On average, 7-10% of Russians have chronic heart failure (CHF), 4.5% suffer from clinical symptoms of heart failure that reduce quality of life and ability to work, and among people over 65 years of age, half of patients with cardiovascular diseases have symptoms of CHF, and These numbers are increasing every year.
Heart failure is a syndrome caused by abnormal structure and decreased function of the heart. It can be the outcome of diseases such as arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart defects, arrhythmias, kidney and thyroid diseases, cardiomyopathies, hereditary or as a result of infections, intoxications, metabolic and other disorders.
The heart works, the heart does not sleep
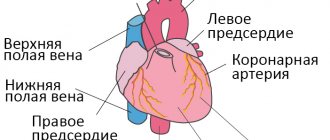
Heart... An organ surrounded by a romantic halo, awarded the attention of writers, musicians, poets... The heart is a unique symbol of love; we associate our feelings and emotions with it. If you descend from heaven to the “sinful” earth and briefly and prosaically define what a heart is, you will get something like this: “the heart is a strong muscular pump capable of pumping blood throughout the body to provide tissues with oxygen.” It would seem like just a pump, but what a pump! Able to work without sleep or rest for years, decades; capable, if necessary, of instantly changing the operating mode. And all this thanks to its amazing structure - muscle, valves, its own circulatory system, innervation and many ingenious mechanisms of regulation and compensation both inside and outside the heart.
The heart is a “fiery motor”!
Normally, the heart is a strong muscular pump capable of pumping blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues of the body, as well as remove their waste products. Depending on whether we are resting or actively working, the body requires different amounts of nutrients. To meet the needs of the body, the frequency and strength of heart contractions, as well as the size of the lumen of blood vessels, can vary significantly. What happens when the heart stops sufficiently supplying tissues and organs with oxygen and nutrients? In this case, doctors diagnose heart failure (HF). The disease is usually chronic and the patient may live with it for many years before being diagnosed.
Symptoms of heart failure
The symptoms are associated with the inability of the heart to provide adequate blood circulation and the development against this background of congestion in the pulmonary and systemic circulation (in the vessels of the lungs and the vessels of other organs and systems). Stagnation of blood in the lungs interferes with its normal saturation with oxygen and is manifested by shortness of breath. Edema - stagnation in the systemic circulation disrupts the functioning of almost all organs. Patients feel:
- increased fatigue;
- shortness of breath;
- swelling of the legs and feet;
- pain or discomfort in the abdominal cavity due to liver enlargement.
Symptoms of heart failure develop gradually and can sometimes go unnoticed for a long time, so it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations. At the cardiology center of the Federal Medical and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency, you can undergo a comprehensive heart examination in order to promptly recognize this syndrome and the diseases that accompany it.
“Glitches”, “coughs”, “sneezes”... Who is to blame?
There are many reasons for the development of heart failure. Among them, the most important place is occupied by coronary heart disease or insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. Ischemia, in turn, is caused by blockage of the heart vessels with fat-like substances. A heart attack can also cause heart failure because some of the heart tissue dies and becomes scarred. Arterial hypertension is another common cause of insufficiency. The heart requires much more effort to move blood through the spasmodic vessels, which results in an increase in its size, in particular the left ventricle. Later, weakness of the heart muscle or heart failure develops. Causes that influence the development of heart failure include cardiac arrhythmias (irregular contractions). A number of beats of more than 140 per minute is considered dangerous for the development of the disease, because At the same time, the processes of filling and ejection of blood by the heart are disrupted. Changes in the heart valves lead to disturbances in the filling of the heart with blood and can also cause the development of heart failure. The problem is usually caused by an internal infection (endocarditis) or a rheumatic disease. Risk factors for the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system, and, ultimately, heart failure, can also include excess weight, a sedentary lifestyle, alcohol and drug addiction, and hormonal disorders.
Causes of the disease
The main causes of acute heart failure include the following diseases:
- pulmonary embolism;
- myocardial infarction;
- decompensation of CHF;
- cardiac tamponade;
- acute valvular insufficiency;
Heart rhythm disturbances and injuries to the heart muscle can also cause the disease.
The main reasons leading to the development of chronic heart failure:
- cardiosclerosis;
- angina pectoris (chronic ischemic heart disease);
- diseases of the valve apparatus of the heart muscle;
- arterial hypertension;
- chronic pulmonary heart disease.
