A sudden change in weather plunges almost 44% of Russians into confusion, according to doctors. It is known that mainly residents of megacities suffer from weather changes, however, in recent years, the disease has begun to affect the provinces as well. It is almost impossible to cure this form of weather dependence completely. But if you follow simple rules, you can significantly alleviate your condition on difficult weather days. People who feel discomfort from weather fluctuations, magnetic storms and solar activity are called weather dependent. In order for a person to feel comfortable, the atmospheric pressure must be 750 mmHg. With a noticeable change in this value, either down or up, the human body often feels a deterioration in well-being. Low atmospheric pressure has a stimulating effect on the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system, increases susceptibility to infectious diseases, suppresses mood and reduces ability to work. With low atmospheric pressure, blood pressure also decreases, which is especially dangerous in people with arterial hypotension; attacks of weakness and nervousness occur, and drowsiness appears. High atmospheric pressure increases the activity of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system. When barometric pressure is high, blood pressure rises, and people with hypertension are more likely to develop hypertensive crises. With both types of changes in atmospheric pressure, the likelihood of developing ischemic attacks from the cerebral, coronary and other vessels increases. Those who have suffered a stroke and myocardial infarction, and people with metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes, react especially hard to changes in atmospheric pressure. General rules: Try to get as much sleep as possible. Moreover, it is more important to go to bed earlier, and not to get up later. The normal amount of sleep during weather changes is at least 9.5 hours. In order to ensure healthy and deep sleep with a normal alternation of phases, try drinking herbal tea with mint and chamomile at night. When you wake up, do not get out of bed abruptly - lie down, then sit in bed, massage your feet and legs, and only then get up. In the morning, to gently cheer yourself up, try doing short and easy exercises - stretch, work your hands and feet. This exercise will help the blood vessels gain tone. Avoid exercises that require balance, and avoid bending or squatting. After charging, take a shower - a contrast shower is better, but if this is too extreme for you, then a regular one will do. Stock up on a good B complex of vitamins and take them during weather changes: they will support the nervous system. During the day, try not to overload your stomach with heavy foods; it is better to eat often and in small portions. If your work involves sitting in front of a monitor for many hours, take a 5-minute break every 40 minutes for short gymnastics, changing positions and self-massage of the temporal, cervical-collar area, and forehead. Avoid stress, demanding events and strenuous activities on days when the barometric pressure changes too quickly. If you are involved in fitness, then it is better to cancel strength training, or replace it with calm swimming in the pool. Remember to drink plenty of plain water or fruit juices diluted half and half with water. If you experience sudden changes in blood pressure, try to rest in a horizontal position several times during the day. If you are prone to low blood pressure, feel free to drink hot sweet tea: it will restore your tone. The most important thing on difficult days from a weather point of view is not to miss dangerous symptoms that may indicate serious health problems: • Unpleasant sensations in the chest area, of unknown origin, radiating to the shoulder (especially to the left), under the shoulder blade or to the navel area . • Sudden loss of sensation in the limbs. • Feeling of numbness in half of the face. • Speech difficulties. • Attacks of nausea. • Visual impairment (flickering of spots before the eyes, out of focus). • Difficulty breathing. If you find yourself with at least one of the listed symptoms, immediately contact a doctor, preferably an ambulance. Changes in atmospheric pressure have different effects on the well-being of different people. In a healthy person, when atmospheric pressure changes, physiological processes in the body are timely adjusted to the changed environmental conditions. As a result, the protective reaction is enhanced, and healthy people practically do not feel its negative impact. In a sick person, adaptive reactions are weakened, so the body loses the ability to quickly adapt. At the same time, training and hardening the body play an important role in prevention. It is necessary to play sports, systematically perform one or another physical work. Food at low atmospheric pressure should be high-calorie, varied and rich in vitamins and mineral salts. GBUZ "Center for Medical Prevention" of the Ministry of Health of the Krasnodar Territory.
Weather dependence: fiction or truth?
These people don’t even need to listen to the forecast. Their predictions will be more accurate than the barometer readings and the predictions of the hydrometeorological center. They know for sure: a headache means an imminent thunderstorm, joints are twisting - it means rain, the pressure has jumped - the wind is rising and the magnetic field is weird.
