Material reviewer
Today, hemorrhoids are considered to be one of the most unaesthetic and “shameful” diseases, which is unpleasant to talk about, let alone close people, even medical specialists. In this regard, many remain silent at an appointment with a proctologist, suffering from severe hemorrhoids or some more serious complication.
Important! Treatment of developing hemorrhoids is quick and painless if you treat the disease with conservative methods in its initial stages.
One of the most serious consequences of hemorrhoids that are not treated in a timely manner is thrombosis of the hemorrhoid (thrombophlebitis). The pain syndrome at this stage of the disease is so severe that the patient has no choice but to seek help from a proctologist. Such lateness does not bode well!
The essence of the disease
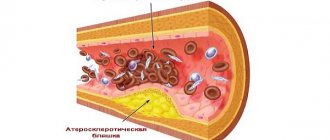
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis is a complication that occurs when hemorrhoids occur in an acute form. It is characterized by the appearance of blood clots in the cavernous vascular plexuses of the anal area. Thrombosis of an inflamed hemorrhoid does not occur by itself. This means that the patient already had a hidden or external hemorrhoid in which a blood clot had formed.
Important! The pathological condition is often caused by a chronic inflammatory process localized on an enlarged hemorrhoidal node, but extremely rarely it occurs in parallel with actively developing hemorrhoids.
Schematically, thrombosis of an inflamed hemorrhoid occurs as follows:
- On the inner or outer side of the anal sphincter there is an inflamed venous plexus, the membrane of which is damaged.
- To avoid bleeding, the venous lumen is clogged with a blood clot, which, in turn, disrupts the flow of blood.
- The location of the pathology swells, which is accompanied by the onset of an active inflammatory process.
- A feeling of sharp pain appears in the rectum or anal area. Moreover, the size of the elements of thrombosis does not in any way affect the strength of the pain syndrome.
- The patient develops a natural fear of going to the toilet, provoking the syndrome of “psychological constipation”.
- Defecation after a long period of time leads to the fact that hemorrhoidal cones are damaged, and the pain, as a result, intensifies.
Statistical data indicate that acute hemorrhoidal thrombosis occurs in almost every 3rd patient with chronic inflammation and enlarged hemorrhoidal nodes.
Classification of local drugs
Pharmaceutical companies produce several large groups of medications that are intended to suppress the symptoms of external hemorrhoids. Each type has its own spectrum of action. The list is presented:
- Venotonics - active ingredients increase the density of vascular walls, normalize capillary permeability. Due to them, there is an increase in the tone of the muscle tissue of the veins, and blood circulation is stabilized.
- Anticoagulants – medications used to treat blood clots. The active components are responsible for reducing the rate of blood clotting and preventing the formation of new blood clots.
- Hemostatics and coagulants - medications accelerate the process of blood clotting. Used to quickly stop bleeding from damaged tissues.
- Antispasmodics – relieve the symptoms of muscle spasms that provoke pain. They are used in the early stages of the pathological process; suppositories are a common form of release.
- Immunomodulators - due to active components, the functioning of the immune system improves. As a result, the body resists pathogenic microflora and easily suppresses outbreaks of infection and inflammation.
Complex therapy involves the use of several additional medications that do not affect hemorrhoidal disease. Anti-inflammatory drugs stop inflammation, antimicrobial drugs reduce the risk of secondary infection. Painkillers are used to suppress severe pain.
Causes of acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Based on the foregoing, we can say that the immediate problem of thrombosis is damage to the vascular walls. The following factors provoke such damage:
- Excessive straining during bowel movements, labor, or increased physical activity.
- "Non-traditional" sexual practices.
- Hypothermia of the pelvic organs. In this case, the vascular canal narrows, the blood stagnates and, as a result, the vessel wall is damaged.
