circulatory system) and its numerous branches. The ejection of blood through the aortic valve occurs during systolic compression of the left ventricle; during diastolic relaxation, another portion from the left atrium enters the cavity of this chamber.
Skin formations
Non-removable "clothes"
Skin is the heaviest organ of the human body. She weighs on average 2.7 kg. The skin does not allow water, germs, or dirt to pass through. Protects us from blows, injections, bites. About 2% of the oxygen consumed by a person enters the body through the skin. A person of average height loses about 800,000 skin microparticles every hour, and an average of 675 grams per year. By the age of seventy, total skin loss is just over 47 kg, that is, 70% of the average person's weight. The human body excretes about 0.5 liters of water per day through the skin. About 10 grams of solids are released.
Who can tell if we are cold or hot?
The entire skin surface of the human body contains about 250,000 “cold” receptors and only 30,000 “heat” receptors. Skin temperature varies in different parts of the body. So, in the armpit it is 36.6ºС, on the stomach - 34ºС, and on the face - 25ºС. Blood and internal organs have a temperature of 37.2–38.5ºС.
Is it better to be clean or dirty?
On one cm2 of dirty skin there are about 40,000 microbes.
Transmitting "SOS!"
Our skin contains 250,000 nerve endings that respond to cold, 30,000 that respond to heat, and about 1,000,000 that respond to pain.
Skin and time
The skin is least sensitive to injections at 9 am and most permeable to cosmetics between 6 and 8 pm.
Space "antennas"
Human hair is 500 times thicker than the walls of a soap bubble, 5 times thicker than a capillary, 12 times thicker than the walls of an alveoli and 20 times thicker than a spider's web. Hair grows in newborns at a rate of 0.2 mm per day, later - up to 0.3–0.5 mm per day. Eyebrow, eyelash and armpit hair lasts 3–4 months, scalp hair lasts 4–6 years. In a month, hair grows by one centimeter. About 100 hairs die on the head every day. Dead hair may not fall out immediately, so up to 20% of dead hair sometimes accumulates on the head.
The braid is not only a girl’s beauty
The longest braid of one Japanese woman is 3 meters, she grew it for 20 years. The longest hair was worn by Swami Pandarasannadi, the head of the Indian monastery of Thirudathurai. In 1949, his hair length was 7 meters 92 centimeters.
And beard and mustache
The longest beard belonged to Hans Langseth - 5 meters 33 centimeters, and the longest mustache belonged to the Swede Birger Pellas - 2 meters 90 centimeters.
Primate Heritage
The tips of all twenty fingers on our limbs bear dense flat horny formations - nails. Nails are the property of primates. The nail grows due to the epithelium of the nail bed. Nails protect especially sensitive fingertips. A fingernail grows at a rate of a hundredth of a millimeter per day, and a toenail grows at a rate of five hundredths. Over the course of a year, the fingernail lengthens by a total of three centimeters. The longest nail on the hand (on the thumb of the left hand) reaches a length of 101.6 centimeters. It belonged to Indian Sridhar Chillar. The total length of the fingernails on his left hand, when measured in March 1990, was 4 meters 40 centimeters. He hasn't cut his nails since 1952.
Internal structure
The heart wall consists of several layers represented by different tissues. If you mentally draw its cross-section, you can highlight:
- the inner part (endocardium) is a thin layer of epithelial cells;
- the middle part (myocardium) is a thick muscle layer that, through its contractions, provides the main pumping function of the human heart;
- outer layer - consists of two leaves, the inner one is called the visceral pericardium or epicardium, and the outer fibrous layer is called the parietal pericardium. Between these two leaflets there is a cavity with serous fluid, which serves to reduce friction during heart contractions.
If we consider the internal structure of the heart in more detail, it is worth noting several interesting formations:
- chords (threads of tendons) - their role is to attach the valves of the human heart to the papillary muscles on the inner walls of the ventricles, these muscles contract during systole and prevent retrograde blood flow from the ventricle to the atrium;
- heart muscles - trabecular and comb formations in the walls of the heart chambers;
- interventricular and interatrial septa.
