The activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) test characterizes the state of one of the three mechanisms of the hemostatic system - coagulation (blood clotting). Using the APTT analysis, all types of hemophilia are diagnosed - A, B and C, as well as hereditary, autoimmune diseases and the phases of DIC syndrome are determined.
You can take the APTT test and get reliable results with a transcript of the analysis in the Laboratory of Hemostasis Pathologies at the MLC, the base clinic of Moscow State Medical University named after. Sechenov.
When is an APTT test prescribed?
APTT is part of the blood tests for hemostasis, which are taken when planning pregnancy. The test is also prescribed for genetic predisposition to thrombosis, spontaneous bleeding of unknown origin, diagnosis of hemophilia, treatment of heart attack, during pre- and postoperative examinations.
Based on the results of the analysis, the presence of coagulation inhibitors is determined - signs of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome, severe autoimmune pathologies. The APTT test is also used to monitor heparin therapy.
Complexes with this research
Pregnancy planning.
Clinical indicators 6,630 ₽ Composition Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 9,620 ₽ Composition
For those at risk of COVID-19 Diagnosis of diseases that complicate the course of coronavirus infection 4,510 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Coagulogram RUB 2,020
- Men's check-up No. 1 RUB 18,570
- Women's check-up No. 1 RUB 19,290
- Risk of severe COVID-19 RUB 1,090
- Preventative check-up RUB 11,960
Benefits of analysis
APTT is a highly focused study that diagnoses several pathologies of hemostasis. The coagulation mechanism of hemostasis ensures the “sealing” of damage in blood vessels with fibrin clots and is influenced by blood coagulation factors.
Using the APTT test, you can detect a deficiency of the main factors affecting coagulation:
- 2nd, prothrombin;
- 5th, proaccelerin;
- 8th, antihemophilic globulin;
- 9th factor;
- 10th, Fr. Stewart-Prower;
- 11th, Dr. Rosenthal;
- 12th, Dr. Hagemann.
Preparation rules
You need to carefully prepare for the clotting test, following the following rules:
- Blood sampling is done only on an empty stomach;
- the fasting period should be at least 12 hours;
- on the eve of the procedure, do not eat spicy and fatty foods, smoked foods, and avoid alcohol;
- You should not smoke before donating blood;
- a few days before the analysis, stop anticoagulant medications (Aspirin, Citramon, Warfarin);
- Immediately before testing you need to be at rest.
Decoding
The standard for the test is 24-35 seconds. Physiological changes in hemostasis occur in the body of expectant mothers, so the APTT during pregnancy is reduced to 17-20 seconds. The type of pathology is determined based on the shortening or lengthening of the APTT.
What does it mean if APTT is higher than normal?
Prolongation of APTT is a sign of deficiency of blood coagulation factors: 8th in hemophilia A, 9th in hemophilia B, 11th in hemophilia C, as well as von Willebrand disease - an inherited tendency to spontaneous bleeding.
If the marker increases, additional tests are performed for lupus anticoagulant and antiphospholipid syndrome, and if the patient receives heparin injections, the dose of the drug is adjusted.
What does it mean if APTT is below normal?
A shortening of the activated partial thromboplastin time indicates the risk of developing thrombosis - blockage of blood vessels, or thromboembolism - a blood clot breaking off and entering the circulating blood. Low aPTT determines the first phase of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
If venous blood is collected incorrectly or the sample is contaminated, a decrease in the marker is also observed - in such cases, the analysis is repeated.
Indications for additional testing
Sometimes a pregnant woman has to take a coagulogram test more often than once per trimester. This happens in cases where a woman has the following pathologies:
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the urinary, endocrine and hematopoietic systems.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Condition after surgery.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Predisposition to increased blood clotting.
- Tendency to bleed.
- Deviations from the norm discovered during the first study.
- Having bad habits.
- Miscarriage.
- Fetoplacental insufficiency, gestosis.
Where to get tested for APTT in Moscow
You can take an APTT test and get advice from an experienced hemostasiologist at the Women's Medical Center on Zemlyanoy Val. Our Hemostasis Pathology Laboratory has high-precision blood analyzers, high-quality reagents and consumables, which guarantees the reliability of the research results.
Along with the APTT test, you have the opportunity to take tests close to it: 2-TEG, extended hemostasiogram, tests for VA and APS, Antithrombin, and also determine the anti-Xa activity of heparin in the blood. In the experimental laboratory of the MLC, we are engaged not only in diagnostics: we research and practice new methods for treating hematological diseases.
In one of the private laboratories you are another statistical unit, but with us you are a patient who is ready to be helped by the best doctors in Moscow.
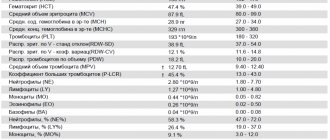
Normal values
In laboratories, methods for studying biomaterial and normal indicators may differ. Reference values are always indicated on the analysis results form. Table. Reference values of coagulogram.
| Main indicators of hemostasis | Norm |
| Clotting time | 5-10 minutes |
| APTT | 30-42 seconds |
| Thrombin time | 15-18 seconds |
| Prothrombin time | 9.3-13.3 seconds |
| Prothrombin index | 70-120% |
| INR (international normalized ratio | 0,82-1,18 |
Fibrinogen:
|
|
| Antithrombin III | 71-115% |
If the analysis data differs from the standard, it means that the patient has problems in the coagulation system.
