Arterial hypertension is a common disease among older people. When people are aware of their illness, they take certain medications on a regular basis. These medications help keep blood pressure within normal limits. But it happens that a person experiences an exacerbation of the disease. It all starts with a headache, nausea appears, and the vision becomes dark. Such symptoms accompany a hypertensive crisis, which can only be stopped by emergency doctors. It is very important to know when you can do without doctors, and when calling an ambulance cannot be avoided and it is better to do this in a timely manner.
What to do if you have high blood pressure
It should be noted that there are no strict recommendations regarding calling an ambulance in case of high blood pressure. It all depends on the patient’s condition and the deterioration of the condition. If sudden changes for the worse have occurred, it is not recommended to hesitate; life may be in danger at any moment. A hypertensive crisis often causes stroke and other complications that can cause death.
It happens that nothing bothers a person, but the numbers on the tonometer go off scale. And in this case, it is these indicators that need to be taken into account, and not your feelings. Here are some tips from doctors:
- If the upper readings are from 110 to 139, and the lower pressure is within 70-89 units, no action should be taken. Take a lying position.
- If the indicators are above 140 to 90, then this indicates hypertension and measures are already being taken from such indicators. You don’t always need to take medication right away; sometimes it’s enough just to create calm conditions, apply warm mustard plasters to the muscles of your legs (on your calves) and the back of your head.
- If your blood pressure is above 160 over 95, this is a serious reason to think about having you examined by a doctor. Before visiting the doctors, take Capoten.
It is necessary to realize that such an increase is dangerous for the body and should not be ignored. Also rely on your feelings.
When to call an ambulance
About freeloaders and false calls
Most people are embarrassed to call an ambulance and wait until the last minute.
As a result, either they come on their own (we treat these as “self-referred”), or they are brought in completely decompensated, and you understand the third way... However, there is a category of people who believe that doctors are the same as waiters - they are obliged to serve in any case. These people are not shy about dialing 03, even when they simply can’t sleep or have no one to talk to.
Undoubtedly, every call, even the most crazy one, is checked, the car leaves. And it cannot be otherwise, because sometimes a person, being in a critical condition, cannot clearly communicate what is bothering him. And sometimes a still living person is overcome by euphoria (for example, euphoria caused by a lack of oxygen in the brain during hypothermia), and then the victim does not understand the danger of his condition.
Until now, in Russia no liability is provided for an unreasonable call to an ambulance. But we live in a time when the state begins to count every penny, and the time is not far off when it will not be possible to call doctors to your home with impunity just because you are bored and sad. I hope that everyone who is “bored” will be billed for such calls. And they will have to pay for medicines, gasoline, time and depreciation from their own pockets.
It’s amazing how our people manage to criticize their native medicine, not knowing how much a false call costs in any Western country, and especially in the USA, where they certainly know how to count money. In the States, a person with a broken lower limb will prefer to call a taxi; it will cost him much, much less than the arrival of a doctor’s car. And a call for nonsense can cost many years of compensation. You will say that everyone there has insurance that fully covers expenses. This is not true: most insurances only partially cover the treatment, and, as a rule, calling an ambulance due to a runny nose is not covered.
The most important thing is that I want you to understand that each such false call can cost the life of a really serious patient whose minutes are counting. That the work of an emergency medical technician should be primarily aimed at those patients who cannot get to the hospital themselves.
And separately for drivers: if you, while driving, see that an ambulance is rushing with a flashing light, this means that someone is really bad, and no matter how right you are on the road - give in, be human.
When an ambulance is needed
Now I still want to clarify the question: how do you know when it’s really time to call an ambulance? Where is the line when a patient will be looked at as a patient, and not as a freeloader asking to be taken to the hospital? Simply put, what conditions require a doctor to be called to your home?
So, calling an ambulance is carried out only in emergency, life-threatening conditions. This means that do not distract doctors from removing ticks, acne, or treating withdrawal symptoms and high (not crisis) blood pressure. You can safely solve all these problems by going to a clinic or hospital on your own.
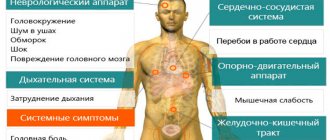
Symptoms of hypertensive crisis
There is a list of symptoms that require help:
- rapid pulse;
- headache and tinnitus;
- visual impairment;
- spots in the eyes;
- goosebumps and numbness in the limbs;
- speech disorders;
- the muscles of the face or tongue become numb;
- breathing problems, wheezing is possible.
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should take a reclining position, move less, call an ambulance and open the door if you are alone at home.
Example of cost of hospitalization for hypertension
Patient:
woman 64 years old
Length of stay in the hospital:
18 days
Hospital:
NCC JSC Russian Railways on the street. Hour, 20
Diagnosis:
Hypertension stage III, degree 2, risk 4. NRS: Paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation, continuously relapsing form.
Complications:
Chronic heart failure (CHF) 1 FC.
Concomitant diseases:
Cerebrovascular disease (CVD). vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI). Discirculatory encephalopathy (DE) 2 tbsp. Nodular goiter, euthyroidism. Chronic cholecystitis, remission. Chronic gastritis, remission. Kidney cysts. Common osteochondrosis of the spine. Varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Hypotension
Blood pressure (BP) is one of the main vital signs along with heart rate, breathing rate and temperature. This is the force with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels.
It is usually represented by two numbers.
- The first is systolic (upper) pressure - this is the pressure formed in the vessels during systole (contraction of the heart).
