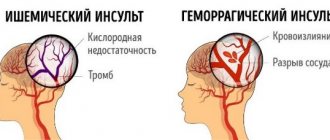
Stroke is a serious brain disease characterized by circulatory disorders, focal lesions of brain tissue, and death of neurons. A stroke can be hemorrhagic or ischemic. Hemorrhagic stroke is less common than ischemic stroke and is characterized by rupture of blood vessels and hemorrhage in brain tissue. Ischemic stroke is more often diagnosed in older people and is characterized by impaired blood flow in the cerebral arteries and the death of neurons in the area of blood supply to brain tissue by the affected artery. When a stroke develops, the patient requires emergency care: the sooner the patient is admitted to the hospital, the more effective the care provided by doctors will be.
In addition to drug treatment of stroke, great importance is attached to rehabilitation therapy, which begins to be carried out in the acute period of the disease. At the Yusupov Hospital, various methods of physiotherapy and exercise therapy are used to restore patients after a heart attack and stroke. With the help of a comprehensive rehabilitation program, the patient is rehabilitated - restoration of motor activity, coordination of movements, visual function, sensitivity. The neurorehabilitation department of the hospital is equipped with modern devices, verticalizers and various simulators, including robotic ones.
The influence of exercise therapy on the patient’s nervous system
Therapeutic exercise is the performance of certain physical exercises, which begin with the simplest movements of the patient after he regains consciousness, then the physical activity gradually increases, the exercises become more complex. Exercise therapy helps improve blood circulation in organs and tissues, accelerates the process of restoration of various body functions, and improves metabolism. Physical therapy exercises for each patient are selected individually depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and concomitant diseases. An individual physical therapy program at the Yusupov Hospital is drawn up by a rehabilitation doctor.
Make an appointment
Pros and cons of the technique
The main advantage of the rehabilitation program developed by Bubnovsky is that patients do not need to take all kinds of additional medications. As for the disadvantages, they consist in the appearance of the effect. It is necessary to perform the exercises for at least 6 months to notice visible improvements. Also, such exercises are not suitable for all patients, because... If the functioning of the great vessels is impaired, patients should not strain their neck. This can lead to a drop in blood pressure in the brain and a deterioration in the patient's general condition.
Passive and active rehabilitation after stroke
The first classes with the patient are conducted by a physical therapy instructor in the ward. The patient performs simple movements with his arms and legs with the help of an instructor - this type of rehabilitation is called passive. Passive rehabilitation of the upper and lower extremities begins with the development of large joints with a gradual transition to small joints. Rehabilitation therapy begins with the shoulder and hip joints. After developing the hip joint, the instructor helps the patient flex and extend the lower limb, develops the knee, then the ankle joint, and lastly the doctor develops the joints of the foot.
The rehabilitation specialist performs massage from the foot to the thigh. During hand rehabilitation, exercises begin with the development of the shoulder joint, then flexion-extension and rotational movements of the hands are carried out in the area of the elbow and hand joints. Massage of the upper limbs is performed from the fingers to the shoulder. A set of exercises combined with massage stimulates brain function. With partial restoration of motor function, exercise therapy exercises become more complex, and the patient begins to perform the exercises independently. The time for gymnastics increases from 10 minutes to half an hour, and active rehabilitation of the patient begins.
If the brain damage is significant, the patient is paralyzed, sensitivity is lost, rehabilitation is carried out with the help of medication, massage, electromagnetic stimulation of nerve cells, acupuncture, and reflexology. After partial restoration of motor function, the rehabilitation doctor introduces therapeutic exercises into the program.
Description of the method
Full rehabilitation after a stroke is impossible without physical therapy. Proper exercises help restore limb function and help restore dexterity and clarity of movement. If the course of the disease is favorable, kinesitherapy treatment can begin in the first days after a stroke. At first, the exercises take no more than 20 minutes a day, and they are performed with the help of an assistant, that is, they are passive. As well-being improves, sessions are lengthened, and the patient is asked to perform more complex tasks to help regain the ability to self-care.
The Bubnovsky rehabilitation method is based on physical activity using specially designed simulators. A set of exercises helps restore blood circulation in the affected area and start recovery processes in brain tissue. Treatment using the Bubnovsky method is carried out without the use of drugs, with the active participation of the patient in the rehabilitation process.
