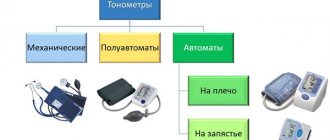
Blood pressure consists of systolic and diastolic, or, as people call it, upper and lower. Diastolic, or lower, is also called cardiac. It is formed at the moment of complete relaxation of the heart muscle. Ideally, it should be 70 mmHg. If this value exceeds 80 mm, then high cardiac pressure occurs. If it increases from excitement or during physical work, then there is no reason to worry: this is a normal phenomenon. We can talk about pathology if there is a persistent increase in lower pressure.
Causes
Elevated heart pressure is most often a concern for various diseases:
- Heart diseases. Common causes of high lower pressure are cardiovascular pathologies. It increases with deterioration of the contractile function of the left ventricle. This happens with myocardial infarction, myocarditis, myocardiosclerosis. If the return of venous blood to the heart is impaired, as a rule, only diastolic pressure increases, while systolic pressure remains normal.
- Diseases of other organs. The reasons for increased blood pressure are some kidney pathologies, thyroid disorders, obesity, spinal diseases, and hormonal imbalances.
Dangers
The absence of symptoms with increased diastolic pressure makes the disease dangerous, since its complications contribute to the development of serious illnesses and fatal attacks.
When diastolic pressure increases, the heart is unable to relax, so during attacks it continuously works at an increased rhythm. These failures provoke disruption of blood flow in the heart muscle, which leads to a change in the structure of the vascular walls: loss of elasticity and impaired permeability. After some time, these pathological changes begin to progress.
Against the background of arterial hypertension, blood clots can form, which can lead to the development of myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Vessels suffer from a regular increase in diastolic pressure, which provokes the development of atherosclerosis. Disturbances are observed both in large arteries and in medium and small ones. After the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the lumen of the blood vessels narrows, which over time threatens their blockage.
- High blood pressure is bad for your kidneys. Because of this reason, nephropathy may develop, which over time turns into renal failure.
- Cardiac hypertension leads to a disorder of the blood supply to the brain, which contributes to the development of stroke, hypertensive intracranial pressure, ischemia or cerebral edema.
- Also, increased diastolic pressure negatively affects vision: unhealthy changes occur in the small vessels of the retina, arterial walls thicken, bleeding into the retina occurs, and blindness occurs.
Arterial hypertension also contributes to the occurrence of other hypertensive conditions that affect the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. The heart consists of 4 chambers (atria and ventricles) that work in perfect harmony. At the moment of the systolic mode of the atria, the cardiac ventricles relax, that is, they are in a state of diastole. With an increase in diastolic pressure, the tension of the cardiac ventricles increases, their function weakens, and this contributes to the occurrence of pathologies, among which hypertrophy is pronounced.
Treatment
High blood pressure requires examination and treatment. Lowering blood pressure leads to an improvement in general condition and reduces the risk of developing dangerous diseases. For this purpose, antihypertensive drugs are used. People often use methods such as mustard plaster on the back of the neck and hot foot baths. You can massage the ears for a minute.
But treatment will be effective only when the causes of this condition are found. To do this, it is necessary to undergo an examination and determine why the lower pressure is high, that is, to diagnose the primary disease.
If it is not possible to find out what pathology caused the increase in pressure, we are talking about essential arterial hypertension. In this case, symptomatic treatment is carried out, that is, medications are prescribed to reduce blood pressure.
How to lower heart pressure
There are a huge number of medications that help lower heart pressure, and almost all of them are available without a prescription. It is important to remember that their uncontrolled use can lower blood pressure before hospitalization and long-term treatment. If you have high blood pressure, you must strictly follow the doctor's prescription and take only those medications that have been prescribed. Even analogs or generics can have different effects on the same patient, so you need to know what to take specifically for you.
Pills
List of the most common modern tablets for high DD:
- Verapamil;
- Atenolol;
- Ramipril;
- Enalapril;
- Veroshpiron (fast-acting sublingual tablets for high blood pressure);
- Indap;
- Hypothiazide;
- Triampur.
Heart medications
Drug therapy makes sense if the persistently elevated DD is more than 90 mmHg. Art. To relieve high blood pressure, a complex of drugs is used. Their extended combination is selected exclusively for a specific patient. With the same degree of hypertension, its causes can be very different, and this implies how to use medications for a particular patient.
List of cardiac drugs:
- thiazides – Hypothiazide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Cyclomethiazide;
- sulfonamides – Oxolodin, Indapamide, Oxodoline;
- beta blockers – selected completely individually;
- Carvedilol is one of the most effective non-selective adrenergic blockers as part of such drugs as Cardivil, Atram, Talliton, Cariol, Bagodilol, Vedicarol, Recardium.
General recommendations
To maintain normal blood pressure, you not only need to take medications, but it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle.
If you have high heart pressure, you need to get rid of bad habits
Daily regime
If you have high blood pressure, proper rest is important. Without this, treatment will not be effective. You need to set aside enough time for sleep. It’s good if you have the opportunity to sleep during the day or at least take a nap for a quarter of an hour. Instead of a quiet hour, you can take a walk in the fresh air. Rest has a beneficial effect on the entire body and overall well-being.
Nutrition
To maintain normal heart pressure, you should eat right. It is important to reduce weight and keep it in optimal condition. Nutrition should be balanced and include all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Doctors recommend sticking to a plant-based diet. You need to eat more vegetables, berries, and fruits. Be sure to include buckwheat and oatmeal porridge and wholemeal products in the menu. Meat and dairy products should be low-fat. Spicy, smoked, fatty, sweet, rich foods should be excluded from the diet, and the amount of salt should be reduced.
