The first manifestations of various heart diseases should be carefully examined to avoid the development of more dangerous symptoms. If you delay in contacting a doctor, the condition of the heart muscle gradually worsens. Its tissues and vessels undergo pathological changes and can no longer perform the functions of pumping a sufficient volume of blood. As a result, the patient is diagnosed with heart failure, which is fraught with serious complications: myocardial infarction, ischemia, arterial hypertension, etc. It is the timely diagnosis of heart problems that will protect you from dangerous consequences. Now you can undergo a consultation and a set of preparatory examinations when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart absolutely free of charge!
Promotion
Just until the end of autumn, undergo a free consultation and a set of preparatory examinations* when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart.**
Send a request
* Check the details of the Promotion by phone. **Has contraindications; consultation with a doctor is required.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) Cardiac shock wave therapy (SWTS)
Hurry up to apply, the promotion period is limited.
What is heart failure?
The evolution of this disease occurs gradually, problems in the functioning of the heart increase with the age of the patient. In his youth, he does not feel interruptions, because the heart tissues and blood vessels have sufficient tone to supply blood to all parts of the body. Gradually, under the influence of various factors, tissues and blood vessels lose their elasticity, the heart does not fully perform its main function and blood supply deteriorates.
Negative factors include:
- passion for bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- eating disorders;
- hereditary heart diseases;
- unfavorable environment.
At the initial stage, changes occur in the structure of tissues - the ventricles of the heart and their muscles increase. Accordingly, the volume of blood in them increases. The heart muscle needs to work harder to push blood into the vascular system.
As a result, the heart is exhausted, and the walls of blood vessels, due to overload, lose their elasticity, narrow, quickly wear out and over time lose their ability to pass a normal volume of blood. At the same time, vascular pressure increases, and the person quickly gets tired. And the greater the degree of wear and tear of the heart and blood vessels, the faster fatigue sets in. With a high degree of cardiovascular insufficiency, the patient feels a loss of strength even when stationary.
Not only changes occur in the tissues of the heart and blood vessels. The body replenishes the lack of blood, primarily in the brain and the heart itself. Therefore, patients experience insufficient flow to the limbs and other organs. Peripheral vascular diseases, chronic renal failure develop, joints suffer from lack of blood circulation, etc.
Classification of the disease
According to the duration of development of symptoms of damage, heart failure is divided into acute and chronic. The first of them can develop in one of two types:
- To the left - left ventricular or left atrial.
- To the right - right ventricular.
Cardiovascular failure is classified, according to Vasilenko-Strazhesko, into three stages:
- First. This is the initial stage, characterized by the fact that hidden symptoms become noticeable only if the person is physically active. He experiences shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. The patient gets tired quickly. In the absence of physical activity, these signs are absent.
- Second. Symptoms of long-term circulatory failure and stagnation of the entire cardiovascular system also appear when a person is at rest. The patient is considered disabled. This stage has two periods. 2nd A is characterized by moderate hemodynamic lesions in one of the sections of the organ. This is the left or right ventricle. Manifestations of shortness of breath are observed even with normal physical activity. The patient's performance decreases. Other manifestations are cyanotic skin color, swelling of the legs, heavy breathing. 2nd B A is characterized by serious violations. The entire cardiovascular system is involved in this process. External manifestations - a person feels shortness of breath even when at rest. Edema and cyanosis appear. The patient is completely disabled.
- Third. This final stage is characterized by a significant deterioration in blood circulation and metabolism. The structure of many organs, in particular the liver and lungs, is irreversibly damaged. The patient is exhausted.
Classification of heart failure
Acute heart failure
Characterized by sudden, dynamic and to some extent unpredictable development. An attack can develop in 3-5 minutes or 3-5 hours. The contractile function of the heart is impaired, so blood circulation suffers, and the load on the heart tissue (either the left or right ventricle) increases sharply.
Various types of acute forms are characterized by:
- stagnation of blood in various large veins or pulmonary circulation;
- a sharp decrease in heart rate, which causes a deterioration in the blood supply to organs and tissues of the body;
- sudden deterioration in the condition of a patient suffering from a chronic form of the disease.