In addition to therapeutic exercises, Bubnovsky’s rehabilitation program after a stroke includes:
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation - non-invasively sends magnetic impulses to the cerebral cortex, promoting the activation of areas of the brain responsible for motor functions.
Stimulation of the cerebral cortex using short magnetic pulses
- Electrical myostimulation - impulses are sent through electrodes attached to the patient’s body, promoting muscle contraction in the same way as they contract while walking. This method helps strengthen the patient’s muscles and prevents unnatural gait.
- Intracellular stimulation to restore pharyngeal function and restore speech.
- Position therapy - in a patient after a stroke, the limbs often take one fixed position, thereby exacerbating muscle hypertonicity. To relax tense arms and legs, special positions are used.
- Heat treatment using paraffin applications.
- Massotherapy.
Rehabilitation exercises on simulators
The Yusupov Hospital uses two types of simulators for the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke - mechanical and robotic. Mechanical exercise machines include exercise bikes, treadmills, and exercise machines for restoring balance and gait. Robotic simulators are equipped with electronic biosensors that stimulate activity by influencing the affected limbs. Robotic simulators have wide functionality; they are programmed taking into account the patient’s needs, promote the transmission of nerve impulses from the brain to the injured limb, and stimulate motor activity.
Rehabilitation exercises after a stroke are performed using multifunctional exercise equipment and sports equipment. There are different types of simulators:
- To restore motor activity, use a flexion/extension simulator, a simulator for developing the joints of the limbs, exercise tracks, and exercise bikes.
- For bedridden patients, exercise equipment in the form of a bed or bicycle is used.
- To restore balance, gait, and motor activity, a horizontal simulator is used.
- For patients who cannot yet stand, a seated exercise machine has been created to develop and strengthen the back muscles.
Therapeutic exercises after a stroke
The use of therapeutic exercises after a stroke allows you to restore the patient’s motor and support function, returning him to normal life. At the first stage of the recovery period, therapeutic exercises are performed in the hospital under the supervision of the attending physician.
After discharge, health-improving exercises are carried out under the supervision of the patient’s family and friends. Relatives of the patient must follow certain rules, which significantly increase the chance of a full recovery:
- Exercise after a stroke should not be accompanied by painful sensations, especially their intensification. If a relative still has minor pain, after a few sessions they will subside - the body will get used to physical activity, which will make doing a set of exercises much easier.
- Before performing therapeutic exercises after a stroke, the body must first be warmed up. A shower or hot bath works well for this. If they are not available, you can use a burner that is applied to the area being restored. This procedure can reduce pain and stiffness in muscle tissue.
- The patient should begin exercises with caution, gradually increasing dynamics and amplitude. A relative or loved one needs to monitor the progress of physical education to avoid pain or unpleasant consequences.
- A complex of physical therapy exercises should be performed daily. The patient must be provided with all the conditions for exercise to become a habit. Exercising every day will speed up the recovery process.
The main advantage of rehabilitation exercises after a stroke, with the help of which an improvement in the general condition of the patient is achieved, is the saturation of paralyzed parts of the body with blood. Correctly performed exercises help restore muscle memory and activate blood vessels.
Hand exercises for stroke rehabilitation
Hand exercises improve motor activity and help restore lost functions. In severe cases and in the absence of early rehabilitation, hand functions are often not restored or partially restored. In some cases, rehabilitation does not help; doctors carry out bipolar stimulation - an effect on immobile joints and muscles of the body using artificially created impulses from the brain to the body. This helps restore reflexes and sensitivity, improve blood circulation in the tissues. Then the patient undergoes rehabilitation using exercise therapy and other methods.
The motor activity of the hands and the motor skills of the fingers are most difficult to restore. You can often see trembling hands in a patient after a stroke; he cannot hold a ballpoint pen in his hand, cannot write, and does not grasp objects well. Especially for such patients, they conduct classes in modeling from plasticine, with a Rubik's cube, teach them to write again, and work on a silicone simulator. Doctors use reflexology if a patient has suffered a severe stroke. This helps restore fine motor skills, improve grasping movements, flexion and extension of fingers, and joints of the hand. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients undergo rehabilitation on computerized simulators using a comprehensive recovery program, which includes massage and physical therapy exercises.
Hand exercises are not complicated and do not require special exercise equipment or devices; the patient can perform them at home:
- Lie on the bed, move your arms back and grab the headboard. Tighten the muscles of your arms and body, imitating a pull-up. Raise your legs up or stretch them straight.
- Using rotational movements of bent arms, knead the shoulder joint.
- Sit upright on the bed, place your hands behind your back as close to each other as possible, tilt your head back, then return to your previous position.
Rehabilitation in the Bubnovsky center
Bubnovsky’s comprehensive kinesitherapy program for recovery after a stroke gradually and very gently returns a person to normal life. This is a long process that requires the patience and desire of the patient himself. The best results are achieved by patients who are emotionally involved in the rehabilitation process and are ready to share responsibility for its results with the doctor.
Rehabilitation work with patients begins with an initial consultation. Through a manual examination, the kinesitherapist assesses the criteria for the patient’s motor deficit and his rehabilitation potential. Based on functional testing and the collected medical history, an individual motor program is drawn up, goals and objectives of rehabilitation are set.
Rehabilitation in the centers includes mandatory training on the Bubnovsky multifunctional simulator (MTB) and basic rehabilitation simulators. During training, special couches, belts, cuffs, and straps are used. All exercises are simple and safe, but have powerful rehabilitation potential.
Stroke patients are always at risk of having another attack. Therefore, all loads at the Bubnovsky Center are individual, strictly dosed and controlled by a kinesiotherapist.
Classes in the gym are held under the mandatory supervision of an instructor. He coordinates the technique of performing exercises, teaches diaphragmatic breathing and independent exercises.
Patients undergo mandatory cardiac monitoring and control ultrasounds of peripheral vessels.
Timely stroke rehabilitation is not only an objective opportunity to restore lost body functions and avoid disability, but also a real chance to return to a full-fledged family and social life.
Sign up for a consultation
Prices in your city
Russia
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Uzbekistan
- Ukraine
Moscow
- Adler
- Almetyevsk
- Anapa
- Angarsk
- Arkhangelsk
- Astrakhan
- Balashikha
- Barnaul
- Belgorod
- Biysk
- Blagoveshchensk
- Bratsk
- Bryansk
- Vladivostok
- Vladimir
- Vologda
- Voronezh
- Grozny
- Ivanovo
- Irkutsk
- Yoshkar-Ola
- Kazan
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kemerovo
- Korolev
- Kostroma
- Kotlas
- Krasnodar
- Kyzyl
- Leninogorsk
- Magnitogorsk
- Makhachkala
- Moscow
- Naberezhnye Chelny
- Nazran
- Nalchik
- Nizhnekamsk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novodvinsk
- Novokuznetsk
- Novosibirsk
- Omsk
- Pavlovo
- Penza
- Permian
- Petrozavodsk
- Pskov
- Pushkino
- Rostov-on-Don
- Ryazan
- Samara
- Saint Petersburg
- Saransk
- Saratov
- Sarov
- Sevastopol
- Smolensk
- Sochi
- Stary Oskol
- Sterlitamak
- Tambov
- Tomsk
- Tula
- Tyumen
- Ulan-Ude
- Ulyanovsk
- Ufa
- Khabarovsk
- Khimki
- Chelyabinsk
- Yaroslavl
Select a branch
- m. Aviamotornaya - Moscow, st. Aviamotornaya, 10, building 2
- m. Academicheskaya - Moscow, st. Dm. Ulyanova, 31
- metro station Altufyevo - Moscow, Altufevskoe highway, 70, building 2
- m. Bagrationovskaya - Moscow, st. Novozavodskaya, 27A
- m. Belorusskaya - Moscow, 1st st. Yamskogo Polya, 24
- m. Boulevard Dm. Donskoy - Moscow, st. Feodosiyskaya, 2
- metro station Butyrskaya - Moscow, 17th proezd Maryina Roshchi, 4, building 1
- m. Kashirskaya - Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 43, building 4
- Khodynka metro station, CSKA metro station, Polezhaevskaya metro station - Moscow, Berezovaya Roshchi passage, 12
For the shoulder joint
Restoration of the forearm and shoulder joint takes place with the help of flexion and extension exercises, rotation, push-ups, muscle tension and relaxation, clapping, and massage. To do this, use exercise machines, dumbbells, and various devices. First, the arm is kneaded, then a set of exercises is performed; therapeutic exercises are always combined with a massage of the limbs. A set of exercises for the shoulder joint:
- The patient lies on his back, arms extended along the body. The instructor holds his hand at the elbow to avoid bending, takes the patient's palm with his other hand and moves the patient's arm up and down.
- The instructor performs circular movements with the patient's arm fixed in a straightened state.
- The patient lies on his back, with his arm slightly to the side. The instructor turns the straightened arm over, palm down, then up.
For lower limbs
Exercises for the lower extremities begin to be performed as soon as the patient regains consciousness. At the initial stage, the instructor helps to bend and straighten the lower limbs; over time, the patient will be able to imitate walking in a prone position, then get out of bed, learn to maintain balance, and walk without support. Exercises for patients in the supine position:
- The patient is in a supine position, the leg is straightened. The instructor turns the leg with the foot inward, then outward.
- The patient is in a supine position, the leg is bent at the knee. Holding one hand under the knee, the instructor performs circular movements with the limb, holding and pressing with the other hand in the hip joint area.
- The patient is in a supine position, the affected leg is bent at the knee. The instructor fixes the leg at a right angle, holding it with the other hand under the knee, bends and straightens the lower limb.
- The patient is in the same position on his back, with the leg fixed at a right angle. The instructor, holding the patient's leg under the knee, moves it away from the body and returns it back.
These exercises are performed by the patient after he is allowed to sit:
- In a half-sitting position, holding the edges of the bed with both hands, stretch both legs forward as evenly as possible, bend over, throwing your head back. While stretching your limbs, take a deep breath, return to your previous position and exhale.
- Remain in the same body position, keep your breathing calm and deep, slowly lift your right leg up and lower it back, then your left leg.
- In a half-sitting position, bend your leg, pull your bent leg at the knee as close to your chest as possible (you can help with your hands), and tilt your head forward during the exercise. Bending the leg, inhale, straightening the limb, exhale, return to the previous position.
Exercise therapy to restore visual function after stroke
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients with visual impairments will be able to undergo examination, treatment, rehabilitation, and, if necessary, surgical treatment in a network of partner clinics. Rehabilitation after a stroke includes exercises that you can then do at home. Depending on the type of visual impairment, rehabilitation therapy is carried out:
- If lateral vision is impaired, intensive medical and restorative treatment is carried out, undamaged areas of the cerebral cortex take over the lost function, and vision is restored. In this case, the doctor marks with a red line a passage of text on the page of the book on the side of which lateral vision is weakened. Before starting to read, the patient must look for the red line - this will be the beginning of the text.
- With oculomotor nerve palsy, the patient cannot look straight and his eyes look in different directions. Such a disorder can resolve over time with proper and timely treatment and rehabilitation. With paresis of the oculomotor nerve, accommodation may be impaired. Over time, the patient gets used to using only central vision. To determine the impairment of perception of objects at far and near distances, the following test is performed: the doctor takes a pencil in each hand and brings one of the pencils closer to the patient’s face, then moves his hand back.
- If atrophy of the oculomotor nerve develops, the patient's function of the upper eyelid muscle is impaired. Nystagmus or trembling of the eyeballs may occur. Often this condition leads to visual impairment.
To restore vision, the doctor asks the patient to draw the other half of an object in a drawing or take part in a certain type of computer game. The patient is asked to follow with his gaze the pencil in the doctor’s hand, which moves in front of the patient’s face to the right, then to the left, up or down. The patient should follow the pencil without turning his head. To improve blood circulation, eye massage is necessary and beneficial. The eyes are closed, with gentle movements in a circle the patient massages the eyeballs, lightly pressing on them. The exercise should be performed for 10-20 seconds.
To restore visual function, a number of eye exercises are performed:
- Rotate the eye to the right, then to the left - repeat several times.
- Look up, then down - repeat the movement several times.
- Movement of the eyes in a circle - to the right, then to the left.
- Take a short break with your eyes closed, open your eyes and blink frequently for a few seconds.
- Close your eyes tightly and relax - repeat several times.
- Fix your eye on the object, then turn your head to the right and left without taking your eyes off the object - do this several times.
One of the primary tasks of the recovery period after a stroke is the restoration of motor function of the limbs. It is to them that the neurological deficit in this disease is largely confined. You need to start restoring movements almost from the first day after the stroke occurs.
General features of the exercises are characterized by the following points:
1. Decreased muscle tone and tension. Any stroke causes paralysis, characterized by muscle hypertonicity and increased excitability;
2. Improved microcirculation. A stroke disrupts the innervation of all tissues. As a result, their blood supply is disrupted;
3. Prevention of contracture. Against the background of long-term neurological deficit and spastic paralysis, stiffening of the muscles, which are in a state of constant tension, additionally occurs;
4. Protection of the skin of the extremities from bedsores. This is especially true for the legs. In places of greatest pressure and contact, which are the heel areas, bedsores most often occur;
5. Resumption of subtle movements. They are among the most important functions of the limbs, which actually characterize the complete restoration of the nervous system. This is most relevant for the hands and upper limbs in general.