Weather dependence is called the sixth sense
First, let's dispel the doubts of skeptics. Weather sensitivity is not an invention of muslin young ladies. This has been confirmed by science: in people who are sensitive to weather changes, the level of leukocytes in the blood increases on such days. And medical statistics have recorded: more than 60% of city residents over 28 years of age react to bad weather. The proportions are as follows: there are one and a half times more representatives of the fairer sex who sense the approach of an atmospheric front than the stronger sex.
Young children are distinguished by the most subtle sensitivity. Mothers of infants notice that babies begin to cackle as soon as the weather changes.
Who is the most accurate "petrel"? Manifestations of weather dependence
Patients with diseases of the bronchi and lungs, asthmatics, arthritis sufferers, and hypertensive patients can accurately predict bad weather. If the temperature outside the window and atmospheric pressure immediately decrease, they expect their condition to worsen, complaining of pain in the joints and stiffness in movement.
Cores can compete with the hydrometeorological center in the accuracy of forecasts. A couple of hours before the weather changes (and it could even be a change in the direction of the wind), they complain of headaches, weakness, anxiety, joint pain, and angina attacks. The hardest days for them are those with high air humidity and when a thunderstorm is approaching.
Heart crises, as ambulance workers note, occur at times of pronounced activity of the geomagnetic field and magnetic storms. A sick heart also reacts to periods of high sun activity.
The state of health these days deteriorates in those suffering from vegetative-vascular dysfunction (previously this disease was called vegetative-vascular dystonia), gastritis, patients with pneumonia, pyelonephritis, eczema. People with mental problems have another influencing factor - lunar tides.
In principle, any chronic responds to bad weather, doctors say.
Why do vessels feel the wind?
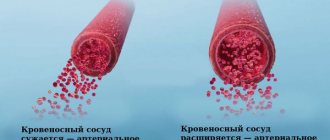
And how are rain and the heart connected? Many situations are explained by elementary physics and simple physiology. Thus, when atmospheric pressure drops, the pressure in the vessels decreases and the speed of blood flow decreases. Gases form in the intestines. They expand the abdominal cavity and accordingly raise the diaphragm, the result is that it is difficult to breathe, the heart and blood vessels experience a lack of oxygen. If the atmospheric pressure rises, then the pressure in the vessels increases accordingly and the speed of blood flow increases, which also causes discomfort.
When there is a strong wind, it is more difficult for us to breathe - and the oxygen content in the blood naturally drops. Also, degrees outside the window and changes in atmospheric pressure affect the activity of some enzymes. Scientists say that in anticipation of an upcoming downpour, hail, hurricane, pressure surges or sudden warming or cold weather, a person’s defense system is triggered: hormonal levels, enzyme activity, platelet content and blood clotting indicators change.
But in principle, one cannot talk about the influence of one weather factor. As a rule, they act together on our well-being. And you can derive such formulas. Cold wind plus high atmospheric pressure equals excess oxygen and vasospasm. Low atmospheric pressure plus high humidity, high (or low) temperature equals a lack of oxygen and heaviness in the head.
Manifestations of weather dependence include fluctuating blood pressure, rapid pulse, shortness of breath, fever, sleep problems, dizziness, headaches, joint pain, cramps, weakness, fatigue, apathy, drowsiness, chills, bad mood, absent-mindedness, and memory problems.
The most critical situations for a weather-dependent person are a sharp drop or rise in atmospheric pressure, a temperature difference outside the window of 8 degrees or more for 48 hours. But in fact, there are no more than two dozen truly difficult days for well-being a year. Once every five to six days a person may react to the weather with a slight deterioration in health.
Drugs for weather dependence - means of salvation
- These days, you should not skip taking medications. With your doctor's permission, you can increase the dose or take a stronger medicine.
- It is believed that weather dependence makes itself felt only when the immune system is weakened or when there is illness. Therefore, heal to the end, strengthen and boost your immune system with simple measures - a contrast shower, proper nutrition, moderate physical activity, spending time in the fresh air, proper sleep and wakefulness, and auto-training techniques.
- For some, vitamins and minerals, antioxidants, and so-called plant adaptogens (including tinctures of ginseng, eleutherococcus, lemongrass, and aralia) help on difficult days . But the last recommendation is not suitable for hypertensive patients.
