Risk factors for cardiovascular disease
Risk factors are not the cause of the disease. Risk factors are external influences and internal characteristics of the body that contribute to the development of the disease. There are modifiable factors - those that a person can change. And unmodifiable, which cannot be influenced.
| Modifiable risk factors | Non-modifiable risk factors |
|
|
In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to psychological factors. Anxiety, social isolation, depression and low levels of social support have an adverse effect on the formation and progression of cardiovascular diseases.
Briefly about the types of cholesterol
In the results of a laboratory blood test, you can find several indicators:
- Total cholesterol - the figure consists of the values of lipoproteins of different densities.
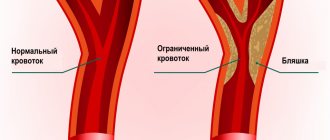
- LDL is a low-density lipoprotein that is deposited as fatty deposits on the inner walls of blood vessels.
- HDL is high-density lipoprotein, the so-called “good” cholesterol, which rids cells of “bad” cholesterol, transporting it to the liver, where catabolism and breakdown occurs.
- VLDL is a very low density lipoprotein produced in the liver from triglycerides. High values indicate cholesterol deposition on artery walls.
- DILI – intermediate density lipoproteins, a type of “bad” cholesterol. Elevated values warn of the risk of atherosclerosis.
There is no single cholesterol standard for all people - the level depends on age, gender, concomitant and previous diseases. Therefore, you should not try to decipher the obtained analyzes yourself. Only an experienced doctor can do this correctly.
What is important for the prevention of heart and vascular diseases?
It is timely to identify patients who DO NOT YET have symptoms of the disease, but ALREADY HAVE laboratory signs of lipid metabolism disorders. One of the main risk factors for fatal cardiovascular complications is elevated cholesterol levels. It is for this reason that in order to assess your personal risk of cardiovascular disorders, it is necessary to examine your blood cholesterol levels.
The higher the risk of cardiovascular diseases, the more radical the prevention measures should be!
- Stop smoking! There is no safe amount of cigarettes. Smokeless tobacco and e-cigarettes are not able to reduce the negative impact on the cardiovascular system.
- Increase your physical activity! Moderate physical activity totaling at least 150 minutes per week or vigorous physical activity for 75 minutes per week will be effective.
- Keep your body weight under control!
- Balance your diet! You must consume at least 5 servings of fresh vegetables and fruits per day. Limit the amount of sugar, table salt, and saturated fats in your diet.
- Monitor laboratory parameters of lipid metabolism!
Laboratory research
- Risk of developing atherosclerosis (screening)
- Risk of developing atherosclerosis (advanced)
Biotransformation of cholesterol
Biotransformation (conversion) into bile acids is the main stage in the metabolism and removal of cholesterol from the body. Bile acids are necessary for:
- digestion of fats (emulsify, transform into a soluble state);
- activation of digestive enzymes of the pancreas;
- absorption of fats in the intestines.
Primary fatty acids (cholic and chenodeoxycholic) are formed in the liver. They enter the bile capillaries from hepatocytes, accumulate in the gallbladder and are released into the duodenum when eating. Enzymes of beneficial intestinal microorganisms convert primary bile acids into deoxycholic and lithocholic acids.
Primary and secondary bile acids are involved in the digestion of fats, then the main amount (about 98-99%) returns back to the liver through the portal vein system. A small amount of bile acids is excreted in the feces, this is the main way to remove cholesterol from the body. To replace the excreted bile acids, new ones are formed from cholesterol reserves.
Less significant (in terms of quantity) processes of cholesterol biotransformation include its conversion into hormones and vitamin D.
A healthy lifestyle: losing excess weight, regular exercise, and a low-fat diet eliminate cholesterol metabolism disorders. However, if positive lifestyle changes do not have a significant effect on LDL or VLDL levels, your doctor will prescribe cholesterol-lowering medications.
Diet
The diet should include two components:
- Maximum reduction in food intake of foods high in cholesterol (see Table No. 1). Eating dietary meat - rabbit, turkey; low-fat dairy products. It is good to replace dairy products (cottage cheese, cheese) with soy products. Reducing the total calorie content of food, especially if you are overweight. Take no more than 300 mg of cholesterol per day with food, see table
- Eating foods with natural lipotropic properties, i.e. Due to the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids in these products, cholesterol levels decrease. These include vegetable oils: flaxseed, corn, pumpkin, olive, walnut. Other vegetable oils do not have this lipotropic effect. Gradually replace butter with these vegetable oils and completely switch to taking and using only these oils in cooking. I recommend eating fatty fish of the following varieties: mackerel, herring, sardines, tuna, halibut.
Many seafood contains cholesterol, but due to the presence of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in fatty fish, it helps break down and eliminate cholesterol. Seafood such as shrimp, squid, octopus, where there is no fat and therefore no omega-3, contains a lot of cholesterol, which enters the bloodstream when these products are consumed. Taking fish oil reduces cholesterol and triglyceride levels. So, according to V.E.Phillipson et al. (1985), the level of total cholesterol and triglycerides decreased by 27% and 64%, respectively, with the use of fish oil.
