Surgery to remove hemorrhoids is a radical treatment method for an unpleasant and difficult pathology.
Surgical intervention is intended for patients with chronic forms of dilatation of the rectal veins, as well as during their acute course.
Modern experts always recommend conservative treatment methods to patients, but if after this the patient does not experience improvement, then surgical removal of the nodes is urgently prescribed. When acute hemorrhoids develop, patients are always prescribed surgery.
The operation is prescribed as a last resort. First, doctors carry out all possible therapeutic measures - eliminate inflammatory processes and stabilize the patient’s condition. Only after this can a decision be made about the operation.
Minimally invasive therapeutic interventions
Ligation of the node with latex rings
Indicated for internal hemorrhoids, when the nodes often fall out during bowel movements, but are able to be reduced on their own. Using a special device, a latex ring is put on the node, which presses on the leg of the node, after which the hemorrhoidal node disappears. Contraindications for ligation are allergy to latex, portal hypertension, patients constantly taking anticoagulants, inflammation and fissures in the rectum.
Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids
Sclerotherapy is performed in case of bleeding of hemorrhoids without prolapse. It is carried out by injecting sclerosing drugs into the hemorrhoidal vessels. The injected drugs cause sclerosis of the hemorrhoid and its subsequent rejection. In some cases, sclerotherapy is performed as a preparatory procedure before hemorrhoidectomy. Sclerotherapy is contraindicated for inflammatory diseases of the anorectal area. During the procedure, severe pain may occur.
Infrared photocoagulation
Infrared coagulation is performed by exposing a powerful beam of light energy to the base of the hemorrhoid. The result of the procedure is coagulation of the node followed by its resorption. This type of treatment is indicated in the presence of bleeding from the nodes, without their loss. During the procedure, pain of varying intensity may occur. Complications of this type of treatment: bleeding, infection of the anal area and urinary retention.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Radical hemorrhoidectomy is a classic surgical treatment for hemorrhoids. The operation is performed by surgically excising the hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidectomy is indicated for advanced cases of hemorrhoids (prolapsed, non-reducible nodes) and in the absence of effect from minimally invasive treatment. Unlike minimally invasive methods of treating hemorrhoids, this operation is a traumatic type of treatment and is accompanied by a long recovery period. At the same time, the wound takes a long time to heal and pain persists, and patients experience discomfort during bowel movements. Complications of surgical treatment include narrowing of the anus, disruption of the sphincter (its weakness) and wound infection.
Desarterization of hemorrhoids
The essence of the operation is to reduce the blood supply to the hemorrhoidal plexus area by ligating the arteries. The effectiveness of the operation largely depends on the completeness of all arteries in a given area and their high-quality ligation. Requires highly qualified specialists and expensive equipment. In addition, for a number of reasons listed below, relapse cannot be ruled out.
Preparatory and operational period
Before the operation, the patient must fulfill certain conditions, namely: pass all the necessary tests, undergo a diagnosis of concomitant pathologies, and undergo a consultation with a therapist to determine possible contraindications.
The preparatory stage consists of complete bowel movement. Cleansing is carried out on the eve of the operation and immediately before the procedure itself.
A similar procedure is carried out using an enema and laxative medications. It is also worth paying special attention to nutrition in order to normalize all functions of the intestine and its walls. It is necessary to restore normal stool. This is a mandatory condition, since constipation during removal of hemorrhoids can cause serious complications. Let us remember that constant constipation is the first step to the development of hemorrhoids.
Before surgery, it is very important to relieve the inflammatory process in the anus, if it is present, of course. It is also worth relieving irritation and swelling. This can be done with the help of medications and traditional medicine.
Causes of recurrence of hemorrhoids
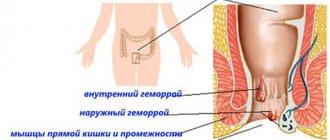
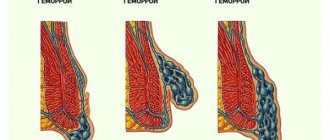
The first reason is the presence of a plexus. In the rectum there is an external and internal rectal, or it is called hemorrhoidal, venous plexus. With severe straining during constipation, physical exertion, and childbirth, excessive venous congestion occurs. The wall of the vein bulges under increased pressure, and hemorrhoids form.
When straining, the entire venous network is instantly and simultaneously exposed to increased pressure in all areas of the plexus, including in the operated area and next to it, and at the site of sclerosis, or the application of a rubber ring, or coagulation, depending on what kind of operation was performed. Thus, wall protrusion can occur at any location in the plexus. Thus, the anatomy of the plexus itself contributes to relapse.
The second reason for the recurrence of hemorrhoids is a violation of trophism. As is known, the nervous system regulates the growth, division, and nutrition of organ tissue cells, preserving their structure and function.
The tissues in the anal area, the venous plexus and the rectum are under constant control of the nervous system. These control structures, the subcortical nerve centers, are located in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem. If the control structures malfunction, the trophism of the venous plexus in the rectum is disrupted, its walls become loose and pliable, and therefore bulge easily, which is how relapses occur. Trophic disturbance can also manifest itself as long-term non-healing cracks due to slow tissue regeneration. Anal itching, reduced local immunity. This results in easy infection of the tissues of the perianal area.
