Anemia: symptoms, treatment, prevention
Probably no one likes feeling lethargic, tired and overwhelmed. It’s one thing when such a condition appears periodically - after a hard day at work, severe stress, or after an illness. And it’s completely different when the state of “brokenness” becomes permanent: fatigue and weakness do not go away even after proper rest. And suddenly the skin becomes pale, the hands and feet are constantly freezing, the heart jumps out of the chest, the hair falls out and there is a ringing in the ears. This is a reason to sound the alarm and consult a doctor, since there can be a great many reasons for this condition. We will talk about one of them in our article. Today we will talk about anemia. What kind of disease is this? How dangerous is she? How to treat and prevent anemia? These, and more, questions will be answered by the therapist at the SMITRA Clinic, a doctor with more than 30 years of experience, Svetlana Aleksandrovna Marchenko.
What is anemia?
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) contain a complex protein - hemoglobin
, which is synthesized by the bone marrow with the help of iron. Its main function is to carry oxygen throughout the body: after delivering oxygen to the tissues, hemoglobin picks up carbon dioxide and delivers it to the lungs.
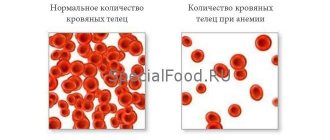
Anemia (or anemia)
is a condition in which there is a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, sometimes with a decrease in the number of red blood cells. Because of this, the transfer of oxygen to tissues deteriorates and hypoxia occurs, i.e. oxygen starvation of tissues.
Causes and types of anemia
Anemia can be either an independent disease or a symptom or manifestation of a complication of another disease or syndrome.
Among the main causes of anemia are the following: 1.
Anemia that occurs when blood formation is impaired
.
These are, first of all, iron deficiency anemia (occurs due to a lack of iron in the body), anemia of pregnant and lactating women (during pregnancy and lactation, the volume of circulating blood in a woman’s body increases, which leads to its “dilution” and a drop in the proportion of hemoglobin in the total blood volume) . 2. Iron-saturated anemia
.
With such anemia, iron in erythrocytes is contained in sufficient quantities, but for various reasons cannot be used by the bone marrow for the synthesis of hemoglobin. Iron-saturated anemias include B-12 deficiency anemia, cancer anemia, helminthic anemia; anemia that occurs during infections. Anemia may occur when exposed to chemical reagents, radiation, medications, as well as due to immune disorders, gastritis, and enteropathies. 3. Anemia that occurs with increased blood destruction (hemolytic).
With this type of anemia, the lifespan of red blood cells is significantly shortened.
Hemolytic anemia can be either hereditary or acquired. In the hereditary form, the problem lies in genetic abnormalities in the structure or function of red blood cells. Acquired hemolytic anemia develops due to excessive destruction of red blood cells due to exposure to antibodies, toxins and other factors. 4. Anemia that occurs during acute or chronic blood loss.
Severe acute or chronic bleeding depletes the body's iron stores, leading to anemia.
Different forms of the disease differ in symptoms and complications. Without adequate treatment, anemia can be complicated by pathology of the cardiovascular system, premature birth, or even death.
What is the danger of long-term anemia?
As we said above, anemia leads to hypoxia - oxygen starvation of tissues. Therefore, even with a mild course, long-term anemia can cause serious harm to health. Prolonged hypoxia leads to metabolic disorders, accumulation of toxic metabolic products, and excessive load on the life-support organs - heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, brain. Against the background of chronic anemia, any acute disease - sore throat, viral infection, etc. – are much more severe and more difficult to treat.
Symptoms of anemia
Each type of anemia has its own manifestations, but a number of general signs of anemia can still be identified:
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- darkening of the eyes;
- heartbeat;
- decreased appetite;
- difficulty swallowing;
- pallor and dryness of the skin, as well as visible mucous membranes;
- hair loss;
- fragility, “striations” of the nails, sometimes their spoon-shaped concavity;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- decreased blood pressure;
- from the gastrointestinal tract, glossitis (inflammation of the tissues of the tongue), atrophy of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, atrophic gastritis, pain in the left hypochondrium are noted.
Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a perversion of taste (addiction to chalk, lime, coal, earth, tooth powder, ice). Hemolytic anemia can be manifested by yellowness of the skin and sclera, enlargement of the liver and spleen, dark urine and feces.
As we can see, the manifestations of anemia can be completely diverse. Therefore, if your health worsens or if the symptoms described above or any other symptoms appear, we recommend that you immediately consult a doctor.
How to diagnose anemia?
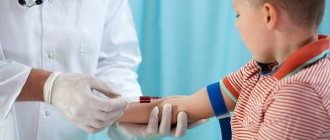
Laboratory tests help diagnose the disease, because it is impossible to determine the disease by eye.
Only correct diagnosis will help choose the right tactics for further treatment and, accordingly, guarantee a successful outcome for the patient. If you suspect one or another type of anemia, your doctor will definitely prescribe blood tests: general and biochemical. Changes in indicators (hemoglobin, iron, red blood cells, ESR, vitamin B12, etc.) will not only answer the question: is there anemia, but will also help the doctor choose the appropriate treatment path.
