A headache in the back of the head is a very unpleasant phenomenon, causing a lot of inconvenience and often limiting performance. The causes of pain in the occipital part of the head can be very different, from diseases of the cervical spine to neuralgic pathologies.
If you don’t know why the back of your head hurts, then this article is for you. It collects the main causes and describes methods of treating headaches in the back of the head. In any case, you must remember: if you have a headache in the back of your head, you should not self-medicate, you need to seek medical help. Of course, we are not talking about isolated cases of pain in the occipital region. As a rule, they are caused by prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, stress, extreme hunger, and also due to excessive consumption of foods with caffeine or chemical additives.
Causes of pain in the back of the head
A severe headache in the back of the head never occurs without a reason. It can be a signal of diseases:
- spine;
- vascular system;
- neurological system.
Depending on the cause of the headache in the back of the head, it can be of a different nature and be accompanied by certain clinical manifestations, which must be clearly described to the doctor.
Pain in the back of the head due to osteochondrosis
If the neck and back of the head hurt, the reasons may be the presence of a disease such as osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The disease manifests itself in the destruction of the discs of the cervical vertebrae, and pain appears constantly and is felt not only in the neck and back of the head, but also in the temples. They become more intense with head movements and may be accompanied by:
- tinnitus;
- nausea;
- coordination disorders;
- veil before the eyes and double vision.
More about osteochondrosis
Pain in the back of the head with hypertension
Hypertensive attacks are characterized by the appearance of bursting pain, which is accompanied by pulsation. They may appear when waking up after a night's sleep. In addition, it is observed:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased pain when trying to tilt your head;
- reduction of pain after sudden vomiting.
Pain in the back of the head with increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is characterized by:
- pressing, bursting pain in the occipital region or throughout the head;
- increased pain in bright light and loud sounds;
- heaviness in the head and pain in the eyeballs;
- vomiting, which does not reduce pain syndromes.
Pain in the back of the head due to cervical myositis
Inflammatory processes in the neck muscles caused by hypothermia or injury are characterized by pain symptoms that spread from the neck to the occipital, shoulder and interscapular areas. It appears when you move your head and is asymmetrical.
More about myositis
Pain in the back of the head due to occipital neuralgia
Neuralgia of the occipital nerve, resulting from hypothermia or accompanying osteochondrosis, is characterized by very strong shooting pains. They occur periodically, like attacks with any attempt to change the position of the head.
During rest, a slight pressing pain is felt in the occipital region.
Read more about occipital neuralgia
Pain in the back of the head due to vascular diseases
Spasms of the cranial arteries cause throbbing pain, which becomes stronger when trying to move the head and subsides somewhat at rest. The pain begins in the back of the head and eventually spreads to the frontal area. It is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the head and begins in the morning after waking up.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individualized screening programs to help determine the cause of your headaches. Procedures are prescribed only according to indications. Among them are electroencephalography, radiography of the cervical spine, MRI, Doppler sonography, laboratory blood tests and other techniques.
As a result of a complete examination, a diagnosis can be made and treatment can be prescribed. When selecting medications, doctors at our clinic take into account the patient’s general condition and the body’s response to taking medications. The process takes place under the supervision of specialized specialists, even if it takes place at home.
Diagnosis of pain in the back of the head
If you suffer from constant or regular pain in the occipital region of the head, contact the CELT clinic. Our specialists will conduct the necessary research and find out the reason why you are experiencing pain. In order to become our patient, you do not need Moscow registration.
In addition to obtaining a history of the nature, timing and intensity of pain, diagnosis may include:
- examination by a doctor;
- blood pressure measurement and monitoring;
- ultrasonography;
- electroencephalography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
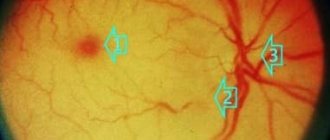
- examination of the fundus by an ophthalmologist.
If there is a suspicion of a brain tumor, a consultation with a neurosurgeon will be required.
Diagnostics
The nature of the pathology is determined by a neurologist. According to indications, an orthopedist-traumatologist, an infectious disease specialist, and other specialists are involved in the examination. The doctor finds out the time of onset, duration and nature of the pain syndrome, and identifies other symptoms. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor pays attention to possible provoking factors and the presence of chronic diseases.
Examination of the back of the head may indicate external changes (swelling, wounds, abrasions). Palpation sometimes reveals tension, muscle tightness, and enlarged lymph nodes. A neurological examination involves assessing reflexes, muscle strength, various types of sensitivity, and detecting focal disorders. To clarify the diagnosis, the following are prescribed:
- X-ray examination
. Indications for radiography of the skull are fractures of the occipital bone, for radiography of the cervical vertebrae - subluxations, spondylitis, osteochondrosis, hernias. - CT scan.
Allows you to detail the data obtained during radiography. The contrast technique displays changes in blood vessels. - Magnetic resonance imaging.
It visualizes brain tissue well and is used to study their structure, detect tumors, hematomas, areas of degeneration, and other changes. - Ultrasound methods.
Ultrasound scanning and Dopplerography make it possible to assess vascular tone, blood flow speed, and other indicators, and to form a comprehensive picture of the blood supply to the brain. - Electroencephalography.
Performed to assess the functional activity of the brain, determine the severity of cerebral dysfunction due to injuries and certain diseases - Lumbar puncture.
Performed for head injury, meningitis, encephalitis. Confirms the presence of intracranial hypertension, inflammation, bleeding. - Lab tests
. Informative for atherosclerosis, inflammatory and infectious processes, as well as somatic and endocrine diseases that provoke secondary arterial hypertension.
Examination by a neurologist
First aid for headaches
If possible, lie down, close your eyes and try to calm down. If you cannot take a horizontal position, just sit with your eyes closed in silence.
Place a cloth or towel soaked in cold water on your forehead and temples. You can also add 1-2 drops of soothing essential oils to the water. But don't overdo it! A couple of drops is enough - too strong a smell can provoke increased pain. Massage your temples and the back of your neck, open a window, breathe in fresh air, drink a soothing caffeine-free tea, such as herbal tea. If attacks of cephalalgia recur regularly or you notice that they have become more frequent recently, call a neurologist or therapist. They will help you find the cause of cephalalgia and overcome the pain. You can call the doctor by phone: +7 (495) 730-21-31.
How to relieve an attack?
With vasospasm and significant circulatory impairment, severe pain occurs, noise and pulsation in the head interfere with work. You can alleviate the condition using the following methods:
- taking painkillers and antispasmodics - helps reduce pain;
- the use of local and systemic anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs - reduce pain, can remove pinched nerve endings, relieving inflammation;
- massage – helps relieve neck muscle spasms and eliminate tension.
With these measures you can get rid of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, but only temporarily. The disease must be treated, and complex therapy is required.
Which doctor should I contact for noise in the head due to osteochondrosis?
A neurologist treats osteochondrosis, its symptoms and consequences.
Since the disease has dangerous complications, you should choose an experienced specialist who can develop an individual and effective treatment program. Neurologists from the medical center in Rostov-on-Don have extensive experience in treating neurological diseases.
To make an appointment, you can call or leave a request on the website. A call center operator will contact you within 10-15 minutes.
How to get rid of headaches with cervical osteochondrosis
To relieve headaches, including those with cervical osteochondrosis, analgesics in combination with antispasmodics help well. For severe muscle tension and irritation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used. However, it must be remembered that these drugs do not treat the underlying disease, providing only symptomatic care, and at the same time they have a number of serious side effects. Thus, analgesics and NSAIDs, including those containing diclofenac, suppress bone marrow function, lower immunity, inhibit gastric secretion, irritating its mucous membrane and provoking the development of gastritis, and reduce blood clotting. In addition, it has been proven that systematic or frequent use of diclofenac increases the risk of heart attack by 40%, and NSAIDs in general lead to the formation of gastropathy, gum ulceration, pancreatitis and aphthous stomatitis. Antispasmodics can cause the opposite effect - increase dizziness, headache, and also cause palpitations and more complex arrhythmias.
Recently, Botox injections have been used to relieve spasms. However, botuloxin is a strong poison; in addition to the unpredictable individual reaction of the body, it can cause headaches, muscle weakness up to paresis of some muscle groups, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system. With each repeated use, the effect of the drug decreases.
Neuroprotectors have a prolonged (long-lasting) effect, improving metabolism in brain tissue and thereby relieving pain. However, such drugs must be taken in long courses, but if used uncontrolled, they can cause dizziness, headaches, anxiety, increased blood pressure and arrhythmia.
It is important to remember that in this case, a headache is only a symptom of the disease. In addition to symptomatic care, it is necessary to direct efforts to fight the disease itself - the spine needs to be treated.
