To measure blood pressure (BP), automatic or mechanical tonometers are used, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. Self-monitoring and keeping a blood pressure diary motivates the patient to comply with all doctor’s recommendations and increases the effectiveness of treatment by 20%. We highly recommend bringing your BP diary to every doctor's visit.
When measuring blood pressure, a number of conditions must be met:
- Blood pressure must be measured in a sitting position. It is advisable to lean on the back of a chair and relax your legs.
- The hand on which the measurement is being taken should lie freely on the table, without tension.
- The measurement is carried out after a 10-15 minute rest, 2-3 times a day, at approximately the same time. The measurement must be taken twice with a break of 2-4 minutes.
- Initially, the measurement is carried out on both arms in order to identify the arm on which the blood pressure is higher (usually the difference is 5-10 mmHg). In the future, measurements are carried out on the hand on which it turned out to be higher.
- It is advisable not to talk while measuring blood pressure.
- 1 hour before measurement, you should avoid eating and smoking.
- The blood pressure cuff should be the right size for you.
- The lower edge of the cuff should be located 1-2 cm above the elbow.
Measuring blood pressure using the auscultatory method (Korotkoff method) with a mechanical tonometer using a stethoscope requires compliance with several additional rules:
- It is necessary to install the head of the stethoscope 1-2 cm inward from the center of the cubital fossa.
- It is enough to quickly pump air into the cuff; the inflation level should be 20-30 mm. rt. Art. higher than “normal” blood pressure.
- You need to deflate the air from the cuff slowly at a speed of 3-4 mm. rt. Art. per second.
- Record the appearance of the first Korotkoff sound - this will be the systolic blood pressure.
- Record the disappearance of Korotkoff sounds; this corresponds to diastolic blood pressure.
It is important to know!
When measuring blood pressure with any tonometer, mechanical or automatic, with an interval of 2-3 minutes, the values may turn out to be slightly different.
Differences in tonometer readings should not be regarded as manifestations of inaccuracy or malfunction of the devices. The value of blood pressure, like all other parameters of the body, is not constant and is within the limits of physiological fluctuations.
It is also necessary to remember that with physical activity blood pressure increases. This is a physiological mechanism; when the load is stopped, blood pressure normally decreases after a few minutes.
Why do you need to measure blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of blood with which it acts on the walls of arteries and blood vessels.
There are diastolic (lower) and systolic (upper) pressure. The norm for an adult is around the boundaries of 120 to 80 mmHg. Significant deviations from these figures often signal the emergence of some disease. Jumps in blood pressure increase the risk of heart attack, ischemia, and stroke.
Increased levels can be observed with the development of the following pathologies:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- vascular diseases;
- renal failure;
- endocrine diseases;
- neurological disorders.
Low blood pressure is caused by: internal hemorrhages, heart failure, aggravated stomach ulcers, stress, vegetative-vascular dystonia, depression.
It is worth noting that reduced levels may be an individual characteristic of the body. However, high blood pressure almost always signals problems in the body.
To find out exactly the reasons for the jumps, you need to regularly monitor your condition, take measurements, and be examined by a doctor.
When is diagnosis prescribed?
The most common reason for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring is to assess the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy, especially in the case of combination treatment using several groups of antihypertensive drugs. Other reasons for prescribing ABPM include the diagnosis of early arterial hypertension, symptomatic arterial hypertension, patients with heart failure, with myocardial hypertrophy, in the presence of brain diseases, and suspected sleep apnea syndrome.
ABPM is used to examine patients suffering from various types of hypotension: constitutional and orthostatic.
ABPM allows you to determine the presence of so-called “office hypertension”, in the diagnosis of which it is necessary to promptly establish a work and rest schedule.
Pressure measurement methods
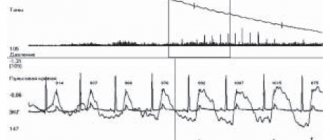
There are 2 types of manipulations for measuring blood pressure: direct and indirect. The direct method is highly accurate, but physically traumatic. A pressure gauge needle is inserted into the wall of the heart or artery. The tube of the device is filled with an anti-clotting agent. The scribe records blood pressure fluctuations in the form of a curve. The technique is used by cardiac surgeons, sometimes in laboratory conditions.
Indirect pressure measurement is a non-invasive method. The measurement is carried out on the peripheral vessels of the elbow or wrist using a tonometer. There may be errors, but the device can be used in any conditions.
Indirect diagnostics of pressure according to the type of technology used (mechanical, electronic) is divided into auscultatory and oscillometric options.
Auscultatory method
Also known as the Korotkoff method. Named after its inventor, surgeon N.S. Korotkova. Mechanical tonometers are used. The cuff is secured to the shoulder and inflated with air through a pear-shaped balloon. The upper and lower limits of pressure are determined by ear using a phonendoscope.
When the cuff is inflated, the blood flow in the artery is blocked, the external pressure exceeds the systolic pressure, and the characteristic sound pulsation stops. The gradual release of air restores blood movement, and tones begin to be heard again. The first beat corresponds to systal (upper) pressure, the last – diastolic (lower).
The Korotkov method is recognized as standard. It has its positive and negative sides. Even an accidental hand movement will not affect the result. However, there is a risk of incorrectly applying the cuff and stethoscope. The objective determination of pressure indicators can be interfered with by noise in the room. The device consists of many parts; during its use, a considerable number of manipulations are expected, so you need to learn how to measure pressure correctly.
Oscillometric method
Electronic tonometers with automatic or semi-automatic control are used. The cuff is attached above the elbow or on the wrist. In a fully automatic system, air is drawn in and released independently. In a semi-automatic machine, you must use a bulb. The indicators are displayed on the display without outside help based on the recorded pulsation.
The advantages of this method include the rapid preparation of the electronic device for operation. In addition, working with it does not require special skills, there is no error in human attention, and the noise in the room is not important.
In order for the indicators to be determined correctly, the hand must be motionless while measuring pressure. It is also forbidden to talk during the procedure.
Contraindications to the procedure
The procedure for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring is a completely safe test and has no absolute contraindications. But there are relative contraindications, which include thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, acute infectious disease (as a temporary contraindication), impaired motor activity due to the severity of some chronic diseases.
Psychological reasons (phobias and fears) are a contraindication for ABPM.
How to measure pressure correctly
The most accurate result of this diagnosis can be obtained by following certain rules. Distorted indicators will not provide the necessary information content and may lead the patient and doctor to a false conclusion.
Preparation for the procedure
It is recommended to measure blood pressure an hour or more after fitness or smoking. Coffee, tea, energy drinks, a hot shower or bath require you to wait 1.5-2 hours. You should also wait 15-20 minutes. after eating.
It is advisable to empty the bladder and intestines before measuring pressure.
Before starting the diagnosis, you need to sit or lie down for 2 to 10 minutes. The posture during the measurement process should be relaxed, sitting, legs not crossed, not tense. The cuff should be placed correctly on the arm at the same level as the heart. The patient must remain silent.
Before measuring pressure, it is recommended to ventilate the room and ensure a comfortable air temperature.
Mechanical measurement algorithm
- Prepare the device. Remove the tonometer from the packaging and place the meter on a flat surface, ensuring a good view of the dial. Straighten all the tubes.
- Put on the cuff. Wrap the material around your bare forearm (2-3 cm above the elbow). Fasten tightly, but not too tight.
- Install a phonendoscope. Place the membrane under the cuff just above the elbow (on the inside of the arm). Insert headphones into your ears.
- Inflate the cuff. Take the bulb in your palm and tighten the valve tightly in a clockwise direction until it stops. Squeeze the bulb with quick movements until the cuff is filled with air and the monometer needle reaches 180 mm Hg. At this stage, a slight numbness of the arm may be felt due to blockage of blood flow in the artery.
- Start the measurement itself. Slowly open the bulb valve counterclockwise, gradually releasing air. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the dial needle and the tone in the ears. The first beat heard will occur at the systolic pressure mark, the last one at the diastolic pressure mark. Remember these indicators.
