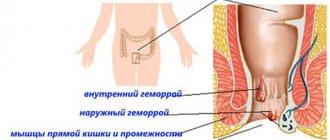
Hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidal disease)
is the collective name for pathologies of the rectum, in which the internal and external hemorrhoidal plexuses located in the anal canal increase in size.
If the outflow of blood is disrupted, internal nodes can fall out and bleed, and sometimes complications arise, for example, thrombosis, which is accompanied by severe pain. Most often, this disease is caused by a genetic predisposition, but the “trigger mechanism” for the development of hemorrhoids most often becomes everyday habits, lifestyle and natural physiological processes (hemorrhoids during pregnancy, in patients over 50 years old)
.
We have collected several important facts about the prevention and treatment of hemorrhoids in one article to refute misconceptions and recall the main points that will help you avoid becoming a victim of this “popular” disease.
If you have the following symptoms of hemorrhoids:
- pain when defecating, sitting and walking,
- bloody stool
- prolapse of hemorrhoids,
- itching in the anus
consultation with a proctologist is required
! A doctor of this specialization will help solve your problem carefully and effectively by prescribing competent therapy.
Our clinic is hosted by a leading proctologist, author of scientific works, and a surgeon with more than 40 years of experience
Sergey Dmitrievich Trukhmanov .
You can make an appointment with the doctor in person or take
an online consultation with a proctologist .
Online consultation with proctologist S.D. Trukhmanov
will be useful if:
1) you do not have the opportunity to come to the Pirogov clinic;
2) you would like to receive expert advice from a doctor and adjust conservative treatment;
3) surgery for hemorrhoids was indicated for you.
To prevent hemorrhoids, it is important to maintain a drinking regime.
Glass of water
on an empty stomach or
a cup of coffee
daily before the morning toilet improves intestinal motility.
For constipation, it is useful to drink water containing magnesium ions or sulfate
. Drink a glass of mineralized water at room temperature 3 times a day.
Special herbal infusions for the intestines and even ordinary green tea are useful. The latter contains flavonoids - natural antioxidants and tannins, which increase vascular tone and reduce the severity of the inflammatory process in the tissues of the anus. It is important that green tea is of high quality and properly brewed. For gastritis and stomach ulcers, green tea may be contraindicated.
at least 2 liters of liquid per day
.
cognac is extremely harmful to the intestines.
- it has a toxic toxic effect on the cavernous tissue of hemorrhoids and “corrodes” it.
Composition and therapeutic effect of the drug Detralex
A therapeutic course of venotonic drugs is also prescribed. Detralex is used most often.
It is based on flavonoids - substances of plant origin. The active ingredients are hesperidin and diosmin, which eliminate venostasis (blood stagnation).
Detralex restores and increases the tone of venous walls and blood microcirculation in small vessels. Capillaries become elastic and plastic, their permeability decreases. The medicine reduces the distensibility of the veins, which reduces the release of plasma and proteins from the bloodstream into the surrounding tissues.
Detralex has an angioprotective and venotonic effect.
In addition, the drug Detralex increases the outflow of lymph, thereby providing lymphatic drainage.
What foods are good for preventing intestinal diseases?
In order not to risk your health and not be a victim of hemorrhoids, it is recommended to include more vegetables, fruits and fiber in your daily diet.
For the prevention of hemorrhoids it is useful:
- Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables (apples, avocado, pumpkin, broccoli)
- Beetroot and beet salad
- Freshly squeezed juice, especially pumpkin juice
- Prunes
- Chew food thoroughly
Harmful:
- Hot, spicy, fried, smoked
- Marinades
- Eat dry
- Soda
- Whole milk
- Baking and flour
- Lots of sweets
- Pasta, white rice and bread
- Canned food
If microflora disorders are detected, it is better to cure them. Sometimes it is necessary to prescribe probiotics that restore the intestinal microbiome, and enzymes that help digest food.
*For patients with diagnosed intestinal disease, the diet is individually prescribed by a doctor.
Is it true that anal sex leads to hemorrhoids?
There is no data that would reliably confirm the correlation between anal sex and, for example, hemorrhoids. The main danger of anal sex is, of course, the transmission of infections, for example, the human papillomavirus, which causes cancer. human papillomas. Even Koch bacilli - the culprit of tuberculosis - in 5% of cases live in the rectum, and not just in the lungs.
