A pulse of 90 beats per minute is considered normal only in childhood, in some older people and athletes. If such an increase in heart rate is observed regularly and is accompanied by additional symptoms such as dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, then this indicates the need to receive qualified medical care.
If tachycardia occurs spontaneously, then you can stabilize the condition at home: you need to take a lying position, calm down, take several deep breaths/exhalations, get a good portion of fresh air and drink sedatives. If your condition worsens, you should consult a doctor - an increase in heart rate may indicate the development of serious pathologies: cardiomyopathy, cardiosclerosis, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, nephropathies.
Once an accurate diagnosis is made, medication will be prescribed, and as soon as the cause is eliminated, the heart rate will return to normal.
Could a pulse of 90 be normal?
A pulse of 90 beats per minute is considered normal, but borderline for humans. Exceeding the indicator even by 1-2 beats already indicates the development of heart pathology.
An increased heart rate is called tachycardia and can occur for physiological and pathological reasons. Most often, a pulse of 90 beats occurs due to a lack of circulating blood in the body. This leads to oxygen deficiency, which is the main reason for the increase in the indicators under consideration.
To determine whether a pulse rate of 90 is normal for a particular person, his or her well-being will help. If there is no dizziness, redness, throbbing pain in the head, trembling hands, or fatigue, then you don’t have to worry. In fact, there are many natural reasons for short-term tachycardia.
If the heart rate rises to 90 beats per minute, then indicators of 92 beats or higher appear, then it is worth being examined by a cardiologist - this condition can be caused by developing pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
A pulse of 90-99 beats is considered an absolute norm only in childhood: up to the age of 15, the body adapts, “tuning” the work of all organs and systems. This heart rate does not alarm doctors; they simply record it and designate it as “within normal limits.”
Some older people may also have a rapid pulse, and if, upon examination, the cardiologist did not reveal any disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, then we are talking about the age norm: the heart ages, it requires more effort to work normally, and the myocardial muscles weaken. This is a natural aging process.
Causes of rapid heartbeat
There is a natural (physiological) tachycardia, when a rapid heartbeat occurs in response to some kind of physical activity, severe stress and emotional stress, with an increase in body temperature, etc. In this case, the heart rhythm returns to normal on its own. Physiological tachycardia is also observed during pregnancy (especially in the third trimester). A variety of reasons can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the heart. First of all, these include heart diseases (for example, defects, endocarditis). Tachycardia is one of the clinical manifestations of anemia.
Increased heart rate occurs with certain diseases of the endocrine system (for example, diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology). Tachycardia appears in disorders of the autonomic nervous system, due to hemodynamic disorders, with regular use of certain medications, etc.
Cardiologists at the EXPERT Clinic take into account the variety of reasons that “make” the heart beat faster. That is why patients are offered a comprehensive examination to accurately determine the causes and correctly prescribe the treatment that the patient so needs.
Natural causes of heart rate rising to 99 at rest
Doctors consider several natural causes of an increase in heart rate to 90-99 beats per minute at rest:
- Female. The weight and height of girls is always less than that of men - this means that the size of the main organ is somewhat smaller. The heart has to work at an accelerated rate, and given the low physical activity of women, a pulse of 91 beats per minute and slightly higher will be the absolute norm.
- Low human stature. It is noted that in such people the pulse rate is always above 90 beats per minute, more often this is observed in the afternoon and evening - after physical activity.
- Persistently low blood pressure. For some people, hypotension is a normal condition and is not considered a pathology, but in this case the heart rate will be above 90 beats per minute - the heart has to perform more contractions to pump blood through the systemic and pulmonary circulation.
- Hormonal changes. An increase in indicators can occur before or during menstruation, as well as during pregnancy. This is always associated with increased production of hormones.
Short-term increases in performance up to 99 beats per minute and above also have their own physiological reasons:
- Active sports – if a person is healthy, then within a few minutes after the end of the workout the heart rate stabilizes and drops to normal limits.
- Strong emotions - excitement, fear, having sex, a flash of joy can provoke an increase in heart rate, which is short-term in nature.
- Eating “heavy” food, alcohol, strong coffee - it may take several hours to restore the pulse, but imaginary tachycardia is not accompanied by other characteristic symptoms.
Slight increase
What does a slight increase in heart rate mean and when should you see a doctor? First of all, it should be recalled that the condition when there is a rapid heart rate above normal is called tachycardia.
If the increase in heart rate was not preceded by anything that could play the role of a provocateur, there may be a serious problem, especially if the heart rate of 90 beats remains constant, even at rest.
This indicator may indicate the following problems:
- various cardiovascular diseases;
- pathologies of blood vessels;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- respiratory tract pathologies;
- disorders in the metabolic system.