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis, in addition to the use of painkillers and antispasmodics, should include the use of hydroprotectors, vitamin complexes, as well as exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
Electrophoresis is the most commonly used physiotherapy procedure. Its essence is a local increase in temperature and improvement of blood circulation, which relieves muscle spasms, eliminates pain and speeds up the healing process. In general, any thermal procedures relieve muscle spasms and improve blood circulation.
Magnetotherapy involves the use of low-frequency magnetic field inductors aimed at the problem area, which leads to local dilation of blood vessels, improved oxygenation and metabolism, accelerated elimination of toxins and reduced blood viscosity. Thanks to this, magnetic therapy has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anti-edematous effect.
Effective assistance in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be provided by a modern drug - the therapeutic pain-relieving anti-inflammatory patch NANOPLAST forte.
The back of the head hurts during a migraine. Causes and treatment
Migraine refers to a primary headache caused by pathological processes in the tissues of the brain itself. Migraine pain feels like a hoop around the head, but can also be localized in the back of the head. They develop periodically, lasting from 2 hours to several days. They can bother people of any age, but more often women 25–40 years old. Migraine is provoked by nervous tension, insufficient rest, and excessive physical activity. The attack can be relieved by taking analgesics. This should be done in the first minutes of discomfort.
Peculiarities
Pain in the back of the head can be associated with inflammatory processes, mechanical damage to tissues or pressure on them, impaired blood supply or ischemia. The reasons for this can be very diverse.
In any case, now modern medical technologies and modern methods make it possible to quickly relieve pain in the back of the head. Sometimes all you need is to buy anti-inflammatory drugs at a pharmacy at an affordable price and carry out a course of treatment in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations
Sometimes the back of the head hurts even in a healthy person of any gender and age. This may be due to the characteristics of the body. Thus, it reacts to negative external stimuli. If you can quickly relieve the pain with medications and after that the discomfort does not recur, then there is no reason to worry. In this case, the development of serious pathologies can be excluded. Dangerous is an intense headache in the back of the head, which occurs frequently.
When the back of your head hurts, you need to go to a medical facility for examination in the following cases:
- If pain persists for 5 days.
- When discomfort of varying intensity is observed in total for more than 220 days.
- In the absence of a positive reaction to taking painkillers.
- When, after taking medication, there is only slight relief for a short time.
How is cervical osteochondrosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with studying the patient's complaints. The doctor conducts a survey, determines for himself the key points: localization, intensity, duration, type, nature, conditions for the occurrence of noise. Then he begins a physical examination, palpating the cervical spine, and measuring blood pressure.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
After the initial examination, a full instrumental examination is required, which includes:
- radiography;
- computed tomography (CT) of the ear, spine;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head;
- audiological examination, including tympanometry, reflectometry;
- duplex scanning or Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
MRI is the most informative for neck pain and noise in the head, so this type of examination is advisable for everyone who has been diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis.
The medical department has a Siemens Symphony 1.5 Tesla tomograph, which provides high information content and allows you to identify the slightest changes. Immediately after the examination, the diagnostician announces the results and explains how serious the detected pathology is.
To assess the nature and extent of the pathological process, examination of the thoracic and lumbar spine may be necessary, especially if there is pain in the lower back or chest.
Sometimes, in addition to a neurologist, consultation with an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, orthopedic traumatologist, cardiologist, and neurosurgeon is required.
Prevention of cephalalgia
Headache attacks, even with hypertension or hypertension, will bother you much less if you lead a healthy lifestyle. Therefore, there are only three basic rules:
- Get enough sleep, but don't sleep too long. Both too little and too much sleep can cause headaches.
- Adjust your nutrition. Eliminate hot dogs, hamburgers, French fries, deep-fried meat, fast food, too salty or spicy foods from your diet, and reduce your consumption of soda and industrial sauces.
- Keep calm!
Stress and nervous tension are one of the main causes of pressure surges and the occurrence of cephalalgia. Avoid stressful situations, try not to stress yourself out, and not to entertain anxious thoughts in your head. In some cases, significant improvements can be achieved with a course of taking a sedative.
The back of the head hurts when blood pressure fluctuates. Treatment
High blood pressure is indicated when values above 140/90 millimeters of mercury are recorded. WHO estimates that hypertension affects 10 to 30% of the population in different countries. Only a third of them went to see a doctor, and only a third of those who did take medications prescribed by the doctor. The rest suffer from headaches, take analgesics, but do not associate their condition with hypertension.
Arterial hypertension is divided into primary - essential and secondary, caused by the pathology of other organs and systems:
- renal,
- endocrine,
- pulmogenic,
- hemodynamic,
- central.
In this case, antihypertensive drugs help.