Angina pectoris is a pathological pain syndrome that manifests itself under the influence of external factors (excessive physical activity, food intake, stress, etc.) and is characterized by a pronounced feeling of discomfort in the chest.
Previously, this disease was called “angina pectoris” in official medical reference books; currently this name is preserved in folk medicine. May be accompanied by arrhythmia (unstable pulse). The pain syndrome is characterized by an unexpected sudden onset and irradiation to adjacent areas of the human body: neck, between the shoulder blades, left shoulder, jaw.
The duration of the attack, as a rule, does not exceed 15 minutes. You can speed up the process of relieving pain by stopping the activity that caused the pain and taking a drug from the pharmacological group of nitrates, which has a short-term effect.
Below we will consider a set of breathing and physical exercises for performing in a hospital setting and at home in order to prevent the occurrence of pain and emergency relief of an attack without the use of drug therapy.
The feasibility and importance of breathing exercises and physical exercises for angina pectoris
Non-drug therapy after diagnosing angina pectoris is aimed at reducing the risk of developing myocardial infarction due to coronary artery disease (CHD) by changing the patient’s usual lifestyle.
- It is advisable to completely quit smoking or minimize the use of tobacco. This is aimed at indirectly restoring the functions of the cardiovascular system through influence through the respiratory system of the human body.
- Moderate physical activity aimed at combating physical inactivity and, as a result, stimulating the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- The appointment of an indefinite therapeutic diet associated with a decrease in the daily diet of salt, as well as fried and spicy foods, is indicated.
These recommendations, together with physical therapy and a complex of breathing exercises, are aimed at ensuring a favorable prognosis for angina pectoris and stopping the transition of the syndrome to coronary heart disease with the subsequent risk of myocardial infarction.
Physical therapy and breathing exercises not only have a beneficial effect on all body systems by improving blood flow and accelerating metabolic processes, but also make it possible to simultaneously suppress an attack of angina.
Physical activity for coronary heart disease
Cardiologist, Cardiology Department No. 2 Grishina I.V.
According to modern medical data, a large number of factors can contribute to the development of IHD (coronary heart disease). Among the most common and “aggressive” ones are poor heredity, alcohol abuse, smoking, chronic stress, metabolic disorders due to poor nutrition, chronic fatigue, and physical inactivity. Of course, it is almost impossible to get rid of a hereditary predisposition to IHD, and you cannot completely protect yourself from stress. But you can adjust your lifestyle so as to avoid the other factors mentioned above. First of all, you should quit smoking, optimize your diet and ensure proper physical activity on the body.
The benefits of physical activity:
- Regular physical activity allows you to stay toned and in good shape.
- With regular physical activity, the amount of “useful” lipids in the blood increases, which helps reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
- The likelihood of blood clots is reduced.
- Blood pressure is normalized, which helps reduce the risk of cerebral hemorrhage (stroke).
- Physical activity promotes weight loss and prevents the development of diabetes.
- Regular exercise helps improve mood, normalize sleep, and make it easier to cope with stressful situations.
- Regular physical activity reduces the risk of developing osteoporosis, the most common cause of bone fractures in old age.
Regular physical activity is beneficial for everyone, as it allows you to protect yourself from the development of many unpleasant diseases. But, unfortunately, it is only the illness itself that often pushes us to change our lifestyle and regular exercise.
Only certain types of physical activity are suitable for patients with coronary heart disease.
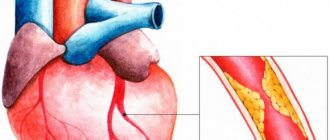
IHD develops as a result of acid starvation, which leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaque. The plaque causes the artery that supplies the heart to narrow, causing less oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle. In this case, the intense work of the heart becomes difficult and, under heavy loads, angina pectoris develops - a painful attack of the heart muscle.
Naturally, angina attacks require limited physical activity. Often, in order to get rid of angina, it is necessary to resort to medication, or even surgical treatment. In the case of a severe heart attack - a heart attack, patients even begin to be afraid of physical activity and, in an effort to “protect” the heart, often limit movement to the point of giving up walking.
For patients with angina and those who have had a heart attack, physical activity can have twofold meaning:
- On the one hand, excessive physical activity and intense physical activity can provoke attacks of angina pectoris and lead to a second heart attack - such excessive activity should be avoided.
- On the other hand, moderate physical activity and periodic exercise (no more than 40 minutes 5 times a week) are very beneficial.
Moderate physical activity helps increase the level of good cholesterol, which prevents the further development of atherosclerosis, reduces the rate of development of heart failure, strengthening the cardiovascular system. Regular aerobic exercise helps normalize the functioning of collateral blood flow - an interarterial connection that serves to redistribute blood flow, which helps to increase the amount of oxygen-rich blood reaching the heart muscle.
As medical studies show, physical activity in patients who have had a heart attack helps reduce the risk of a second heart attack by 7 times, and reduce mortality by 6 times, compared with patients who prefer to reduce physical activity as much as possible.
Therefore, for patients who have had a heart attack, performing normal household activities (light daily housework) is mandatory. After an inpatient course of treatment, it is preferable for such patients to undergo a course of physical rehabilitation under the supervision of specialists in a cardiological sanatorium. If rehabilitation in a sanatorium is impossible for one reason or another, it is necessary to undergo a course of physical rehabilitation on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a cardiologist.
The easiest option for physical activity in this case is daily walking. At the same time, you should not overload yourself: the walk should take place at a slow or moderate pace (depending on how you feel), for half an hour to an hour, but not less than 5 days a week. If during a walk you feel weak or tired, you need to take a break - sit down on a bench or return home at a slow pace. Don't be upset - you will be able to go through more and more during the rehabilitation process. However, an increase in physical activity, just like the beginning of physical exercise, after hospitalization must be agreed upon with a physical therapy specialist or the treating cardiologist.
Physical activity should never lead to another attack of angina. During exercise, severe shortness of breath or rapid heartbeat is unacceptable. During physical activity, you need to monitor your heart rate - its frequency should increase in accordance with the increase in load. In this case, the optimal increase in heart rate should be determined by the attending physician on an individual basis, according to the severity of coronary artery disease and associated pathologies.
In the first stages of physical rehabilitation, heart rate can increase by no more than 20 - 30%, approximately 15 - 20 beats per minute. If the loads are tolerated without complications, an increase in heart rate can be allowed by more than 30%, however, no more than the value calculated using the following formula: 200 - the patient’s age. For example, for a patient with coronary artery disease aged 60 years, the maximum permissible heart rate should not exceed 140 beats per minute.
What physical activity is optimal for patients who have had a heart attack?
The priority is the types of loads aimed at developing endurance. However, it is best to combine these exercises with loads aimed at developing flexibility and strength.
Activities aimed at developing endurance include: walking and cycling, swimming, dancing, tennis and housework.
Strength activities include: walking up an inclined plane, including climbing stairs; lifting and carrying weights such as shopping; digging up plots of land, some types of housework.
The following types of work are aimed at developing flexibility: dancing, swimming, gymnastics, working on a personal plot or in the garden.
Do not forget that the loads should be gradual, especially at the beginning of physical rehabilitation. Expanding your physical activity without prior consultation with a cardiologist, especially after coronary complications such as myocardial infarction, unstable angina, progressive heart or coronary failure, can only worsen your condition and provoke complications.
For complete rehabilitation after suffering coronary complications, it must be comprehensive and include drug therapy, an individual physical rehabilitation program, and, if necessary, surgical correction. All restorative procedures must be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
And finally, a couple of useful tips:
- Give preference to those exercises and loads that bring you pleasure. Do the exercises in the company of family or friends. Positive emotions are the key to a speedy recovery.
- Try to walk at least one floor a day. Gradually, without sudden jerks, increase the number of floors that you overcome without the help of an elevator.
- In order to gradually increase physical activity, you can go to the stop earlier and cover the remaining distance on foot.
If walking alone makes you sad, get a small dog as a travel companion. Firstly, you will have more fun together, secondly, a pet is always a positive emotion, and thirdly, a dog in the house is a guarantee that you will go for a walk regularly.
Contraindications for angina pectoris
The main contraindications for angina are related to preventing the development of hypertension. In this regard, it is important to avoid excessive physical activity and the use of psychostimulants (coffee, ginseng, eleutherococcus, dishes high in hot pepper and salt, and so on). The presence of angina pectoris syndrome in most cases indicates weakness of the blood vessels, and therefore it is not recommended to make sudden movements (including quickly getting out of bed when waking up, etc.). In most cases, it is not recommended to prescribe spa treatment.
Therapeutic physical training for angina pectoris: a set of exercises recommended by experts
When prescribing a set of physical exercises, it is important to observe the basic principles based on the fundamental axiom “do no harm”:
- Gymnastics for angina pectoris involves the selection of individual loads depending on the stage of the disease and the frequency of pain attacks: the more severe the course of the pathology, the less physical activity and the duration of the exercises.
- It is mandatory to divide the set of exercises into three parts: warm-up, main group of exercise therapy and cool-down. A warm-up allows you to prepare the body for performing exercises, the main group provides an optimal effect on the body’s systems, a cool-down allows you to consolidate the effect obtained and exit exercise therapy without pressure drops.
- When prescribing exercises, it is important to adhere to the rule of no sudden movements during exercise therapy.
Important!
Prescribing a set of physical exercises is important in the first and second stages of the disease. When diagnosing the third stage, it is recommended that in the first months you can get by with normal walking and increasing the time spent in the fresh air.
Warm-up
- You need to lay a rug on the floor and lie down on it. Take three deep breaths in and out, tuning into the exercises.
- Raise your torso perpendicular to the floor. Right hand up - tilt to the left, left hand up - tilt to the right. Ten cycles and a minute break. Repeat three times.
- Lie down again. Bend your knees - straighten your legs. Do ten times and rest for one minute. Repeat three times.
Important!
If you have difficulty performing these exercises on the floor, you can warm up on a chair. Avoid sudden movements - concentrate on stretching.
Basic set of exercises
- Squats with arms extended forward: from 10 to 30 times. It is recommended to divide the total number of squats into three cycles, with a one-minute break between each cycle. This statement is true for all of the exercises below.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, torso tilted forward perpendicular to the floor, arms to the sides, and make cable turns left and right to the maximum possible limit. Quantity: 10 to 50 times.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, left hand up - tilt to the right, right hand up - tilt to the left. For each hand we do 10 – 30 times.
- Run in place (it's best to use a treadmill, but you can do without it) with gradual acceleration for 10 minutes.
Important!
To achieve optimal results, it is advisable not only to perform a set of exercises daily, but also to make adjustments to your daily regimen: instead of driving a car, it is better to walk, instead of using the elevator, it is better to go up to the required floor on your own.
Hitch
Return to the mat. Sit down, stretch your legs forward, and bring your heels together. Without bending your knees, try to reach your feet with your palms and touch your knees with your head. Do it slowly, stretch. Then lie down on the mat, recover, and bring your breathing back to normal.
Important!
If pain or other discomfort occurs that precedes an angina attack while performing exercises, exercise therapy must be stopped immediately, sit or lie down on the mat and restore breathing with deep inhalations and exhalations. If the pain does not stop, you need to drink a short-acting nitrate to stop the attack.
Therapeutic exercise for cardiovascular diseases
Exercise therapy for cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death and disability worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2021—31% of all deaths worldwide. The consequence of CVD is disruption of the heart and the condition of blood vessels, which leads to functional changes in the body. Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy) is used to treat existing and prevent cardiovascular diseases. In addition to medications and vitamin preparations, doctors supplement the complexes of therapeutic measures with physical therapy. Regular exercises help normalize the condition of blood vessels and restore impaired organ functions.
Therapeutic effect of exercise therapy
The heart muscle is strengthened and contractility increases. Blood circulation improves, including peripheral circulation. Thanks to physical exercise, blood flow increases, causing mechanical massage of the walls of blood vessels. As a result, they become more elastic. In addition, cholesterol levels are reduced, which means the risk of blood clots. What generally inhibits the formation of atherosclerotic changes in the body. They are the culprits in the development of heart disease.
Control of stress in cardiovascular diseases is mandatory and necessary
For what cardiovascular diseases is exercise therapy indicated?
- coronary heart disease (myocardial infarction, angina pectoris);
- heart defects;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- thrombophlebitis;
- atherosclerosis;
- myocarditis;
- endocarditis;
- obliterating endarteritis;
- phlebeurysm.
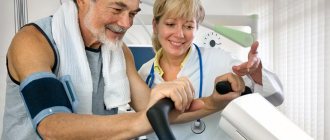
Before classes, you should consult with your doctor. A physician's approval is required for older patients and those who have had a myocardial infarction. There are contraindications for physical therapy for cardiovascular diseases. Rehabilitators prescribe an individual set of exercises that takes into account the nature of the pathological process, the characteristics of the body, and covers different muscle groups.