- The second is diastolic (lower) pressure - this is the pressure that exists in the vessels during relaxation of the heart (diastole).
Systolic pressure is always higher than diastolic.
Normal pressure is considered to be in the ranges
- from 100 to 139 mm Hg. for systolic (“upper”) blood pressure
- from 60 to 89 mm Hg. Art. for diastolic (“lower”) blood pressure.
Hypotension is a condition in which blood pressure (BP) drops below normal.
Tachycardia (high pulse) is an acceleration of the heart rate in an adult to 90 beats per minute or more.
Low blood pressure with a high pulse may require emergency medical attention.
Usually, a person’s blood pressure decreases first, and then tachycardia develops as a compensatory reaction, which is aimed at improving blood supply to organs and tissues. Less common is a situation where a rapid pulse precedes a decrease in blood pressure.
The causes of low blood pressure lie both in external influences on the body and in serious diseases.
Causes of high pulse with low pressure Physiological tachycardia against the background of reduced blood pressure can occur
- During physical activity. Professional and novice athletes do not always correctly calculate the necessary physical activity and overstrain the body. It, in turn, goes into “energy-saving mode,” reducing heart rate and blood pressure.
— When adapting to new conditions . This is especially common among travelers. Climate change when moving to another country, changing time zones, as well as changes in altitude when climbing mountains can be associated with changes in atmospheric pressure.
- In case of emotional turmoil, stress or depression.
— In case of violation of the body’s usual diet . When the body doesn't have enough nutrients to function properly, it responds by lowering blood pressure. A deficiency can be caused by long-term fasting, which is carried out to cleanse the body of toxins, as well as mono-diets, in which a person consumes only one product, depriving his body of the flow of nutrients. After consuming certain foods or drinks, for example, caffeine-containing drinks, sweet carbonated drinks in large quantities.
- after a hot bath, a visit to a sauna or bathhouse, staying in a stuffy room, or in a subway car. The body is in unusually warm conditions. As a result, blood vessels dilate and blood pressure decreases.
Reasons why your heart rate increases when your blood pressure is low include:
- sudden and severe blood loss caused by illness, wounds or injuries. Losing blood, the heart begins to beat faster to maintain blood pressure, reducing the level of blood flow in the vessels. As a result, blood pressure decreases and the skin turns blue.
- shock conditions due to allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock), poisoning, injuries;
- pregnancy period;
- with prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, heat stroke;
- exacerbation of internal diseases. Heart failure leads to the fact that the heart stops pumping blood normally, and the blood vessels lose their former elasticity.
- alcohol abuse;
- atherosclerotic damage to blood vessels;
- vitamin deficiency;
- decrease in body temperature;
- panic attacks;
- a sharp drop in blood glucose levels.
- a sharp increase in the level of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
- taking certain medications: antibiotics, antidepressants, painkillers, diuretics, some alcohol tinctures and a number of other drugs.
- An overdose of narcotic substances also threatens the development of tachycardia, accompanied by hypotension.
Sometimes blood pressure decreases due to a significantly accelerated heartbeat, since the heart does not have time to fill with blood, which leads to a decrease in the volume of blood ejected with each heartbeat.
Tachycardia that leads to hypotension is rare. It can develop suddenly in the presence of coronary heart disease.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
- weakness, drowsiness, absent-mindedness, decreased performance;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- loss of consciousness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- pale skin;
- slowing or increasing heart rate.
- headache.
- Hypotension is often accompanied by autonomic disorders - sweating of the palms and feet, thermoregulation disorders - a decrease in temperature to 35.8 - 36? C, sometimes there may be a feeling of incomplete inspiration or shortness of breath during physical activity.
FIRST AID FOR HYPOTENSION
The first thing to do if there is a sudden drop in blood pressure is to make sure that the victim is not diabetic and does not have an injury or injury that could cause internal bleeding. Indeed, in the presence of internal bleeding, measures designed to increase blood pressure can accelerate blood loss, and an attempt to medicinally narrow the blood vessels to increase pressure with low glucose levels will not give any result.
Patients with diabetes, as a rule, have special tokens or cards in their documents confirming the presence of diabetes. This can help if the patient is unconscious or incoherent. Among the external signs of a sharp drop in glucose in a diabetic is the smell of acetone from the mouth.
If you are sure that the cause of the victim’s drop in blood pressure is not diabetes or internal bleeding, then the following actions should be taken.
- Place the victim on a horizontal surface, on his back,
- Elevate your legs and place a pillow or folded blanket under your shins.
- provide access to fresh air, open a window or vent,
- remove tight clothing, unbutton or remove clothing that restricts breathing.
- measure blood pressure - you need to make sure that it is below normal, write down the result, record the time.
- drink strong, hot, sweet tea.
- cover with a blanket or blanket, because a drop in pressure is usually accompanied by a significant decrease in body temperature.
If, despite the measures taken, the pressure continues to drop and the patient loses consciousness, call an ambulance immediately.
What absolutely NOT to do to increase blood pressure.
— Do not give the patient tablets containing caffeine or coffee. Caffeine causes an increase in heart rate, and this is extremely undesirable in a situation with low blood pressure.
— Do not give alcohol to the patient under any circumstances. It dilates peripheral vessels, and this will cause an even greater decrease in pressure.
— If the patient is conscious, there is no need to let him snort ammonia or other substances with a pungent odor - this will only increase the heaviness and pain in the head.