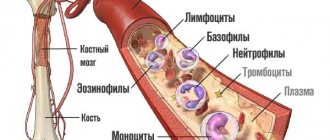
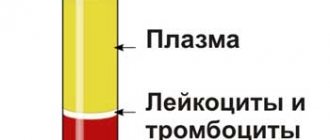
What can affect the result?
The level of ALT in the body can increase when:
- Intense physical activity
- Intramuscular administration of drugs
- Taking dietary supplements
- Fast food abuse
Important! The interpretation of the analysis is carried out only by a doctor. If necessary, the patient is referred for other examinations (including instrumental and functional).
We recommend that you consult your doctor and get a check-up.
Important Notes
Material for research
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood.
Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age and adults whose veins are difficult to access (for special indications)!
According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
MEDSI cares about its patients
- Experienced specialists.
They professionally conduct research on biological material, which guarantees diagnostic accuracy - Comfortable conditions for taking the analysis.
You can take the test throughout the day. The results will be available in your personal account - Modern laboratory equipment.
It corresponds to a high European and global level. The laboratory uses equipment from leading manufacturers such as Beckman Coulter, Siemens, Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Thermo Fisher, Sysmex, BD. All areas of testing and evaluation of biomaterials are equipped with the latest equipment that allows for high-level/high-precision diagnostics - Regular maintenance of equipment and automation of research processes.
All analytical installations are serviced and meet quality standards. All processes are automated as much as possible and built in accordance with LEAN management. This allows the laboratory to control processes, minimize time and errors during analysis - Automation of the process of sorting biomaterials.
Preliminary identification of the biomaterial is carried out in front of the patient. Eliminates the possibility of losing the test tube - The shortest processing time for materials.
They are provided with modern equipment and experienced specialists - There is an opportunity to undergo a comprehensive examination.
This ensures a quick and accurate diagnosis
To make an appointment with a doctor and clarify the conditions for taking the test (including its cost), call +7 (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer your questions and suggest the optimal time to visit the clinic. Registration and payment for services are also possible through the SmartMed application.
ALT and AST: what are these tests?
ALT and AST - these abbreviations can often be seen in blood tests for biochemistry. What do they mean? What can they tell the doctor? Vasilisa Vladimirovna Ishchenko, a gastroenterologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk, answers our questions.
— Vasilisa Vladimirovna, what do the abbreviations ALT and AST mean?
- ALT, or alanine aminotransferase, is an endogenous enzyme produced by liver cells - hepatocytes. Its content in blood serum is insignificant. The highest concentration of ALT is found in the liver, so this enzyme is a specific marker of diseases of this organ. In addition, small amounts of ALT can be found in the kidneys, cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, and pancreas.
AST, or aspartate aminotransferase, is also an enzyme from the group of transaminases that is involved in the metabolism of amino acids. Contained mainly in the liver, myocardium, nervous tissue, skeletal muscles, in smaller quantities in the kidneys, pancreas, spleen, and lung tissue.
When cells are damaged under the influence of infectious or toxic factors, energy metabolism in cells changes. Due to impaired permeability of cell membranes, components of the cytoplasm and disintegrated intracellular structures, including enzymes, enter the blood serum. As a result, the level of ALT and AST in the blood increases. This complex of disorders is called cytolytic syndrome.
— What will the ALT and AST indicators tell about in a biochemical blood test?
— Normally, the concentration of transaminases and their ratio to each other in the blood plasma are constant values. They reflect the balance of formation and release of these enzymes. In addition, this balance indicates the normal course of physiological destruction of aged cells (apoptosis). Deviations from the norm in the levels of ALT and AST and changes in their ratio are observed in pathological processes.
The degree of increase in the activity of these enzymes allows us to judge the severity of the cytolytic syndrome. However, these indicators do not always indicate the severity of organ damage and do not allow the doctor to judge the prospects for the development of the disease. Therefore, along with the analysis of ALT and AST, specialists usually prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental examination methods, and also monitor the level of enzymes over time.
— In what cases are these tests recommended?
— Data on the level of ALT and AST may be important for such nonspecific symptoms as general weakness, decreased performance, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. These indicators must be determined to diagnose diseases and assess liver function.
Read materials on the topic:
Not always gastroscopy. Examination for abdominal pain. Insidious pain-mask. Does abdominal pain always indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract? Mom, my stomach hurts! What is hidden behind a child’s abdominal pain? How to avoid becoming a balloon? Getting rid of gas formation in the intestines Why do people turn yellow?
— What are the reasons for increased ALT and AST in the blood?
— Acute and chronic viral, toxic hepatitis, autoimmune diseases, fermentopathy, liver cirrhosis, tumor processes and metastases in the liver, infectious mononucleosis, pulmonary embolism, poliomyelitis, malaria, leptospirosis — in many pathological conditions we observe an increase in the level of these enzymes in the blood. Also, ALT and AST levels increase during myocardial infarction. Small short-term changes in their levels can be observed during heavy physical activity.
