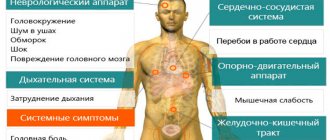
At the present stage, almost every adult knows how to measure blood pressure at home, since this is a vital indicator of the functioning of the cardiovascular system, which doctors emphasize. And there is a tonometer (a device for monitoring blood pressure levels) in almost every home. Unfortunately, hypertension (increased blood pressure values) and hypotension (decrease in values) are now much younger, that is, they are recorded not only in older patients, as before, but also in the younger generation.
The article provides recommendations on how to measure blood pressure correctly, what methods of recording indicators are used and how often the procedure for measuring blood pressure (BP) levels can be carried out. The most commonly used types of tonometers are also considered.
How to choose a device for measuring blood pressure
Devices for measuring pressure are divided into several groups. Depending on the automaticity of operation, mechanical, semi-automatic and electronic devices are distinguished. And there are also mercury models. In addition to shoulder tonometers (standard), there are also those that measure blood pressure at the level of the wrist, finger, and thigh. Such a large selection allows you to select a device for a specific patient if it is not possible to record blood pressure values in the region of the brachial artery.
Mercury
Mercury devices are highly accurate. They are not used at the present stage at home, due to the need for competence in working with such devices. The error of such devices does not exceed 2 mm Hg. Art., which meets the requirements of international standards. Unfortunately, manufacturers of mercury tonometers indicate that they do not supply such devices to European countries. Why this is so is unknown, because the products are of the highest quality.
Mechanical
They are most often used to determine blood pressure levels in medical institutions. These devices are least dependent on external influences and do not require a battery or batteries. The device consists of a cuff, an air pump equipped with a special valve, tubes and a sphygnomanometer. The only condition for correctly measuring blood pressure is the presence of certain skills that allow you to hear the beginning and end of the appearance of specific knocks, sounds, and noises.
Mechanical blood pressure monitors are considered affordable, accurate, and durable. It is better to have one of your friends or relatives help you measure the patient’s blood pressure, since when you independently pump air into the cuff, oscillatory movements of the hands occur, which can distort the results of the study.
Semi-automatic
Such models are also equipped with cuffs and air blowers, but they do not require the ability to listen to tones, since the diagnostic result is displayed digitally on the device screen. You can purchase a semi-automatic blood pressure monitor equipped with voice functions, which is suitable for visually impaired people.
Machine
Electronic devices are great for measuring your blood pressure yourself, without assistance. All the patient needs is to fix the tonometer cuff in the desired place and press the appropriate button. The device independently pumps in air, releases it independently, and the final result is displayed on the device screen.
Automatic blood pressure monitors belong to the most expensive category of models and require the use of batteries. However, blood pressure measurements may be slightly distorted, since the error of such devices is greater than, for example, that of mechanical or mercury tonometers.
On the wrist and finger
These are automatic compact devices that can be easily carried in a bag and are convenient to use. Devices that are fixed at the level of the wrist joint are recommended for use not only by relatively healthy people, but also by patients with burns and dermatological diseases in the shoulder area. Unfortunately, wrist tonometers have a high error in the results. This is due to the fact that the amplitude between compression and relaxation of the wrist artery is insignificant (due to the size of the cuff).
Measuring the blood pressure level on your finger is a funny, but not logical, from a medical point of view, thing. Finger blood pressure monitors are best viewed as modern gadgets, but not as serious and precise devices. After all, the pressure numbers displayed on the device’s screen will depend on many indicators: air temperature, temperature of the finger itself, humidity level, etc. Finger tonometers are not used in medical institutions.
For the hip
The algorithm for measuring pressure on the femoral artery is practically no different from the standard procedure for recording indicators. The difference in the tonometers used is the size of the cuff and the strength of the Velcro. The girth of such cuffs ranges from 40–66 cm, with the standard 15–22 cm for children, 22–32 and 32–42 cm for adults.