Chronic heart failure
The most common form. It is characterized by a progressive course and an increase in functional heart problems. The disease has several stages.
Initially, the heart muscle compensates for the insufficient volume of blood ejection by increasing the number of contractions. At this time, myocardial hypertrophy gradually occurs, the vessels begin to reflexively narrow, and the patient experiences periodic ailments.
This state lasts until the compensation mechanism exhausts its resources. Organs and tissues experience a greater lack of oxygen supplied by the blood, and metabolic products are excreted worse. Dystrophic phenomena develop in the body.
What awaits patients
Half of all patients diagnosed with heart failure live more than five years. It is difficult to talk about maximum life expectancy; this indicator is determined by many factors. These include the severity of the disease, concomitant background, and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. The kind of life the patient leads and much more is of great importance.
If the disease is detected in the initial stage, with the help of therapy the patient’s condition can be completely compensated. At stage 3 of the disease, experts talk about a worse prognosis.
Causes of heart failure
Causes of acute heart failure
The main cause of the disease is damage to heart tissue, leading to a change in its functionality. It is often caused by other diseases that negatively affect the heart and blood vessels:
- arrhythmias;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- myocardial infarction;
- increase in chronic symptoms;
- diabetes;
- cardiac tamponade;
- pulmonary artery blockage;
- heart defects.
- Causes of non-cardiac origin include:
- infectious infections;
- strokes;
- brain injuries.
Acute heart failure in men
In the male part of the population, the occurrence of the disease in an acute form is most often provoked by myocardial infarction, toxic poisoning (including alcohol), stress, and overwork.
Acute heart failure in women
A high risk of the disease occurs in women during pregnancy, when the heart is under heavy stress. And during menopause, hormonal changes occur in the body, affecting the functioning of the heart.
Causes of chronic cardiovascular failure
There are several specific causes of chronic (congestive) heart failure:
- cardiac ischemia;
- endocrine diseases;
- eating disorders;
- cardiomyopathy;
- arrhythmias, heart block;
- pericardial diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- congenital and acquired heart defects.
Chronic heart failure in men
Men suffer from this disease mainly due to coronary heart disease, characterized by pathology of the coronary arteries. Negative factors are obesity, alcohol abuse and smoking.
Chronic heart failure in women
In Russia, the risk of developing the disease is higher in women, because their life expectancy is generally longer, and heart failure is a disease of old age. The most common cause of the disease in the female population is arterial hypertension. The greatest risk of developing the disease occurs during menopause.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since such an ailment is considered secondary and its development occurs in the presence of other diseases that are already known to specialists, the goal of diagnosis is to identify it at an early stage, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
The first symptoms of heart failure in women and men are fatigue and shortness of breath. Therefore, first of all you should pay attention to them. It is necessary to monitor patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. People who have suffered a heart attack or rheumatic attacks are at risk. Specific symptoms of the disease include swelling of the legs and accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. You need to be wary when the 3rd heart sound appears and its boundaries shift.
If there are concerns that the patient is developing heart failure, the gas and electrolyte composition of the blood is analyzed. Acid-base balance studies are carried out and other tests are taken.
The presence of coronary heart disease, arrhythmia, and myocardium can be determined by an electrocardiogram. In addition, a variety of load tests are often used. To do this, they resort to the help of treadmills and exercise bikes. Such testing, in which the load gradually increases, indicates the reserves of the heart.
The use of ultrasound echocardiography helps determine the cause of heart failure. In addition, in this way the pumping activity of the myocardium is assessed. MRI performed on this organ helps to identify ischemia, various heart defects, etc.
Using X-ray examination of the lungs and other organs, it is possible to determine the presence of blood stagnation in the pulmonary circulation. Radioisotope ventriculography, performed in patients with signs of heart failure, makes it possible to accurately determine the contractility of the myocardium. In addition, using this method you can install out of capacity.