I would like to note that an important diagnostic indicator is the ratio between ALT and AST (the so-called de Ritis coefficient). This coefficient helps us distinguish, for example, viral hepatitis from alcoholic liver damage, myocardial infarction from liver diseases.
Read materials on the topic:
How to protect yourself from Botkin's disease? Shield and sword against hepatitis C. How to protect yourself and your loved ones? “The silent killer” of our contemporaries An invisible disease: fatty liver disease What can you get infected on vacation? Watch out for malaria! Is polio coming back? How to prevent myocardial infarction?
— What could be associated with a decrease in ALT and AST levels in the blood?
— With vitamin B6 deficiency, severe liver cirrhosis, pancreatic pathologies, and renal failure (especially in patients on hemodialysis).
— How do the levels of ALT and AST in the blood change during pregnancy?
- Since the liver during this period detoxifies the body not only of the mother, but also of the fetus, an increase in the level of these enzymes can be observed.
— Vasilisa Vladimirovna, is preparation required for taking the test for ALT and AST? If so, which one?
- Of course it is required. Blood from a vein must be donated in the morning on an empty stomach (last meal 12 hours before the test). On the eve of the test, you should avoid heavy physical stress, changes in diet, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. Half an hour before blood sampling, you should also refrain from smoking.
I would like to emphasize that determining only the level of ALT and AST is not always sufficiently informative, so most often doctors prescribe them in combination with other biochemical indicators.
Would you like to read about other analyses? You will find articles about them in our laboratory diagnostics section
You can sign up and get tested here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
The editors recommend:
Blood biochemistry: frequently asked questions Liver reboot. What are we going to clean? Delete or leave? What to do if gallstones are found?
For reference:
Ishchenko Vasilisa Vladimirovna
Graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of Kursk State Medical University in 2015.
In 2021, she completed her internship in the field of Internal Medicine and underwent retraining in gastroenterology.
Currently holds the position of gastroenterologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk. Reception is conducted at the address: st. Karl Liebknecht, 7.
Definition of indicators
Today in our country there is no unified scale for determining enzyme units in the blood. Each laboratory has its own standards and indicators, so in one center the level can be calculated in units/l, and in another in mmol/l. Therefore, it is impossible to decipher the analysis independently.
Only an experienced doctor will be able to correctly interpret the results of your tests and prescribe additional examinations if necessary.
When deciphering, it is necessary to take into account not only the gender, but also the age of the patient, as well as the presence of possible provoking factors. Therefore, the normal level of enzymes in different healthy people can differ significantly and it is completely unacceptable to judge your health based on the results of acquaintances and friends. The table of normal indicators is used by doctors taking into account all these factors.
Data on microelements and vitamins
Often, normal blood biochemistry levels are checked when clarifying vitamin levels in men or women. Attention should be paid to sodium and potassium. If there is too much sodium, you may experience muscle cramps, irritability and excessive thirst. A minimal amount of the element leads to headaches, the desire to constantly sleep, vomiting, and coma.
If potassium is elevated, arrhythmia, underestimation of blood pressure, and confusion are possible. Vomiting and nausea are signs of low potassium, and sometimes the condition leads to involuntary bowel movements or urination.
Reasons for increased AST
Detection of an increase in AST, especially repeated, may indicate the following diseases:
- Acute myocardial infarction in the initial phases of its development. Based on the dynamics of the indicator, one can judge its extensiveness and recovery period;
- Closed and open heart injuries;
- Myocarditis of autoimmune or infectious origin;
- Acute and chronic viral hepatitis;
- Toxic liver damage from hepatotoxic poisons and drugs;
- Fatty and alcoholic hepatosis;
- Endogenous intoxications against the background of infectious and purulent-septic diseases of internal organs and soft tissues;
- Severe chronic heart failure;
- Cholestasis caused by a mechanical obstruction in the bile ducts (stones, tumors, congenital anomalies);
- Impaired hepatic blood flow and portal hypertension;
- Cirrhosis of the liver with preservation of intact areas of this organ. In decompensated cirrhosis, the enzymatic activity of plasma in relation to AST decreases due to the complete replacement of the liver with connective tissue;
- Metastases to the liver of malignant tumors;
- Primary cancer of the liver or bile ducts;
- Damage to the liver and heart in malignant forms of myeloblastic leukemia;
- Massive destruction of muscle tissue (myodystrophy, generalized myositis, crush syndrome, reperfusion syndrome against the background of restored blood flow in the ischemic limb;
Not every increase in AST should be perceived as a sign of cellular cytolysis. If the indicator is several units of measurement higher than normal values, this does not mean anything. An increase in AST two or more times higher than normal is of diagnostic significance.