Exercise therapy rules
- Gradual increase in load on the body.
- The break between eating and starting exercise is at least one and a half hours.
- If you experience any discomfort or pain, such as headache, breathing problems, colic or a burning sensation in the heart, you should stop immediately and consult a doctor.
- It is important to monitor your heart rate during exercise. It is considered normal for the heart rate to increase by 25-35 units by the end of classes, with a maximum of 120 beats/min. Return your heart rate to normal values within ten minutes.
Contraindications for exercise therapy for cardiovascular diseases
- acute cardiovascular failure;
- exacerbation of rheumatic endo- or myocarditis;
- severe pathologies of the vascular and cardiac conduction system;
- circulatory failure in the stage of decompensation.
For hypotension, walking, jogging, skiing, cycling, and outdoor games are recommended. Daily morning exercises are required, which include isometric exercises with dumbbells and an elastic bandage. Good hardening procedures are contrast showers, self-massage using massagers.
To prevent coronary heart disease, physical exercise is necessary: walking, jogging, skiing, hiking, cycling, swimming. Every morning gymnastics. Avoid heavy lifting in the morning and long runs, which cause fatigue. To do this, it is necessary to regularly harden the body.
For varicose veins of the lower extremities in pregnant women, therapeutic exercises are indicated in a supine position on a couch with an elevated foot (angle 15-25°). Back and leg massage, contrast showers, and moderate walks are also recommended.
An example of a physical therapy complex for cardiovascular diseases
Practical recommendations for carrying out exercise therapy
Introductory part
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Raise your hands up, spread them to the sides - inhale, lower your hands - exhale. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Spread your arms to the sides with your palms up, turn your body, look at your palm - inhale, return your torso and arms to their original position - exhale. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Sitting on a chair, imitate active walking, raising your knees high. Perform for 2-3 minutes.
Main part
- Starting position: standing, hold on to the back of the chair. Move your left arm and leg to the side with a rotation of your torso - inhale, return the leg to its original position - exhale. And do the same with the other arm and leg. Repeat in each direction 5 times.
- Starting position: standing, hold on to the back of the chair. Step back with one leg, bend the other leg at the knee, keep your head straight. Repeat with each leg 5 times.
- Starting position: standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the waist. Make rotational movements with your pelvis in one direction, then in the other. Repeat 3-4 times in both directions.
- Starting position: standing, feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the waist. Hands up, stand on your toes and stretch after your hands - inhale, lower yourself onto your toes, lower your hands too - exhale. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Starting position: stand with your side to the wall, hold on to it with a bent arm and swing your leg forward and backward. Turn your other side to the wall and perform the same swings, but with the other leg. Repeat 5-6 times.
Final part
- Walk in a circle, observing the pace of breathing - inhale for 2 steps, exhale for the 3rd. Perform for 2 minutes.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Spread your arms to the sides with your palms up - inhale, lower - exhale. Repeat 5 times.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your belt. Stepping from heel to toe, spread your legs to the sides, then bring them together. Repeat 3-4 times.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Flex and straighten your feet and hands. Perform for 1 minute.
- Starting position: sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Hands up - inhale, lower to your knees - exhale with relaxation. Repeat 3-4 times.
Breathing exercises: the most popular and reliable techniques
Breathing control is one of the important components when performing physical exercises and in everyday life to prevent angina attacks.
Strelnikova's technique
The Strelnikova method includes a large number of exercises, the most interesting of which are techniques aimed at emergency relief of an angina attack. An example of an exercise according to Strelnikova to relieve an attack of angina:
- Sit on a chair or kneel on the floor, close your eyes.
- Take a powerful, sharp breath with a strong-willed muscular compression of the chest.
- Without holding your breath, exhale slowly.
- Repeat until the pain subsides.
Important!
If there is no relief within 10 minutes, you should urgently call a doctor. After an attack, temporary rest is recommended.
Bubnovsky's technique
In Bubnovsky’s breathing techniques, the emphasis is on breathing using the diaphragm, that is, minimizing chest breathing. It is worth noting that chest breathing is rejected by almost all experts as the most harmful. An example of breathing exercises according to Bubnovsky for angina pectoris:
- Lay out a mat, sit on your knees on it, close your eyes, feel the diaphragm (the place between the chest and abdomen).
- Inhale slowly, counting to 5 and expanding the diaphragm with muscle effort; hold your breath, counting to 3, fixing the diaphragm widened; exhale slowly, counting to 5 and drawing in the diaphragm with muscle effort. Repeat this cycle 20 - 50 times (depending on your level of training).
- Get into dog pose, relax your stomach and breathe intensely and quickly - first for one minute, then gradually increasing the time of intense breathing to 5 - 10 minutes.
Important!
If you feel dizzy when breathing intensely, you need to stop the exercise and reduce the time of breathing practices the next day.
Buteyko technique
The Buteyko technique is based on reducing the frequency and increasing the quality of human breathing. The main points of the Buteyko technique:
- The number of inhalation-exhalation periods per minute should not exceed 16.
- Breathing should be through the nose. Mouth breathing is harmful and dangerous to health.
- Breathing should be light and slow.
- The inhalation should be at least two times shorter than the exhalation.
- It is recommended to hold your breath after inhaling.
An example of a Buteyko exercise:
- Sit on a chair, straighten your back, place your palms on your knees, close your eyes.
- Inhale for 10 seconds, hold your breath for 20 seconds and exhale for 20 seconds. These time intervals are achieved gradually; in the first stages of training, it is important to maintain a 1:2:2 ratio, varying the number of seconds in a way that will be more comfortable for the patient.
Important!
Buteyko breathing practice should not be violent or cause tension. Accustoming yourself to easy breathing using the “inhale - hold your breath - deep exhale” system should be done gradually.
LLC "MGBS"
Breathing and contractions of the heart muscle represent a single mechanism for maintaining the vital functions of the body. Therefore, by changing the duration of inhalations and exhalations, as well as pauses between them, you can train your heart. Breathing exercises do not require endurance, money or time; it is accessible to everyone and only requires systematic implementation.
The benefits of breathing exercises for the heart
If you observe a person who is under stress or experiencing an attack of heart pain, then rapid and shallow breathing will be noticed in everyone. Since our body works on the principle of feedback, slowing down and deepening breathing can have a healing effect on many organs. Even simple fixation on an even rhythm and awareness of the duration of the breathing cycle is used in meditative practices.
The positive effect of breathing exercises is manifested in this way:
- the blood and muscle fibers of the heart are saturated with oxygen;
- with deep breathing, the cavities of the heart are better filled with blood and are released from it during contraction;
- when holding your breath, an artificial oxygen deficiency is created, which dilates the cerebral and coronary vessels;
- the rhythm of contractions is normalized;
- the balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex is restored.
Breathing exercises are effective for preventing congestion in the lungs. It is recommended in the early recovery period after a heart attack and cardiac surgery. Sometimes this is the only type of activity available to the patient.
We recommend reading the article about exercises for the heart. From it you will learn about physical activity and basic rules for training, useful exercises for the heart muscle.
And here is more information about exercises for arrhythmia.
Useful exercises to strengthen the myocardium
In diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is the loads that can increase the resistance of the myocardium to oxygen starvation that bring benefits. These include walking, running, swimming, dancing. Breathing exercises have a similar effect on the heart muscle. Methods for carrying it out may differ, but the most important rule is that the exercises must be performed at an individual, comfortable level.
First aid for arrhythmia
The method of restoring heart rhythm using breathing is based on the fact that a measured rhythm of inhalation and exhalation, which a person can control, normalizes the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle. Therefore, any option with counting the duration of respiratory movements helps with arrhythmia.
To do this, you can inhale for 2 - 3 counts and exhale for 4 - 6 counts. In this case, you need to be in a sitting position with a straight back. It is recommended to gradually stretch your inhalations and exhalations, focusing on your sensations.
After mastering this exercise, the following type of pulmonary exercises is recommended to prevent attacks:
- Left hand behind back.
- The right hand is located near the face.
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Inhale through the left nostril.
- Close the left nostril with your ring finger and exhale through the right nostril.
After 8 - 10 breathing cycles, you need to change hands. The duration of the first lesson should not exceed 2 - 3 minutes, then you can slowly increase it. The duration of inhalations and exhalations is determined by comfortable sensations.
For cardiac aneurysm
The use of any load for training, even breathing, with an aortic or cerebral aneurysm, is possible only after consulting a doctor, since stress can provoke intense internal bleeding and death.