Indications for prescribing a hemostasiogram
- general assessment of the state of the hemostatic system;
- planned examination before operations;
- spontaneous childbirth or caesarean section;
- severe gestosis;
- control of therapy with indirect anticoagulants (aspirin, warfarin, trental), heparin preparations (clexan, fraxiparin);
- diagnosis of hemorrhagic pathologies (hemophilias, thrombocytopathy and thrombocytopenia, von Willebrandt disease);
- varicose veins of the lower extremities (see treatment of varicose veins at home);
- with a high risk of thrombosis (atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease);
- definition of DIC syndrome;
- taking oral contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids, anabolic steroids;
- chronic liver diseases (cirrhosis);
- acute inflammatory processes in the body;
- diagnosis of various thromboses - vessels of the lower extremities, intestines, ischemic stroke, pulmonary embolism.
See How to distinguish coronavirus from acute respiratory viral infections, flu, and colds. Pneumonia with coronavirus: symptoms, treatment Nobasit for covid Ingavirin for coronavirus Symptoms and treatment of coronavirus
To whom and why is a coagulogram prescribed?
The study of hemostatic and fibrinolytic properties of blood is indicated in the following situations:
- Preparation for planned or emergency surgery, including cesarean section;
- Heart and vascular diseases - myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis;
- Pathologies of the hematopoietic system - hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, von Willebrand-Diane disease, frequent nosebleeds, unexplained bruises, abnormally heavy menstruation and intermenstrual bleeding;
- Chronic liver diseases - fatty or alcoholic hepatosis, cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- Autoimmune diseases – scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Pregnancy (for preventive purposes), severe toxicosis, gestosis, threat of miscarriage, miscarriage;
- Suspicion of existing DIC syndrome;
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives that thin the blood (Warfarin, Aspirin, Heparin, Trental and others);
- Treatment with hirudotherapy sessions.
How much does a coagulogram cost, when can I expect results?
You can take such an analysis at any private diagnostic center, and the cost will depend on the region and the pricing policy of a particular institution. In Moscow, a screening coagulogram will cost an average of 1000 rubles, and an extended one - 3500 rubles. Meanwhile, the study can be done free of charge, if there is evidence for it: just contact a doctor at your place of residence, present your compulsory health insurance policy and get a referral. A blood coagulogram is performed in any state laboratory at a clinic or hospital.
The period for receiving analysis results depends on the workload of the institution, but usually is no more than two days. In emergency situations, a hemostasiogram is performed immediately and the report is sent to the attending physician.
Expectant mothers have the right to a free blood coagulogram as part of pregnancy management and preparation for childbirth. If there are no signs of pathology, the analysis is performed three times, that is, in each trimester.
Video: Dr. Evdokimenko - simple tips on blood thinning, prevention of atherosclerosis and thrombophlebitis.
Coagulogram during pregnancy
During pregnancy, colossal changes occur in a woman’s body, affecting all systems, including the hemostatic system. These changes are due to the appearance of an additional circulation (uteroplacental) and changes in hormonal status (prevalence of progesterone over estrogens).
During pregnancy, the activity of coagulation factors increases, especially 7,8,10 and fibrinogen. Fibrin fragments are deposited on the walls of the blood vessels of the placental-uterine system. The fibrinolysis system is suppressed. In this way, the woman’s body tries to protect itself in the event of uterine bleeding and miscarriage, and prevents placental abruption and the formation of intravascular blood clots.
Indicators of hemostasis during pregnancy
| Index | 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | 3rd trimester |
| Fibrinogen, g/l | 2,91-3,11 | 3,03-3,46 | 4,42-5,12 |
| APTT, s | 35,7-41,2 | 33,6-37,4 | 36,9-39,6 |
| AVR, with | 60,1-72,6 | 56,7-67,8 | 48,2-55,3 |
| Prothrombin index, % | 85,4-90,1 | 91,2-100,4 | 105,8-110,6 |
| RFMK, ED | 78-130 | 85-135 | 90-140 |
| Antithrombin III, g/l | 0,222 | 0,176 | 0,155 |
| Platelets, *109/l | 301-317 | 273-298 | 242-263 |
In pathological pregnancy (early and late gestosis), disturbances in the regulation of blood coagulation occur. The life of platelets is shortened and fibrinolytic activity increases. If a woman does not consult a doctor and treatment of gestosis is not carried out, a very serious complication arises - disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
DIC syndrome or intravascular disseminated coagulation syndrome consists of 3 stages:
- hypercoagulation - the formation of many small blood clots, impaired blood circulation between mother and fetus;
- hypocoagulation - over time, coagulation factors are depleted in the blood, blood clots disintegrate;
- acoagulation - absence of blood clotting, uterine bleeding occurs, which threatens the life of the mother, the fetus in most cases dies.
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist