Life after valve replacement
The lifespan after surgery directly depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and on whether the patient complies with the necessary rules or not.
Having a valve replacement procedure not only improves a person's overall well-being, but also minimizes the likelihood of death due to heart failure. Only 0.2% of people die after surgery, so the prognosis can confidently be called favorable. Patients need to avoid stress and psycho-emotional stress in every possible way.
Diet after surgery
Many patients forget about general recommendations as soon as the rehabilitation period passes.
In fact, a certain diet must be followed throughout your life. It means:
- caffeine withdrawal;
- giving up alcohol and nicotine;
- refusal of unhealthy foods (fried, fatty, floury);
- inclusion of fruits, vegetables, herbs in the diet;
- consumption of cereals, lean meat and fish.
After surgery you need to give up coffee
Such nutrition increases the patient’s life expectancy, since it partially eliminates the risk of blood clots. People with a biological prosthesis are also not recommended to indulge in junk food, alcoholic drinks and cigarettes.
Gymnastics
For the first year after surgery, the person will need to see the doctor monthly. It is the specialist who, if necessary, can prescribe a course of therapeutic exercises. You should not resort to performing any strenuous exercises. As an alternative, you can do the simplest exercises, or better yet, do therapeutic walking.
In the second postoperative year, you will need to visit a specialist every 6 months, and all subsequent times – once every 12 months.
The patient is prohibited from engaging in heavy work or participating in various sports competitions. The patient needs to spend at least 1-2 hours in the air every day.
- Life against the tide. Mitral valve prolapse and what is behind it
The patient needs to spend 1-2 hours in the fresh air every day
After open surgery, a scar or a noticeable scar remains on the chest, which plastic surgery (in particular, laser correction) can help remove. Such procedures must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Valve replacement is a procedure that significantly increases the patient's chances of living a normal life. It can restore a person’s efficiency, cheerfulness and activity.
Who needs such an operation
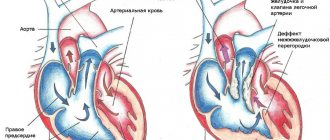
In a situation where the valve ceases to fulfill its purpose, a disruption occurs in the direction of blood flow. As a result, the heart muscle begins to wear out extremely quickly and gradually leads to heart failure. This, in turn, does not allow the blood to circulate well and provide the human body with the necessary amount of oxygen and nutrition. These problems will eventually lead to irreversible processes throughout the body and even to the death of the patient. The only way out of this situation can be heart surgery.
Important! The main reasons why a doctor recommends surgical intervention is a severe organic pathology that can develop into a heart defect.
- Birth defects, which today are most often diagnosed in childhood.
- Adhesions or seals between valve petals. Quite often, such patients undergo a surgical operation known as commissurotomy, but sometimes, due to individual characteristics, this manipulation cannot be performed. It is in this case that the valve is replaced.
- Wrinkling of valve leaflets or tendon strands. This may be a consequence of rheumatic carditis, which usually develops due to a streptococcal infection in the body.
- Myocardial fibrosis is a disease in which the valves become covered with connective tissue. This pathology usually develops as a consequence of complications of certain inflammatory heart diseases.
- Calcification. Calcium salts accumulate on the valves. Most often this happens as a consequence of metabolic disorders or hormonal imbalances. Quite often this is a hereditary pathology. In addition, cardiac rheumatism also has such consequences.
- Aortic stenosis, which developed as a complication after previous coronary artery bypass grafting.
Rehabilitation period
Typically, patients remain on a ventilator for some time after surgery. After restoration of independent breathing, it is necessary to combat congestion in the lungs: rubber balls (or special devices) are well suited for this, which the patient inflates 10-20 times a day, thereby ventilating and straightening the lungs.
The next task is to treat and bandage the sternum wound. After 7-14 days, the skin wounds heal and the patient is allowed to shower.
During the operation, the sternum is dissected, which is then fastened with metal sutures, since it is a very massive bone and bears a large load. For faster healing, it is necessary to provide her with rest; for this purpose, special medical bandages are used. It is possible to do without a corset, however, there are known cases when the sutures cut through in operated patients and the sternum diverged, as a result of which repeated operations were performed, although not such large ones. Therefore, patients are recommended to purchase and use a chest bandage.
In case of violation or cessation of medication, dietary and physical measures during the recovery period, so-called prosthetic complications are possible.