Listen to your heart
Thus, heart failure is not an independent disease, but a stage of heart disease. Its severity and speed of development can vary and depend on the severity of the primary heart disease, the patient’s lifestyle, his age, concomitant diseases and, finally, on the quality of treatment. Heart failure is manifested by such symptoms as increased fatigue, swelling of the legs, shortness of breath, asthma attacks, causeless weight loss, etc. Any of these symptoms, especially taken individually, can occur in a variety of diseases. Therefore, the correct diagnosis is made, unfortunately, rarely and most often in the later stages of the disease. Thus, significant weight loss, which is typical for severe degrees of heart failure, is often mistaken for a sign of cancer. Or, for example, harmless swelling of the legs caused by stagnation of lymph gives rise to a diagnosis of “heart failure.” In my practice, there was a case when a patient with a severe form of heart failure was treated for several months for... constipation.
Treatment of the disease
It is necessary to distinguish between the treatment of heart failure occurring in acute and chronic form.
Treatment of acute heart failure. This disease begins sharply and suddenly. It grows quickly and then turns into an attack of suffocation. There is a severe cough with expectoration of foamy contents and other symptoms of pulmonary edema or cardiac asthma. Therefore, treatment of heart failure begins with calling a doctor and providing first aid. The patient is admitted to the hospital, where he is under strict supervision. The cardiologist, in accordance with the patient’s condition, prescribes an appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment of chronic heart failure. It is usually carried out at home. The process begins with treating the disease that caused the syndrome to develop. It is important to maintain psycho-emotional peace and engage in physical therapy in a medical institution (only under the supervision of a specialist with appropriate education).
A diet must be prescribed, limiting fluid intake to 1,200 ml and salt to 4 g (sometimes to 1-2 g per day). Food should be high in proteins, minerals and vitamins. Consumption of carbohydrates and fried foods is necessary to reduce the risk of obesity. Patients with heart failure are prohibited from eating spicy foods.
If edema is present, diuretics are prescribed. Sometimes they are combined with drugs containing potassium. During the period of use, you need to monitor the results of a blood test to determine the level of uric acid, potassium, sodium and monitor the acid-base balance.
Surgical methods for treating heart failure. Such treatment methods include:
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- operations on heart valves, which lead to a decrease in the load on the myocardium;
- heart transplantation.
Sad facts
Meanwhile, the prognosis for heart failure is unfavorable, if not fatal. When some primary symptoms of the disease (for example, pulmonary edema) appear, there is immediately a threat of death. These statistics are disappointing - within 3-5 years, 50% of patients die from heart failure, and after 9 years only 0.2% remain alive, of course, provided that the disease was not treated appropriately. Conventional drug treatment can only keep such patients alive in a state of severe disability with frequent hospitalizations. Of course, there is a radical way to help them - transplant a new heart. However, significant limitations for this intervention (age limit, high cost of surgery, lack of a sufficient number of donor hearts) make it unrealistic for the majority of heart failure sufferers. Now they have begun to talk about a new, promising method of restoring decrepit heart muscle, based on planting so-called “stem” cells. But, unfortunately, for practical use this is a matter of a rather distant future.
Stages of the disease
There are several classification options for heart failure by stage. The New York Heart Association proposes dividing CHF into 4 functional classes:
- FC 1 - absence of symptoms (shortness of breath, palpitations, weakness) during physical activity.
- FC 2 - shortness of breath and weakness occur with moderate physical activity. Load resistance is reduced. At rest there are no complaints.
- 3 FC - symptoms of HF are present at rest, but when performing minor physical activity they intensify.
- 4 FC - inability to perform minimal physical activity without increasing shortness of breath, palpitations, weakness, which is also present at rest.
... and the other side of the coin
At the same time, in recent years, the development of medical science and pharmacology, in a successful combination with medical experience, has made it possible to achieve amazing success in the treatment of even the most severe forms of heart failure. Patients manage not only to save life, but also to regain its quality, an active lifestyle, and regain weight (and this after losing 20-30 kg!). Moreover, all treatment takes place on an outpatient basis, without hospital stay. Having worked for decades in a cardiac surgery center where there was a heart transplant department, I, along with other doctors, was a powerless witness to the death of patients after many months of fruitless waiting for donor hearts. How many of them could be saved thanks to today's knowledge, capabilities and experience!
Diagnostics
If you have symptoms of heart failure and high blood pressure, it is important to consult a physician or cardiologist as soon as possible. The earliest signs are shortness of breath on exertion and decreased exercise tolerance.
To make a diagnosis of CHF, a specialist will specify:
- Typical complaints are shortness of breath, increased fatigue, swelling of the legs, palpitations at rest and during moderate physical activity.
- History: duration of hypertension, coronary artery disease, previous heart attacks, myocarditis and other heart diseases, presence of respiratory pathology.
- Objective signs: an increase in heart size, heart rate and respiratory movements, blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, the presence of edema and enlargement of the liver, wheezing in the lungs, pathological tones in the heart.