- And another piece of advice - don’t focus on the weather : if you think, “This hurricane will make me feel bad,” so it will be. Remember that our body easily adapts to any climate, it is not for nothing that residents of the far north do not react so sharply to strong winds, high humidity, periods of prolonged cold, and those who live in the sultry south breathe dry air easily and do not feel high levels of radiation, accustomed to low humidity and eternal heat. By the way, paradoxically, the weather is the best immunity trainer.
If you still have questions, you can ask your therapist online in the Doctis application.
Breathing at low atmospheric pressure
A person finds himself in conditions of reduced atmospheric pressure when ascending to a height (climbers, pilots when the cabin is depressurized, parachutists).
Conditions of low pressure at altitude are reproduced in pressure chambers, from which the required amount of air is pumped out. Similar changes are also created when breathing gas mixtures with a reduced oxygen content.
The main consequence of a decrease in atmospheric pressure is hypoxia, which develops due to the low partial pressure of oxygen in the inhaled air.
Ascent to a height of 1.5-2 km above sea level is not accompanied by a significant decrease in the body's oxygen supply and changes in respiration. At an altitude of 2.5-5 km, an increase in pulmonary ventilation occurs, caused by stimulation of carotid chemoreceptors. At the same time, blood pressure rises and heart rate increases. These reactions are aimed at increasing the supply of oxygen to tissues; they partially compensate for the reduced partial pressure of oxygen.
An increase in pulmonary ventilation at altitude can also have a negative effect on breathing, as it leads to a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air and its removal from the blood. As a result, at low atmospheric pressure, hypoxia is combined with hypocapnia. With hypocapnia, stimulation of chemoreceptors, especially central ones, is weakened, which limits the increase in ventilation of the lungs.
With a further decrease in atmospheric pressure, at an altitude of 4-5 km, high-altitude (mountain) sickness develops: weakness, cyanosis, decreased heart rate, blood pressure, headaches, and the depth of breathing decreases. At altitudes above 7 km, loss of consciousness and life-threatening breathing and circulatory disorders can occur.
A particularly high danger is the rapid development of hypoxia. At the same time, a person does not have unpleasant sensations associated with hypoxia, there is no feeling of anxiety and danger. Loss of consciousness may occur suddenly.
Breathing pure oxygen through a mouthpiece or mask allows a person to maintain normal performance at an altitude of even 11-12 km. When climbing to high altitudes, even when breathing pure oxygen, its partial pressure in the alveolar air is significantly lower than normal. Therefore, flights into the stratosphere are possible only in pressurized cabins or spacesuits in which sufficiently high atmospheric pressure is maintained.
Resistance to hypoxia has large individual differences. Thus, some people develop altitude sickness at an altitude of 2.5 km. Resistance to hypoxia can be significantly increased by training in a pressure chamber, which allows you to maintain performance at an altitude of 7000 m.
Long stays in conditions of low atmospheric pressure and life in mountainous areas are accompanied by acclimatization to oxygen starvation. The latter is due to a number of factors:
- an increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood due to increased erythropoiesis;
- an increase in hemoglobin content in the blood and, consequently, an increase in the oxygen capacity of the blood;
- increased ventilation;
- acceleration of oxyhemoglobin dissociation in tissue capillaries due to a shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right caused by an increase in the content of 2,3-glycerophosphate in erythrocytes;
- an increase in the density of blood capillaries in tissues, an increase in their length and tortuosity;
- increasing the resistance of cells, especially nerve cells, to hypoxia, etc.
Periodic breathing. This type of breathing is characterized by periodic changes in breathing frequency. Thus, breathing can be observed with periodic increases and decreases in depth (wave-like breathing). With greater severity of such periodic breathing, groups of respiratory movements are separated from each other by pauses - periods of apnea lasting 5-20 s. After a pause, weak respiratory movements occur, they gradually intensify to a maximum, and then weaken. A new pause begins (Fig. 164). This breathing is called Cheyne-Stokes breathing.
The duration of the cycle of such breathing can be 20-60 seconds.