Physical exercise
Moderate physical activity has a good effect on the heart and blood vessels and overall well-being. If you have high blood pressure, you should exercise only after consulting a doctor who can prescribe a course of therapeutic exercises. It is useful to take walks in the evenings. If possible, you should walk to work.
How to reduce lower blood pressure
The natural desire of a healthy person is to bring the body’s indicators back to normal. Before taking pills for blood pressure, you need to remember how to reduce it using traditional medicine at home. The use of chemistry gives a guaranteed effect, but has many side effects on the body. You can reduce your lower pressure by adhering to the following list of rules:
- the diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits plus some fermented milk products;
- Eliminate sugar (can be replaced with honey);
- drink decoctions of medicinal herbs, diuretics or lowering blood pressure;
- drink beet juice to strengthen the walls of blood vessels - 1 tablespoon half an hour before meals;
- reduce the load on the kidneys.
How to lower lower blood pressure without lowering upper blood pressure
Sometimes you need to lower the DD without lowering the top one. Even in this case, you can reduce its level at home. This method is recommended by almost all experts. You need to lie on your stomach and place an ice bag or some frozen product on your neck. Stay in this position for about half an hour. Afterwards, massage the cooled area using cream or aromatic oils. In 90% of cases, increased DD decreases without the upper one.
- Causes of increased heart pressure, methods of treatment and first aid for yourself
Normal difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
The difference between the upper and lower blood pressure readings is called pulse pressure (PP), normally it is 40 units. A deviation in both directions of 5–10 units is allowed; this condition is not considered critical, therefore, if the normal PD is 30–50 units, there is no cause for concern. Both the physical and mental state of a person’s health can affect pulse pressure.
No ads 3
Insufficient nutrition, weather sensitivity, physical activity and emotional stress can temporarily reduce PD values, but when normal living conditions are restored, they return to normal on their own. A large, stable difference between systolic and diastolic pressure indicates pathologies developing in the body, the causes and etiology of which need to be clarified with the help of doctors.
A change in well-being will be noted when the PD deviates by more than 10 units in one direction or the other. For example, if a person has always recorded a difference between blood pressure readings of 50 units, then a drop in the norm to 30 units will already affect his condition, he may be talking about the emergence of health problems. Even if the pulse pressure remains within acceptable limits, it will still be considered low.
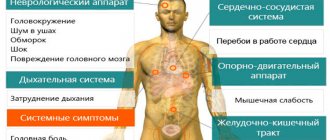
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
If you feel unwell and don’t have a blood pressure monitor at hand, pay attention to the symptoms
.
They may indicate problems with blood pressure.
Signs of high blood pressure
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
- Heart pain.
- Headache.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Nausea.
- Noise in ears.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Facial redness.
- Swelling.
If you measure your blood pressure and it turns out to be high, it is recommended to repeat the measurement at least within a week. Do this at the same time and record the indicators. If the pressure constantly exceeds the age norm by 15 units or more (for example, does not fall below 135/85 when the norm is 120/80), this is a reason to consult a doctor. Regardless of age, do not allow readings of 140/90 or higher.
If measures are not taken in time, there is a risk of hypertensive crisis - a critical increase in blood pressure that threatens life.
Risk factors for developing hypertension
There are a number of conditions that influence the occurrence and development of hypertension. About sixty percent of adults have some risk factor for hypertension, and half of them have more than one factor, resulting in a significantly increased overall risk of the disease.
Heredity
Arterial hypertension in first-degree relatives (father, mother, grandparents, siblings) reliably means an increased likelihood of developing the disease. The risk increases even more if two or more relatives have high blood pressure.
Floor
Men are more predisposed to developing arterial hypertension, especially at the age of 35-50 years. However, after menopause, the risk increases significantly in women.
Age
High blood pressure most often develops in people over 35 years of age. The older a person is, the higher their blood pressure numbers tend to be.
Stress and mental strain
The stress hormone adrenaline causes the heart to beat faster, pumping more blood per unit of time, resulting in increased blood pressure. If stress continues for a long time, then the constant load wears out the blood vessels. Increased blood pressure becomes chronic.
Alcohol consumption
This is one of the main reasons for high blood pressure. Daily consumption of strong alcoholic drinks increases blood pressure by 5-6 mm. rt. Art. in year.
Atherosclerosis
Excess cholesterol leads to loss of elasticity in the arteries, and atherosclerotic plaques narrow the lumen of blood vessels, which makes it difficult for the heart to function. All this leads to increased blood pressure. However, hypertension, in turn, spurs the development of atherosclerosis, so these diseases are risk factors for each other.
Smoking
When components of tobacco smoke enter the bloodstream, they cause vasospasm. Not only nicotine, but also other substances contained in tobacco contribute to mechanical damage to the walls of the arteries, which predisposes to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in this area.
Excess dietary sodium
Modern man consumes much more table salt with food than his body needs. Excess salt in the body often leads to spasm of the arteries, fluid retention in the body and, as a consequence, to the development of arterial hypertension.
Physical inactivity
People who lead a sedentary lifestyle are 20-50% more likely to develop hypertension than those who are actively involved in sports or physical labor. An untrained heart copes worse with stress, and metabolism is slower. In addition, physical activity helps cope with stress, while physical inactivity weakens the nervous system and the body as a whole.
Obesity
Overweight people have higher blood pressure than thin people. This is not surprising, since obesity is often associated with other listed factors - an abundance of animal fats in the diet (which causes atherosclerosis), consumption of salty foods, and low physical activity. It is estimated that every kilogram of excess weight means an increase in blood pressure by 2 mmHg.
If you have counted at least two risk factors, the risk of developing hypertension is already quite high. We advise you to pay attention to prevention and periodically be examined by a therapist or cardiologist.