If a serious form of the disease is present, an ultrasound examination of the liver, pancreas, and other important organs is performed to assess the condition of the internal organs.
Stages of heart failure
In medicine, there are 4 stages (degrees) of heart failure.
- First . Mild manifestations of the disease during physical activity (fatigue, shortness of breath, increased heart rate), which most patients usually do not pay attention to. In a calm state, the symptoms disappear.
- Second . Quite long-term, increasing changes in the functions of the heart occur. The patient begins to feel interruptions in heart rhythm and shortness of breath already at rest, but their degree still remains moderate. Moreover, symptoms may appear suddenly, for example, when trying to get out of bed.
- Third . In the end, interruptions in the functioning of other organs and blood vessels make themselves felt, accompanied by pathological changes in their tissues and the circulatory system.
Preventive measures
For preventive purposes, to prevent the occurrence of such a disease, it is necessary to prevent the development of diseases that lead to it. Among them is ischemia, hypertension, heart defects. In addition, it is necessary to prevent as much as possible the emergence of factors that favor the appearance.
If you have heart failure, the symptoms of which have already appeared, you must first of all try to prevent its progression. To do this, you should not exceed the recommended physical activity, take all medications prescribed by your doctor, and be regularly examined by a cardiologist. The doctors of the Clinical Hospital “RZD-Medicine” in Nizhny Novgorod will help you monitor your health.
Functional classes of heart failure
- First . The patient is physically active and does not feel obvious signs of the disease.
- Second . The patient experiences well at rest, but physical activity causes symptoms of the disease to appear.
- Third . The patient is comfortable at rest, but much less physical activity is required for signs of the disease to appear.
- Fourth . Already at rest the patient feels discomfort, and with minimal exertion the symptoms increase sharply.
Symptoms of acute heart failure
Symptoms increase quickly and even rapidly. Pathological changes occur in different ventricles of the heart, therefore the following symptoms of heart failure are distinguished.
If the right ventricle is damaged:
- veins in the neck swell;
- fingers, ears, tip of nose turn blue;
- limbs swell;
- the liver enlarges, and the skin turns slightly yellow.
- For left ventricular failure:
- shortness of breath and suffocation develop;
- coughing attacks are accompanied by the release of sputum and foam;
- the patient tries to sit up in bed with his legs down;
- Moist rales are heard in the lungs.
A common symptom is dizziness, loss of balance due to a sharp deterioration in blood supply to the brain. In response to a decrease in the amount of blood in the vessels, tachycardia rapidly develops. The patient may also feel nauseated.
Symptoms of chronic heart failure
- One of the most characteristic symptoms of heart failure is shortness of breath . As the disease progresses, its intensity increases.
- Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues, oxygen starvation develops, which is expressed in rapid fatigue , chronic fatigue .
- Stagnation of fluid in the lungs, associated with deterioration of hemodynamics in the pulmonary circulation, causes a wet cough .
- Enlargement of the ventricles leads to the fact that the heart needs to contract more often in order to push out the required amount of blood - the heart rate increases .
The chronic form is characterized by an increase in the manifestations of the disease. If at an early stage patients may not pay attention to them, then later the severity of symptoms increases and fatigue sets in faster. Even at rest, the patient feels significant shortness of breath, palpitations, at night his limbs swell, and in the morning he may experience pain in the heart area.
Methods of treating the disease
The main goal of treating patients is to eliminate the factors that cause heart failure. Among them are rheumatism, ischemia, hypertension, etc. In some cases, surgery is required, this happens with heart defects, aneurysm, and other problems that cause a mechanical barrier to the functioning of the organ.
If the patient has severe or acute cardiovascular failure, the specialist prescribes him to adhere to bed rest. In addition, complete rest is recommended for him. If the condition is not so serious, the load may be moderate and will not affect your well-being.
It is not advisable for the patient to consume more than 600 ml of liquid per day; salt should be either completely excluded from the diet or limited to 1-2 grams. Food should be easily digestible, with plenty of vitamins.