Therefore, despite various methods of surgical treatment, none of them guarantees a complete cure. In a significant number of cases, the disease recurs, which forces repeated surgical interventions.
Postoperative period
The complexity of the rehabilitation period depends on the technique that was chosen to remove hemorrhoids, and, of course, on the general well-being of the patient. Almost all patients need to follow a special diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume foods that can burden the intestines. You should refrain from bowel movements for the first 24 hours.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
It is worth following all the recommendations of the proctologist. As a rule, after surgery, he prescribes thorough treatment of the wound with special preparations. To reduce pain, doctors prescribe nitroglycerin ointment and analgesics in the form of ointments, which are applied to the affected areas.
Unfortunately, patients may experience serious complications after surgery, so you should adhere to absolutely all recommendations.
When is surgery indicated?
Hemorrhoids are a rather unpleasant disease that can haunt a person for years with constant relapses and steadily progressing. At the initial stage, the pathology is treated with conservative methods. These include the use of various gels, ointments and other products. Mandatory prevention of relapses is the establishment of regular soft stools, which is achieved through a diet rich in fiber. Hemorrhoid surgery is prescribed when conservative methods are ineffective and a person experiences characteristic symptoms that require surgical intervention.
If surgery is prescribed to remove hemorrhoids, each situation should be considered individually. This approach is used in the coloproctology department of the Yusupov Hospital. After an examination, the doctor determines whether surgery is necessary and what type of surgery will be most effective under the circumstances.
Surgery to remove hemorrhoids may be used if the following factors are present:
- The presence of external hemorrhoids, or their regular prolapse even at rest;
- There is constant bleeding, which can lead to anemia;
- The patient is predisposed to thrombosis;
- There is obvious progression of the disease, despite the therapy;
- Hemorrhoids cause severe discomfort, which is manifested by pain, itching, decreased performance, etc.;
- Conservative methods turned out to be ineffective.
In case of severe bleeding, it is initially stopped, which can be done with medication. And only after that they begin surgical operations.
Contraindications
• Surgery will have to be postponed for any acute illness or exacerbation of a chronic illness . • Severely obese are first advised to lose weight. • Hemorrhoids during pregnancy are treated conservatively, since there is a high probability of healing after the end of the child's feeding period. • Some relative contraindications may be: ___• blood clotting disorders; ___• colon oncology; ___• diabetes; ___• cirrhosis of the liver; ___• unstable angina; ___• recovery period after injuries, operations, etc.
Surgical intervention can be performed after stabilization of the condition and consultation with a medical specialist (cardiologist, endocrinologist, hematologist, hepatologist, etc.).
It must be remembered that only a doctor can assess the indications and contraindications and decide on the need for surgery. If you have questions about choosing a treatment method, be sure to consult a proctologist!
Information about the disease
- Hemorrhoids are one of the most common human diseases. More than half of the population has symptoms. They usually develop after age 30.
- Most often, a person who discovers symptoms does not seek specialized medical help for a long time and tries to treat himself.
- Pregnant women often experience symptoms of this disease, but they usually go away after pregnancy. However, some women may develop chronic hemorrhoids. In case of exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, specialized medical care is required.
- For any bleeding from the anus, it is very important to consult a specialist, since it can be caused not only by hemorrhoids, but also by other serious diseases.
- About half of the patients who visit a specialized medical facility to treat hemorrhoids have other diseases of the anorectal area, such as anal fissure, anal fimbria, or irritation of the perianal skin.
- Outpatient treatments are usually relatively painless.
- Only a small number of patients require surgical treatment of hemorrhoids; drug therapy and minimally invasive techniques are sufficient.
Physical activity
Recovery after hemorrhoid removal is impossible without physical activity. 5–7 days after the intervention, the patient is recommended to sit, stand up, and walk around the hospital ward. This will help restore metabolic processes, which is important for the rapid healing of sutures, preventing the formation of hemorrhoidal fimbria, and general restoration of the body.
Intense physical activity, heavy lifting and strength sports are completely excluded. You cannot engage in cycling or exercise on machines. It is useful for patients to walk and perform breathing exercises on the recommendation of the attending physician. Daily walks in the fresh air will help you recover quickly.
Preparation, diagnostics
Before performing a hemorrhoidectomy, it is necessary to undergo a number of tests and undergo some examinations:
- blood tests (general, biochemical, infections, coagulation, group and Rh factor);
- Analysis of urine;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorography or chest x-ray;
- colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy (with or without sedation);
- consultation with an anesthesiologist, therapist and other specialists (if there are concomitant diseases)
A systemic examination allows you to assess your general health, the condition of the rectum and anus, determine the scope of intervention, and exclude contraindications.
At GMS Hospital, the examination takes one day, after which the surgeon will decide on the advisability of hemorrhoidectomy and set the date for the operation. A week before the scheduled procedure, give up alcohol, do not smoke, drink, or eat on the day of the operation - hemorrhoidectomy is performed on an empty stomach. Be sure to tell your doctor during your consultation if you are forced to take any medications regularly; you may need to stop them temporarily.