Types of heart valve replacement surgeries
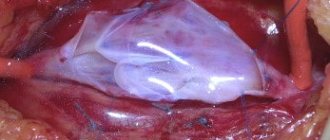
The operation is performed on an open heart with the patient connected to the artificial circulation system. Currently, innovative minimally invasive techniques have been introduced in advanced clinics such as the Almazov Center, where heart valve replacement is carried out under local anesthesia without dissecting the chest.
Read more about the types of prostheses
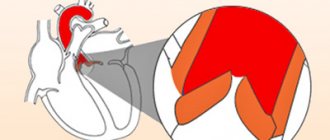
The prosthesis is selected individually, depending on the diagnosis, the patient’s condition, and the presence of comorbid pathology. The shape of the implant depends on which heart valve is affected. Prostheses are made either from artificial materials (mechanical) or from tissues of animal origin (biological). The patient is often interested in which option is better to choose. Let's try to figure it out.
Characteristic features of mechanical products:
- Made from plastic, carbon, metals.
- They are highly durable and have a 15-20 year warranty.
- Recommended for young patients.
- Increase the risk of blood clots.
- In the postoperative period, lifelong use of anticoagulants is required.
Biological prostheses can be described as follows:
- Pain in the late period of rehabilitation after knee replacement
- They are xenografts and allografts.
- Relatively short-lived, requiring replacement after 8-12 years.
- It is advisable to implant in people of older age groups, with a risk of blood clots, and allergies to anticoagulants.
- There is no need to prescribe antithrombotic drugs.
Among cardiac surgeons, the popularity of the Ross operation is increasing - replacing the aortic valve with a pulmonary valve (autograft), and the pulmonary valve with a prosthesis made of biomaterials.
Patient preparation
During hospitalization, the clinic’s doctors will ask the patient to take with him all the extracts, examination data, ask about existing diseases, taking medications, and then prescribe additional tests on the eve of the operation.
Preparing for heart valve replacement has two goals:
- Identification of possible risks during and after prosthetics.
- Planning the course of surgical intervention and rehabilitation procedures.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on this. It is important to inform specialists even of minor points, in the patient’s opinion.
The doctor needs to know the following:
- heart valve condition;
- degree of severity of disorders in the myocardium;
- changes in heart function;
- the patient has a tendency to bleed;
- danger of respiratory and allergic complications;
- features of the liver, endocrine and excretory systems;
- history of bad habits;
- taking medications and biological supplements.
It is usually recommended to undergo a laboratory examination (general clinical tests and biochemistry), instrumental diagnostics (x-ray, ultrasound, functional methods), and obtain consultations with specialized specialists (including an anesthesiologist, even if a minimally invasive intervention without general anesthesia is planned). On the eve of prosthetics, the patient will be asked not to smoke, eat or drink.
Technique of the operation
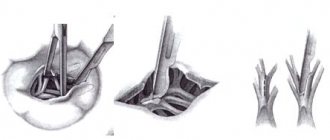
The technique for performing prosthetics is almost the same when replacing different valves. The order of the stages of the operation is strictly observed. Access to the heart is carried out by dissecting the sternum or ribs along the lateral lines.
A longitudinal incision is made to open the pericardium. The artificial blood circulation machine is connected. Procedures are carried out to cool the heart and prevent air embolism. Temporary electrodes are sutured to the myocardium, and drainage is left in the pericardial cavity and mediastinum.
Progress of the procedure
The person is given general anesthesia. The cardiac surgeon removes the affected valves, installs artificial ones in their place, then connects the myocardium, starts the organ’s work, and sutures the covering tissue.
- Mechanism of development, diagnosis and treatment of aortic calcification
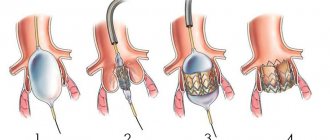
A self-expanding artificial biovalve is passed by a catheter through an artery or vein (depending on which valve needs “repair”) to the required part of the heart, melts under the influence of body temperature, and is put into operation immediately after transportation.
It is also possible to replace the valve using a mini-access - an incision up to two and a half centimeters in the fifth intercostal space to the left of the sternum. An artificial valve is inserted to the apex of the heart.
It is important to know! A huge advantage of such techniques is not only the absence of the need to open the heart cavity, but also the ability not to resort to connecting a heart-lung machine.
Suspected complications
When replacing a heart valve, adverse consequences can occur both during the procedure and in the postoperative period. The attending physician will definitely inform the patient about possible complications. In the operating room, the patient’s condition is completely controlled by a team of doctors.
During rehabilitation, a person should immediately seek help in the following situations:
- the color of urine or feces has changed;
- shortness of breath appeared;
- have problems with hearing or vision;
- numbness of the limbs is felt;
- inexplicable fatigue sets in;
- there is swelling and hyperemia of the sutures;
- an increase in body temperature is recorded.