In addition, you should pay attention to your blood pressure level:
- If your pulse rate is 95 beats/min, your blood pressure is within normal limits, but you feel unsatisfactory, the right decision would be to see a doctor. As a rule, at such moments the patient’s state is close to panic: a feeling of heartbeat in the temples, ears, throat, fear, anxiety. Before the doctor arrives, every effort should be made to calm the patient, put him to bed and provide enough fresh air.
Blood pressure readings
- In the case of pulse values close to 93-95 and low blood pressure (90/60), if this is not the norm for a particular person, it is recommended to urgently call an ambulance. Since such a ratio of indicators can lead to serious consequences:
- respiratory dysfunction;
- anxiety and panic conditions;
- tremor of the limbs;
- dizziness, double vision, flashing “midges”;
- the appearance of cold sweat. If help is not provided in time, this condition may end in collapse. While waiting for the doctor, you need to move the patient to a horizontal position, raise your legs a little and lower your head - this way, blood will flow better to the brain and the lack of oxygen will decrease. The windows should be opened and the patient's face, neck and chest should be moistened with cool water.
chest pain;
First aid for hypotension
If the increased heart rate persists, you can brew tea with chamomile, mint, St. John's wort or lemon balm. Over the next 24 hours, you still need to carry out control calculations, and if the tachycardia does not disappear, go to the hospital.
If your pulse is 90-96 beats per minute: what to do at home
If the pulse is 90-96 beats per minute, and the person reports his usual, normal, stable state of health, then there is no need to take any medical measures, you can:
- measure blood pressure - it should be normal or slightly low;
- lay the person down in silence, let him close his eyes and try to relax;
- open windows/doors - with increased heart rate, you need free access to fresh air.
If your pulse is increased, you should not drink coffee and tea, but the body should receive a large amount of liquid - pure water or mineral water, not carbonated, compotes and fruit drinks with low sugar content.
It is imperative to measure your pulse rate every 3-4 hours throughout the day, and if the readings do not return to normal, you should call a doctor.
Additional measures to normalize heart rate at home are:
- Take 1 tablet of Anaprilin or Carvedilol. It is strictly prohibited to consume more than the specified dose, because this can lead to a heart attack or sudden cardiac arrest.
- Taking a sedative such as motherwort or valerian, but absolutely not in an alcohol solution. Ethanol increases heart rate and may worsen the condition. Sedatives should not be taken if the tablet has already been taken.
- Drink tea from chamomile, St. John's wort, and mint, if a person is not allergic to the listed medicinal plants. This drink goes well with any medications.
- Perform a short set of breathing exercises: inhale for 5 seconds – hold your breath for 1-2 seconds – exhale for 5 seconds. You need to perform 10-15 such exercises.
Will it be possible to reduce the rate at home?
It is worth taking some actions, the main thing is not to go too far and “work” strictly according to the instructions.
The algorithm is as follows:
- Measure blood pressure and heart rate. This will be needed to assess the effectiveness of first aid. If necessary, baseline data is reported to the emergency team.
- Take 1 beta blocker tablet. Anaprilin (preferably) or Carvedilol will do. Violation of the dosage can lead to cardiac arrest or heart attack.
- Use a mild sedative based on motherwort or valerian. Just not in the form of an alcohol tincture. Ethanol excites the nervous system.
- Drink 20-30 drops of a drug based on phenobarbital. Corvalol or Valocordin. Exceeding the dosage is also unacceptable. In the case of organic origin of tachycardia, the effect of such a measure will be minimal.
- Brew tea based on chamomile, St. John's wort, peppermint, motherwort, valerian and anise. Drink at one time, in one gulp. You can eat a tablespoon of lemon, grated with honey.
- Take a horizontal position. Do not make unnecessary movements, especially do not engage in physical activity.
- Use breathing techniques: inhale for 5 seconds, exhale for the same amount. For 10 minutes.
Now it is important to look at the condition. If the heartbeat does not return to normal within 20 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
It is not recommended to engage in amateur activities, it is dangerous. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, stroke and other “delights” are possible.
The absolute indications for seeking medical help are the symptoms described below.
When to see a doctor if your heart rate is high
If, against the background of a rapid heartbeat, a person notices the presence of additional unpleasant symptoms, then a doctor should be called immediately, these include:
- breathing difficulties - shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air, inability to take a deep breath;
- pain in the chest - it can be pressing, sharp, diffuse;
- an enduring feeling of anxiety and fear “in the soul”;
- dizziness and headache;
- excessive sweating, cold sweat on the face and palms;
- trembling of arms and legs, small movements of the head that cannot be controlled;
- the appearance of black dots and “floaters” before the eyes.
