Causes of anemia
In the vast majority of cases (up to 90%), anemia is caused by iron deficiency. Iron is part of hemoglobin and is involved in the process of hematopoiesis. Iron-deficiency anemia
occurs when there is insufficient consumption of iron-containing foods (primarily meat and vegetables). Anemia can also occur with the right diet, for example, if iron is not absorbed by the body due to existing problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Blood loss can also contribute to the development of anemia. However, blood loss does not have to be large. Frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums, hemorrhoids, and heavy periods can cause anemia.
Possible causes of anemia include a lack of vitamin B 12 or folic acid, but these types of disease are much less common. Hemolytic anemia is also isolated, characterized by increased (faster) destruction of red blood cells.
Anemia can be genetically determined, that is, it can be hereditary.
Why does the body need hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin provides oxygen transport. In the capillaries of the lungs, a maximum of four oxygen molecules bind to one oxygen molecule and form oxyhemoglobin. Then, in the blood stream, red blood cells deliver this ligament to organs and tissues. Here, the oxygen necessary for oxidative processes is freed from bonding with hemoglobin.
Iron is necessary for the normal functioning of the human immune system. A lack of this microelement can lead to problems with potency in men and disrupt the menstrual cycle in women. Low hemoglobin levels can also warn of other serious diseases.
Signs of iron deficiency in the body may include loss of energy, depression, hair loss and dry skin, drowsiness and irritability. However, to determine true anemia and replenish iron deficiency, it is necessary to conduct a detailed blood test.
At risk are vegetarians and fans of strict diets, teenagers during hormonal changes in the body, and child athletes who do not take additional vitamin and mineral complexes. If pregnant women do not take special multivitamins, they are also at risk of developing anemia.
The doctor reminds you that you should not buy drugs to replenish hemoglobin and ferritin reserves at the pharmacy yourself. They are prescribed only by doctors. In addition, the effect of the drugs begins only after six months and therefore the course of treatment cannot be interrupted.
Symptoms of anemia
Lack of hemoglobin leads to oxygen starvation, manifested by symptoms typical of anemia such as:
General weakness
With anemia, muscle tissue does not receive sufficient nutrition. The patient feels constantly tired, he does not have enough strength for normal life activities.
Drowsiness
The body lacks strength, which means it needs additional rest. Drowsiness develops. A person suffering from anemia is almost never alert; as a rule, he wants to sleep.
Pallor
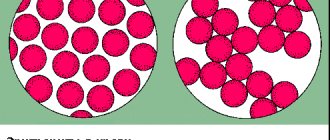
Pale skin due to anemia is caused by a decrease in the number of red blood cells (erythrocytes) in the blood.
Dizziness
With anemia, the brain also receives insufficient nutrition. This may cause dizziness.
flickering
The flickering of “flies” before the eyes is caused by insufficient nutrition of the structures of the visual apparatus.
Fainting
If the decrease in hemoglobin is significant, fainting is possible - episodes of loss of consciousness.
Headache
With anemia, headaches are often observed.
More about the symptom
Cardiopalmus
You may experience palpitations with little physical activity or at rest.
More about the symptom
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath with anemia is caused by the fact that the body tries to compensate for the lack of oxygen by increasing its supply. Breathing becomes more frequent.
More about the symptom
Anemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells and/or hemoglobin in the blood becomes lower than normal.
Red blood cells and the hemoglobin they contain are involved in the transport of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Without oxygen, many tissues and organs may experience hypoxia (oxygen starvation), which has an extremely negative effect on their work. Depending on the degree of decrease in red blood cell and/or hemoglobin levels, anemia may be mild, moderate, or severe.
The most common cause of anemia is iron deficiency.
Synonyms Russian
Anemia.
English synonyms
Anemia, Anaemia.
Symptoms
Despite the fact that different types of anemia are caused by different reasons, their symptoms are very similar:
- fatigue,
- weakness,
- fast fatiguability,
- dizziness,
- pallor,
- headache,
- feeling cold,
- numbness of the limbs,
- dyspnea,
- feeling of lack of air,
- increased heart rate,
- chest pain.