A negative consequence may be associated with the proliferation of fibrinous tissue, bleeding due to taking anticoagulants, the formation of blood clots, hemolysis of red blood cells, and the addition of an infection. Careful preoperative preparation and adherence to medical recommendations will help avoid dangerous conditions.
Rehabilitation
On average, the duration of hospitalization in the clinic takes 7–10 days, including the first days after prosthetics in the intensive care unit. But even a successful result requires a recovery period of up to 3-6 months.
A few simple tips that will make your rehabilitation easier:
- take all medications prescribed by your doctor;
- eat easily digestible carbohydrates;
- regularly check your sugar and cholesterol levels;
- give up baths and saunas for at least a year;
- perform measured physical activity.
Sometimes, even with very good health indicators, depression awaits a person in the postoperative period. Therefore, it is important that the person recovering is under the supervision of an experienced specialist and has psychological support.
Preparation for coronary artery bypass surgery
At the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, before performing coronary artery bypass surgery, the doctor draws up a preoperative examination plan. It includes laboratory tests and instrumental studies:
- general blood test, urine test;
- blood biochemistry;
- expanded coagulogram;
- ADP platelet aggregation;
- blood type and Rh factor;
- markers of infections: HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis;
- Pro-BNP, SRP;
- ECG;
- Echo-CG;
- X-ray examination;
- EGDS (maximum duration – 1 month). An exception is patients with lesions of the left artery trunk;
- Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (maximum duration – 3 months);
- Ultrasound scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities (maximum duration – 3 months);
- Ultrasound scanning of the veins of the lower extremities (maximum duration – 7 days);
- FVD (maximum duration – 7 days);
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- coronary angiography.
If there is a concomitant pathology, additional tests may be prescribed:
- History of stroke - CT scan of the brain.
- thyroid diseases - TSH, T4, T3 (maximum duration - 30 days). Consult an endocrinologist if there are changes in the hormonal profile.
- diabetes mellitus - glycemic curve (maximum duration - 7 days). Consultation with an endocrinologist for glycemia more than 10 mmol/l.
- Gout - uric acid (maximum duration - 1 month). If the value exceeds 420 µmol/l, consult a therapist and select therapy.
- consultation with a dentist, urologist, gynecologist.
The day before surgery, the patient is examined by a surgeon and an anesthesiologist. On the eve of CABG, it is recommended to have a light dinner no later than 12 hours before surgery, not to eat or drink the night before, and to stop taking medications. A cleansing enema is given at night. In the morning the patient takes a shower.
After signing the informed consent, the patient is given premedication - medications are administered that will reduce emotional tension and help calm down. After 40-60 minutes, the patient is taken to the operating room.
At the cardiology center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you can take all the tests and undergo studies recommended by your doctor before the operation. The structure of our center allows you to quickly go through the preparatory preoperative stage and get the results in hand. Having our own laboratory, we are responsible for the accuracy of tests and the quality of clinical and laboratory studies.
About the purpose of disability and prognosis
Non-working group II is determined for a period of one year after completion of the operation to restore the myocardium. In the future, transfer to group 3 is possible.
When establishing disability, cognitive deviations (decreased mental abilities) are taken into account individually.
How long do you live with an artificial valve? The average life expectancy in this case is approximately 20 years. However, theoretically, the valve’s lifespan is much longer (up to 300 years, according to doctors).
After aortic valve replacement surgery
Once the operation is completed, the patient is sent to the intensive care unit. Here he is brought out of anesthesia and vital functions are monitored:
- The heart rate is determined.
- Breathing and blood pressure are monitored.
- The oxygen level in the blood is checked.
- A tube is inserted into the mouth and lungs to provide additional ventilation.
- A drain is installed to drain fluid from the chest.
- The patient has a catheter placed in the bladder to drain urine.
- Pain medications, fluids, and electrolytes are injected directly into a vein.
After aortic valve replacement, the patient usually spends 5-7 days in the hospital if there are no complications.
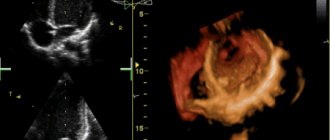
Diagnostics
At the clinic, the patient undergoes a number of diagnostic tests, including:
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- angiography;
- transthoracic echocardiography;
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitor;
- advanced biochemical analyses.
If necessary, an additional examination program is prescribed. After receiving the diagnostic results and collecting an anamnesis, the attending physician decides on the procedure for performing the operation to replace the mitral heart valve.