Patient preparation
First of all, you need to be sure that the device used to measure pressure is working properly. If we are talking about a mechanical device, the cuff must be completely deflated and the arrow must be at the zero mark. Otherwise, you should contact a specialist to calibrate the device. It is also important to ensure that the cuff used is fully suitable for the person being examined. The diagnostic results will depend on this.
An hour before measuring blood pressure, you need to give up cigarettes, coffee and other drinks containing caffeine, and alcohol. And physical activity and the use of medications that affect blood pressure levels and heart rate are also not recommended (with the exception of vital conditions, in which the use of such medications is discussed with the attending physician). You can measure blood pressure in a standing, sitting, or lying position. Before the procedure, it is advisable to spend 7-10 minutes in a calm environment, catch your breath, and empty your bladder. The numbers should be measured on both arms (or legs) at intervals of several minutes.
How often should you measure your blood pressure at home?
For the initial assessment of hypertension and the effects of antihypertensive medications, home blood pressure should be measured for at least 3 and preferably 7 days. Daily blood pressure measurements should be taken both in the first half of the day (immediately after waking up and before taking the drug during treatment) and in the evening. In each case, a repeat measurement must be taken 1 minute later. The average of all measurements must be calculated after discarding the first day's measurements. This 7-day schedule should be followed before each subsequent doctor's visit. For long-term follow-up, it is advisable to take home measurements less frequently. Measurement under stressful conditions can be misleading and should be avoided. Excessive use of home blood pressure measurements to make self-medication changes (take extra pills or change dose) should be avoided. Results should be logged immediately after each measurement, unless the device stores blood pressure readings with the date and time of each measurement or has a built-in data transmission system.
Measurement methods and techniques
Next, we consider the rules for recording indicators using various types of tonometers and in different projections of large arteries.
Standard mechanical measurement
We are talking about the Korotkov method. The arm is freed from clothing so that the sleeve does not squeeze the shoulder above the level of the cuff. The cuff of the device is applied to the projection of the brachial artery (several centimeters above the elbow). Before starting the procedure, you need to check that one finger fits between the cuff and the patient’s hand. Use your finger to find the pulsation point of the artery and place a phonendoscope in this place.
Next, the air blower valve is closed, the air is pumped until the noise and knocking in the phonendoscope disappear. Next, another 30 mmHg is added. Art., after which the air gradually descends, at the same time the appearance of the first knock is heard. The first knock is the first Korotkoff sound, which corresponds to the systolic (upper) pressure figure. Next, specialists listen to the second, third and fourth Korotkoff sounds. Only medical staff can understand the differences between them. The fifth tone is the moment during which the sound of the tones disappears. The number at which the fifth tone is recorded corresponds to the diastolic (lower) indicator.
Important! Some patients do not have a fifth Korotkoff sound. In this case, the fourth tone corresponds to diastolic blood pressure.
How to use a semi-automatic
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- In addition to the general preparation of the patient, which is described above, you need to check the connection of the cuff and bulb tubes to the corresponding connectors on the device.
- Attach the cuff in the same way as when measuring with a mechanical device.
- Press the button responsible for removing excess air from the cuff.
- Inflate air only after the heartbeat icon appears on the device screen.
- An audible signal will alert the patient when to stop pumping. Then the air will descend on its own at the required speed. Blood pressure numbers will appear on the tonometer screen.
Example of a semi-automatic tonometer
automatic devices are good because they can record the presence of arrhythmia in a patient. If the heartbeat rhythm is abnormal, a corresponding icon appears on the monitor.
Electrical appliance
After the cuff is fixed slightly above the elbow bend, you need to select a memory block on which the result will be recorded. Next, all the necessary symbols will be displayed on the device’s display, followed by “00”. The next stage is automatic air injection, during which the heart rate is measured. After reaching the required peak, the air gradually descends. As a result, the following indicators are displayed on the device display:
- HELL;
- pulse;
- arrhythmia (if present);
- pressure level according to the World Health Organization scale.
Optimal pressure numbers are indicated in light green, normal – green, borderline – orange. The appearance of red flowers indicates hypertension: the higher the indicators, the darker the shade.