In this regard we can talk about:
- Moderate increase (when AST increases five times);
- Average increase (when an increase in the indicator is recorded up to ten times higher than normal);
- Severe elevation (AST level is ten or more times higher than normal).
The main diagnostic value of AST is heart damage during a heart attack. The study is carried out dynamically with short time intervals (about an hour). Any changes in the indicator that exceed the norm, in doubtful cases, speak in favor of a heart attack!
Data on nitrogen metabolic processes
A too slow metabolic process, fasting, polyuria or liver failure will be indicated by an underestimation of creatinine, urea, and uric acid in the blood. Normal blood biochemistry values increase the likelihood of problems with the diseases in question.
An overestimation of urea is also possible. If it is found during blood biochemistry, then arterial hypertension, poisoning or kidney disease will be suspected. Readings above normal for uric acid are a sign of poisoning, infectious diseases, skin pathologies, gout, leukemia or diabetes. One of the signs of abnormalities in kidney function is also high creatinine. The indicator also signals diabetes mellitus, muscular dystrophy or obstruction in the intestinal area.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
Quite often it is necessary to take a test such as blood biochemistry, so for many it is important to decipher the data obtained and normal indicators for comparison with those obtained in the laboratory. At the same time, the presence of any deviations does not indicate the fact of certain health problems, so it is worth finding out all the nuances from the doctor. The numbers are considered in aggregate and separately; they can only indirectly indicate the presence of possible diseases or deviations from the ideal state. We suggest studying normal blood biochemistry indicators, the reasons for underestimated or excessively high data in women or men.
When to get checked
Many dangerous diseases of the liver and heart are completely asymptomatic in the early stages. Transaminase analysis is quite suitable for their early diagnosis. You should immediately consult a doctor if you experience the following ailments:
- Causeless periodic weakness.
- Long-term loss of appetite.
- Frequent nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach ache.
- Yellowness of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
- Discoloration of urine to dark brown.
- Lightening of stool.
- Skin itching in combination with other symptoms.
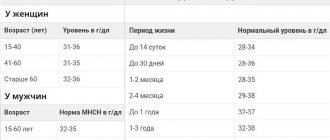
Norm of AST in the blood
In order to correctly evaluate the obtained indicators of plasma enzymatic activity in relation to AST, you need to know its normal values. Most laboratories usually indicate the norm next to the result obtained. This is due to the fact that different reagents and methods can be used to determine the AST indicator. The types and standards given in the table are considered generally accepted.
| Determination method | Norm for men | Norm for women | Norm for children |
| Optical (in ME) | Up to 40-41 IU | Up to 34-35 IU | Up to 50 IU |
| Reitman-Frenkel reactions (in mcomol/(h/ml)) | 0,1-0,45 | 0,1-0,35 | 0,2-0,5 |
If a biochemical blood test yields AST values that do not exceed standard values, this indicates the normal functioning of the enzyme systems of the heart and liver and the preserved integrity of the cellular composition of these organs. If there are clinical symptoms of their damage, other specific markers (ALT, troponins, creatine phosphokinase, etc.) must be examined!
How to downgrade?
An increase in AST in the blood is always caused by the development of some pathology associated with the destruction of cells of the heart muscle, liver and some other tissues. It is important to understand that it is impossible to reduce the concentration of the enzyme without treating the primary disease. Therefore, the main task of the doctor when detecting increased AST activity in the blood plasma is to diagnose and prescribe treatment. A decrease in AST will occur only after the disease is eliminated. With proper and timely treatment, normalization is possible within a month to a month and a half.
Indications for analysis
A biochemical blood test, during which the AST level is determined, is prescribed for a number of diseases, including:
- All liver pathologies.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Chronic and acute heart diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Infections.
- Intoxication.
- All types of jaundice and bilirubin metabolism disorders.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Purulent-septic pathologies.
- Encephalopathy of unknown etiology.
- Bile outflow disorders, cholelithiasis.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Malignant tumors.
- Allergic skin diseases.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics, chemotherapy and various toxic drugs.
- Injuries to the abdomen and chest.
- Preparation for a complex surgical operation.
- Evaluation of treatment of liver and cardiac pathologies.
How is the research conducted?
To determine AST in the blood, a biochemical blood test is performed. The sample is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach. A tourniquet is applied to the arm above the elbow. The needle and injection site are disinfected with alcohol. A needle is inserted into a vein and 15-20 ml of blood is taken, after which the tourniquet is removed, and the injection site is clamped with a cotton swab. The patient should bend his arm at the elbow and wait until the bleeding stops.
Using centrifugation, plasma is separated from formed elements, then the activity of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood is determined using chemical reactions.
Results are usually ready the next day. Decoding is the responsibility of the attending physician, who is familiar with the standards of the laboratory in which the analysis was carried out. It should be said that different laboratories may use different methods and reagents.