Get a consultation Hemorrhoids are a common pathology of the vascular system. As a rule, it occurs for various reasons: poor nutrition, heredity, sedentary lifestyle and others. Most people do not pay attention to the symptoms of hemorrhoids because they consider them not serious. But if such a disease is not treated, it progresses, and complications develop over time, for example, acute thrombosis of the hemorrhoid. This condition is accompanied by pain and is quite dangerous, as it can lead to death. Surgical intervention will help prevent the latter. This treatment for hemorrhoidal thrombosis is also carried out in Cheboksary. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis and quickly relieves the person of discomfort.
This disease is very dangerous, hemorrhoidal thrombosis, treatment for this reason must be prescribed immediately.
The essence of thrombectomy of hemorrhoids
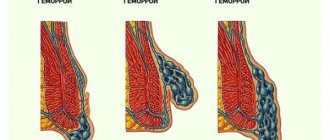
Most often, thrombosis is observed in the later stages of hemorrhoids: it causes physical suffering to the patient and knocks him out of the usual rhythm of life. Complications of the disease can develop inside the rectum, on the outside of the anus, and sometimes in combination. This disease is accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, and swelling.
External changes are observed only with thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid. The latter falls out of the rectum and cannot be reduced. At the same time, it is red or purple in color and increased in size. At the same time, there are no external signs of internal thrombosis of the hemorrhoid. Changes in the mucous membrane can only be detected by rectoscopy and palpation.
External excision of the hemorrhoid will help relieve acute symptoms. Surgery occurs under local anesthesia. Its essence is as follows: a thrombus is removed from a thrombosed nodule through an incision (5 mm). As a result of surgery to remove thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, the pain goes away almost instantly.
Attention! Surgery only removes the blood clot and the symptoms it causes, but does not in any way affect the cause of hemorrhoids.
How does a blood clot occur?
A blood clot can occur as a result of:
- Changes in intra-abdominal pressure;
- Injuries to perianal tissues;
- Hypothermia.
Why might pressure in the abdominal cavity rise?
- After strong pushing (constipation).
- After lifting something heavy.
- After natural childbirth.
What else can contribute to the formation of blood clots?
- Sedentary lifestyle, reduced activity.
- Large loads (static).
- Psychological discomfort, stress.
- Junk (spicy) food and alcoholic drinks.
It all starts with venous stagnation in the pelvis. Under the influence of one or more unfavorable factors, the venous plexus is deformed, the structure of the inner wall of the vessel is disrupted, platelets stick together, fibrin falls out, and a blood clot is formed. With the formation of a blood clot, venous stagnation begins, swelling appears, and inflammation develops. This is accompanied by pain; during defecation, feces affect the node, which leads to damage and thrombophlebitis. You will not be able to correct the situation on your own, so immediately make an appointment and examination with a doctor. The hospital will carry out the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe surgery. First you need to identify the nature of thrombosis:
- Internal;
- External;
- Combined.
When is thrombectomy necessary?
At the initial stages of development of thrombosed hemorrhoids, doctors prescribe drug therapy. It consists of using anti-inflammatory ointments and suppositories. The latter reduce swelling and relieve pain. Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is recommended only at the third stage of the disease.
There are certain indications for thrombectomy:
- severe pain syndrome;
- acute form of hemorrhoids;
- significant risks of developing necrosis;
- insufficient effectiveness of drug treatment.
In some cases, such surgical intervention is the only acceptable method of treating hemorrhoids. This applies to those patients who suffer from allergies to medications and are in poor health.
Types of operations
Hemorrhoids complicated by thrombosis can be removed using several methods. Their choice depends on the severity of the person’s condition and existing contraindications.
Types of thrombectomy:
- Thrombolysis. The procedure involves the prolonged administration of drugs into the vessel that soften the blood clot.
- