Many people tend to endure pain, cope with discomfort with improvised means, take painkillers and limit themselves to complaints to loved ones that their temples are pressing and they are dizzy. This is often attributed to overwork due to heavy physical or mental labor, nervous tension and other reasons. At the same time, only a few go to doctors, and yet there can be quite a lot of causes for the occurrence of squeezing, aching or even acute pain in the temples in combination with dizziness, and not all of them are harmless.
Reasons why headaches occur in the temples and forehead
There are many reasons why a headache occurs in the forehead and temples. These symptoms often indicate a temporary or chronic disruption of the blood supply to brain cells. It is important to find out the exact cause of the deterioration in health in order to select an effective treatment regimen. The development mechanism for various pathologies is different, so treating a single symptom is ineffective - it is necessary to eliminate the main factor that provokes oxygen starvation of brain cells.
Physiological reasons
There are physiological reasons for headaches in the temples and forehead in a healthy person. This means that a medical examination will not show any abnormalities. In most cases, the patient needs proper rest, and in case of acute pain, take painkillers. Deterioration in health may be caused by the following factors:
- intense physical activity without sufficient rest is one of the causes of vascular disorders and pressing pain in the temples;
- mental stress, prolonged work at a monitor or with small parts are one of the causes of pain;
- heat stroke - prolonged exposure to open sunlight or high temperatures provokes acute headaches, dizziness and weakness;
- disruption of sleep, work and physical activity - lack of rest is especially dangerous;
- a sharp change in weather conditions, including atmospheric pressure, causes disturbances in vascular tone and painful sensations in the temples.
Stress and chronic fatigue are a common cause of headaches and pressure on the temples and forehead. These symptoms disappear after proper rest and return when the regime is violated again. Doctors recommend avoiding overwork, as it causes increased stress on the heart and blood vessels, disorders of the nervous and other systems.
Migraine
Migraine is an acute headache that occurs without a specific cause. The examination does not reveal any organic disorders, damage to blood vessels or the brain. It is often one-sided, affecting the left or right side of the head, the temple area. Migraines manifest themselves in attacks that last up to several hours, and moderate pain can persist for up to several days.
A characteristic feature of migraine is its aura. It includes symptoms that begin to appear some time before the main headache attack. It can be determined by the following characteristics:
- weakness, drowsiness, decreased concentration;
- increased sensitivity to bright light, loud sounds;
- nausea;
- auditory and visual hallucinations (appearance of dark circles in the field of vision) are possible.
Migraine is a chronic disease that can first appear in both childhood and adults. If attacks occur frequently, you may notice a certain relationship with the factors that cause them. Thus, in some patients, migraine worsens at certain times of the year and is associated with moving or other reasons. To treat this disease, special medications are prescribed, since conventional painkillers available for use at home do not have the necessary effect.
Vascular diseases
Severe headaches in the forehead and temples are often caused by insufficient blood supply to certain areas of the brain. The main reason for this is the weakness of the blood vessels and insufficient elasticity of their walls. Vascular pathologies can be congenital or acquired, and often appear in old age. They lead to ischemia of cells and tissues, as a result of which they cannot perform their functions. There are several diseases that can cause oxygen starvation of brain cells, headaches in the temples and frontal part.
- Hypertension is a persistent increase in blood pressure. This condition leads to a decrease in vascular tone and provokes a greater load on the heart. Blood pressure readings must be stabilized by taking medications and a special regimen of physical activity. Attacks of hypertension are dangerous because there is a risk of rupture of important vessels and the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Hypotension – decreased blood pressure. This is an equally dangerous condition in which ischemia of brain tissue occurs. Blood and nutrients are supplied to the cells in insufficient quantities. Chronic low blood pressure can cause ischemic stroke, as well as pressing pain in the temples and frontal part of the head.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disorder in which the level of cholesterol and lipoproteins in the blood increases. This leads to the formation of plaques on the inner wall of the arteries. The main danger of the disease is the narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which entails insufficient blood flow to certain areas and at the same time an increase in blood pressure.
The elasticity of veins and arteries decreases in old age. However, vascular disorders can also occur in young people and children. Among the main causes of headaches in the frontal region and temples caused by vascular diseases are poor diet, excess consumption of fatty foods, excess weight, excessive physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle. Doctors recommend periodically undergoing examinations and measuring blood pressure, since chronic diseases in the early stages can be asymptomatic.