Who is at risk?
Anemia is very common and occurs in both women and men of all ages. However, there are groups of people who are more susceptible to developing this disease than others:
- those who consume little iron and vitamins in their diet,
- patients with chronic kidney disease, diabetes, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease,
- people whose relatives had a form of anemia that can be inherited,
- patients with chronic infections, such as tuberculosis or HIV,
- patients who have lost a lot of blood after injury or surgery.
General information about the disease
There are two main mechanisms for the development of anemia:
- decreased or impaired production of red blood cells, as in iron deficiency or aplastic anemia,
- decreased lifespan of red blood cells in the vascular bed, excessive destruction of red blood cells, as in hemolytic anemia.
Mechanisms of development of the most common types of anemia
| Type of anemia | Mechanism | Possible reasons | Recommended tests |
| Iron deficiency | A decrease in the amount of iron in the body leads to a decrease in hemoglobin and, as a consequence, a decrease in the number of red blood cells. | Blood loss, low iron diet, impaired iron absorption. | Complete blood count (without leukocyte count and ESR), serum iron, serum iron-binding capacity, transferrin, reticulocytes. |
| B12-deficient | A lack of vitamin B12 interferes with the growth and development of red blood cells, which in turn causes a decrease in the number of red blood cells. | Lack of intrinsic factor, diet low in vitamin B12, impaired absorption of vitamin B12. | Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR), vitamin B12. |
| Aplastic | Reduced production of all types of cells in the bone marrow, including red blood cells. | Antitumor therapy, exposure to toxins, autoimmune diseases, viral infections. | Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR), reticulocytes, erythropoietin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). |
| Hemolytic | The lifespan of red blood cells, which is normally about 120 days, decreases due to their destruction in the bloodstream. | Congenital disorders of red blood cell development, blood transfusion reactions, autoimmune diseases, taking certain medications. | Complete blood count (without leukocyte count and ESR), reticulocytes, bilirubin. |
| Anemia in chronic diseases | Various long-term diseases lead to a decrease in the formation of red blood cells. | Kidney diseases, diabetes, tuberculosis, HIV. | Complete blood count (without leukocyte count and ESR), erythropoietin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). |
All anemia can be divided into 2 groups: acute and chronic. Chronic develops slowly, without obvious symptoms, over a long period of time, for example in chronic kidney disease or oncology. In this case, the symptoms of anemia can be smoothed out by the manifestations of the underlying disease. Therefore, this species may remain unrecognized for a long time.
Acute anemia occurs as a result of sudden, heavy blood loss, for example after damage to blood vessels due to injury or gastrointestinal bleeding. Its symptoms appear immediately: severe dizziness, weakness, pallor, tinnitus.
Diagnostics
The main method for detecting anemia is a complete blood count, which shows the number and ratio of various cells in the bloodstream. It allows the doctor to assess the size, shape and maturity of blood cells. Other tests may be prescribed, such as a test for ferritin, serum iron, etc. If anemia is already diagnosed, a biochemical blood test is used to determine its type.
Treatment
The treatment of the most common forms of mild anemia is most often carried out by a general practitioner. Based on the results of a general blood test, he may refer the patient to another specialist, such as a hematologist.
Prevention
To prevent anemia, a balanced diet is necessary, and most importantly, it should be varied, because this disease can be caused by a lack of various substances: iron, proteins, B vitamins, folic, ascorbic acid, copper, cobalt, etc. In addition For example, to satisfy a person’s need for iron, the diet should, in addition to iron itself, also contain substances that promote its absorption, primarily vitamin C.
Also recommended
- General blood analysis
- Reticulocytes
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
- Serum iron
- Erythropoietin
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Methods for diagnosing anemia
Anemia is diagnosed based on laboratory tests.
General blood analysis
A complete clinical blood test is the basic test for determining anemia. For a more detailed diagnosis of certain types of anemia, additional studies may be prescribed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
How does hypochromia manifest?
A feature of hypochromia is a long asymptomatic course. The patient often does not realize the presence of hypochromic anemia, attributing poor health to frequent stress and excessive exertion.