In the middle part of the interatrial septum, the oval window sometimes remains open (it functions only in the fetus in utero, when there is no pulmonary circulation). This defect is considered a minor developmental anomaly; it does not interfere with normal life, unlike congenital defects of the interatrial or interventricular septum, in which normal blood circulation is significantly impaired. Whatever blood fills the right half of the human heart (venous), this will also enter the left side during systole, and vice versa. As a result, the load on certain parts increases, which over time leads to the development of heart failure. The blood supply to the myocardium is carried out by two coronary arteries of the heart, which are divided into numerous branches, forming the coronary vascular network. Any disruption of the patency of these vessels leads to ischemia (oxygen starvation of the muscle), up to tissue necrosis (infarction).
Water, tears
A sip of water - is it a lot or a little? Numerous measurements have shown that a man swallows an average of 21 milliliters of liquid in one gulp, and a woman swallows 14 milliliters.
Thirst occurs when water loss equals one percent of body weight. A loss of more than 5% can lead to fainting, and more than 10% can lead to death from desiccation. Tears are constantly produced by the lacrimal glands and moisturize the cornea of the eye, protecting it from exposure to air and dust.
Even stern men shed 1-3 milliliters of tears every day.
Humans are 60% water. It is distributed unevenly: for example, in fatty tissues there is only 20% water, in bones 25%, in the liver 70%, in muscles 75%, in blood 80% and in the brain 85% of water of the total weight.
When looking at these figures, one is struck by the apparent paradox - there is less water in liquid blood than in the rather dense brain. But it’s not only about the quantity, but also about the “packaging” of water.
It is known that jellyfish are 98-99% water, however, the jellyfish does not dissolve in the sea, it can be picked up.
The remaining 40% of the human body weight is distributed as follows: proteins - 19%, fats and fat-like substances - 15%, minerals - 5%), carbohydrates - 1%.
Cardiac performance indicators
If all departments work in a balanced manner, the contractility of the myocardium is not impaired, and the vessels of the heart are well-passed, then a person does not feel its beating. While we are young, healthy and active, we do not think about how the human heart works. However, once chest pain, shortness of breath or interruptions appear, the work of the heart immediately becomes noticeable. What indicators should everyone know:
- The value of the heart rate (HR) is from 60 to 90 beats per minute, the heart should beat at rest in an adult; if it beats more than 100 times, it is tachycardia, less than 60 is bradycardia.
- Stroke volume of the heart (systolic volume or CO) is the volume of blood that is released into the human circulatory system as a result of one contraction of the left ventricle; normally it is 60-90 ml at rest. The higher this value, the lower the heart rate and the greater the body’s endurance during exercise. This indicator is especially important for professional athletes.
- Cardiac output (minute volume of blood circulation) is defined as CO multiplied by heart rate. Its value depends on many factors, including the level of physical fitness, body position, ambient temperature, etc. The norm at rest while lying down for men is 4-5.5 liters per minute, for women it is 1 liter per minute less.
A person has a unique organ thanks to which he lives, works, loves. Taking care of the heart is all the more valuable, and it begins with studying the features of its structure and function. In fact, the cardiac engine is not so eternal; its work is negatively affected by many factors, some of which a person can control, others he can completely exclude in order to ensure a long and fulfilling life.
The functioning of the body is impossible without the main organ - the heart. It performs an important job - it pumps blood in the body, ensuring its flow to all internal organs, while simultaneously delivering nutrients and oxygen to them through the bloodstream. Many people are very figuratively familiar with the work and structure of the heart, and cannot always even indicate its location with maximum accuracy; as a rule, this comes down to general knowledge that it is located “in the chest.” In order to know how the body functions and the heart works, what diseases it is susceptible to and how to treat them, it is necessary to know its structure, phases and blood pumping cycles. It is foolish to think that this information will be useful only to medical workers, it will be useful to ordinary people, and in some cases it may help save lives.
Receptors, sense of smell
There are about 9,000 taste buds on the tongue. The best temperature for their operation is 24 degrees Celsius. (Gourmets should take this into account!)
The area of the olfactory zone of the nose is 5 square centimeters. There are about a million olfactory nerve endings located here. In order for an impulse to arise in the olfactory nerve fiber, approximately 8 molecules of an odorous substance must reach its end. For the sensation of smell to occur, at least 40 nerve fibers must be excited.