Before starting any exercises after a stroke, it is advisable to consult with your doctor, or even better, with a specialist - a rehabilitation specialist. It will help you not only choose the right set of exercises, but also tell you about all the subtleties and stages of their implementation. In general terms, it is worth pointing out this feature: all exercises should begin from simpler ones with a gradual expansion of their volume depending on the patient’s functional abilities.
Against the background of physical therapy, even patients with an identical problem and severity of stroke can recover differently. Therefore, you should not overload a person too much. This is just as harmful as no therapeutic exercises at all. Before performing any set of exercises, it is better to warm up the tissues on which their action will be directed. If possible, warm water procedures are suitable for these purposes. If there are contraindications or other reasons why this action is not feasible, a light massage for 15 minutes immediately before exercise will be sufficient. As a last resort, you can warm the affected limbs using a heating pad.
All patients after severe strokes with severe neurological deficits must be helped by someone close to them, since they are not able to cope with such a task on their own. It is better if the set of exercises is performed 2-3 times a day in short courses that take about one hour. They should not cause severe fatigue and overwork in the patient. If any arise, this indicates an incompatibility between the loads and the patient’s actual abilities at a specific stage of the rehabilitation period.
A strict individual approach with strict adherence to the general rules of physical therapy can be called the only right step towards the rapid recovery of patients after a stroke.
Exercises while in bed
Of course, in this case it is extremely difficult to do anything on a large scale, since the functional abilities of patients are very limited. Therefore, it is necessary to help the people around such patients. This set of exercises should be performed by all persons in the acute period after any stroke, as well as by those who have severe spastic paralysis of the limbs with a pronounced increase in muscle tone. Such patients are unable to straighten their limbs, as they are firmly fixed in a bent position. Exercises should be aimed at reducing tone and gradually increasing the range of movements.
A typical gymnastics routine looks like this:
1. Simple extension and flexion of fingers and hands, forearms and elbows, feet and knees, movements of the limbs in the shoulder and hip joints;
2. Rotational movements of the indicated segments. Performed with the help of those caring for the sick. They should imitate the movements that a healthy person is capable of performing;
3. Exercise to restore the arm. Stretching spasmodic limbs using splints and other devices. Indicated for persistent paralysis. To do this, the bent limb is gradually unbent from the fingers and fixed with a bandage to a hard flat board or other device. The same actions are carried out step by step with the overlying areas of the hand (hand and forearm). In this position, the limb is fixed for half an hour, but it can be longer if it does not cause discomfort to the patient;
4. A towel is hung above the bed. The following exercise can be performed by persons with restored hand function. To do this, grab the towel with it and perform all possible movements (abduction and adduction, raising and lowering at the shoulder, flexion and extension at the elbow). Gradually the towel is raised higher and the exercises are made more difficult by the patient’s own weight;
5. From a strip of rubber of medium thickness and width, you need to make a ring with a diameter of 40 cm. Using this device, you can perform a large number of exercises. It is thrown between the hands, forearms, arm and leg, hand and any object. At the same time, the elastic band is stretched by moving its ends apart from each other;
6. To eliminate muscle spasm of the lower limb, a hard cushion is placed in the popliteal region, the thickness of which gradually increases. In this way, muscle stretching and increased range of motion are achieved;
7. Grasping the shins above the ankle joint with further flexion and extension of the legs at the knee joints by sliding the feet along the bed;
8. Lying in bed, you need to smoothly raise your arms above your head and try to grab the back of it. After this, partial pull-ups are performed with simultaneous stretching of the feet and fingers (as if stretching);
9. Exercises for the eyes. Restores the function of eyeball mobility and vision adaptation. To do this, you need to move your eyes in different directions several times. Circular movements. Repeat the procedure with closed eyelids;
10. Fixation of the gaze at one point, followed by rotational, nodding and circular movements of the head without moving away from this point of fixation;
Exercises while sitting
They are aimed at restoring purposeful arm movements, strengthening the back and preparing the legs for walking. Their technique is like this:
1. The patient is transferred to a sitting position and grabs the edges of the bed with his hands. As you inhale, you bend your back while simultaneously stretching your torso in a state of tension. As you exhale, relaxation follows. The cycle consists of 8-10 repetitions;