Patients often complain of general malaise, muscle weakness, decreased endurance, fatigue (especially after physical labor), and a constant feeling of drowsiness. As hypochromic anemia progresses, the symptoms increase.
The table shows the symptoms of hypochromia depending on the severity:
| Stage of hypochromia | Hemoglobin indicators | How does the disease manifest itself? |
| light (I) | less than 90 g/l | general malaise, weakness; There are no obvious symptoms. |
| medium (II) | 70–90 g/l | dizziness; violation of the frequency and depth of breathing, feeling of lack of air; pallor; tachycardia. |
| heavy (III) | below 70 g/l | numbness of the limbs; increased irritability; fragility of nail plates; hair loss; |
hypotension; painful redness of the tongue; change in taste preferences.
To avoid severe complications, it is important to promptly diagnose and treat hypochromic anemia, otherwise the consequences of the pathology can be different, even life-threatening.
Anemia Treatment Methods
Treatment of anemia is aimed, first of all, at identifying and eliminating the cause of the disease. In case of detected iron deficiency (vitamin B12, folic acid), replacement therapy is carried out with drugs that compensate for this type of deficiency. A special diet high in essential substances is also prescribed.
Doctor visit
If you are concerned about weakness, dizziness, drowsiness and other symptoms that suggest anemia, we recommend that you consult a general practitioner or family doctor at any of the clinics of JSC “Family Doctor”. The high professionalism of our specialists and modern equipment allow us to effectively treat anemia, including during pregnancy, breastfeeding and other periods that require a special approach.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Treatment and medications for low hemoglobin
Of course, treatment of anemia always includes the prescription of medications. It is impossible to eliminate iron deficiency anemia without iron supplements, only with a diet that includes a lot of iron. The absorption of iron from food is limited, its maximum is 2.5 mg/day. From medicinal preparations, iron is absorbed 15-20 times more.
However, the food must be complete and contain a sufficient amount of well-absorbed iron and protein. It is better to take iron supplements together with ascorbic acid. The latter improves the absorption of iron in the intestines. Since food significantly reduces the absorption of inorganic iron, taking the tablets before meals is more effective.
There are a wide variety of iron supplements. Experience has shown that organic salts of ferric iron and iron compounds with various organic radicals are most easily absorbed by the body and do not cause side effects. Such drugs are safer, they have less risk of overdose and poisoning than coarser inorganic salts. The gums and teeth do not darken, there is no heaviness in the stomach, and quite rarely there is a need to discontinue the drug.
Iron supplements
Now there are many medicines on the market that can be taken orally: coated tablets, for example Sorbifer Durules, chewable tablets Maltofer and Ferrum Lek, Actiferrin drops, Ferrum Lek and Actiferrin syrups for children, Actiferrin and Maltofer drops for infants, there are also injectable forms : Ferrum Lek, at the moment they are used strictly under the control of blood tests.
During pregnancy, it is especially necessary to carefully monitor the hemoglobin level in the blood. For pregnant and lactating women, there are special forms: chewable tablets Maltofer Fol, long-acting tablets coated with Tardiferon, which contain not only iron salts, but also folic acid, which is necessary during pregnancy in higher doses. Depending on the age of the child, a drop form or syrup (Aktiferrin, Maltofer, Ferrum lek) is selected and treatment is carried out.
Functions of iron in the body
The main studied processes occurring with the participation of iron include:
- blood cell formation;
- synthesis of hemoglobin and myoglobin;
- supplying body tissues with oxygen and evacuating carbon dioxide;
- synthesis of ATP (energy carrier molecules) from blood glucose;
- synthesis of cytochromes (P450) and enzymes (catalases) - natural antioxidants involved in the processing of drugs, xenobiotics and the removal of hydrogen peroxide;
- DNA synthesis;
- participation in the regeneration of cells and tissues;
- synthesis of hormones and neurotransmitters;
- regulation of thyroid function;
- regulation of immune system function;
- participation in the processes of physical and psychomotor development.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of anemia, you need to eat right, following a balanced menu. To do this, you need to include beef liver and kidneys, quail and chicken eggs, fresh vegetables and fruits in your diet.