When chewing food, the jaw muscles develop a force of up to 72 kilograms on the molars, and up to 20 kilograms on the incisors. Chewing bread requires an effort of 25 kilograms, chewing fried veal requires 15 kilograms.
Location and functions of the heart
The heart is an important human organ, which is located in the center of the chest between the lungs, with a slight shift to the left. In exceptional cases, it may be located on the right, when a person has a mirror structure of the body. At its core, it is a muscle that, by contracting, maintains normal blood circulation in the body. The heart has a cone shape, the average weight of the organ is 250-300 grams, and its dimensions are 10-15 cm in height and 9-10 cm at the base.
Heart function
Pumping blood is the main function of the heart. This process must occur continuously to ensure that the internal organs are supplied with oxygen and nutritional components.
The work of the heart muscle consists of two stages:
- Diastole is relaxation of the heart. At this stage, blood enters the left atrium and flows through the mitral orifice into the ventricle.
- Systole is a contraction of the heart, during which blood flows into the aorta and spreads throughout the body, transporting oxygen to the internal organs.
The cardiac cycle includes the following stages: contraction of the atria, which lasts 0.1 seconds, and ventricles (duration 0.3 seconds) and their relaxation.
Eyes, vision
The human eye is capable of distinguishing 10,000,000 shades of color. Women blink approximately 2 times more often than men - 6,205,000 times a year, with each blink lasting 0.3 seconds. It is not difficult to calculate that by blinking, we keep our eyes closed for 21.5 days a year.
It is impossible to sneeze with your eyes open.
People with blue eyes are more sensitive to pain than others.
One eyeball weighs 28 grams.
If you like to download free books from the Internet, keep in mind that our eyes perceive printed information from a computer screen 25% slower than from a paper sheet.
Men are about 10 times more likely than women to suffer from color blindness.
The eye is able to distinguish a well-lit object with a diameter of one tenth of a millimeter at a distance of 25 centimeters. But if the object itself glows, it can be much smaller.
A hole with a diameter of 3-4 thousandths of a millimeter, pierced in a sheet of tin, behind which a light bulb is lit, is clearly visible to the normal eye.
The eye is capable of distinguishing 130-250 pure color tones and 5-10 million mixed shades.
Complete adaptation of the eye to darkness takes 60-80 minutes.
Anatomical structure of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ that is surrounded on the outside by the pericardium. The cavity between the two components is filled with liquid, which performs an important function - it reduces friction of the heart muscle and ensures its hydration. The pericardium includes three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium.
The heart itself consists of 4 sections: two atria and two ventricles. The left ventricle and atrium circulate arterial blood enriched with oxygen, the right side of the heart helps pump venous blood. Entering the heart, blood accumulates in the atria and, upon reaching the required volume, is redirected to the ventricles.
All sections are separated by valves - the mitral on the left and the tricuspid on the right. Their main purpose is to ensure the movement of blood in one direction - from the atria to the ventricles.
During normal functioning of the heart, the right and left parts do not communicate with each other. With the development of pathology (usually congenital heart defects), holes may remain in the septum. In this case, during contraction of the heart muscle, blood from one half can enter the other.
Heart diseases
Heart disease has increasingly affected people in recent decades. This is caused by a low quality of life, poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle and a large number of bad addictions that every second person on earth has. Older people are more likely to suffer from heart disease. This is due to physical fatigue of the muscle, thickening of the blood, slowdown of all processes in the body and the presence of other concomitant diseases. According to statistics, heart disease is the most common cause of death. All diseases are conventionally divided into three groups, depending on which part of the organ is affected - blood vessels, valves and membrane tissue.
Let's look at the most popular heart diseases:
- Atherosclerosis is a disease in which blood vessels suffer. As the disease develops, they become blocked and atherosclerotic plaques form, which disrupt the blood flow process and, accordingly, interfere with the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
- Heart failure is a set of pathological changes in which the contractility of the organ is significantly reduced, resulting in the formation of stagnation in the pulmonary or systemic circulation.
- Heart defects are defects of the heart muscle, individual components of the organ, which disrupt its normal functioning. Congenital heart defects are more common; acquired ones are diagnosed much less frequently.