“Non-standard” sex can lead to anal fissures, damage to the mucous membrane, and bleeding. Insufficiency of the anal sphincter also develops, which can lead to fecal incontinence. And weakening of the ligaments leads to prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Evidence-based medicine does not answer this question, but it’s better to be careful.
Indications
Indications for the use of the drug Detralex are organic and functional venous-lymphatic insufficiency of the lower extremities. Detralex is also used for the symptomatic treatment of acute hemorrhoidal attacks.
The medicine Detralex can be used for tired legs
Detralex is indicated for:
- pain;
- cramps of the lower extremities;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the legs;
- "fatigue" in the legs.
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- trophic changes in the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- venous trophic ulcers.
Is it possible to cure hemorrhoids using traditional methods?
Herbal baths, decoctions and compresses are appropriate only as part of combined conservative therapy for uncomplicated hemorrhoids. We are not aware of cases in which these isolated measures would be truly effective. Traditional methods of treating hemorrhoids should be treated especially carefully and from a critical point of view. Still, we are talking about a serious pathology of the rectum, often with cracks, prolapse of nodes and even thrombosis. Self-medication can be dangerous.
A separate group of proctologist patients are those whom doctors treat for complications after treatment with traditional methods.
They will definitely not help with hemorrhoids:
- ice candles
- fresh potato paste
- aloe leaf
- cucumbers from the garden
- steam baths
- leeches
Non-surgical treatment of acute and chronic hemorrhoids
G
Emorrhoids are one of the most common human diseases.
Although there are no exact statistics on this matter, there is every reason to believe that up to 80% of the adult population suffers from hemorrhoids
. Patients with this disease often seek help not only from coloproctologists, but also from specialists related to the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, i.e. internists and gastroenterologists. The ability to correctly diagnose and choose adequate treatment tactics is the main task of a doctor.
Etiology
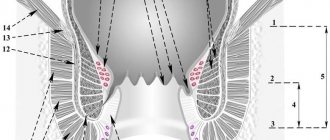
In the light of modern concepts, hemorrhoids are based on the pathology of cavernous vascular plexuses that arise during normal embryogenesis in the submucosal layer of the distal part of the rectum. There are two theories explaining the development of hemorrhoids: “mechanical” and “hemodynamic”.
According to the “mechanical” theory, hemorrhoids are formed as a result of distal movement of the anal ridges. The latter are a normal anatomical structure and play an important role in retaining the contents of the rectum. The venous plexuses, contained in their submucosal layer, are normally fixed by connective tissue fibers of the longitudinal muscle, and below by the ligament of Parks. As intra-abdominal pressure increases, the ridges move distally. With prolonged straining and other unfavorable conditions, accelerated natural wear of the fixing apparatus occurs. Fiber rupture, degenerative and dystrophic changes are observed. Hemorrhoids increase in size and fall out of the anal canal. According to the “hemodynamic” theory, the formation of nodes is facilitated by stagnation of venous blood, which occurs as a result of mechanical obstacles (hard feces, its constant presence in the ampulla of the rectum) and the lack of relaxation of the internal sphincter during defecation. The reverse flow of venous blood is aggravated by the opening of arteriovenous shunts and spasm of precapillary arterioles. Apparently, both mechanisms are equally involved in the genesis of hemorrhoids. However, venous congestion more often causes thrombosis of nodes, and increased arterial blood flow and the opening of shunts lead to bleeding, varicose veins and inflammatory changes in the rectal mucosa. Predisposing or resolving factors include insufficient dietary fiber, constipation and straining during bowel movements, sedentary lifestyle, hot baths, heavy lifting, pregnancy and childbirth. Loose stools, abuse of laxatives, enemas, excessive anal hygiene, and spicy foods also have a negative impact.
Clinic
Characteristic manifestations of hemorrhoids are bleeding from the anus and prolapse of hemorrhoids.
.
The blood is bright red, without clots. The patient notices its presence most often in the toilet. It is released in drops or streams during bowel movements. Blood is never mixed with feces, as is the case with inflammatory diseases of the colon, and is absent from toilet paper, which is typical for an anal fissure. When hemorrhoids prolapse, blood may stain your underwear. Very rarely, the blood may become dark in color and appear in clots. This occurs due to the accumulation of blood in the ampulla of the rectum and its release during subsequent bowel movements. Pain and discomfort are usually associated with thrombosis of nodes or anal fissure. Anal itching
is a symptom that occurs for many reasons.
These include insufficient hygiene after defecation, fecal contamination of linen, prolapse of nodes with or without mucous discharge. Typically, such a patient complains that after defecation he has to repeatedly use toilet paper in order to properly clean the anus. Sometimes the patient experiences perianal edema due to the filling of the external venous plexus with blood or thrombosis of the external hemorrhoids. Since internal hemorrhoids are covered with columnar epithelium, trauma leads to inflammation and copious secretion of mucus
. The predominance of certain symptoms in the clinical picture of the disease will dictate the choice of appropriate drugs for local treatment.
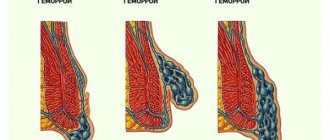
Clinically, hemorrhoids manifest themselves in two main syndromes:
chronic and acute. These syndromes are phases of the same process. For the first stage of chronic hemorrhoids, a characteristic sign is the discharge of blood from the anal canal without prolapse of hemorrhoids. The second stage is accompanied by the loss of nodes, which are independently retracted into the anal canal. A distinctive feature of the third stage is the need for their manual reduction. Prolapse of nodes occurs not only during bowel movements, but also during heavy lifting and coughing. The fourth stage is characterized by constant loss of nodes and the impossibility of their reduction into the anal canal. With each stage, the symptoms become more diverse. By this time, the connective tissue frame of the anal ridges is significantly damaged and cannot be restored. This classification makes it possible in practice to select a treatment method. The basis for the development of an acute process is thrombosis of hemorrhoids - internal or external.
Treatment
Indications for conservative treatment are the initial stages of chronic hemorrhoids and the acute uncomplicated course of the disease. At the first stage, preference is given to drug treatment or infrared photocoagulation. In the second stage, drug treatment is still acceptable, but ligation with latex rings is considered an alternative. It is also acceptable in the third stage, but in the fourth stage the only adequate treatment method is hemorrhoidectomy. It should be noted that currently minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids have become widespread. They provide a positive effect in 88% of cases, are associated with a low risk of complications, are painless and can be performed on an outpatient basis without loss of ability to work.
Conservative treatment of hemorrhoids
Includes general measures in the form of diet, careful personal hygiene, physical activity, taking analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, systemic venotonics, as well as local treatment with combination drugs.
Regardless of the type of hemorrhoids, special attention should be paid to simple hygiene practices
. These include refusing to use toilet paper, using baths or showers at a comfortable temperature with washing both the perianal skin and the anal canal itself with plain water without soap or other detergents. Eliminating fecal contamination reduces inflammation and itching, and warm water relieves pain associated with sphincter spasm.
Some types of exercise
that help eliminate venous stasis, for example, swimming or gymnastics.
It is very important to regulate stool consistency and frequency
. Diarrhea and constipation are equally unacceptable. In case of stool retention and strained bowel movements, irritating laxatives should be avoided. Patients are recommended to increase their intake of plant fiber (vegetables, fruits) and fluids. Additionally, wheat bran, microcrystalline cellulose or other hydrophilic colloids are included - seaweed, flaxseed. It is recommended to take preparations from plantain seeds or macrogol 4000. The choice is quite individual. These drugs are useful both during exacerbation of hemorrhoids, and in preparation for surgery, and in the postoperative period. In controlled studies, plantain seeds - Plantago ovata - have been shown to effectively reduce the incidence of bleeding and other symptoms of stage 1 and 2 hemorrhoids, but have no significant effect on the size and blood supply of hemorrhoids (Perez-Miranda et al., 1996). Patients with diarrhea are prescribed astringents, loperamide, hydrophilic colloids in combination with oral hydration. Drinking alcohol, spicy food, tea or coffee is prohibited.
An important element of the treatment program is the use of phlebotropic drugs
. This should include preparations from horse chestnut fruits, troxerutin, rutoside, escin and others. Purified micronized diosmin has been better tested in clinical trials, which effectively reduces the clinical manifestations of acute and chronic hemorrhoids, and also prevents its exacerbations (Godegere, 1994; Meyer, 1994). Drugs in this group increase the tone of the veins and the speed of lymph flow, improve microcirculation, and reduce capillary permeability caused by ischemia and inflammatory mediators. It should be noted that micronized diosmin can be safely used for acute hemorrhoids in pregnant women (Buckshee et al., 1997), in whom outpatient surgical treatment is contraindicated. The drug is prescribed 4-6 capsules for 7 days, but treatment can be prolonged - 2 capsules per day for many months.
multicomponent ointments and suppositories are widely used.