Pharmacotherapy brings good results; it makes it possible to significantly improve the condition of patients and improve their quality of life. Treatment of heart failure involves taking several groups of medications:
- Cardiac glycosides. They are needed to improve myocardial contractility. As a result, its pumping function and diuresis increase. The products help to tolerate physical activity normally. Among the drugs are strophanthin, digoxin, etc.
- ACE inhibitors, vasodilators. Their effect is a decrease in vascular tone. The drugs cause the blood vessels to dilate. Thus, as the heart contracts, its resistance decreases, therefore, cardiac output becomes greater.
- Nitrates. The purpose of the funds is to improve the filling of blood in the ventricles. Their use allows you to increase cardiac output and make the coronary arteries wider. Among them are sustak, nitroglycerin, etc.
- Diuretics. Prevents the retention of excess water in the body. This is furosemide, etc.
- Beta blockers. Their use leads to a decrease in heartbeats, improvement in its filling with blood, and an increase in cardiac output.
- Anticoagulants. Prevents the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. This is, in particular, aspirin.
- Means leading to improvement of myocardial metabolism. These are vitamins B, C, riboxin.
If a patient develops pulmonary edema, he should be admitted to a hospital where he will receive emergency treatment. He will need to take diuretics and nitrates. The patient is given drugs that increase cardiac output. In addition, he is prescribed oxygen inhalations.
When water accumulates in the abdominal cavity, it is removed using punctures. If pneumothorax occurs, pleural puncture is necessary. If a patient has a low oxygen content in the tissues, oxygen therapy is recommended. That is, if there is heart failure with symptoms, treatment - tablets, other drugs - should be prescribed by a specialist.
Diagnosis of heart failure
At an early stage, methods are used to detect interruptions in the functioning of the heart under load that are not noticeable in a calm state. At the CBCP clinic, patients are offered the most effective of these methods:
- daily ECG monitoring;
- stress ECG;
- Holter ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- stress echocardiography.
To diagnose chronic heart failure and study various abnormalities in the structure of the heart and blood vessels, CBCP also uses 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), cardiac rhythmography, and a special cardiac screening program.
First aid for heart failure
First aid for heart failure is mainly required for acute illness, when the risk of myocardial infarction increases. Only a team of resuscitators with special equipment can provide qualified help. Therefore, you urgently need to call an ambulance.
While you are waiting for doctors, provide first aid for acute heart failure:
- make the patient sit with pillows around him;
- give him a nitroglycerin tablet;
- provide air access.
If the patient has lost consciousness, it is necessary to perform an indirect cardiac massage.
Acute left ventricular failure
Acute left ventricular failure is a serious condition caused by decompensation of heart pathology and requiring emergency medical care. In the structure of mortality of cardiac patients, this disease is the first cause of death. What are the main causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, how is left ventricular failure treated - information about this is further in the article.
Risk factors
Acute cardiac left ventricular failure occurs as a result of complex pathogenetic mechanisms causing primary hypertension (increased pressure) in the pulmonary circulation. Risk factors for decompensation of severe cardiac pathology are physical or emotional stress, fluid overload of the vascular bed, infections, etc.
The development of heart failure is associated with impaired systolic or diastolic function, which is caused by various reasons. In order to understand the pathogenetic mechanism, one should recall some aspects of the anatomical and functional features of the heart.
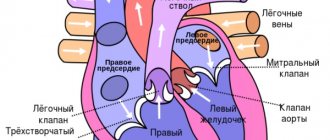
The heart is a muscular “pump” that continuously pumps blood through 2 circles of blood circulation – large and small. Acute left ventricular failure occurs when there is difficulty in the functioning of the left sections (atrium and ventricle) of the heart and is caused by overload of the pulmonary circulation (PB).
8
24/7
In a simplified manner, the ICC diagram can be described by the following sequential stages of blood circulation through the cardiovascular system:
- Right ventricle.
- Pulmonary trunk.
- Right and left pulmonary arteries.
- Arteries, arterioles, capillaries of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Venules and veins.
- Left atrium.