In some cases, laboratory blood tests alone are not enough, so the patient is prescribed a myelogram - a bone marrow test. A myelogram helps in the differential diagnosis of blood diseases.
Also, the doctor will definitely advise you to conduct a stool test for occult blood, stool for worm eggs and protozoa, caprogram, and, if necessary, stool for calprotectin (a specific marker of intestinal inflammation).
To exclude acute and chronic blood loss, fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) and colonoscopy are performed; if these procedures are impossible, irrigoscopy is prescribed. Consultation with a proctologist, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys are also indicated. Women are recommended to consult a gynecologist.
At the initial stages, anemia is treated by a general practitioner. Then, if necessary, the patient can be referred to a hematologist - a specialist who deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of blood and hematopoietic organs.
Treatment of anemia
There are a huge number of types of anemia.
And they are all treated differently. That is why when treating an illness it is so important to take into account the cause that caused it. In case of bleeding, this is, first of all, the fight against bleeding; for inflammatory diseases - antibiotics, hormones; for chronic renal failure - hemodialysis; for iron deficiency anemia - iron supplements, sometimes even blood transfusions; for B12-deficiency anemia - injections of vitamin B12; if there is a lack of vitamin B9 (folic acid), use folic acid supplements. Treatment of any anemia can only be prescribed by a qualified doctor after a thorough examination!
Otherwise, all attempts to independently increase hemoglobin will be ineffective, in vain, or even dangerous.
Is it possible to treat anemia with folk remedies?
To treat anemia, first of all, you need to contact a specialist and receive a course of drug therapy.
Folk remedies can be used as auxiliaries when undergoing the main course of treatment prescribed by the doctor. For example, rose hips contain a huge amount of vitamins and other useful substances - iron, copper, magnesium. Rosehip decoctions and infusions are useful for iron deficiency anemia. Garlic is also an effective aid for anemia, and if you don’t want to eat it because of the smell, you can take garlic infusion.
Folk remedies cannot be the main treatment for anemia! If you suspect a disease, be sure to consult a doctor!
Nutrition for anemia
Pay close attention to the foods in your daily diet.
Do they have enough iron? To prevent a deficiency of this important element in the body, it is necessary to eat foods rich in iron. Both animal and plant products are rich in iron. Animal iron is found in meat, organ meats, poultry and fish. Moreover, the darker the meat, the more iron it contains. This type is absorbed most efficiently (from 15 to 30%). Among plant products, the richest in iron are legumes, spinach, apples, cereals, nuts, and dried fruits. Iron from plant foods is absorbed less efficiently by the body. To improve the absorption of iron from plant foods, they should be taken with foods rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, greens, tomatoes, bell peppers, rose hips, cabbage). Folic acid also goes well with iron. It can be found in grain bread, corn, avocado, rice, oatmeal, barley, and pearl barley. It is not recommended to simultaneously consume foods rich in iron and calcium (for example, buckwheat with milk), since these two elements make it difficult to absorb each other. In addition, it is not recommended to drink tea and coffee with foods rich in iron. The tannin contained in drinks prevents iron from being absorbed.
When trying to boost your iron levels through food, don't overdo it! Large amounts of iron-rich foods can lead to an increase in iron levels, which can lead to new problems.
Anemia is a common and serious disease that should not be left to chance. In order to avoid the development of anemia and other diseases, it is necessary to undergo an annual preventive examination: take a general blood and urine test, feces for occult blood, undergo fluorography, visit a therapist, urologist, dentist for women - a gynecologist.
If there are signs of chronic bleeding and inflammation, as well as any symptoms of anemia, consult a doctor immediately! The therapist will prescribe the necessary examination and, based on its results, adequate treatment, which will help you return to a healthy, fulfilling life as soon as possible!
Be healthy!
The material was prepared with the participation of the physician-therapist of the SMITRA Clinic, Svetlana Aleksandrovna Marchenko.
© 2010-2021 SMITRA. All rights reserved. No material on this site may be copied or used without written permission except for private, non-commercial viewing.
Pharmacy products
As a rule, drugs that increase iron levels in the blood are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. These are the well-known Ferrum, as well as vitamin complexes with a high iron content. But it is still worth purchasing such drugs after examination and consultation with a doctor.
You should also carefully study the excipients included in such medications for components that may cause allergic reactions (if you are prone to allergies). When studying the instructions for such drugs, pay attention to the compatibility of the components of the drug with various foods.
Most iron-containing drugs are incompatible with the use of alcohol, nicotine and other drugs. For example, smoking and taking iron-containing vitamins can cause complications in the kidneys. In the presence of chronic genitourinary diseases, taking iron-containing drugs and smoking can trigger a relapse of the disease.
The most delicious cure for anemia is hematogen, familiar from childhood. Naturally, this delicacy in itself cannot replace effective medications. But as a preventive measure it can be quite effective. Recently, various iron-containing bars coated with chocolate or various additives have appeared in pharmacies.
Before purchasing, you should carefully study the composition of these delicacies, because quite often the presence of various dyes, thickeners and fixatives not only neutralizes possible beneficial elements, but can also cause allergies.