Considering the relationship between thrombosis of hemorrhoids and hemorrhoids, it is worth noting the factors contributing to the development of these two pathologies:
- Sedentary lifestyle and frequent sitting. Physical inactivity is one of the root causes of congestion in the intra-abdominal part and pelvis.
- Regular and prolonged physical activity associated with work or sports activity. Due to this “heaviness,” the elasticity of the walls of the vascular canal decreases.
- Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Hardening of feces, caused by difficulties in removing it from the body, leads to regular damage to the mucous membrane and hemorrhoidal nodule located in its path.
- Poor nutrition and addiction to alcohol. Any foods and substances that irritate the gastrointestinal tract contribute to excessive blood flow to the organs.
- Tumor formations localized in the rectum. Such elements also provoke blood flow and, as a result, stagnation in the blood vessels. Inflammatory processes put pressure on hemorrhoidal formations and deform the nodes.
- Changes in the body associated with pregnancy. Changeable hormonal levels and uterine growth cause constipation and hemorrhoids.
Thus, very often the course of hemorrhoids contributes to the development of thrombosis localized in the enlarged hemorrhoidal node. Accordingly, when treating thrombosis, the primary task is to get rid of the enlargement of venous cones.
Prevention of acute external hemorrhoids
- timely treatment of the initial stages of hemorrhoids and minimally invasive treatment;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle with the introduction of a rational diet, physical activity, and absence of sedentary work;
- elimination of chronic constipation (nutrition, drinking regime);
- compliance with the principles of personal and intimate hygiene;
- visiting a specialized specialist, conducting diagnostics when the first symptoms of hemorrhoids appear;
There are contraindications - specialist consultation is required!
Types and degrees of development of the disease
Based on where the blood clot formed, proctologists distinguish between internal and external thrombosis, as well as a mixed type, in which the pathology affects the node on both sides. Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid is most common, so most of the information will concern this type of pathology.
There are three main degrees of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which correspond to the successive stages of its development.
- Blood clots begin to form. Because of this, pain appears, but not accompanied by an inflammatory process.
- Inflammation appears, accompanied by the growth of cones and increased pain. There may be an increase in temperature, swelling and redness of the skin at the site of localization of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
- At the final stage of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, the area surrounding the site and the groin area are affected. There is a risk of severe complications.
The main characteristics of each stage of hemorrhoidal thrombosis are summarized in the table.
| Sign | 1st stage | 2nd stage | 3rd stage |
| The dimension that a node has | Small | Average | Large |
| Elasticity of the bud | Highly elastic | Tight elastic | Very dense |
| Color | Slight redness | Dark red or bluish tone | Black necrotic areas or areas with a white coating |
| Degree of pain | Moderate, aggravated by physical contact | Pronounced | Tormenting |
| Localization | Outside the rectum | Inside or outside the anal area | Domestic or mixed |
| Swelling | Unexpressed | Edema and hyperemia surrounding the node | Pronounced with hyperemia of the entire anal part |
| Sphincter spasms | No | Present | Expressed process |
| Bleeding | No | Mostly no | Expressed |
Hemorrhoids: types, stages, treatment
Shlosser Kirill Vladimirovich
Surgeon, Proctologist
April 30, 2021
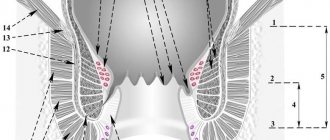
Hemorrhoids are a pathological expansion of cavernous (that is, cavernous or spongy in structure) vascular plexuses located in the anus, with the formation of external and/or internal nodes.
Causes of hemorrhoids
- A lifestyle associated with prolonged static loads: hemorrhoids are an “occupational” disease of drivers, office workers, security guards, etc.
- Excessive physical activity, heavy lifting, sudden tension.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol, spicy and pickled foods.
- Constipation, straining with difficulty defecating (defecation).
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Heredity.
Symptoms of hemorrhoids
- Discomfort or pain in the anus.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the anal canal.
- Discharge of blood during bowel movements, blood in the stool.