- Angina pectoris is a dangerous pathology that is characterized by oxygen starvation of the heart, and its cells die.
- Arrhythmia is a violation of the heart rhythm, which is characterized by its acceleration (tachycardia) or slowdown (bradycardia). This pathology is usually accompanied by a number of other heart ailments.
- Myocardial infarction is a disease in which there is insufficient blood supply to the myocardium.
- Pericarditis is inflammation of the outer lining of the heart - the pericardium.
Muscles, skin
When a person smiles, 17 muscles work.
The strongest muscle in the human body is the tongue.
The smallest muscle is the stapes muscle. When the sounds are too strong, she turns the stirrup so that the ratio of the lengths of the arms of the bone-lever changes, and the sound amplification factor drops.
It is impossible to accurately indicate the number of muscles. Experts count from 400 to 680 muscles in humans. For comparison: grasshoppers have about 900 muscles, some caterpillars have up to 4000. The total muscle weight in a man is about 40% of his body weight, and in a woman it is about 30%.
Man is the only representative of the animal world capable of drawing straight lines.
During a lifetime, a person's skin changes approximately 1000 times.
Treatment of heart diseases
A cardiologist treats heart diseases. Before starting therapy, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient, which includes: an electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart, general and biochemical blood tests, Holter ECG and other studies.
Only after complete diagnosis and diagnosis is therapy prescribed. Basic methods of treating heart disease:
- Conservative treatment: maintaining physical and emotional peace, taking prescribed medications, regulating proper nutrition.
- Drug therapy is used for any disease. Most often, drugs are prescribed to reduce bad cholesterol, blood thinners (especially in old age), inhibitors and many others, depending on the diagnosis.
- Surgical intervention is performed if it is impossible to achieve the desired effect using conservative methods, for example, when a pacemaker is required, a hole between the parts of the heart needs to be repaired, or the patient needs an organ transplant.
Diagnosis and treatment of heart disease should be carried out exclusively by a doctor (general practitioner, cardiologist or cardiac surgeon). Self-medication is strictly forbidden - at best it will not bring the expected result, at worst it will aggravate the situation and lead to a number of complications.
Disease Prevention
A healthy heart is the key to excellent health and normal functioning of the body. It is extremely important to take proper care of it to reduce the risk of developing heart disease. To do this, just follow the doctor’s simple recommendations:
- Monitor your diet, giving preference to healthy and healthy foods. It is necessary to exclude from your diet dishes that adversely affect the condition of blood vessels and the functioning of the heart muscle (fatty, fried, smoked).
- Avoid excessive physical activity, but this does not mean that you should completely exclude sports from your life. Moderate exercise and walking in the fresh air will only strengthen the heart muscle and help avoid illness.
- Minimize stress, strong emotions and experiences. An increase in adrenaline accelerates blood circulation and forces the heart to work harder - this provokes the development of a number of pathologies.
- Promptly treat diseases that can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, for example, sore throat.
The heart is an important organ that circulates blood in the body. It is extremely important to maintain its health and normal functioning. By taking care of your heart, you will ensure a long and healthy life.
Selection
Why are we crying?
Children cry to get attention, to express their emotions: fear, anger or joy. And also so that with tears the harmful substances that are produced from pain and suffering are removed from the body. In addition, when we blink, tears wash the eyeball, clearing it of dust and germs. A healthy human body produces approximately 0.5 liters of tear fluid per year. Even the sternest man sheds 1–3 milliliters of tears every day.
Blood filters
The total length of the renal tubules is 120 kilometers. A person has about 2,000,000 nephrons in both kidneys. During the day, the kidneys pass 2,000 liters of blood through themselves, and this is a whole tank. An adult excretes 1,200–1,600 ml of urine per day and 15–45 mg of oxalic acid should be excreted in the urine.
What are uroliths?
The chemical composition of uroliths—kidney stones—may vary. 40% of uroliths are oxalates (oxalic acid salts), 27% are phosphates (orthophosphoric acid salts), 12–15% are urates (uric acid salts), 2% cystine, xanthine and protein stones and 20–30% are mixed stones type.