Diseases of the cervical spine
If a patient often has headaches, forehead and temples, this may indicate diseases of the cervical spine. This area contains important arteries that carry blood to the brain. Their compression leads to ischemia of cells and tissues, deterioration in the functioning of individual areas. For pain in the head, forehead and temples, a comprehensive diagnosis is required to determine the most common neck diseases.
- Cervical osteochondrosis is one of the most common disorders. The disease is manifested by dystrophic changes in the bone and cartilage tissues of the vertebrae, deterioration of their nutrition and blood supply. This leads to overgrowth of the bone surfaces of the joints, the formation of uneven edges, osteophytes and growths. These formations compress the vessels and block blood access to important areas of the brain, causing ischemia.
- Vertebral subluxations are a displacement of the articular surfaces of bones, as a result of which the segments do not lose their integrity, but change their location relative to each other. They arise as a result of injuries, degenerative processes, weakness of muscles and ligaments. Subluxation causes acute pain in a certain area of the neck and decreased motor activity. In addition, it may be the reason why the frontal part of the head and temples hurt.
- Deformation of the spine is a deviation of its axis in the anterior, posterior or lateral directions. The process can develop both in childhood and in adults. It is accompanied by headaches in the frontal and temporal parts, dizziness, and painful sensations during movement. It is important to undergo periodic examinations and follow recommendations for the treatment of scoliosis, lordosis or kyphosis, since the disease can progress.
For pain in the frontotemporal part of the head associated with diseases of the cervical spine, complex treatment is recommended. The doctor prescribes exercises to strengthen muscles and stretch ligaments that will support the spine and prevent its further curvature. In some cases, surgery may be required. It is necessary if the vertebrae are severely deformed, block movements in the neck and cause acute pain.
Eye diseases
Diseases of the visual system can also cause pain in the frontotemporal part of the head. The cause is constant eye strain, inflammatory processes, and blurred vision. These diseases require regular examination by an ophthalmologist, wearing glasses or contact lenses, and drug treatment. In some pathologies (cataracts), surgical intervention is possible, which will restore vision and stop the further development of the disease.
- Cataract is clouding of the lens. This organ acts as a lens and is involved in the refraction of light. If it becomes opaque, vision gradually deteriorates until it is completely lost. Most cases of cataracts are associated with age-related changes. The disease can also be caused by injuries, diabetes, certain eye diseases, or be congenital.
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane of the eye. The disease is most often caused by a viral infection, less often by a bacterial infection. It is manifested by redness of the eyes, lacrimation, exacerbation of the reaction to bright light, headaches in the temples and frontal part. All cases of conjunctivitis require timely treatment, since they can be complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of purulent inflammation.
- Astigmatism is a disease caused by an irregular shape of the cornea, or less commonly, the lens of the eye. In this case, the ability to focus on near or distant objects is impaired, and the image looks blurry. For astigmatism, glasses or contact lenses are prescribed, and some patients require surgery.
If the patient has a severe headache, forehead and temples after changing glasses or contact lenses, it is worth contacting an ophthalmologist. Their incorrect selection causes tension in the muscles of the eyeball due to difficulties focusing on near or distant objects. In this case, you should contact your ophthalmologist to change lenses. However, a short period of adaptation to new glasses is considered normal, and during the first few days a person may experience headaches, temples and forehead pain.
Infectious diseases
Flu, sore throat, ARVI are common consequences of decreased immunity during the cold season. These diseases are manifested by soreness and sore throat, fever, cough, headache in the frontal and temporal parts. They are caused by a viral infection that spreads quickly through airborne droplets and is therefore highly contagious (infectious). Treatment involves bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and, if necessary, taking antipyretics, vitamins and antibiotics.
Meningitis is one of the most dangerous reasons why the frontal part of the head and temples hurt. It is manifested by inflammation of the soft, arachnoid or hard membranes of the brain. The main symptom is acute pain that does not stop even with bed rest. Meningitis can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection; the most dangerous form is meningococcal inflammation. The treatment regimen is based on antibiotics, which must be selected separately according to the type of pathogen.