Oxygen-enriched blood through the mitral valve, during diastole, enters the left ventricle, and from there in systole, it is pushed into the aorta.
Acute left ventricular failure develops under the influence of such unfavorable factors as:
- cardiac ischemia;
- long-term surgical intervention;
- infections;
- hypertonic disease;
- excess fluid in the body;
- bronchial asthma;
- severe kidney disease;
- taking certain medications;
- congenital and acquired pathology of the valve system;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
Under the adverse influence, backflow occurs, overflow and volume overload of the left atrium and pulmonary vascular bed. This causes swelling of the intercellular spaces, reactive narrowing of the bronchial lumen, and foaming of the protein contents of the alveoli. All this leads to the development of a clinical picture of cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema.
Causes
The causes of acute left ventricular failure are cardiac (heart) and non-cardiac in nature. The reasons causing the development of this pathology include:
- chronic heart failure in the decompensation phase;
- myocardial infarction;
- aortic dissection;
- cardiac tamponade;
- infection of arteries and valves;
- severe acute myocarditis;
- arrhythmia attack;
- hypertensive crisis.
Factors that do not affect the anatomical structures of the heart, but significantly affect its work with the development of failure, include:
- violation of treatment tactics (overdose of drugs, non-compliance with the rhythm and frequency of taking medications);
- fluid overload (especially with intravenous infusions);
- alcohol abuse;
- tumor of the adrenal cortex (pheochromocytoma);
- renal failure;
- severe lung pathology (bronchial asthma, COPD, pneumonia, tuberculosis);
- stroke;
- sepsis.
In addition, conditions such as severe anemia and thyrotoxic crisis cause increased cardiac output syndrome, which also negatively affects the condition of the left ventricle.
8
24/7
What happens
Acute left ventricular failure, according to the etiological factor or origin, can be primary and an exacerbation of chronic failure. Primary heart failure is caused by:
- acute nephritis (inflammation of kidney tissue);
- acute myocardial infarction;
- hypertensive crisis.
And among the acute manifestations of chronic left ventricular failure are:
- mitral heart defects;
- defects of aortic origin;
- blood stagnation in the ICC in chronic heart failure;
- left ventricular aneurysm.
According to the clinical course, according to the new recommendations of the Society of Cardiology, heart failure (HF) can be:
- acute decompensated (newly occurring, exacerbation of chronic HF);
- hypertensive – symptoms of heart failure are combined with arterial hypertension;
- pulmonary edema;
- cardiogenic shock;
- HF combined with high cardiac output (more often with infections).
When taking into account the clinical course together with radiographic data, acute HF is divided into 4 degrees of severity:
- There are no clinical signs of heart failure.
- The appearance of symptoms and radiological signs consistent with cardiac asthma.
- Detailed picture of pulmonary edema.
- Cardiogenic shock with a drop in blood pressure.
Based on systematic observation of the clinical course, depending on the volume of blood ejected by the left ventricle, left ventricular HF with high or low cardiac output is distinguished.
Symptoms
At the moment when acute left ventricular failure develops, assistance should be provided according to the clinical variant, each of which has its own characteristics.
Precursors and acute forms of left ventricular failure manifest themselves in the form of:
- increased or onset of shortness of breath;
- forced body position (orthopnea), which alleviates the condition;
- rawness behind the sternum during physical activity;
- cough when changing body position;
- the appearance of wheezing in the lower parts of the lungs.
With stagnation in the pulmonary vessels and their increased tension, fluid leaks from the bloodstream into the intercellular tissue (interstitium). It is interstitial pulmonary edema that underlies the development of cardiac asthma, which has the following clinical manifestations:
- nocturnal asthma attack;
- shortness of breath accompanied by chest pain;
- orthopnea;
- participation of auxiliary muscles in breathing;
- sticky, cold sweat on the face and chest;
- cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the nasolabial triangle, lips, neck, fingertips;
- dry and moist wheezing in the lungs;
- pulse is rapid and arrhythmic.
If help is not provided or treatment is ineffective, the following type of manifestation of left ventricular failure develops - pulmonary edema, which is characterized by symptoms such as:
- suddenness of occurrence;
- bubbling breathing;
- feeling of fear of death;
- moist rales heard at a distance;
- discharge of white-pink frothy sputum;
- Moist rales are heard over all the lungs.
If acute left ventricular failure develops, pulmonary edema must be stopped immediately, since severe respiratory failure leads to acute oxygen starvation of the entire body. This is a critical condition that leads to death in a short time.
8
24/7
Diagnostics
The basis of diagnostic measures aimed at confirming the diagnosis is the collection of objective data, especially auscultatory data (when listening to the lungs with a stethoscope).
The following additional laboratory and instrumental methods are used:
- electrocardiography;
- chest x-ray;
- ECHO-cardioscopy with Dopplerography;
- blood chemistry;
- study of blood gas composition;
- general blood and urine tests;
- study of the coagulation system and D-dimer.
When recording an ECG, a number of characteristic changes are revealed that confirm decompensation of the pathological condition. On the cardiogram, changes in the isoline are recorded in the leads corresponding to the damage.
X-ray allows you to assess the presence and extent of damage to the lung tissue, displacement of the cardiac border, enlargement or displacement of the borders of the heart and mediastinum.
ECHO cardioscopy is performed using an ultrasound sensor with the function of measuring the speed and volume of blood flow through the vessels (Doppler). This study helps to visualize the site of damage, the valve apparatus, measure the volumes of the heart chambers, the thickness of the heart walls, the speed and magnitude of blood flow, and ejection fractions.
A biochemical blood test involves the identification and quantitative assessment of substances that are markers of acute cardiac pathology. Among the biochemical indicators, total protein, ALT and AST, creatine phosphokinase, haptoglobin, creatinine, potassium, sodium, urea, and sugar are taken into account.
Blood gases allow you to determine the degree of decrease in oxygen in the blood and increase in carbon dioxide. The criteria for these indicators reflect the severity of hypoxia – oxygen starvation and help monitor the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of therapeutic measures.
Treatment at different stages
If acute left ventricular failure develops, emergency care should be provided even before the ambulance arrives. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Call an ambulance.
- Position the patient in a semi-sitting position.
- Provide access to fresh air.
- Unbutton your shirt collar and loosen your belt.
- If possible, calm down, give Valoserdin, Valocardin, Corvalol to drink.
- Measure and record blood pressure and pulse, do this every 10 minutes.
- When systolic (upper) pressure is above 100 mm Hg. suggest dissolving a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue.
- Apply tourniquets to the thighs (15-20 cm below the inguinal fold), loosen them every 15 minutes.
- If you lose consciousness, place yourself in a safe position on your side.
- Clear your mouth of foam.
- If there is no breathing or heartbeat, begin chest compressions and artificial respiration.
Acute left ventricular failure, the treatment of which must be carried out in an intensive care unit or resuscitation room, is an absolute indication for hospitalization in a cardiological or therapeutic hospital.
Therapeutic measures aimed at relieving this pathological condition include methods such as:
- oxygen therapy - inhalation of heated, humidified oxygen through a mask or nasal cannulas, for pulmonary edema, passed through an antifoam agent - ethyl alcohol;
- administration of narcotic analgesics (Morphine), which provide a sedative (calming) and analgesic effect;
- intravenous administration of Nitroglycerin;
- use of diuretics (Lasix, Furosemide, Ethacrynic acid);
- prescription of cardiac glycosides (Strophanthin, Korglykon, Digoxin);
- cardioversion – used for atrial flutter or fibrillation.
For successful treatment of acute HF caused by non-cardiac pathology, it is important to establish and eliminate the cause that causes it. With continued exposure to a negative factor, therapeutic measures turn out to be ineffective, which leads to rapid death.
Forecast
The prognosis for this disease is rarely favorable, and despite the achievements of modern resuscitation, pulmonary edema is very often the cause of death. The forecast largely depends on the following factors:
- etiology of the development of heart failure (acutely occurring or decompensation of chronic heart failure);
- the extent of damage to the cardiac structure due to cardiogenic causes;
- possibilities for rapid relief of non-cardiac causes of heart failure (pneumonia, sepsis, thyrotoxic crisis);
- age;
- the presence of concomitant pathology.