Since women are at risk for developing anemia, they should donate blood for clinical testing more often than men, which will allow timely detection of the disease. If a person, regardless of his gender and age, discovers signs of anemia, he should consult a doctor and begin treatment. Otherwise, it will not be possible to avoid serious health problems.
Author of the article:
Shutov Maxim Evgenievich |
Hematologist Education: Graduated from Kursk State Medical University in 2013 and received a diploma in General Medicine. After 2 years, he completed his residency in the specialty “Oncology”. In 2021, she completed postgraduate studies at the National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov. Our authors
Diagnosis of iron deficiency
Currently, several laboratory tests have been developed to diagnose iron deficiency. The main ones include determining the following blood parameters:
- the amount of serum iron;
- indicator of total iron-binding capacity of serum (TIBC);
- transferrin iron saturation percentage;
- ferritin amount;
- amount of hemoglobin.
It is important to understand that it is a big mistake to prescribe iron supplements solely based on the results of determining low ferritin. In the presence of a MTHFR mutation that disrupts the processing and absorption of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12, ferritin is always low and serum iron is high, which does not allow prescribing iron supplements to such patients.
The goals of laboratory tests for iron deficiency anemia are:
- identification of disturbances in iron metabolism;
- determination of the nature of anemia;
- assessing the risk of developing iron overload in the body.
Preparation for laboratory tests for anemia is simple and fairly standard. It is necessary to donate blood in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach (with an 8-hour break after eating). The day before testing, you must stop taking iron supplements and/or multivitamins. If radioisotope diagnostics were carried out the day before, the study of iron metabolism should begin no earlier than 4-5 days after its completion. It is also important to consider that some medications may interfere with test results. For example, estrogen or oral contraceptives can increase TBI, while corticosteroids and testosterone, on the contrary, lower TBI.
Anemia of the 1st degree - how to determine?
You can suspect grade 1 anemia based on some symptoms, but this is not always possible. Often, pathology at such early stages of development does not reveal itself. Therefore, a person learns about his diagnosis only in the doctor’s office, when he comes for the results of a blood test.
The asymptomatic course of the disease should not be misleading. Outwardly, a person may look absolutely healthy. The absence of any signs only indicates that the body has launched compensatory mechanisms designed to overcome disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems, but sooner or later its reserves will be exhausted. You should always remember that anemia is dangerous.
Prognosis and complications of hypochromic anemia
If treatment was started on time, then most often it is possible to completely get rid of anemia.
When there is no therapy, this risks the following complications:
- Immune forces weaken.
- Children begin to lag behind in mental and physical development.
- The heart works harder, which can lead to the development of cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
- The liver increases in size.
- Anemia becomes chronic.
- The nervous system suffers.
Cost of consultation for anemia?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Epidemiology
IDA was first described by the German physician J. Lange in 1554, and drugs for its treatment were first used by T. Sydenham in the 17th century. Anemia that develops as a result of iron deficiency in the body is the most widespread in clinical practice. According to WHO, about 2.5 billion people on Earth have hidden iron deficiency and 1 billion people suffer from IDA.
In women it is observed 2–5 times more often than in men; children are in 2nd place in frequency of occurrence.
The influence of IDA on the increase in the incidence of maternal and child mortality has been reliably proven. IDA occurs in 12–13% of children aged 6 months and older. up to 2 years. In developing countries, this figure is much higher: in India and African countries it reaches 72–76%. In developed countries of Europe and North America, IDA is detected in 7.5–11% of all women of childbearing age, and 20–25% have hidden tissue iron deficiency. The frequency of IDA is significantly higher in the countries of Asia, Africa and Latin America, where it reaches epidemic levels and amounts to 45–60%. Of all anemias encountered in clinical practice, about 80% are iron deficiency. In the Russian Federation, there is no information on the frequency of IDA, however, according to our data, in Moscow its frequency is 30–35% among women of childbearing age, and hidden iron deficiency is up to 60%.