- Nodes in the anal area.
Classification of the disease
Acute hemorrhoids are thrombosis of hemorrhoids. The external manifestation is a dense, painful external or internal bluish-colored node filled with a blood clot.
Acute hemorrhoids are divided into three degrees of severity:
I degree – Thrombosis of external or internal hemorrhoids without an inflammatory process.
II degree – Thrombosis, complicated by inflammation of hemorrhoids.
III degree – Thrombosis of hemorrhoids, complicated by inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue in the perianal area.
Therapeutic tactics involve both complex conservative treatment and surgical treatment.
The indication for surgical treatment is acute thrombosis of the hemorrhoid. In the early stages of the disease, optimally up to 72 hours, thrombectomy is indicated - removal of thrombotic masses. Performed on an outpatient basis. The operation leads to a significant reduction in treatment time.
In later stages, either removal of the thrombosed node or conservative treatment followed by planned surgery is possible. Hospitalization is indicated for stage III of the disease, when the inflammatory process spreads to the surrounding tissues of the perianal region and anal canal.
Stages of disease development
Chronic hemorrhoids are divided into four stages.
Characteristic symptoms:
Stage I – Periodic bleeding from the rectum without prolapse of hemorrhoids. The method of treatment is conservative therapy.
Stage II - Hemorrhoids fall out during defecation, but are reduced on their own. There may or may not be bleeding. It is also possible for nodes to fall out during intense physical activity.
The second stage combines conservative treatment and minimally invasive proctological manipulations, which are carried out by Medical specialists in an outpatient setting.
Stage III – Manual assistance is required to reduce the nodes into the anal canal. Bleeding becomes more profuse, and periodic inflammation of the hemorrhoids is observed.
Treatment is surgical. The operations are performed by proctological surgeons at the Medical Outpatient Surgery Center.
IV – Hemorrhoids are constantly in a prolapsed state. This is the most difficult stage. Prolapse occurs even with the slightest stress: change in body position, coughing, release of gas from the intestines. The walls of the node are constantly injured and inflamed.
Only surgical treatment is indicated.
Treatment of hemorrhoids
Methods for diagnosing proctological diseases
- During an external examination, the doctor pays attention to the shape of the anus, its gaping, scar changes or deformations, fistulous openings, the condition of the skin and mucous membrane of the anal canal when straightening the folds. It determines the severity of external hemorrhoids, the stage of the disease, the degree of bleeding and prolapse of the nodes, the possibility of their independent reduction into the anal canal, and evaluates the anal reflex.
- Digital examination helps determine the tone of the sphincter, the presence of neoplasms, mucosal defects and the degree of their pain.
- Anoscopy is performed using a special disposable anoscope device, which allows you to examine the inner surface of the rectum and anal canal up to 10 cm. The procedure is painless, preparation is not required. Using anoscopy, a proctologist can assess the condition of internal hemorrhoids, the presence of inflammatory changes in the mucosa, detect anal canal polyps, mucosal defects, blood clots and possible sources of bleeding.
- Sigmoidoscopy is an examination of the rectum and distal sigmoid colon up to 25 cm using a special endoscopic device that allows you to assess the condition of these sections from the internal lumen of the intestine.
Thanks to a complex of diagnostic tests, a specialist can identify not only hemorrhoids, but also concomitant diseases.
Conservative treatment of hemorrhoids
The therapy is based on a specialized diet aimed at normalizing stool. The patient's diet should include foods rich in plant fiber and plenty of liquid. The doctor also prescribes medications that stimulate bowel movements.
To relieve inflammation, ointments, creams and suppositories with an anti-inflammatory combined effect are used. Therapy is supplemented by taking phlebotonics - drugs that increase the tone of the vascular wall.
In case of severe bleeding, local and general hemostatic (hemostatic) agents are prescribed.
For the conservative treatment of hemorrhoidal thrombosis, combined local agents with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, absorbable, and decongestant effects are used.