To confirm systolic or diastolic dysfunction, doctors prescribe laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Blood test for natriuretic peptides. These are biological markers of CHF. Needed to monitor treatment. Normal levels of natriuretic peptides in untreated patients virtually exclude cardiac damage.
- All patients with suspected HF undergo a clinical blood test with platelet count, determination of blood sugar and glycated hemoglobin (determines the average blood sugar value over the last 3 months), a general urine test, blood creatinine, glomerular filtration rate, liver function indicators (bilirubin, AST , ALT, alkaline phosphatase, GGT), study of lipid profile (cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoproteins), blood sodium and potassium, total protein, thyroid hormones (TSH, T3 and T4), blood transferrin (for the diagnosis of hidden anemia).
- Echocardiography is an ultrasound method for diagnosing the heart, which allows you to determine the thickness of the myocardium and the volume of the chambers of the heart, the characteristics of all valves, the condition of the interatrial septum, pressure in the pulmonary artery, myocardial contractility with determination of the ventricular ejection fraction.
- ECG (electrocardiogram) is a study of the electrical potentials of the heart in 12 leads. At the same time, the heart rate, the correctness of the rhythm, the presence of cardiac conduction disorders in the form of blockades, myocardial ischemia, left ventricular hypertrophy, fresh and scar changes in heart attacks are assessed. With a normal ECG, the diagnosis of CHF is unlikely.
- Chest X-ray. Needed to detect an increase in heart size (cardiomegaly) and possible pathology of the bronchopulmonary system.
- Coronary angiography is a radiopaque examination of the coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle. Performed for heart failure or angina pectoris that do not respond to drug therapy. Helps determine the degree of coronary artery stenosis for the need for further surgical interventions.
- MRI of the heart and great vessels. It is carried out in complex diagnostic cases when echocardiography is not informative enough. A special role of MRI belongs to the diagnosis of cardiomyopathies and complex heart defects.
When should I make an appointment with a doctor?
Symptoms that occur with heart failure may vary.
Some of them are dangerous and require calling an ambulance, others are a reason for another visit to the doctor or an initial visit to an outpatient appointment. An ambulance should be called if:
- severe and prolonged shortness of breath;
- persistent chest pain that does not go away after taking nitroglycerin;
- hypertensive crisis that cannot be corrected with pills;
- fainting.
You should make an appointment with your doctor if you have symptoms such as:
- shortness of breath and cough at night, the need for additional pillows for a comfortable sleep;
- increased shortness of breath and deterioration of exercise tolerance;
- the appearance of interruptions in the activity of the heart, increased heart rate (more than 90 per minute), the appearance of bradycardia;
- increase in edema of the lower extremities;
- rapid weight gain (2 or more kilograms in 3 days);
- increasing fatigue and weakness;
- an increase in cough, the appearance of concomitant ARVI.
According to the feat and the reward...
Angioplasty and stenting of arteries
- Cost: 100,000 - 250,000 rubles.
- Duration: 40 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1-2 days in hospital
More details
I will not hide that the treatment of such patients, in addition to experience, requires considerable effort and time from the doctor and great pedantry in carrying out the patient’s prescriptions. However, it would be too arrogant to attribute all the successes in the treatment of heart failure only to yourself, as the attending physician. The ability to quickly and accurately diagnose the underlying disease that caused heart failure has a huge role. In 50% of cases, this is coronary heart disease, the identification and treatment of which with coronary angiography and angioplasty greatly facilitates the subsequent correction of myocardial weakness. Equally important for successful treatment is the identification of the earliest, so-called “preclinical” (i.e., before the onset of complaints) forms of heart failure, which is only possible with the use of instrumental research methods: echocardiography, Holter monitoring, stress tests. The Center for Endosurgery and Lithotripsy has not only the most modern equipment, but also highly qualified specialists, which is necessary for the detection and timely treatment of heart failure. All these conditions help to successfully achieve the task of long-term preservation of active life in one of the most severe categories of patients with heart disease - patients with heart failure. But the reward is high: over the past 5 years, there has not been a single death among my 187 patients with heart failure!
4.Diagnosis of the disease
A special test called ejection fraction (EF) . It helps determine how well the heart pumps blood with each beat and can be used to diagnose both systolic and diastolic dysfunction. Ejection fraction as a percentage measures the amount of blood pumped with each beat.
In patients with systolic heart failure, the ejection fraction is less than 40%. Other diagnostic tests such as an echocardiogram or cardiac ultrasound can show how the heart is dilating and not pumping out enough blood with each beat.
Patients with diastylic heart failure have a normal ejection fraction test and their heart is pumping well, but an echocardiogram will show that the heart is not filling sufficiently during the relaxation phase that occurs between beats.
For timely diagnosis of heart failure, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist and periodically undergo a comprehensive cardiac examination.