This information explains how to relieve shortness of breath.
Sometimes you may find it difficult to breathe and feel like you are out of breath. This condition is called shortness of breath or dyspnea. Shortness of breath may be caused by:
- damage to the lungs due to cancer or its treatment;
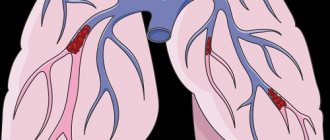
- blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism);
- fluid around the heart or lungs;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- asthma or emphysema;
- heart damage (chronic heart failure);
- anemia (low levels of red blood cells in the body).
Depending on the cause, shortness of breath may be transient or permanent.
to come back to the beginning
Types of shortness of breath
During significant physical exertion, the body does not have enough oxygen, so usually in such cases the breathing rate increases. This is the so-called physiological shortness of breath
. However, if shortness of breath occurs with light exertion or at rest (for example, in a lying position), then its nature is pathological.
It is of great importance which stage of breathing causes difficulty - inhalation or exhalation. Shortness of breath that occurs during inspiration is called inspiratory dyspnea
, on exhalation -
expiratory shortness of breath
.
Mixed shortness of breath is also common, in which both inhalation and exhalation are difficult.
Causes of development of chronic heart failure
Chronic heart failure can develop in patients suffering from coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, and heart defects. In coronary heart disease, a common cause of left ventricular systolic dysfunction and chronic heart failure is acute myocardial infarction and ischemic cardiomyopathy. The progression of chronic heart failure is caused by changes in the geometry and local contractility of the heart muscle.
In patients suffering from hypertension, regardless of the cause of arterial hypertension, a structural restructuring of the myocardium occurs, which is called a “hypertensive heart”. Chronic heart failure develops as a result of acquired and uncorrected rheumatic defects. Other causes of chronic heart failure include infective endocarditis, toxic cardiomyopathy due to exposure to drugs, alcohol, radiation therapy, systemic vasculitis, metabolic and endocrine disorders.
Causes of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is caused by various reasons. The most common causes of shortness of breath are:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system
. Cardiovascular pathologies lead to insufficient blood circulation. The organs do not receive the required amount of oxygen, and carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. The body reacts to this condition by breathing faster - more air is pumped through the lungs per unit of time. Shortness of breath due to cardiac pathology occurs or worsens after physical exertion or while lying down. In a sitting or semi-sitting position, shortness of breath goes away. This type of shortness of breath is characterized by difficulty breathing; - pathologies of the respiratory system
. Shortness of breath may be caused by obstructions to the passage of air through the respiratory tract, for example, by narrowing of the lumens of the bronchi. Therefore, shortness of breath is a typical symptom of bronchial asthma. In this case, exhalation is difficult. Shortness of breath can also be caused by a decrease in the respiratory surface of the lung tissue. As a result of such a decrease, in order to maintain the required amount of oxygen entering the blood, more intensive work of the lungs is required, that is, more frequent inhalation. The list of diseases of the respiratory system in which shortness of breath may occur is extensive and includes such dangerous pathologies as tumors, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and others; - anemia
. A lack of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and hemoglobin leads to the fact that even with normal functioning of the heart and lungs, the blood is not able to provide the organs with the necessary amount of oxygen, and the body tries to compensate for this by increasing the breathing rate; - neuroses and panic attacks
. In this case, a clinical examination does not reveal pathologies of the heart and lungs, but subjectively the patient experiences a lack of air, and psycho-emotional changes lead to increased breathing. - Obesity and diabetes also often lead to shortness of breath.
Breathing exercises
Your nurse can show you how to take slow, deep breaths to help relieve shortness of breath. You can do them with the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity (see Figure 1). This type of breathing is called diaphragmatic breathing.
Figure 1. Aperture
Try to relax while doing breathing exercises. Relieve muscle tension. This will allow the abdominal cavity (belly), chest, and lungs to expand.
Here are some breathing exercises that can help relieve shortness of breath.
Deep breathing 4-8-8
This exercise improves the movement of air in the lungs. This helps increase oxygen levels throughout the body.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4.
- Hold your breath and count to 8.
- Exhale through pursed lips (as if you were whistling) for a count of 8.
- Repeat 4 times.
Chest wall stretch
This exercise will help the chest muscles become more elastic.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4. As you inhale, extend your arms in front of you and raise them above your head.
- Exhale through pursed lips. As you exhale, open your palms and lower your arms down to your sides.
- Repeat 4 times.
Rapid breathing through the nose
This exercise can help strengthen your diaphragm.
- Shut your mouth.
- Inhale and exhale quickly through your nose for 15 to 30 seconds.
- Practice this exercise several times until you can do it for 60 seconds.
Walking and breathing
These tips will help you breathe easier when walking.
- When walking on a level surface, inhale and exhale through your nose without opening your mouth.
- On inclined surfaces (slopes), inhale through your nose and exhale through pursed lips.
- When climbing stairs, exhale at each step through pursed lips.
Recovery from an attack of shortness of breath (from coughing or exercise)
- Tuck your chin to your chest.
- Take 10 short and sharp exhalations through your mouth. If necessary, take short breaths between them.
- When your neck muscles relax a little, inhale through your nose.
- Exhale 3 times through pursed lips. Inhale between exhalations.
- Inhale through your nose, counting to 4.
- Exhale through your open mouth, counting to 8 and making the sound “ah”.
- Repeat 3 times.
to come back to the beginning
Treatment of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is not an independent disease, but a symptom indicating a malfunction of certain organs. To make it easier to diagnose the disease, before visiting a doctor, try to answer the following questions:
- When did you notice that shortness of breath appeared?
- Does shortness of breath always occur after physical exertion, or does it bother you even at rest?
- What is more difficult - inhaling or exhaling?
- In what position does it become easier to breathe?
- What other symptoms bother you? This may include chest pain, swelling, weakness, dizziness, cough, and fever.
Relief from anxiety
Shortness of breath can cause feelings of fear. Some people say they feel anxious when they start to feel short of breath. However, anxiety can make breathing even more difficult.
Breathing exercises from this material can help you relax. You may also want to know other ways to help relieve anxiety. Talk to your doctor about any anxiety you have. He may prescribe anti-anxiety medications such as alprazolam (Xanax®) or lorazepam (Ativan®) to help you.
Our Integrative Medicine Service also offers relaxation programs that may be beneficial for you.
to come back to the beginning
Prevention
Prevention of an acute obstructive process in the bronchi is identical to the prevention of influenza and ARVI - these are annual, seasonal flu vaccinations. During the onset of cold weather in the off-season, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia and contact with already sick patients.
To prevent exacerbations of chronic obstructive bronchial disease, first of all, eliminate the external factors that cause it - tobacco smoking, dust in enterprises, work in a mine. Flu vaccination is carried out annually. For patients with chronic obstructive bronchitis, vaccination against pneumonia is carried out. It is carried out once every 5 years.
Treatment at special respiratory resorts is considered an important element of prevention. They exist in our country - Crimea. In Germany (Bad Reichenhall), southern coast of France, coast of Italy. The main task of a patient at a resort is active physical exercise in the fresh air.
When to see a doctor?
In some cases, if shortness of breath and weakness occur, emergency medical attention is needed. An ambulance should be called in the following cases 2.7:
- severe sudden shortness of breath, accompanied by severe weakness, sweating;
- the appearance of sharp chest pain, palpitations, fainting, nausea;
- convulsions;
- impairment or complete loss of vision;
- speech disorder.
In other cases, a routine consultation with a general practitioner or family doctor is necessary to find out the cause of the ailment, conduct a diagnosis and begin correct treatment. To establish a diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe a number of examinations:
- laboratory tests - blood and urine tests;
- instrumental studies - ultrasound, sometimes MRI, CT.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes consultations with specialized specialists - a cardiologist, pulmonologist, hematologist, geneticist and others. Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is prescribed.
References
- Mukhambetova G. A. et al. Diagnostic criteria for Pompe disease // Bulletin of the Almaty State Institute for Advanced Medical Studies, 2013. No. 3.
- Shortness of breath. Mayo clinic. URL: https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/shortness-of-breath/basics/causes/sym-20050890 (accessed 10/18/2019).
- Chikina S. Yu. Principles of assessing shortness of breath in the practice of a pulmonologist // Practical Pulmonology, 2006. No. 2.
- Avdeev S. N. Thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries // Practical Pulmonology, 2009. No. 3.
- Carbon monoxide poisoning. MSD Handbook. URL: https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%BE%D1%84%D0%B5%D1%81%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BE %D0%BD%D0%B0%D0%BB%D1%8C%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B9/%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BC% D1%8B-%D0%BE%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F/%D0%BE% D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%8F/%D0%BE%D1%82%D1%80%D0 %B0%D0%B2%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5-%D1%83%D0%B3%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BD%D1% 8B%D0%BC-%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BE%D0%BC (accessed 10/24/2019).
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency anemia, 2015.
- Stroke. Mayo clinic. URL: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113 (accessed 10/24/2019).
GZEA.PD.18.09.0435t
Self-diagnosis problems
Difficulty breathing, for example, during nasal congestion and when the functioning of the lungs is impaired, are completely different things. It is impossible to figure out the cause of shortness of breath on your own.
treatment of shortness of breath due to coronavirus
You should seek medical help from your family doctor or pulmonologist. You should not self-medicate.
Should I worry if unpleasant symptoms occur?
In most cases, such symptoms are not life-threatening and go away quickly without additional medical intervention. The most common and relatively safe deviation is a condition where the ventricle contracts prematurely. This causes a slight delay in the next beat, which is felt as a “freezing heart”.
“Frozen heart” is not a figure of speech, but the body’s reaction to specific stimuli
Typically, shortness of breath combined with cardiac arrest occurs after:
- drinking alcohol;
- experienced stressful situation;
- performing heavy physical exercise;
- taking a high dose of caffeine.
This reaction of the body to the above factors is considered normal and does not require any drug treatment. It is enough to give up heavy loads and spend at least a day in complete solitude and tranquility.
Causes of palpitations and shortness of breath not related to heart disease
Most often, shortness of breath with an abnormal heartbeat is caused by heart disease, but in some cases the causes of unpleasant symptoms are less obvious.
Taking medications
Medicines used to treat asthma and thyroid disorders can cause heart palpitations and shortness of breath. These side effects occur especially often at night. It is necessary to make an appointment with your doctor to prescribe a different type of pill with fewer side effects. But in no case should you stop taking medications on your own, or select analogues on the Internet.
Hormonal imbalances
Pregnancy, menopause, and irregular periods can cause unexplained weakness, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath. Unpleasant symptoms disappear as soon as hormone levels normalize. In rare cases, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Breathing exercises will help get rid of shortness of breath that occurs during a panic attack
Panic attacks
If shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat are accompanied by a feeling of anxiety against a background of constant stress, a panic attack may occur. This condition is not life-threatening and can occur periodically in every healthy person.
But if panic attacks occur regularly, then you should seek help from a psychotherapist. It is enough to take a course of cognitive behavioral therapy, during which the doctor, in the form of persuasion, will help you give up negative thoughts or replace them with positive beliefs. There are also special breathing techniques that will help quickly equalize your heart rate and prevent the development of shortness of breath. In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe antidepressants that regulate serotonin levels.
Leading an unhealthy lifestyle
Some doctors believe that chronic fatigue, constant use of tobacco, alcohol or drugs (even mild ones) can cause rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath. It is enough to give up bad habits and the unpleasant symptoms will go away without additional treatment.
It must be remembered that, despite the fact that neither shortness of breath nor rapid heartbeat themselves pose a direct threat to life, they can be quite an alarming signal. Isolated cases of shortness of breath do not indicate illness in the body, but a constant lack of air and abnormal heartbeat is a direct path to the family doctor’s office. Only a specialist will be able to correctly identify the cause of unpleasant symptoms, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment to improve the patient’s health.
How to assess lung function after coronavirus?
A breath test should be performed. You can do it yourself at home:
- take a deep breath through your nose,
- hold your breath for ten seconds,
- exhale slowly.
In the absence of any discomfort, cough or sore throat, the lungs are healthy. If your health worsens and these symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical help. You can find a video on the forum on how to properly do a lung assessment.
Characteristic symptoms
Shortness of breath with coronavirus: how to understand ? It is difficult for the patient to take a deep breath. He makes at least twenty respiratory movements, which is typical for the moderate severity of the disease. As for the severe degree, it is characterized by more than thirty respiratory movements per minute.
At the same time, severe inflammatory processes occur in the lungs: a person’s body temperature rises, but in some situations, shortness of breath with coronavirus without fever , a dry cough is bothersome. But in some cases there may be no symptoms. Then the cough is caused by fear and panic.
If pneumonia is present, during auscultation the doctor hears whistling and wheezing in the bronchi. This is often typical for patients with concomitant bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis and in the presence of secondary lung damage. Subsequently, if treatment is not timely, edema of the pulmonary tissue may develop - this is a life-threatening condition.