If there is a small and stable aneurysm or an operation has been performed to remove this vascular defect, then the doctor may allow you to do gymnastics, including breathing. In this case, any low-intensity and slow movements with simultaneous inhalation and exhalation are indicated:
- spread your arms to the sides - inhale, hug yourself by the shoulders with them - exhale;
- with the pelvis stationary, turn the chest to the right - inhale, return to the starting position - exhale;
- in a position lying on your back, inhale with your stomach for 2 counts, raising the abdominal wall; for 4 counts, exhale, drawing in your stomach.
Watch the video about doing exercises for the heart and their benefits:
After operation
From the second day, with an uncomplicated postoperative course, patients begin breathing exercises under the guidance of a doctor to prevent congestion in the lungs. To do this, it is recommended to spend 5-6 times a day for 5 minutes:
- exhale through closed lips (movements like when blowing out a candle);
- inflating balloons or rubber toys;
- exhaling air through a straw into a glass of water.
After 5-6 days it is allowed to sit on the bed and walk within the ward. At this time, breathing exercises are carried out in an expanded mode. Recommended:
- deep belly breathing with accentuated exhalation,
- smooth stretching of the exhalation length,
- inhale for 3 counts and exhale, and then 2 more short exhalations.
With tachycardia
To slow down your heart rate you need maximum relaxation. This can be achieved by changing the ratio of the duration of inhalation and exhalation, as well as by pausing after exhalation. In the first lessons, the ratio of these phases is 3:5:2.
Every day they are increased by 1 count, if discomfort appears, they are stopped until a stable result is obtained, and then you can continue to stretch each breathing movement. If at first it is difficult to breathe like this, then after 3-4 cycles they return to normal breathing; after its restoration, it is recommended to extend the lesson.
Tachycardia is an indication for breathing exercises
To improve blood vessels
To normalize vascular tone and increase performance, the following exercise is performed: after a normal (non-forced) inhalation, you need to exhale sharply and briefly, while drawing in your stomach as you exhale. This is followed by a passive inhalation and a sharp exhalation.
Do 10 cycles of the right nostril with the left one closed, change sides, also take 10 inhalations and exhalations, then with both nostrils 15 times.
General recommendations for performing breathing exercises
Such classes do not require special equipment or a special room, but this type of training also has rules:
- the room should be well ventilated, it is better to study near an open window;
- drafts must be avoided;
- the optimal option is nature, park, river bank;
- The recommended time is in the morning; if classes are held in the afternoon, at least 3 hours must pass;
- the clothes chosen are spacious, natural, without tight belts and collars;
- Most often they practice while sitting on a chair or on the floor with their legs crossed;
- the head does not fall back, the back is straight;
- the whole body is sure to relax.
We recommend reading the article about physical activity for arrhythmia. From it you will learn about whether it is possible to play sports if you have an illness, acceptable options for physical activity, and the reasons for the development of arrhythmia after playing sports.
And here is more information about playing sports with bradycardia.
Breathing exercises can be used to restore normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. It is prescribed at any age and even with minimal training; it is recommended for bedridden patients and after heart surgery. It activates metabolic processes and trains the body's adaptive capabilities. The basic rules are comfortable performance and regularity of classes.
Doing exercises for the heart is useful both for healthy people and for those with organ disease. This can be minor physical activity, breathing exercises, to improve the health of the main muscle. It is advisable to conduct training daily.
In some cases, exercises for arrhythmias can help control rhythm disturbances. This can be physical exercise, breathing, Nordic walking and running. Complete treatment of arrhythmia without a set of exercises is extremely rarely carried out. What complex should be done?
You need to train your heart. However, not all physical activity for arrhythmia is permissible. What are the permissible loads for sinus and atrial fibrillation? Is it possible to play sports at all? If arrhythmia is detected in children, is sport taboo? Why does arrhythmia occur after exercise?
Options for how to strengthen the heart depend mainly on its condition. They also affect blood vessels and nerves. For example, in old age, exercise will support the heart muscle. After a heart attack, folk remedies can be prescribed for arrhythmia.
Physical inactivity develops in adults and children. The concept includes quite broad problems. If cardiovascular failure has developed, then returning to normal life is very problematic; the consequences in some cases are complete atrophy of organs. It is necessary to change your lifestyle.