. Almost all of them include anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, sclerosing, anticoagulant agents, anesthetics, venotonics and reparants in various combinations. The optimal composition of agents for topical treatment of hemorrhoids has not been precisely established. It remains not entirely clear whether the presence of anticoagulants, antibiotics or anesthetics in the composition has a significant impact on the therapeutic effectiveness, whether they potentiate each other, whether they are necessary and, therefore, mandatory components of therapeutic drugs. In our study (unpublished data), we compared the therapeutic effectiveness of well-known antihemorrhoidal ointments - aurobin, proctosedyl and Hepatrombin G in identical groups of patients with acute hemorrhoids of the first and second stages. The choice of these drugs was determined by the fact that each of them contained a different component. Thus, Hepatrombin G and proctosedyl contained heparin, proctosedyl and aurobin contained an antimicrobial agent, Hepatrombin G and aurobin contained an anesthetic. Thus, Hepatrombin G should be used for conditions such as:
- external and internal hemorrhoids;
— thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoidal veins of the anus;
- fistulas, eczema and itching in the anus;
- anal fissures;
— preparation for surgical intervention in the anorectal area;
- as part of combination therapy for thrombosed and operated hemorrhoids.
The ointment can be applied to the affected areas or inserted into the rectum using a screw-on tip.
When using the drug in recommended doses, no toxic effects are observed.
As the results of the study showed, Hepatrombin G reduced the frequency of bleeding from 80% to 5% within a week.
. Pain and inflammatory manifestations in the nodes and anal canal quickly subsided, and thrombosis of the nodes decreased. Excellent and good results according to the survey of doctors and patients were 90% and 85%, respectively.
If we evaluate the efficiency and cost indicators
, then
undeniable advantages were on the side of Gepatrombin
G.
The conducted study emphasizes the need for a conscious choice of certain agents for local therapy, taking into account their composition and clinical manifestations in a particular patient. In case of thrombosis of external nodes and prolapse of internal nodes, preference should be given to ointments. Suppositories are indicated only for hemorrhoids in the initial stages. They should not be pushed into the ampulla of the rectum, but held by hand until they melt completely into the anal canal. For pain, drugs with lidocaine are prescribed, for predominant inflammatory changes - with corticosteroids (Hepatrombin G, aurobin), for thrombosis - with heparin (Proctosedyl, Hepatrombin G), for swelling and enlargement of nodes - with venotonics. In patients with erosive sphincteritis and anal itching, in order to accelerate reparative processes, drugs that have an immunostimulating effect and improve tissue regeneration are used. Adverse reactions occur rarely. However, you should refrain from long-term use of corticosteroid ointments due to the dryness and microcracks they cause in the anal canal, with infectious diseases of the perianal skin, and during pregnancy. Ointments and suppositories are administered 4-6 times a day during the acute period of the disease for 2-3 weeks.
Two days before surgery and for 2 weeks after it, lactulose is prescribed (20 ml twice a day); administer suppositories with diclofenac 50 mg 3 times a day, as well as 0.2% nitroglycerin ointment; prescribe metronidazole 400 mg 3 times a day for a week; paracetamol and dehydrocodeine as indicated (Carapeti & Phillips, 2000).
Thus, the choice of treatment method for hemorrhoids is determined by the stage of the disease, the severity and nature of the symptoms.
Treatment is carried out as a complex of general measures of medicinal and non-medicinal nature. In this case, the option of modern therapy must necessarily include a combination of systemic venotonics, for example, micronized diosmin, and local treatment agents, for example, Hepatrombin G. The same measures are acceptable before preparing for ligation of nodes with latex rings and hemorrhoidectomy. It is necessary to realistically imagine the purpose and possibilities of conservative treatment, and not try to treat conservatively when the only way to relieve the patient from suffering is surgery. References:
1. Buckshee K., Takkar D., Aggarwal N. Micronized flavonoid therapy in internal hemorrhoids of pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 1997, 57, 145-151.
2. Carapeti EA, Phillips RKS Treatment of hemorrhoids. In: J.Beynon, NDCarr (eds): Recent advances in coloproctology, Springer-Verlag London Limited, 2000, 155-166.
3. Godegere P. Daflon 500 mg in the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease: a demonstrated efficacy in comparison with placebo. Angiology, 1994, 45, 574-578.
4. Meyer OC Safety and safety of Daflon 500 mg in venous insufficiency and in hemorrhoidal disease. Angiology, 1994, 45, 579-584.