Pathologies of the central nervous system
If you often have a headache in your temples and frontal area, this may indicate various pathologies of the central nervous system. Inflammatory or degenerative changes in nerve fibers provoke acute headaches. They must be distinguished from brain tumors and infectious diseases. Traumatic brain injuries can also cause long-term effects such as headaches.
Disorders of the central nervous system can be diagnosed at any age. However, older people are more susceptible to developing dystrophic changes in cells and tissues. It is important to monitor your well-being and if you experience frequent headaches, absent-mindedness, or memory loss, consult a doctor for a comprehensive examination.
Other reasons
There are a huge number of reasons why the head hurts in the frontal part and temples. Some of them do not require emergency treatment and occur periodically in most people. However, a number of disorders can progress and lead to dangerous complications, so it is important to seek medical help in a timely manner. Painful sensations may be a symptom of the following disorders:
- inflammatory diseases of the maxillary sinuses;
- inner ear diseases;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the brain;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, which leads to hormonal imbalance and chronic metabolic diseases;
- Stroke is an acute disorder of blood circulation in the brain.
A large part of the population suffers from dependence on weather conditions. The most difficult period is a sharp change in atmospheric pressure. When the weather changes, as well as when moving to another climate zone, acute headache, nausea and weakness, and decreased performance are observed.
How is throbbing pain formed?
Pain in the temporal areas has a pulsating nature due to several reasons. The vascular component plays a major role in shaping the nature of pain. Ripple occurs as a result of:
- Rapid reflex angospasm. The narrowing of the diameter of the cerebral arteries, in particular the temporal one, leads to a sharp increase in vascular pressure.
- Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels lead to thickening of their walls and a significant loss of elasticity, which leads to the formation of a more rigid pulse wave.
Environmental factors can lead to spasm of cerebral vessels. and internal factors of the body. Stressful situations often act as a provocateur, which lead to the release of biologically active substances into the blood - catecholamines, which have a spasmodic effect and sharply increase blood pressure. Also, throbbing pain can appear as a result of a sharp temperature change, for example, if you go out into the cold without a hat in winter, a spasm of the cerebral arteries occurs, which causes throbbing pain in the temples.
When should you consult a doctor?
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend undergoing an examination if your headaches are too intense or occur frequently. If they go away on their own during the day, there is no cause for concern. However, some symptoms should promptly consult a doctor. These include:
- memory losses;
- exacerbation of reaction to light, auditory stimuli;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- increase in body temperature to critical levels;
- dizziness, fainting.
You can also take care of your own health at home. Regardless of age and type of activity, it is recommended to periodically measure blood pressure using a tonometer. Scheduled examinations are also a prerequisite. They include examination by a general practitioner, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, and electrocardiography.
Cephalgia and pregnancy
Most often, girls in this position suffer from migraines, and the illness appears from physical activity, food, lack of sleep, stress, and fatigue. There are also other reasons that cause throbbing pain in women in the position:
- VSD;
- blood pressure problems;
- problems with blood supply;
- voltage;
- disorders in the brain;
- sinus inflammation;
- glaucoma.
For pregnant women suffering from cephalalgia, there are recommendations to combat discomfort, namely:
- do a light massage;
- restful sleep;
- take a contrast shower.
Regarding pain relief with medications, in this case it is important to consult a specialist, since not all painkillers are approved for pregnant women.
Examination methods
Accurate and timely diagnosis is the main condition for recovery from headaches. After examination, the therapist will prescribe additional examination techniques that will help determine the exact cause of the symptoms. Depending on the results of the initial examination and medical history, the following methods may be required:
- blood test to determine inflammatory processes, identify viral and bacterial pathogens of various diseases;
- Dopplerography - examination of blood vessels using ultrasound with the addition of a contrast agent, used to diagnose the arteries of the neck and head;
- MRI, CT are the preferred methods for diseases of the cervical spine and are the most informative in cases of suspected vascular pathologies and neoplasms in the brain;
- electrocardiography is one of the basic methods of examining the heart, which consists of determining the heart rhythm;
- specific blood tests that will determine the level of hormones, vitamins and other substances;
- examination by an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing headaches. If necessary, inpatient monitoring of the patient may be offered to monitor various indicators around the clock.