2. Starting position sitting on the bed, legs at body level (do not lower). Alternately raise and lower the left and then the right leg several times;
3. Starting position sitting in bed. Hands are pulled back. As you inhale, bring your shoulder blades as close as possible to each other while simultaneously throwing your head back. As you exhale, relaxation follows;
Exercises while standing
Indicated after expansion of the motor regime and partial recovery of the patient. Their main goal is to restore fine movements to maximize the elimination of neurological disorders. Typical examples look like this:
1. Lifting a matchbox from the floor or table. Practices targeted subtle movements;
2. Starting position standing with arms down. As you inhale, raise your arms above your head, simultaneously stretching and standing on your toes. As you exhale, relax, bending your torso down and lowering. Repeat several times;
3. Flexion and extension of the hand into a fist using an expander while simultaneously moving the arms away from the body;
4. In a standing position, feet shoulder-width apart, hands placed on the belt. The body is tilted to the right and left, back and forth;
5. From the previous starting position, perform the scissors exercise (alternately moving crossed arms outstretched in front of you to the opposite side;
6. Squats from a standing starting position with feet connected. During the exercise, you need to keep your back as straight as possible and not lift your heels off the floor;
While performing exercises related to the stage of restoration of fine movements, you can continue gymnastics from the previous stages, especially if it strengthens the muscles and expands the range of movements in general. Physical therapy using light dumbbells and strength exercises is allowed.
In order for physical therapy to truly be restorative in nature, it must become part of the patient’s lifestyle.
Restoring fine motor skills after stroke
Fine motor skills are restored with the help of simple exercises that allow you to restore fine hand movements and finger flexibility. The most effective activities for restoring fine motor skills are putting together puzzles, various objects from small parts of a construction set, drawing, fastening buttons on clothes, and lacing shoes. To restore the function of the hand and fingers, the patient is asked to take two nuts in his hand and roll them with the movement of the palm and fingers. Recommended for patients after a stroke to develop fine motor skills:
- Sort through the beans and peas, separating the peas from the beans.
- Use special silicone hand trainers with spikes to massage your palms and fingers.
- Tighten and unscrew nuts, close and open the lock with a key, turn on and off the lights in the room, write texts.
Restoring speech after a stroke
Speech function after a stroke is restored much worse than motor function. Its recovery can take a long time, over several years. Speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital are developing a program and working with the patient to restore speech throughout the entire period of his stay in the hospital; after discharge from the hospital, his relatives are involved in the patient’s rehabilitation. To restore speech, the following techniques are used:
- Pronunciation of an incomplete word - the patient must complete the word independently.
- If speech function is completely lost, rehabilitation begins with the pronunciation of individual sounds.
- When the patient learns to pronounce words, he is forced to repeat short poems and sayings.
- Singing is considered one of the best methods of speech restoration.
- In order for the patient to learn to speak faster, the facial muscles and tongue muscles should be trained. For this purpose, the patient is taught to curl his lips into a tube, stick his tongue out of his mouth as far as possible, and lick his lips with his tongue, first in one direction, then in the other. Lightly bite your lower lip, then your upper lip, and bare your teeth.
Make an appointment
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The “disadvantage” of kinesitherapy can be considered the need for regular and long-term training
Like any other technique, Bubnovsky’s rehabilitation program has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include the versatility of the method - it is suitable for the treatment of many diseases and injuries; safety, since it does not involve the use of drugs; no restrictions on gender and age; preventive effect - the likelihood of relapse is reduced; general health – after a course of rehabilitation, the patient’s immunity and muscle tone increase. The technique is patented, that is, all the necessary permits are available.
The disadvantages of the method are the regime, that is, the need to follow the prescribed training regimen, as well as the long onset of the effect. According to Dr. Bubnovsky, it is better to gradually restore lost functions after a stroke than to achieve positive dynamics through the use of chemicals.
Rehabilitation of the patient at home
Before the patient is discharged from the hospital, relatives receive recommendations on caring for the patient after a stroke. Recommendations for rehabilitation will be provided by the attending physician. The rehabilitation exercise program is performed every day without breaks, 2-3 times a day. Performing physical exercises should not tire the patient or cause him pain. Exercises in a sitting position help prepare the patient for walking.