I remember being forced to drink fish oil in kindergarten. Of course, not for the prevention of atherosclerosis, apparently, for the prevention of rickets. I can still smell its disgusting smell and taste even now at the mere mention of “fish oil.” It’s good that fish oil is now available in capsules. The beneficial effect on lipid metabolism is due to the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids contained in fish oil. In addition to fish oil, preparations containing omega-3 are also produced.
Let's talk about drinking alcoholic beverages as a means of lowering cholesterol. Undoubtedly, drinking alcohol does not lower cholesterol. Moreover, alcohol irritates the liver, leading to fatty hepatosis and the development of cirrhosis. Drinking red natural dry wine helps improve the lipid profile due to the special substances contained in the skins and seeds of grapes. However, we must remember that the intake of dry red wine should be no more than 150 ml per day! Often, under the pretext of improving their health, people drink alcoholic beverages without following the suggested dosage.
Remember that even the most severe diet can reduce total cholesterol by 15–20%. Let me remind you that the main amount of cholesterol is synthesized by the liver.
According to the British Dietetic Association on Vitamins and Dietary Supplements, there is no evidence that taking vitamins, antioxidants and other dietary supplements helps prevent or treat atherosclerosis. However, according to Canadian scientists, a low-fat diet rich in plant styrene and dietary fiber can reduce low-density lipoprotein levels (Journal of the American Medical Association, 2005). Therefore, I will present a number of herbal preparations for the complex treatment of hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.
Collection: fruits of blood-red hawthorn – 15 g., fruits of chokeberry – 15 g., fruits of wild strawberries – 15 g. Pour two tablespoons of the mixture into 500 ml of water, heat in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, cool for 10 minutes, strain and bring the amount of broth to the original volume with water. Take 100 ml 3 – 4 times a day.
Now let's talk a little about garlic and the myth that it helps lower cholesterol. In 1972, a UNESCO expedition found clay tablets with mysterious recipes for traditional medicine in a Tibetan monastery. We managed to decipher them. The following was written there: “cleanses the body of fatty and lime deposits, dramatically improves the overall metabolism in the body, as a result of which all blood vessels become elastic. Thanks to this, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, sclerosis, the formation of various tumors are prevented, headaches and noise in the head disappear, and vision is restored. When the treatment is carried out accurately and meaningfully, the human body is completely rejuvenated.” In the late 70s of the twentieth century, this recipe for garlic infused with alcohol made the rounds of all popular science publications in the Soviet Union. Many people used it without any visible positive dynamics. Currently, it is of interest from the standpoint of studying the history of medicine. Although there are still followers of this recipe. In my medical practice, I also encountered patients who did everything strictly in accordance with the instructions, but without results.
It is interesting that in Russian folk medicine there is evidence of garlic as a rejuvenating agent. Garlic is a powerful biostimulant. It helps with dysbacteriosis, asthenia (lethargy, weakness, fatigue), helminthic infestation. It is no coincidence that Hare Krishnas (followers of one of the Indian religions) do not consume garlic along with alcoholic beverages and other substances. Since this stimulant will distract from the spiritual awareness of the postulates of Krishnaism, and therefore “enlightenment”.
An undoubted negative property of garlic is its sharp, specific smell. Now they sell garlic extract in special capsules in the pharmacy chain. It should be remembered that the use of garlic is contraindicated for persons with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, etc.). It has a strong irritant effect.
There are products that reduce cholesterol levels in the body and promote its elimination. These include: oatmeal, apples, plums, various berries, legumes (beans, peas), rice (especially brown). They all contain soluble fiber (pectin, gluten) and form a jelly-like mass when cooked. It is good to eat nuts. And also drink green tea. And if you add cardamom when brewing green tea, it will have a very interesting taste and is healthy. Green tea contains flavonoids, which strengthen the walls of blood vessels and have antioxidant properties. Flavonoids are also found in rose hips, black currants, chokeberries, and lemons. And these products are rich in vitamin C, which is also very useful for patients with hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis.
Juices from potatoes, beets, carrots, watermelon, cabbage, and pumpkin are useful for atherosclerosis. It is good to eat seaweed. A table has been compiled for your convenience.
General diet tips:
- Egg whites do not contain cholesterol, so substitute them for whole eggs in recipes (add 2 whites to each whole egg).
- When preparing soup, cool the meat broth and skim off the layer of congealed fat. When cooking, trim fat from meat and remove skin from poultry.
- Avoid fried foods.
- Combine meat dishes with vegetables or pasta.
- Season vegetable salads and snacks with lemon juice, herbs, spices (cardamom, celery, parsley, curry, garlic, etc.).
- Limit the use of mayonnaise, fatty sauces, and ketchup.
- If you want something sweet, oatmeal cookies or popsicles are your best bet in these situations.