For most patients, cardio training for the heart is simply necessary. Any cardiologist will confirm their benefits, and most strengthening exercises can be done at home. If your heart hurts after exercise, it means something is not being done correctly. Caution is required after surgery.
Respiratory arrhythmia in children, adolescents and adults is often detected on an ECG. The reasons may lie in an unhealthy lifestyle or excessive stress. Symptoms include breathing problems, cold extremities and others. Sinus readings on the ECG influence the choice of treatment.
Exercise therapy begins after a heart attack from the first days. The set of exercises gradually increases. To do this, doctors determine the degree of exercise therapy for which the patient is ready after myocardial infarction and stenting, if any.
If a cardiac aneurysm is detected, surgery may be the only chance for salvation, only with it the prognosis improves. It is generally possible to live without surgery, but only if the aneurysm, for example, of the left ventricle, is very small.
Will yoga help as a breathing exercise?
Yogic practices have much in common with the breathing systems developed by Bubnovsky and Buteyko. In particular, the breathing method “inhale - hold - exhale”. However, yoga uses less gentle techniques, and the use of these practices for angina pectoris is not recommended due to insufficient knowledge of the subject by the official medical community.
It is advisable to combine breathing practices and exercise therapy to achieve the best preventive and therapeutic effect. It is also recommended to practice breathing techniques according to Buteyko or Bubnovsky when performing massage in the heart area in order to stabilize the pulse rhythm.
It is possible to live with angina.
Angina pectoris is a disease the main symptom of which is periodic attacks of deterioration in the blood supply to the heart muscle. Attacks are characterized by severe pressing or burning pain after physical activity or during stress. This significantly worsens a person’s quality of life; many patients suffering from this disease believe that their life is over. But is it? Definitely not.
Medicines prescribed by a doctor will certainly make a person less sick. But without your own efforts, they will not have the same effect as you expect, and angina will continue to progress.
First of all, with angina pectoris, daily physical activity is necessary. Suddenly? Of course, you shouldn’t overexert yourself; the intensity of the exercise should be such that you can talk while doing it. However, moderate physical activity, especially walking in the fresh air, slows down the development of atherosclerosis, trains the heart muscle, helps normalize blood pressure, and improves blood circulation. In addition, we should not forget that people who lead an active lifestyle are less susceptible to stress factors, which is extremely important for angina pectoris. But to achieve the effect, physical activity must be regular. If you do this “occasionally”, it will not bring any benefit. Cycling is also useful; if you are obese, it is better to give preference to swimming. But lifting weights and other similar activities are not recommended for angina pectoris, since, on the contrary, they cause ischemia. And you should remember that if chest pain appears, you need to immediately stop and sit down somewhere, and do not get up until the pain stops. If the pain does not go away on its own, take a nitroglycerin tablet.
Another important factor is nutrition. You should eat more vegetables and fruits, cereals, lean meat and fish, skim milk, low-fat cheeses and yoghurts. Avoid fried foods, preferring boiled ones. Vegetable oils, walnuts, and almonds are very useful. For sweets, it is better to choose dark chocolate and low-fat yogurt. Such a diet normalizes the level of cholesterol, sugar, triglycerides in the blood, and also helps to get rid of excess weight, which will significantly reduce the rate of progression of atherosclerosis, and, consequently, the deterioration of your health.
Quitting smoking and alcohol, losing excess weight will be useful not only for angina, but also for many other diseases, and even for a healthy person, since these are complex factors that affect the entire body, worsening the functioning of not only the heart, but also the lungs and liver , digestive tract, kidneys, brain. Obesity also harms the joints of the legs by placing excessive stress on them.
Diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension are especially dangerous for angina. When uncontrolled, they greatly harm blood vessels, thereby, among other things, worsening the course of angina pectoris, so it is necessary to control blood pressure, if you have hypertension, and sugar levels if you suffer from diabetes, and in no case interrupt taking medications prescribed against them as a doctor. If the drugs are not enough, you should contact the clinic at your place of residence, or any other outpatient clinic.
An established diagnosis of angina pectoris is not a sentence to disability. If you follow these recommendations, in combination with medications prescribed by your doctor, you can live without suffering from regular chest pain. And remember: your health is in your hands!
Kudryavtseva Olga Vitalievna
Functional diagnostics doctor
Novopolotsk city hospital