- Finish the procedure. As soon as the beats in the headphones have completely stopped, you can deflate the remaining air, remove the cuff and stethoscope, and put away the device.
If you were unable to listen to the readings, you can inflate the cuff again during the measurement process. You cannot repeat the manipulation more than once, because this distorts the data.
Electronic measurement algorithm
- Preparing the device. Place the tonometer body on a flat surface and straighten all the tubes well.
- Prepare your hand. Take off your watches, bracelets, roll up your sleeves.
- Put on the cuff. Place the fabric on the forearm above the elbow 2 cm.
- Patient preparation. Take a relaxed sitting position with straight legs. Keep your hand calm, it is better to rest it on the table with your palm up. Shut up and breathe evenly for about 30 seconds.
- Measurement. Press the start button according to the instructions. The cuff will begin to inflate and running numbers will appear on the screen. Without changing position, wait until the air is completely deflated and the readings on the monitor stabilize.
- Remove the device. Remove the cuff and stop the device.
When measuring with a wrist tonometer, you should also remove jewelry from your hand and expose your skin. The cuff is put on with the display up 1 cm above the hand. The hand with the device is placed palm down on the opposite shoulder. This is followed by startup, inflation of the cuff, appearance of indicators and deflation.
For maximum accuracy, the diagnosis can be repeated after 15 minutes.
Rules for the patient
Correct measurements depend entirely on the patient's behavior. Keeping a diary is a prerequisite that guarantees diagnostic results. The daily routine is entered into the diary: sleep, exercise, psycho-emotional experiences, walks, clinical symptoms that arise during the day, taking medications. Detailed records will allow you to assess the condition of the body and the factors that worsen the patient’s well-being.
If any negative symptoms appear, the patient consults a doctor. Headaches (severe migraines), weakness or nausea are reasons to suspend ABPM. It is recommended to avoid crowded places and places with a lot of noise for two days - it will affect the recorder and prevent you from taking correct measurements. If the edge of the cuff moves, it needs to be corrected - the correct position of the cuff is 2 cm below the elbow. If the patient is concerned about the correct conduct of ABPM, the attending physician will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Measurement errors
An important condition is not to touch the phonendoscope membrane and cuff with your hands during the measurement process. Pulse from holding fingers will distort the readings. The tissue between the skin and the cuff interferes with the membrane's receptivity.
You cannot deviate from the level of the heart in the position of the cuff; the numbers will turn out to be too high or too low. The same result will be achieved if the Velcro is fastened too loosely or too tightly, a tired state, a hunched back, or the patient moving and talking.
When using a mechanical tonometer, you should not choose to round the indicators to 0 and 5. Only the actual data shown is taken as truth.
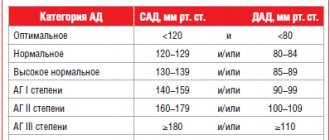
Interpretation of indicators
The blood pressure of an adult is distributed by doctors as follows:
- optimal. 120 by 80 units and slightly lower;
- normally acceptable. Up to 130 to 85;
- moderately elevated. Up to 139 to 89.
Numbers above the moderately elevated limit indicate hypertension.
Children's blood pressure may have different standards depending on age; they are determined by the doctor.
Pressure monitoring
Monitoring refers to repeated measurements over a certain period. This practice is used to select the right medications, control pregnancy, and certain diseases. The doctor may prescribe diagnostics at regular intervals, at set hours, require you to keep a blood pressure diary or wear a smart blood pressure monitor with a memory function. The latter option is more expensive, but is convenient for recording more than 100 indicators with the date and time of measurement without the participation of the patient.
Determining blood pressure using devices is used everywhere in everyday life and medicine. Different tonometers have their own errors and advantages. It is better to buy a specific type after consulting a supervising doctor, taking into account the situation.
In this article:
- Pressure measurement methods
- How to measure blood pressure
- Types of devices for measuring blood pressure
Blood pressure is one of the main indicators of the functionality of the cardiovascular system. To correctly measure blood pressure, you need to know the basic methods and rules, as well as the features of research instruments.