Minimally invasive methods of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
- Sclerosation of hemorrhoids
Indications for surgery are chronic hemorrhoids of stages I–II, accompanied by bleeding.
A special substance – sclerosant – is injected into the lumen of the hemorrhoid using the thinnest injection needles. This drug glues the walls of the vessels inside the node, preventing further progression of the pathology. The operation is performed in an outpatient clinic.
Contraindications:
– Thrombosis of hemorrhoids
– Paraproctitis
– Anal fissure
- Ligation of internal hemorrhoids
Indicated for chronic hemorrhoids of degrees II and III, if the nodes are located separately from each other and have clearly defined boundaries.
The operation is performed in an outpatient setting. A latex ring (ligature) is placed on the base of the internal node, the nutrition of the node is disrupted and it is rejected along with the ligature after 7-10 days. Ligation of several nodes at once can cause pain, low blood pressure and bradycardia in the patient, so the procedure is usually performed at 2-3 week intervals.
Surgical treatment methods performed at the Medical Center
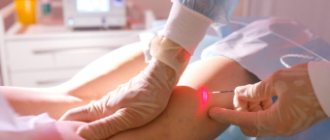
- Laser vaporization of hemorrhoids
It is performed for chronic hemorrhoids of stages II and III. Also suitable for the treatment of small external hemorrhoids. The operation is performed using a Milon-Lakhta surgical laser, which destroys (evaporates) fluid-rich hemorrhoidal tissue, while preserving the mucous membrane. The light guide is inserted into the lumen of the internal hemorrhoid through a small 1-2 mm puncture of the anoderm. The manipulations are performed under general anesthesia in the Outpatient Surgery Center of our clinic.
Advantages of the technique:
– Reduced operation time.
– Significant reduction in pain intensity in the postoperative period compared to classic hemorrhoidectomy.
– Significant reduction in the healing time of surgical wounds and punctures.
– More comfortable course of the postoperative period and rapid recovery of work capacity.
Contraindications:
– Stage IV hemorrhoids
– Purulent and oncological diseases of the rectum
- The Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy operation is indicated for stages III–IV of chronic hemorrhoids
There are two main types of hemorrhoidectomy: open and closed.
Open surgery is performed under general anesthesia in the operating room. The doctor alternately stitches and ties the vascular legs of the nodes and then removes the external and internal hemorrhoids. Postoperative wounds are not sutured. Next, the surgical site is injected with a local anesthetic, and an absorbable tampon with an anesthetic is placed in the anal canal.
A closed operation is performed in the same way as an open operation, but after removing the nodes, the wounds of the anal canal are sutured with absorbable suture material.
Also, a similar operation is performed using a high-frequency ligation device LigaSure. It is considered open. LigaSure allows the operation to be performed almost bloodlessly, since the device automatically coagulates (seals) large vascular formations that make up the hemorrhoid. The nodes are excised down to the vascular pedicle, and after “welding” the pedicle, they are finally removed.
Advantages of the technique:
– The operation goes faster.
– Reduced blood loss during surgery.
– The risk of bleeding in the postoperative period is reduced.
– Recovery after surgery is faster.
Postoperative treatment of hemorrhoids takes place in an outpatient clinic. The proctologist observes, makes dressings, gives nutritional recommendations and prescribes medications for the recovery period.
Experienced medical proctologists will be happy to help you solve your problems.
Clinical picture
Knowing its expressed symptoms will allow you to recognize the disease in a timely manner in order to begin treatment. Most often, thrombosis corresponds to the following manifestations:
- itching in the anus;
- burning sensation that accompanies bowel movement and persists after;
- ichor and mucus coming out of the anus;
- pain in dense nodes (this density is especially felt when external hemorrhoids are detected);
- acute pain during physical activity affecting the anal canal and nearby areas (standing up/squatting, sudden movements, going to the toilet);
- the node falls out, which is accompanied by swelling of the venous plexus.