Left ventricular failure, which occurs as a transient condition, has a more favorable prognosis, which depends on the volume and timeliness of medical intervention. Often acute heart failure is accompanied by massive damage to the heart and becomes chronic.
Disease prevention
The basis for preventing the development of acute left ventricular failure is a commitment to strict adherence to doctor’s prescriptions. It is important to exclude all provoking factors that contribute to damage to the cardiovascular system.
Measures to prevent heart disease include the following:
- to give up smoking;
- avoiding the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- compliance with diet therapy (limiting cholesterol-rich foods, fatty, fried, canned foods, coffee, confectionery, animal fats);
- performing feasible physical exercises daily (jogging, yoga, Nordic walking, swimming);
- exclusion of stressful situations and neuro-emotional experiences;
- limiting physical overexertion.
8
24/7
Acute left ventricular failure is based on cardiac and non-cardiac causes, which cause hypertension in the pulmonary circulation. The main manifestations of the pathology are cardiac asthma and its complication – pulmonary edema. Timely provision of emergency and specialized care for acute heart failure affects the prognosis of the disease.
Treating Heart Failure Symptoms
Treatment of chronic heart failure takes a lot of time, and many drugs (diuretics, glycosides, inhibitors, beta blockers) are prescribed to the patient for life. Basically, the action of the drugs is aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease and making life easier for the patient. In particular, shortness of breath in heart failure is treated, swelling of the extremities is relieved, and blood pressure is normalized.
In acute cases of the disease, in addition to medications, surgical methods are used. The goal of treatment is to eliminate the causes that led to the disease: narrowing of the coronary artery, consequences of myocardial infarction. In case of severe pathological changes in cardiac tissue, a defibrillator is implanted in the patient.
Nutrition and daily routine
Meals should be fractional: 5-6 times a day in small portions. Limit the consumption of meat, salt, exclude smoked foods, chocolate, and alcohol. To replenish their strength, patients should eat foods high in potassium: buckwheat and oatmeal, bananas, dried apricots, Brussels sprouts, etc. A protein and vitamin diet is prescribed.
The daily routine depends on the form of the disease. In the acute form, only rest is necessary. In chronic cases, on the contrary, rest is contraindicated. The patient is advised to exercise in moderation, and a special system of exercises is developed to prevent the disease.
Qualified care for heart failure at the CBCP clinic
At the slightest suspicion of this disease, undergo diagnostics of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the true cause of the disease in order to promptly block its further development.
The CBCP clinic has the latest expert-class equipment for diagnosing all types of this disease. Experienced, qualified cardiologists will advise you and give recommendations on how to treat heart failure.
Make an appointment right now on the website or during business hours by phone.
Causes of the disease
In two thirds of all people with heart failure, the cause of the disease is myocardial infarction and ischemia. 14 percent of cases are caused by heart defects, 11 by dilated cardiomyopathy.
Among people over 60 years of age, four percent of cases are caused by hypertension. In elderly patients, a common cause is type 2 diabetes, especially if arterial hypertension is present at the same time. How heart failure is treated depends on the specific cause.
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of the disease. It usually manifests itself if there is a decrease in the compensatory mechanisms of the heart. These factors differ from the causes in their reversibility. If they are eliminated or even reduced, the development of the disease can be stopped. There are cases when this leads to saving the patient’s life.
Such factors include intense physical activity and stressful situations. Among them are pulmonary embolism, arrhythmia, and progressive ischemic disease. Factors include pneumonia, acute respiratory viral infections, and kidney failure. Negative consequences are caused by taking cardiotoxic drugs, as well as medications that retain fluid in the body and increase blood pressure. Addiction to alcohol and sudden weight gain have a negative effect. Predisposing factors are myocarditis, rheumatism, as well as neglect of the recommendations of a treatment specialist.