Diagnostics
The cause of pain in the temples can be determined in different ways. The first thing a specialist begins with is interviewing the patient and clarifying the location of pain, because one-sided pain can already lead to the correct diagnostic path. Neurologists have noted that in almost 70% of cases, inflammation of the peripheral nerves innervating the temporal and facial zones is localized on the left side. Accordingly, a common cause of throbbing pain in the left temple is neuritis of the facial or trigeminal nerve.
In a diagnostic examination, in addition to collecting an anamnesis of the patient’s life and illness, instrumental examination methods are of great importance. So absolutely every patient with such a symptom as throbbing pain in the temples should be examined by a cardiologist, with electrocardiography and ultrasound examination of the heart. To confirm the vascular origin of pain in the temporal regions, duplex scanning of the carotid arteries and, if necessary, angiography of the vertebral, cerebral and carotid arteries are required to determine the degree of compensation of cerebral blood flow. Instrumental diagnostic studies also include: radiography of the cervical spine, magnetic resonance and computed tomography of the brain and neck. As well as other narrowly focused studies.
In addition to the cardiologist, the patient is examined by such specialists as:
- Neurologist and neurosurgeon;
- Psychiatrist;
- Therapist;
- Ophthalmologist;
- Cardiovascular surgeon.
Laboratory diagnostic methods are of great importance in the examination, because in most cases the cause of such pain is cardiovascular pathology. To confirm or exclude diseases of a vascular nature. As well as inflammatory studies, the following studies are carried out:
- Determination of lipid spectrum;
- Conducting general and biochemical blood tests;
- Determination of coagulogram;
- Lipid profile analysis;
Conducting a complete diagnostic study is necessary for the correct formation of treatment tactics, since only pathogenetic treatment with the elimination of the main source of pain in the temporal areas can be effective.
Treatment of headaches in the temples and forehead
Treatment for headaches at the Clinical Brain Institute is prescribed individually. The scheme will include steps aimed at eliminating both the root cause and symptoms of the disease:
- painkillers - help with mild headaches, can be found in any home medicine cabinet;
- antibiotic therapy is the main stage of treatment of inflammatory diseases of the eyes, brain, and inner ear;
- drugs to normalize blood pressure in case of hypotension or hypertension - they are often taken in a course to prevent acute attacks;
- additional techniques effective for diseases of the cervical spine: physiotherapy, exercise therapy;
- surgical intervention - is prescribed only in cases where conservative therapy is ineffective (for neoplasms, aneurysms, cataracts and other pathologies).
At home, it is important to follow all doctor’s recommendations and take prescribed medications on a precise schedule. In addition, it is necessary to follow the principles of proper nutrition and monitor your weight - this will help avoid chronic vascular diseases. For headaches, full sleep and a cold compress on the forehead and temples are recommended.
If you have a headache in the frontal region and temples, this can either be a sign of dangerous diseases or a consequence of ordinary fatigue. The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of such disorders. The main advantages are modern equipment for examinations and analyses, high qualifications and many years of experience of specialists.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The plan of conservative measures is determined by the etiology of the pain syndrome:
- Migraine
. To relieve attacks, simple and combined analgesics are used, and sometimes therapeutic blockades are performed. To prevent new paroxysms, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and psychotropic drugs are used. - Tension headaches
. Medicinal methods include NSAIDs, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, occipital nerve blocks, non-medicinal methods - massage, manual therapy, acupuncture, biofeedback, relaxation techniques. - Bundle cephalalgia
. Paroxysms are eliminated with the help of triptans; in case of intolerance, oxygen inhalations are prescribed, and local anesthetics are injected into the nasal cavity. Calcium channel blockers are effective for preventive purposes. - Hydrocephalus
. In the case of an acquired variant of the pathology, the causative disease is treated and diuretics are prescribed. - Arterial hypertension
. Etiopathogenetic therapy is carried out. It is recommended to control blood pressure and take antihypertensive drugs. - Temporal arteritis
. The basis of drug therapy is glucocorticoid hormones. If there is no result, they switch to cytostatics. To eliminate symptoms, vasodilators, anticoagulants, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. - Trigeminal neuralgia
. Anticonvulsants are considered the first line treatment. Additionally, antispasmodics, microcirculation correctors, antihistamines, and therapeutic blockades are used. - TMJ dysfunction
. It may be necessary to eliminate dental pathologies. Soft food is recommended. Pain is reduced with the help of NSAIDs, antidepressants, botulinum therapy, glucocorticosteroid blockades, massage, and physiotherapy.