On the hip
How is pressure measured in the femoral artery? Experts recommend using mechanical devices. In this case, the cuff of the device is fixed at the level of the middle third of the thigh, and the phonendoscope is applied to the site of pulsation of the popliteal artery (below the knee). The diagnostic algorithm is fully consistent with standard measurements in the shoulder area. If blood pressure was measured in the lower extremities, 10–30 mmHg should be subtracted from the results obtained in the upper extremities. Art., and the lower indicator remains unchanged.
On the wrist
The wrist tonometer is placed at the level of the wrist joint with the display facing you. There should be a distance of 1 cm to the palm. When recording the results in a sitting position, the hand should be positioned so that the tonometer is at the level of the middle of the sternum. Wrist tonometers are automatic models, the instructions for use of which are described above. The permissible error in blood pressure results is 3 mm Hg. Art., heart rate – 5%.
Additional recommendations
Is it possible to measure blood pressure without a tonometer?
There should be at least 2 minutes between measurement intervals. This is the time needed to restore blood circulation. If strange numbers are recorded on the tonometer, you need to measure blood pressure on the second arm. If both results differ from each other by no more than 5 mmHg. Art., measurements can no longer be taken. Is it possible to measure blood pressure often? This is a painless and safe procedure. It can be carried out as many times as necessary.
To obtain correct diagnostic results in elderly people, it is necessary to take measurements several times in a row. Averages are calculated. Elderly patients are characterized by unstable numbers, which is associated with a decrease in the elasticity of the vascular walls, the development of atherosclerosis and disturbances in the functioning of the blood supply regulation system.
To obtain correct blood pressure results in patients with cardiac arrhythmia, several measurements should be performed in a row, without taking into account results that are obviously incorrect. For example, if the top number is less than 40 mmHg. Art., lower - less than 30 mm Hg. Art., and the difference between them is less than 15 mm Hg. Art.
It is better to record blood pressure numbers in women during pregnancy in a reclining position. Only qualified specialists should measure the pressure of children, using mechanical tonometers or semi-automatic devices with a special children's cuff.
Blood pressure levels differ with changes in body position
How to measure blood pressure while sitting or lying down is decided independently by the person and his attending physician. The main thing is that regular procedures should be performed in the same position of the body. The procedure is carried out at the same time of day, in the same position. A sharp change in blood pressure when changing body position is usually called orthostatic hypertension, which is observed:
- for diabetes mellitus;
- in old age;
- with regular use of vasodilator drugs.
In such patients, it is customary to carry out serial measurements with a tonometer every 1–3 minutes. The final value is equal to the average of the derived values. For persistently high or low blood pressure levels over a long period of time, medical assistance is strictly indicated. In a hospital setting, the patient is prescribed an examination, during which the causes of hypotension or hypertension are determined.
Important! Delaying a visit to a specialist can lead to an exacerbation of a progressive disease and the manifestation of unwanted complications.
People with a history of illness or pathology of the cardiovascular system should regularly monitor blood pressure values. In this way, the development of life-threatening diseases is prevented, in particular, heart attack, stroke, and timely measures are taken to stop them.
Common mistakes and interpretation of results
Getting incorrect results can be caused by the following:
- using a cuff that is too large or too small;
- ignoring the rules of preparation for the examination;
- fixing the cuff to clothing;
- talking, fidgeting in a chair, performing movements with arms and legs;
- full bladder;
- abnormal heart rhythm in the patient;
- device breakdown.
When using any measurement methods, it is important to know the rules for deciphering the results. When recording the final data, two numbers are indicated, for example, 140/95. In this case, 140 is systolic pressure, 95 is diastolic. The difference between them is pulse blood pressure. By the way, the last indicator is also important for monitoring the condition of the heart and blood vessels.
Factors distorting indicators
When favorable conditions are created, pressure readings may change. Among them the following are highlighted:
- Regular stress, physical activity, anxiety, and constipation cause an increase in blood pressure.
- Blood pressure increases after consuming foods and drinks that contain tannin and caffeine.
- Alcohol-containing substances uncontrollably expand and narrow arterial passages and disrupt general hemodynamics.
- Sharp jumps in blood pressure are observed when air and water temperatures are too high or too low.