An increased heart rate due to low or high blood pressure is also a reason to seek qualified medical help.
If you ignore a pulse of 90-95 beats per minute, which is often present, then the following are possible:
- early myocardial wear, degenerative processes in the heart muscle;
- progression of ischemic disease;
- acute oxygen deficiency in tissues;
- incomplete filling of the heart ventricles with blood;
- myocardial infarction;
- hemorrhagic or ischemic strokes.
What needs to be examined
The functioning of the cardiovascular, excretory, nervous, and endocrine systems is subject to assessment. Relevant specialists. The main one is a cardiologist, the rest are connected as needed.
Among the techniques:
- Collection of medical history and complaints of the patient about his own condition. Objectification of symptoms plays a key role in diagnosis and determining its directions.
- Measurement of blood pressure, heart rate. Using an automatic device.
- Listening to heart sounds.
- Electrocardiography. Profile research. They resort to him first of all. Allows you to identify subtle changes in the functional activity of a muscle organ. Deciphering requires a highly qualified cardiologist.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasound examination of the condition of the heart muscle.
- Assessment of neurological and nephrological status.
- Blood and urine tests.
Specialists whose consultation may be required, in addition to the cardiologist: endocrinologist (hormonal levels), neurologist (CNS), nephrologist (excretory system, kidneys). In other situations, a neurosurgeon (identified brain tumors), an oncologist.
Examinations with a constant pulse of 90
Echocardiography
If a pulse of 90 beats per minute is constant, then you should be examined by a cardiologist to exclude hidden pathologies of the cardiovascular and hormonal systems. As part of the diagnostic examination, the following are prescribed:
- Anamnesis collection. It is a detailed description of symptoms, an accurate description of the condition and control indicators of pulse rate and blood pressure that allow doctors to understand what is happening in the body.
- Obtaining data on blood pressure and heart rate immediately at the time of seeking medical help. The specialist should also listen to the heart sounds - clear/clear, muffled/quiet, rare/within normal limits.
- Electrocardiography. This is a primary examination that allows you to detect even minor changes in the functioning of the heart. Interpretation of the results is available only to an experienced cardiologist.
- Echocardiography. This is an ultrasound examination of the main organ, which allows you to identify and evaluate changes in all tissues and structures of the heart.
General urine and blood tests are also prescribed. If necessary, the nephrological and neurological condition of the patient is assessed.
Additionally, you may need to consult a neurologist, endocrinologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, or urologist.
High pulse. Why does this happen? Is it dangerous?
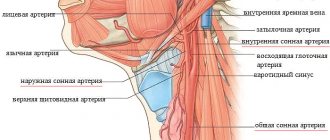
By high pulse we mean an acceleration of the heart rate above 90 beats per minute. It must be borne in mind that the pulse range from 60 to 90 implies a somatically healthy body, for example, with coronary heart disease, 90 beats is no longer normal, since in conditions of constant oxygen deficiency, the most complete blood supply is to the coronary arteries (vessels that directly supply the heart itself) occurs at a frequency of 60 to 65 beats per minute.
Consequently, if a patient with the above pathology constantly has a heart rate above 80 beats per minute, then his shortness of breath will gradually increase, swelling of the legs will appear and heart failure will worsen.....
What types of high heart rate are there?
There are several options for high heart rate:
- The pulse rises during exercise or emotional stress, or when using, for example, coffee, smoking, using energy drinks, or fear. When the stress factor disappears, it returns to normal.
- Heart rate rises regardless of physical activity. You can calmly watch TV, or drink tea, or sit on the sofa, lie in bed - and suddenly it begins to rise sharply. You begin to feel weakness, palpitations, there may be other symptoms in the form of increasing shortness of breath, chest discomfort, unfortunately, there are options when a person, at this moment, loses consciousness, which is a prognostically unfavorable sign. This phenomenon either stops on its own (sometimes, on the recommendation of loved ones, Corvalol and other medications available in the house are used, which is not always correct), or the attack stops by calling an ambulance. The duration of this phenomenon can vary - from a few seconds to several days, or, if professional help is not provided, it can end fatally.
- pulse is always high - both day and night (exceeds 90 beats per minute)
In all the above-mentioned situations, the pulse can be either uniform (simply fast), or uneven or irregular (sometimes faster or slower).
In the first situation, when we talk about the presence of some kind of stress factor, this is, as a rule, a normal, physiological response of the body. In the remaining two cases, it is already a pathology and requires clarification of the causes of such phenomena and appropriate treatment.
What is this pathology called?
These phenomena are called tachycardia (tachyarrhythmia). There are many types of arrhythmias. The most dangerous of them are ventricular tachycardias (when the pathological focus is located directly in the ventricles of the heart). Unfortunately, this type of arrhythmias most often manifests itself as a pronounced deterioration in well-being in the form of syncope (loss of consciousness) and, in the absence of outside help, can lead to death.
It is necessary to take into account that the concept of “syncope” is very broad and can occur not only for this reason, but also, for example, during asystole (temporary cardiac arrest) and in other situations.
Why is this happening?
The reasons for these manifestations can be divided into two groups:
1. Having an “wrong” lifestyle that causes overstrain of the heart (anything that changes the electrolyte composition of the heart (balance of potassium, magnesium, calcium, sodium, etc.) can cause a high pulse):
- Alcohol and smoking (we are not trying to take away the joys of life from you, but if genetics has “awarded” you with the ailments described above, then you have to choose in favor of health and give up something. These two “substances” indeed significantly affect the electrolyte composition of the heart muscle)
- Brewed coffee
- lack of sleep, overwork
- energetic drinks
- excessively intense physical activity (otherwise, additional intake of vitamins and microelements is necessary, but even this may not help)
- emotional stress
2. Presence of congenital and/or acquired disease:
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen), for example, lung diseases (COPD, bronchial asthma)
- dehydration, for example, due to overdose of diuretics or insufficient fluid intake.
- pathology of the thyroid gland in the form of thyrotoxicosis (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland)
- autonomic disorders (disorder of the autonomic nervous system is manifested by various functional disorders with a disorder of vascular tone and the development of neuroses
- overweight
- various heart diseases (WPW syndrome, long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, short PQ syndrome, coronary heart disease, myocarditis, pulmonary embolism (PE), heart attacks, various cardiomyopathies, etc.)
- anemia (low hemoglobin in the blood)
- fever (an increase in body temperature by one degree increases the pulse by an average of 10 beats per minute).
What examinations should I undergo?
At the outpatient stage, the following examinations are most often prescribed:
- electrocardiogram
- daily (Holter) ECG monitor (quite often the monitor does not detect arrhythmia, since it does not happen every day; in this situation, this study is used, among others, to exclude contraindications when prescribing antiarrhythmic therapy.
- if necessary, a stress test (some variants of arrhythmias appear only during exercise)
- thyroid hormone tests (TSH or T4) to rule out hyper or hypothyroidism
- a routine clinical blood test to determine hemoglobin levels.
24-hour (Holter) ECG monitor
How to treat high pulse?
- exclusion of the provoking factors described above
- treatment of the underlying disease
- if tachycardia persists, symptomatic (conservative) therapy is prescribed; if there is no effect or if there are indications, surgical treatment is performed.
The operation involves cauterizing the area of the heart that causes tachycardia.
Under local anesthesia, a puncture is made in the vessel, usually in the area of the wrist joint or inguinal fold, the conductor is inserted into the heart cavity, the localization of the source of arrhythmia is searched and ablation (cauterization) occurs, and also, in case of life-threatening tachycardias, an ICD (cardioverter) can be installed - defibrillator, a device that releases a shock and restores the rhythm when an arrhythmia occurs)
Unfortunately, surgery to cauterize the source of arrhythmia does not provide a 100% guarantee of the absence of relapse, but the probability of cure is above 90%.
How to stop an attack of high pulse once, you need to consult your doctor, since these drugs are selected individually, taking into account contraindications.
Thank you for your attention. See you!
Treatment methods
The main treatments for patients with a rapid heart rate include:
- medication prescriptions;
- folk remedies;
- lifestyle correction;
- surgical intervention.
The latter is prescribed extremely rarely, when therapeutic methods do not produce positive results, the patient’s condition worsens and becomes life-threatening.
Lifestyle
Any prescriptions are made by a doctor after identifying the cause of increased heart rate, but lifestyle correction is required in any case. The patient should:
- stop smoking;
- exclude the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- stabilize the drinking regime - you need to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day;
- limit the amount of salt consumed - no more than 7 g per day;
- give the body regular physical activity - classes with a specialist in physical therapy, walking;
- perform breathing exercises, the complex is selected by the attending physician.
The diet must also be adjusted, from which baked goods, fatty meats and fish, smoked meats and marinades, canned food, semi-finished products, hot spices, coffee and strong tea are excluded. At night, eating is prohibited, meals are based on a fractional principle, all foods are baked, boiled, steamed or stewed with minimal addition of fat.
Medicines
Medication prescriptions come down to the choice of specific drugs:
- Beta blockers - Anaprilin, Carvedilol, Metoprolol. They are necessary to reduce the sensitivity of some receptors in the body, which eliminates the acute reaction of the pulse to emotional experiences and excessive physical activity.
- Calcium channel blockers – Verapamil, Diltiazem. Prevent calcium deposition, vasoconstriction, and deterioration of blood flow.
- Herbal sedatives - tinctures of motherwort and valerian. They have an accelerating effect on the transmission of impulses by the nervous system.
Rarely, drugs from the group of cardiac glycosides - Digoxin, tincture of lily of the valley - can be prescribed.
Folk recipes
If the cardiologist does not see a threat to the patient’s life, then he can recommend traditional methods for stabilizing the pulse rate:
- Honey + lemon. You need to chop the citrus fruit along with the peel and pour 2-3 tablespoons of honey over 1 fruit. After a day, the medicine is ready, take 2 teaspoons three times a day.
- St. John's wort + mint + motherwort. A collection is prepared from equal parts of medicinal plants, then 1 teaspoon of the raw material is poured with boiling water (150 ml) and infused for 10-15 minutes. Tea is consumed 2-3 times a day.
- Chokeberry. A tincture is prepared from it - 200 berries are poured with 400 ml of vodka and infused for 3 weeks. The finished product is taken 2 teaspoons 2 times a day.
Folk remedies require long-term use. If a person works in transport or with dangerous mechanisms, then tinctures with alcohol-containing liquids are prohibited for him.
Symptoms
A physiological increase in heart rate should not be accompanied by any discomfort. And if symptoms arise that are unusual for a person, this serves as a good reason to contact medical institutions.
Signs that should alert you include:
- dizziness;
- “cloudness” in the eyes, double vision, flickering of “midges”;
- pain in the chest and chest area;
- shortness of breath, intermittent breathing;
- sudden profuse appearance of cold sweat;
- sudden weakness and trembling of the limbs;
- feeling of coldness in the hands and feet.
These signs, if you do not pay attention to them, can lead to serious consequences: disruption of the functioning of vital body systems and the development of severe pathologies.
Prevention of high values
Doctors recommend:
- adjust your diet;
- limit the consumption of alcoholic beverages as much as possible;
- do not abuse coffee and strong tea;
- eliminate smoking;
- to live an active lifestyle.
It is advisable to undergo clinical examination on time so that pathologies of the cardiovascular, endocrine, and nervous systems are identified at the early stages of development. Most pathological causes of increased heart rate are eliminated by therapy or surgery and are compensated for a long time.
A heart rate of 90 beats per minute or higher is normal only for children under 15 years of age, some older adults, and professional athletes. A short-term increase in heart rate can be caused by physiological reasons, but in case of recurring conditions, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination - often an increase in heart rate is the only symptom of complex pathologies.
Are these indicators normal?
As has already been clarified, no. A heart rate of 90 beats per minute is not normal. This abnormality is called tachycardia. This level should not occur in elderly patients, women, or the stronger sex.
The only exception is for younger people: in children, standard levels are several times higher than in adults, which is explained by the small size of the heart and the need for more active activity.
The heart rate stabilizes by the age of 15-18, by the age of 25 it remains at the same level, the heart rate reaches its peak by the age of 30, persists for 10 years, then falls again.
How to do an ECG correctly so that the pulse is normal?
Often, a pulse of 95 - 96 per minute becomes a problem for young people who want to enroll in military service under a contract or study at a military university. To ensure that doctors at the commission have fewer questions, you need to adhere to the following recommendations before registering an ECG:
- in the morning on the day of the ECG, a light breakfast is recommended; overeating should be avoided;
- 1 hour before the procedure you should not drink tea, coffee, cola, alcoholic drinks or smoke;
- if the ECG room is located on one of the upper floors of the clinic, it is better to take the elevator up there rather than run up the stairs;
- before recording an ECG, you need to rest in a sitting position for 10 - 15 minutes, you can read a book or listen to calm music;
- During registration, you must lie quietly, without straining, without holding your breath without the request of the medical staff.
Risks and consequences
An elevated heart rate with certain symptoms can be very dangerous and require immediate medical attention. If neglected, there is a very high risk of developing dangerous conditions such as arrhythmia, tachyarrhythmia, thromboembolism and even heart attack. In addition, very low blood pressure along with a rapid pulse may indicate internal bleeding, chemical poisoning, or an attack of hyperthyroidism.
A constant low heart rate can be dangerous for the heart, since there is a constant heavy load on this organ, and this creates favorable conditions for early wear of the myocardium, insufficient blood supply to the ventricles and oxygen to the body.
As a result, ischemia develops and the risk of early heart attack increases.