Cheyne-Stokes breathing is observed with altitude sickness, sometimes during sleep, and also in premature infants. The main condition for the occurrence of periodic breathing is a decrease in the excitability of the neurons of the respiratory center due to hypoxia or influences coming from the overlying parts of the brain. also contributes to the occurrence of Cheyne-Stokes respiration . Under these conditions, the activity of the respiratory center is largely determined by the oxygen content in the arterial blood. The occurrence and intensification of breathing after a pause is caused by excitation of carotid chemoreceptors due to lack of oxygen. When the degree of hypoxemia decreases as a result of increased ventilation, breathing weakens and temporarily stops.
This is facilitated by a decrease in the tension in the blood of carbon dioxide, which is excreted during the period of increased breathing. When the degree of hypoxemia increases again and the oxygen dioxide tension in the blood increases, gradually increasing breathing reappears.
Intermittent breathing usually changes to normal breathing when breathing oxygen with the addition of 5% carbon dioxide.
Medical Internet conferences
The influence of atmospheric pressure on human health
Kushnereva T.M.
Scientific supervisor: academician biology Badak I.I.
Municipal educational institution Secondary School No. 8 of Novouzensk
The influence of atmospheric pressure on a person is inevitable and most often affects well-being; this effect is especially noticeable on people suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system. Such people who feel discomfort from magnetic storms and fluctuations in weather conditions are called sensitive.
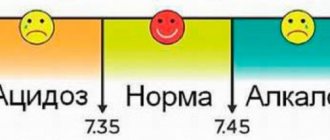
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure of atmospheric air on objects in it and on the earth's surface. For a person to feel comfortable, the atmospheric pressure must be 750 mmHg; this figure is called normal atmospheric pressure. If the value changes by more than 10 units, both up and down, the human body reacts with a general deterioration in well-being.
The danger to humans lies not only in fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, but also in one’s own blood pressure. A person may not be aware of the problem of high blood pressure, exposing himself to the risk of cardiovascular accidents (stroke or heart attack), which rank first in the structure of mortality. The relevance of the work is determined by the need to prevent hypertensive crises and reduce the risk of organic damage to large vessels.
The purpose of this study:
-to study the effect of atmospheric pressure on patients with arterial hypertension of the therapeutic department of the Novouzenskaya Central District Hospital
— establish the relationship between fluctuations in atmospheric pressure and the well-being of patients, changes in blood pressure levels.
Research objectives:
- analyze literature and other sources on the issue under consideration
— find out what effect atmospheric pressure has on human well-being and health.
Materials and methods: an examination was carried out, complaints were collected, and blood pressure levels were measured twice daily (morning and evening) in 40 patients with arterial hypertension who were undergoing inpatient treatment in the therapeutic department of the Central District Hospital of Novouzensk.
Results: I analyzed the medical records of patients with arterial hypertension in the therapeutic department of the Central District Hospital of Novouzensk, who were hospitalized in November 2013. The period of hospitalization was 12±2 days.
During the hospitalization period, an increase in atmospheric pressure was observed for 3 days, a decrease in atmospheric pressure for 5 days, and for 4 days the atmospheric pressure was within normal limits.
Conclusions: When atmospheric pressure fluctuates, an increase in blood pressure and a deterioration in the subjective state are more often observed in people suffering from arterial hypertension.
Breathing rhythm disturbance
Stroke
Hepatitis
Diabetes
Encephalitis
Thyrotoxicosis
18410 08 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Irregular breathing: causes, diseases in which it develops, methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Definition
Respiration is a set of physiological processes whose ultimate goal is the delivery and consumption of oxygen, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide.
The respiratory organs include the airways and lungs. In addition, the muscular and nervous systems take part in the breathing process. Thanks to the diaphragm, intercostal and some other muscles, respiratory movements are performed, a change in the volume of the chest occurs, which is a necessary condition for the expansion and collapse of lung tissue during inhalation and exhalation. The respiratory center is located in the central nervous system, namely in the medulla oblongata. The key feature of the functioning of the respiratory center is the automatic generation of impulses in it - that is, the person does not think about the fact that he needs to take a breath. At the same time, the activity of the respiratory center can be suppressed by higher-lying parts of the brain; for example, a person can voluntarily hold his breath while diving.
It is the respiratory center of the medulla oblongata that plays a key role in maintaining the rhythm of breathing.