Elderly age
The older a person is, the more often he suffers from throbbing pain in the head, and most often this is associated with pressure and changes in the cervical spine. But there are also a number of reasons that pose a danger to older people, and these include:
- presence of a tumor in the brain;
- presence of hematomas in the brain;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- temporal arteritis;
- intoxication;
- presence of infectious diseases;
- stroke.
Pain in the head can also be a consequence of menopause in women, weather sensitivity, which occurs in any gender, and depression.
What is intracranial pressure?
This is the pressure inside the cranial cavity. The brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid, a fluid that is necessary to nourish nerve tissue. It is constantly produced and flows from the skull. Due to this process, optimal pressure inside the skull is maintained. Normally it is 10-15 mmHg. Art.
Intracranial pressure is the force with which the brain presses on the walls of the skull
We are talking about high intracranial pressure when the readings exceed 25 mmHg. Art. The critical value is 35 mmHg. Art. and more. The patient is diagnosed with intracranial hypertension or liquor-hypertensive syndrome.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Pathology never occurs independently; it appears for a number of reasons - both congenital and acquired. Slight fluctuations in the direction of increasing intracranial pressure (ICP) are possible when tilting the head, physical activity, or sneezing. But high rates are a consequence of more severe conditions:
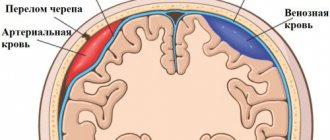
- traumatic brain injury (TBI), back injury with spinal cord damage;
- brain tumors, cysts, abscesses;
- hydrocephalus;
- aneurysm or vascular thrombosis;
- infectious diseases: encephalitis, meningitis;
- swelling of the brain after a stroke;
- encephalopathy;
- intracerebral hemorrhage;
- taking potent drugs that can disrupt the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid: hormonal agents, antibiotics and others;
- intoxication with chemicals.
At risk are hypertensive patients, people with metabolic disorders, obesity, vascular pathologies, patients who have had a stroke, or surgery on the brain or spinal cord.
Note! Patients with hypertension do not necessarily develop intracranial hypertension. Sometimes even hypotensive people suffer from high ICP.
The causes of high ICP in adults and children are similar. But often the appearance of intracranial hypertension in a child is facilitated by congenital developmental anomalies (hydrocephalus or microcephaly), birth injuries, oxygen starvation, and asphyxia. Premature babies are at risk.
The pressure inside the skull increases for two reasons: cerebrospinal fluid is produced in excess or it flows worse
Depending on the cause of its occurrence, the syndrome can occur in acute or chronic form. The first one is caused by injuries and neuroinfections. The chronic form develops gradually as brain tumors grow and cerebrovascular accidents occur.
If intracranial pressure increases, it is necessary to obtain qualified help from a neurologist. It is important not only to detect the underlying cause and eliminate it, but also to restore impaired cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. If this is not done, the symptoms of the disease will persist even after treatment of inflammation, head or back injury, or tumor removal.
How to quickly relieve an attack of cephalalgia
In cases where a headache does not appear frequently or systematically, and a person definitely does not have diseases that can provoke it, then you can deal with the discomfort on your own. To do this, it is not necessary to use strong medications and call a doctor.
When you feel a severe headache, forget about bad habits, such as smoking and give up alcohol. You should also not apply ice or increase the dose of the analgesic yourself unless your doctor recommends it.
There are a number of actions that need to be taken so that a person with a headache begins to feel better, namely:
- Bring fresh air into the room.
- Free the patient from tight clothing and constricting jewelry, unbutton the shirt collar and raise his legs so that they are higher than head level.
- Reduce indoor lights and sounds to a minimum.
- Give water, it can also be a decoction of soothing and relaxing plants.
- Take a warm foot bath and apply a compress to your head.
- It is necessary to warm a person in cases where the pain intensifies and there is chills.
- Lightly massage the temple area, neck, head, while the person should lie down.
If the above methods do not help within 30 minutes, and only get worse, give the patient an analgesic. If this does not help, then call the ambulance doctors.