Cervical spinal stenosis is a process of reducing the lumen of the spinal canal due to the development of various pathological structures. As a rule, the tendency to form stenosis most often occurs in people over 55 years of age. In a quarter of cases of the disease, cervical vertebral stenosis is diagnosed. In the absence of timely measures taken, spinal stenosis causes disability and disability.
Types of cervical stenosis
This pathology is represented by the following groups.
- Congenital (primary) stenosis, when the disease develops as a result of congenital abnormalities in the structure of the spine.
- Degenerative , acquired or secondary stenosis of neck vessels is a consequence of destructive-degenerative acquired changes.
- Combined or mixed stenosis is determined in the presence of various causative development factors.
Based on the area of the lesion, a distinction is made between relative and absolute stenosis (area less than 75 mm² or more than 75 mm², respectively).
Lateral stenosis is defined as a narrowing of the intervertebral foramen to 0.4 cm or less.
The term sagittal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the canal in the same plane.
Anatomically, the following types of cervical spinal canal stenosis are distinguished:
- lateral or lateral , when the exit site of the roots (radicular canal) of the spinal cord decreases in volume;
- central , when on the arch of the cervical vertebra (at the point where the roots exit) the distance from the posterior surface to the lateral surface decreases.
What's happened
First, it’s worth understanding what a carotid artery is: in the human body there are two carotid arteries, running from the chest through the sides of the neck to the head. Their main task is to nourish the brain. Like any artery, they are confirmed by atherosclerosis - a serious disease, the nature of which is not fully understood, as well as the causes. This disease manifests itself in the deformation of the walls of blood vessels, when the tissues lining the vessel grow, cholesterol deposits appear between them, and the lumen of the vessel becomes smaller and smaller until it becomes completely blocked (obstruction). Oxygen-enriched blood flows through the carotid arteries for brain cells, so narrowing the lumen of the vessel is very dangerous - it can cause a stroke.
Why does cervical stenosis occur?
Cervical spinal stenosis develops for several reasons:
- Spinal fracture with compression of the vertebrae (compression);
- Congenital pathological changes in the structure of the vertebrae;
- Inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- Tumor processes;
- Intervertebral disc herniation;
- Chronic diseases of the articular surfaces of the spine;
- Adhesions after surgery;
- Overweight;
- Intervertebral disc displacement;
- Bone growths and osteophytes;
- Violation of the structure of the posterior yellow ligament;
- Osteochondrosis.
Stenosis of the neck vessels develops due to a decrease in the cavity where the spinal cord, nerves and vessels of the spine are located. First, complaints arise during certain turns and bends, then blood flow is disrupted and the situation worsens.
Over time, the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases, provoking congestion and inflammatory processes.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms may vary depending on whether the process is acute or chronic.
In case of acute pinching, the main symptom is severe pain in the neck. It may intensify when turning the head, or the person will complain of a feeling of numbness when it is physically impossible to turn the head. This happens when a person has suffered a minor injury (strained neck muscles) or slept in an uncomfortable position.
Arteries pass through the cervical vertebrae, feeding brain tissue and carrying out venous drainage. When pinched, this process is disrupted. As a rule, this process develops gradually; the body is able to compensate for a long time for the lack of oxygen and other substances entering the brain with the bloodstream. Therefore, the clinical picture increases progressively.
Symptoms of chronic pinching of the vertebral artery from the side of the brain are expressed as follows:
Cervical gymnastics
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- memory loss;
- deterioration of attention;
- visual disturbances (floaters or spots before the eyes);
- hearing loss, ringing in the ears;
- fainting or dizziness.
When such symptoms are constantly present, a person’s quality of life decreases: sleep is disturbed, depression develops, and motivation for any activity disappears. Therefore, if you notice any of the described signs, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Headache and dizziness are the most common symptoms of pinched vessels in the cervical spine
If the pinching is caused not by osteochondrosis, but by another disease (problems with the skeletal system of the body, pathologies of vascular origin, tumor) or injury, the clinical picture may differ. Its intensity will depend on how quickly the underlying disease develops.
Symptoms
The symptoms of absolute sagittal stenosis are determined by which structures are being compressed. The disease progresses slowly.
- Pain in the neck occurs - first in a certain position, gradually turning into permanent pain, which can radiate to the arms, shoulders, back of the head or shoulder blades.
- Feeling dizzy with sudden bends and turns, fainting is possible.
- Headaches in the temples and back of the head.
- The sensitivity of the scalp, arms and neck is impaired.
- You feel discomfort and weakness in your hands.
- The tone of the upper limbs and muscle frame increases.
- Changes in the functioning of the pelvic organs are observed: diarrhea alternates with constipation, fecal and urinary incontinence.
- Weakness in the legs.
- Breathing is labored, shallow, or rapid.
- Paralysis of limbs or complete immobility.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy for vertebral artery syndrome is an effective method of eliminating the main pathological symptoms, the effectiveness of which is based on strengthening the muscular structures of the neck, which create a framework for the neurovascular bundle. With the help of special therapeutic exercises, it is possible to achieve a positive effect of therapy and prevent complications of the process. The doctor will tell the patient in more detail about the duration and scope of such treatment after studying the clinic’s problem, the extent of the disorders and the presence of complications.