Types of breathing rhythm disturbances
The following types of breathing are distinguished:
- eupnea
– normal breathing rhythm (in a healthy adult it is about 14–18 respiratory movements per minute); - hyperpnea
– deep and rapid breathing, observed during muscular work, emotional stress, thyrotoxicosis, anemia, acidosis, decreased oxygen content in the inhaled air; - tachypnea
- an increase in the frequency of respiratory movements due to pronounced stimulation of the respiratory center during hypercapnia, hypoxemia; observed with increased body temperature, congestion in the lungs, etc.; - bradypnea
- a decrease in the frequency of respiratory movements, which occurs when the respiratory center is damaged and depressed against the background of hypoxia, edema, ischemia and exposure to narcotic substances; - apnea
– temporary cessation of breathing (considered the extreme severity of bradypnea); - Cheyne-Stokes breathing
- characterized by alternating groups of respiratory movements with increasing amplitude and periods of apnea; - breathing according to the Biota type
- characterized by alternating periods of apnea with groups of respiratory movements of equal amplitude; - Kussmaul breathing
is noisy and deep breathing, which is characterized by separate convulsive contractions of the main and auxiliary respiratory muscles. This type of breathing indicates significant hypoxia of the brain.
Possible causes of respiratory rhythm disturbances
The immediate cause of respiratory rhythm disturbances is a change in the functioning of the respiratory center. The respiratory center has numerous connections with other parts of the nervous system and with receptors (nerve endings) that perceive changes in the internal environment of the body: changes in the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, blood acidity, etc. For example, with a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the blood, an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide and acidification of the blood, receptors that activate the respiratory center are excited. In turn, an increase in the frequency and depth of breathing compensates for changes in the gas and acid-base composition of the blood.
The respiratory center can be directly affected by certain brain-toxic substances circulating in the blood.
Disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory center occur as a result of structural changes in the corresponding area of the brain during strokes, cerebral edema, etc.
Diseases that cause breathing problems
Among the diseases that lead to the accumulation of toxic substances in the blood, which can subsequently irritate or damage the respiratory center, it is worth mentioning the following:
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation
, when carbohydrate metabolism products accumulate in the blood; occurs at the onset of previously undiagnosed diabetes mellitus or with insufficient control of the disease during insulin therapy and glucose-lowering therapy; - liver failure
, developing acutely against the background of hepatitis (viral, alcoholic, autoimmune etiology, etc.), toxic liver damage (for example, paracetamol poisoning), as well as chronic intoxication with liver failure against the background of cirrhosis. Toxic damage to the brain in liver diseases is primarily due to the fact that the pathologically altered liver is not able to perform a barrier function (retain and neutralize harmful substances), and therefore toxins accumulate in the blood; - renal failure
, which can manifest acutely or have a long-term chronic course, develops against the background of inflammatory diseases (glomerulonephritis, tubulointerstitial nephritis, etc.), toxic damage to the kidney (for example, tubular necrosis) and other diseases; - Severe infectious diseases
can cause severe intoxication or lead to direct brain damage, for example, in viral or bacterial encephalitis.
Respiratory rhythm disturbances can occur during poisoning with opium-type drugs that cause bradycardia and apnea.
Structural changes in the brain are observed during strokes (acute cerebrovascular accident due to hemorrhage or blockage of cerebral vessels by a blood clot), neoplasms, and cerebral edema.
Separately, it is worth mentioning Pickwick's syndrome, which develops in patients with severe obesity, one of the manifestations of which is episodes of respiratory arrest during sleep.
Which doctors should I contact if my breathing rhythm is disrupted?
Irregular breathing is a serious symptom, so often the first specialist to assist a patient is an emergency physician or resuscitator.
If a violation of the breathing rhythm does not pose a threat to life, then diagnostic measures are carried out by a doctor of a narrower specialty: a hepatologist (a specialist in liver diseases), a nephrologist (a specialist in kidney diseases), a toxicologist, an infectious disease specialist, etc.
Diagnostics and examinations for respiratory rhythm disorders
Diagnosis begins with a survey of the patient, during which the doctor establishes possible causes and risk factors for the development of arrhythmic breathing.
Laboratory tests include determination of blood glucose levels, arterial blood gases and the acid-base status of the blood CBS.