5. Orkin B., Schwartz AM, Orkin M. Hemorrhoids: what the dermatologist knows. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999, 41, 449-456.
6. Perez-Miranda M., Gomez-Cenelilla A., Lean-Colombo T. et al. Effect of fiber supplements of internal bleeding hemorrhoids. Hepato-Gastroenterology, 1996, 43, 1504-1507.
Is it true that pregnancy can cause hemorrhoids?
Unfortunately, hemorrhoids during pregnancy are a really common problem. The fact is that in pregnant women, the growing uterus puts pressure on the lower abdomen. It is the compression of the veins, combined with low physical activity, that leads to the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Very often, the disease makes itself felt in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, but in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, it manifests itself earlier - already from 10-15 weeks.
If you have problems with the intestines, we recommend treating them in advance, at the stage of
pregnancy planning .
You should not worry about hemorrhoids during pregnancy - they can be treated conservatively (without surgery). We recommend that you consult an experienced doctor: he will give recommendations on adjusting your diet, exercise, and prescribe safe medications.
Angioprotectors and venotonics
The list of common and popular medications includes tablets:
- containing flavonoids - hesperedin, diosmin, etc., which relieve inflammatory processes (therapy is carried out with the help of Detralex, Venarus, Vasoket, Phlebodia 600);
- with rutin - the substance is an artificial substitute for bioflavonoids (treatment is carried out with Ascorutin, Venoruton, Troxevasin);
- with pentoxifylline – to stabilize local microcirculation (Vazonit);
- with extracts of medicinal plants (Aescusan, Ginkor Fort, Venoprotect).
Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Detralex – for acute hemorrhoids, exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, severe weakness of the veins. The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance; in rare cases it provokes dyspeptic disorders and allergies.
- Venarus – for any form or stage of pathology, venous insufficiency. May cause similar reactions: convulsions, dyspepsia, headaches, rashes, itching.
- Phlebodia 600 – prohibited for minors, used for acute and chronic hemorrhoids, venous insufficiency. Reported side effects include migraines and attacks of nausea. The drug is approved during pregnancy and lactation.
Medicines in this subgroup are intended for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease and varicose veins. Their active components solve the problem of weakened venous walls, protect blood vessels from damage, and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
Treatment of hemorrhoids without surgery: what therapy does the doctor prescribe?
Hemorrhoids are a collective name for diseases of the rectum with a corresponding set of symptoms. The classification of hemorrhoids is extensive, so adequate treatment is prescribed after examination, and recommendations for a treatment regimen are strictly individual.
Generally speaking, treatment for hemorrhoids without surgery includes:
- Correction of diet and diet to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Herbal medicines;
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Minimally invasive non-surgical treatment methods: sclerotherapy, coagulation or ligation of hemorrhoids.
Hemostatics
A group of coagulants or hemostatic agents that help get rid of discharge from damaged hemorrhoids. Medicines are prescribed by a proctologist after diagnosis and identification of the complexity of the pathological process.
Commonly used types include:
- Vikasol - normalizes blood clotting processes, used at any stage of the disease or after surgery. Contraindicated in patients with allergies or bleeding disorders.
- Dicynone is a hemostatic medication, prescribed for hematuria, hemorrhoids with bleeding, for preoperative preparation. Contraindicated in case of thromboembolism, thrombosis. May cause attacks of dizziness, dyspepsia, and allergic reactions.
- Methyluracil – with anti-inflammatory, angioprotective, regenerating effects. Prescribed for erosions, cracks, pain syndrome. Contraindicated in patients with pathologies of the blood system.
Treatment is carried out with Aescusan, Asklesan A, Proctonis, Litovit B, etc. The drugs of the group stabilize vascular permeability, increase the stability of capillary walls, and normalize local blood circulation.
Is it true that hemorrhoid surgery is painful?
Any surgical intervention is associated with some discomfort during the rehabilitation period. However, our clinic performs minimally traumatic operations using a laser or ultrasonic scalpel, as well as using the improved technique of Milligan-Morgan, Longo, etc. Thanks to modern technology and the experience of our surgeons, patients recover after surgery without prolonged bed rest.
Read more about the treatment of hemorrhoids at the Pirogov Clinic (St. Petersburg)
9. What methods of intestinal examination exist?
This or an X-ray examination - irrigoscopy
,
passage of barium through the intestines;
or endoscopic: sigmoidoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy. Capsule endoscopy also allows complete visualization of the small intestinal cavity.
For other methods there are separate, strictly limited indications.