Diagnostic features
The doctor begins with a conversation with the patient, during which he finds out:
- complaints at the time of application;
- factors predisposing to the disease;
- previous diseases.
For the doctor, the body position that the patient is forced to take is important; he palpates the spine in order to determine the affected area.
The patient is prescribed additional examination:
- X-ray of the spine in two projections to determine bone growths, identify destroyed and fused vertebrae, disruption of the structure of joints, the presence of neoplasms, determine their size, location and structure;
- CT scan of the spine to find the cause of the disease, taking into account the smallest changes;
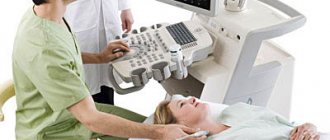
- MRI (if there are no contraindications) to detect changes in cartilage, nerves and blood vessels;
- myelogram to find changes in the structure of the spinal cord, the patency of the canal and the condition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Complications of cervical-vertebral syndrome
Cervical-vertebral syndrome is dangerous due to its complications, which often pose a threat to the patient’s life. This disease can cause the following consequences:
- ischemic stroke in the blood supply of the vertebral artery;
- myocardial infarction associated with dysfunction of the neurovascular bundle that supplies the heart muscle;
- suffocation as a result of impaired swallowing reflex.
All complications of SPA can be prevented with the help of timely and competent treatment, which can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist with extensive experience.
How is cervical artery stenosis treated?
Stenosis of the cervical arteries is treated using conservative methods (physiotherapeutic procedures and medications) and surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment is selected for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his condition:
- painkillers (NSAIDs) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- injections of hormonal agents into the spine to reduce swelling, tissue compression and pain;
- diuretics to reduce cerebrospinal fluid pressure and relieve swelling;
- electrophoresis with novocaine to relieve pain in the affected area;
- magnetic therapy to reduce swelling and relieve pain;
- when the muscle frame is tense, massage is used;
- physical therapy – special exercises for stenosis help strengthen the cardiovascular system, arm and neck muscles;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- spinal traction.
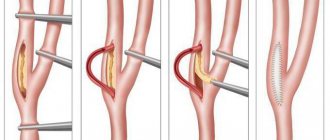
Surgical treatment
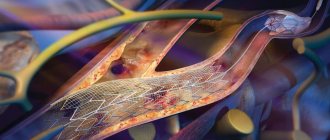
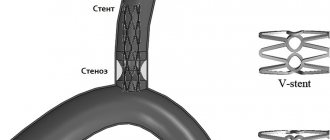
Surgical methods are used if a conservative approach does not provide a lasting effect or the development of the disease calls into question the patient’s life and ability to work. Today there are many methods of surgical treatment, but three operations provide maximum effectiveness:
- decompressive laminectomy - an operation to remove a structure that causes a narrowing of the canal (hernial protrusions, tumors, intervertebral discs and arches, osteophytes;
- installation of stabilizing systems;
- installation of an implant after removal of the affected fragment.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of vertebral artery syndrome with spinal osteochondrosis and other disorders of the cervical region includes a number of medications, the action of which is aimed at restoring lost functions, eliminating pathological symptoms and preventing the development of complications. For vertebral artery syndrome the following are prescribed:
- decongestants that help eliminate compression of blood vessels by neighboring tissues;
- muscle relaxants to relieve compression and tension of muscle tissue;
- drugs to improve brain nutrition;
- vascular dosage forms;
- neuroprotectors that protect nervous tissue from ischemia;
- drugs for the treatment of atherosclerosis;
- B vitamins to strengthen nerve fibers;
- antispasmodics that relieve headaches.
Medicines for vertebral artery syndrome can be taken only with the permission of the attending physician, without changing the dosages prescribed by the specialist and without exceeding the prescribed course. It is important to understand that any self-medication and ignoring the doctor’s recommendations has dangerous consequences, which often pose a threat to the patient’s life.
Prevention of cervical stenosis
To prevent the development of the disease, preventive measures should be used:
- kneading the neck - eliminating physical inactivity;
- exercise therapy;
- correct posture, including while working at the computer;
- proper nutrition;
- if necessary, timely contact a specialist.
Feedback from patients suggests that when contacting a medical facility in the early stages, within 6-12 weeks, the pain syndrome disappears in most of them. In advanced cases, as a rule, cervical vertebral artery stenosis requires hospital treatment for a long time.
Causes and prevention
The causes of vasoconstriction are being actively studied, but there is still no clear understanding. A hereditary cause is identified, and everything else can be attributed to risk factors. Among them:
- arterial injuries,
- obesity,
- smoking,
- diabetes,
- sedentary lifestyle,
- older age,
- high level of “bad cholesterol” in the blood (low-density lipoproteins are a combination of cholesterol and protein that do not take excess cholesterol from the vessels, but, on the contrary, attach them to the walls, forming cholesterol plaques).
Prevention of carotid artery stenosis, like any other arteries, consists of maintaining a healthy active lifestyle and a balanced diet to prevent an imbalance in the ratio of low- and high-density lipoproteins, and therefore the development of atherosclerosis.