For mixed, external or internal hemorrhoids in the last stage, each symptom intensifies. Heavy bleeding and unbearable pain are reasons for prompt hospitalization, since in this condition there is a risk to the patient’s life.
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a proctologist (assessment of patient complaints, medical history, external examination of the anus, digital examination of the rectum, anoscopy if indicated)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Make an appointment
1500 ₽
Repeated appointment with the proctologist
Make an appointment
700 ₽
There are four stages of chronic internal hemorrhoids:
- At the first stage, hemorrhoidal veins protrude into the anal canal, but do not fall out (internal hemorrhoids);
- At the second stage, the nodes already fall out, but at the same time they are independently retracted into the anus;
- The third stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by the need for the patient to reduce the hemorrhoids by hand after bowel movements or physical activity;
- The fourth stage - the fallen nodes are not reduced.
The treatment strategy for hemorrhoids is determined by the stage of the disease.
Critical risks for the disease without treatment
There is a certain chance of hemorrhoidal thrombosis going away on its own if, when the blood walls are destroyed, the blood clots leave the hidden or external node. However, such luck is unlikely - often qualified treatment for thrombosis of hemorrhoids is required. Without timely treatment of thrombosis, the risk of developing the following critical complications is high:
- necrosis in the node - the death of inflamed areas with the formation of ulcers in their place;
- perarectal abscess - suppuration in the subcutaneous part of the anal area.
When treating thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodes, it is possible to avoid death, which can result from blood poisoning.
Treatment of mixed hemorrhoids
Proctologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide differentiated treatment for combined hemorrhoids depending on the presence and location of painful hemorrhoids. With combined hemorrhoids of the first degree, patients are recommended to normalize intestinal activity by eating large amounts of foods that contain a lot of coarse fiber. Symptoms of combined hemorrhoids decrease if the patient properly cares for the anal area. He is advised to stop using toilet paper and wash himself with cool water using products intended for intimate hygiene.
To treat second-degree combined hemorrhoids, proctologists prescribe venotonic drugs. The gold standard for conservative treatment of combined hemorrhoids is diosmin preparations. Detralex is the most effective. Ointments, gels and suppositories are used locally, which include venotonics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, local anesthetics and anticoagulants (relief, anisole, ultraproct, proctosan).
For combined hemorrhoids, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital rehabilitation clinic develop an individual set of gymnastic exercises for each patient. Training is carried out first under the guidance of a senior exercise therapy trainer, then patients perform the exercises independently. To treat combined hemorrhoids, proctologists use innovative minimally invasive techniques:
- Sclerotherapy;
- Laser coagulation;
- Ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings;
- Photocoagulation.
If a patient has combined fourth-degree hemorrhoids, proctologists will suggest performing a radical operation - hemorrhoidectomy. In order to undergo examination and treatment of combined hemorrhoids using the optimal method, call and make an appointment with a proctologist at the Yusupov Hospital.
Diagnosis of the disease
The severity of symptoms simplifies the process of making a diagnosis for thrombosis of internal or external nodal elements. Experts use three main research methods:
- visual – you can observe the presence of formations and determine the degree of pathology, taking into account the color of the node;
- finger - palpation allows you to determine the structure of the lump, but can be performed with anesthesia if palpation increases acute pain;
- instrumental is the most effective (a rectal speculum is used), but also requires anesthesia in case of severe pain.
Often, patients' assumptions about the presence of typical hemorrhoids lead to the detection of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal nodes during examination.
Diagnosis of acute external hemorrhoids
The process of diagnosing acute external hemorrhoids includes:
- interviewing the patient regarding existing complaints, collecting anamnesis of life and illness;
- external and internal digital rectal examination by a coloproctologist;
- if possible: anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy;
- additional methods: fibrocolonoscopy, rectal ultrasound, laboratory tests, specialist consultations.