When the condition improves, exercises are performed in a standing position; they help eliminate neurological disorders as much as possible by restoring fine movements. The patient performs exercises with an expander. From a standing position, he bends down and picks up a matchbox from the floor. Performs breathing exercises with raising your arms up while inhaling, standing on your toes, then lowering yourself onto your entire foot, lowering your arms, exhaling, leaning forward. A comprehensive recovery program is aimed at reducing muscle tone, improving blood circulation, preventing joint contracture, restoring and maintaining fine motor skills, speech, preventing the formation of bedsores and the development of inflammatory processes.
The Yusupov Hospital uses modern rehabilitation methods, uses various types of exercise equipment, and physical therapy exercises. Rehabilitation doctors develop an individual rehabilitation program for each patient.
Other therapeutic exercises
In addition to physical therapy, the following are used to treat spinal hernia:
- Bubnovsky method;
- exercises according to Dikul;
- water gymnastics;
- yoga and pilates.
Each of these methods has its own characteristics. Before you start performing them, find out their differences from conventional physical therapy, the benefits and harms of a hernia, when you can do it or not.
According to the Bubnovsky method
Dr. Sergei Bubnovsky wrote about back hernia in the book “Spinal hernia is not a death sentence.” He developed most of the exercises taking into account the simulators that are available in his clinic.
Opinions about the method are mixed. There are many cases that after treatment in his clinics hernia:
- not only did it not decrease, but increased, it was even necessary to resort to surgery;
- the pain disappeared in one place, appeared in another, requiring hospital treatment and even surgical intervention.
The main reasons for failure are rigid, heavy exercises, which are strictly prohibited in case of a spinal hernia (strength loads, twisting).
If you still decide to try gymnastics using this method, avoid training that is prohibited if you have a back hernia. It is better to do the complex for prevention, when the acute phase has passed, there is no pain.
According to Dikul
Exercises suggested by Valentin Dikul, director of a rehabilitation center for patients with back injuries, have a good effect on the spine. You can learn about his method in his book “Treating the back from hernias and protrusions.” He offers different types of training, including standard therapeutic exercises that can be performed for spinal hernia (half-cobra, cat).
The complex that Dikul offers consists of several stages:
- Exercises aimed at eliminating pain. They are performed with a small amplitude, without additional load. Basic movements are a standard exercise therapy complex. Course – 3 times a week for 2-4 months.
- Exercises aimed at strengthening muscles are a rehabilitation period when the pain has gone away. At this stage, you can include strength training. Course – 4 times a week for 2-3 years.
- Complete workouts designed taking into account the presence of a hernia, without negative effects on the affected area.
Exercises must be performed in strict sequence, do not change places, and do not increase the number of repetitions. The load (light dumbbells) can be taken no earlier than the complex is mastered and the pain disappears. Between exercises you need to rest for 2-3 minutes.
Exercises in water
Swimming gives good results in the treatment of spinal hernias. Water relieves stress from the back and calms the nervous system. It helps to better stretch the space between the discs and reduce the pressure of the hernia on the nerve fibers. The main thing is to choose the right instructor and exercises.
The following activities have a good effect:
- The face is lowered into the water, the arms are extended, holding a swimming board (you can use a crossbar installed around the perimeter of the pool), the back is straight. The legs swim in the crawl style.
- Lie on your side, your right hand rests on the board, your left along your torso. The legs work in the crawl style.
- Swim on your back. Hands hold the board on your stomach, legs swim in crawl style.
If the pool is shallow (water up to your chest), you can take steps in place with your knees raised high. At this time, the arms move as if running. Gentle turns of the body to the right and left have a good effect.
The only contraindication for water exercises is the acute phase of pain. Jumping into the water is strictly prohibited. You can't swim with your head held high. The breaststroke and butterfly styles are undesirable.
Yoga and Pilates for hernia
Yoga and Pilates are based on slow loads without overexertion. They improve the condition of muscles, tendons, and stretching. But with a herniated disc, many exercises are prohibited (bridges, twisting, strong stretches). Moreover, they cannot be done during an exacerbation period.
When giving preference to these methods, pay attention to exercises that are designed specifically for spinal hernia. The basic complex is not much different from exercise therapy - cobra, cat, bird-dog.
During the period of pain, avoid any strength or other prohibited exercises. If pain occurs, stop exercising. Additional equipment that is often used in Pilates (dumbbells, other weights) can be taken only at the stage of remission, when the pain has gone.