During an external examination, the condition of the skin of the perianal area, the tone of the anal sphincter, the shape, the presence of scar changes and deformities of the anus, the presence of formations, and fistulous openings are assessed.
When assessing hemorrhoids, attention is paid to their severity, the presence of contact bleeding, ulceration, and pain.
Features of conservative treatment
The type of treatment determined for the patient by the physician depends on the degree of development of thrombosis. Therapeutic stages are relevant for thrombosis of stages 1 and 2, as well as during pregnancy. During the treatment the following tasks are solved:
- relieving severe inflammation;
- elimination of swelling and pain;
- relieving tension from the anal sphincter;
- dissolution of blood clots and prevention of thrombus formation.
Conservative treatment involves the use of medications or ointments that dissolve the blood clot localized in the node. The choice in favor of one or another means takes into account the location where the nodes are located. The course can also be supplemented with various painkillers that block the pain syndrome that occurs during thrombosis. Naturally, during pregnancy the range of drugs available for treatment is significantly reduced.
Treatment of acute external hemorrhoids
The choice of the most effective method of treating hemorrhoids depends on the clinical picture of the disease and concomitant pathologies in the patient.
- Surgery:
- thrombectomy
- excision of the hemorrhoid (possibly on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia)
- Conservative therapy:
- Drug treatment:
- painkillers (ointments, suppositories);
- combination drugs that have anti-inflammatory, astringent, decongestant and regenerating effects;
- use of heparin-containing agents (thrombolytic and hemostatic effects);
- prescription of venotonic drugs, mild laxatives.
- Lifestyle correction: giving up toilet paper (rising shower), caring for the perianal area and perineum, diet, work and rest.
Make an appointment
The duration of rehabilitation after surgical treatment is determined by the volume of surgical measures performed and the initial characteristics of the pathology in each patient.
Surgical intervention
Thrombosis in the most acute forms requires immediate surgical elimination. There are the following types of surgical effects on nodes:
- Thrombectomy. The thrombosed lump is opened to remove the blood clot. There is a risk of recurrence, since the cut is perceived by the body as a reason for the formation of new clots.
- Hemorrhoidectomy. The node is removed along with the clot. This form of surgery is more effective and there is no risk of relapse.
Attention! Surgical intervention is relevant not only for acute forms of pathology, but also in cases where medications and active ingredients of ointments are incompatible with the patient’s body.
Only a specialized specialist who has carefully examined the patient and determined the main characteristics of painful formations can determine the most appropriate method of dealing with nodes, or the optimal treatment course for eliminating hemorrhoids.
Forecasting and preventive measures
It is worth repeating that there are certain chances of cure if the disease is only in the 1st stage. However, contacting a medical specialist is necessary in any case, even if the main symptoms disappear after some time. The prognosis for cure will also be favorable if all the previously mentioned symptoms were noticed in a timely manner. It is unacceptable to start the disease by transferring it to the 3rd critical stage of development.
Preventive measures to avoid acute thrombosis:
- proper nutrition (avoiding spicy and salty foods);
- stabilization of the gastrointestinal tract (it is extremely important to prevent the formation of constipation and physical complications during bowel movements);
- avoiding hypothermia;
- increasing physical activity (mobility) as a permanent way of life.
It is extremely important to follow all the recommendations in order to restore your usual way of life and not feel discomfort when being in society.
Relevance of the problem
Although published data on the prevalence of hemorrhoidal disease among populations in developed countries vary, 1,2 it can be said that it is one of the most common diseases in surgical practice. In the United States, more than 2.2 million new cases are diagnosed as outpatients each year3. There is a wide variety of clinical symptoms that can be misinterpreted by doctors and patients as a manifestation of hemorrhoidal disease. Thus, it is necessary to determine exactly what hemorrhoids are causing the symptoms before starting treatment for the disease. These recommendations are devoted to both diagnostic methods and modern approaches to the treatment of hemorrhoids.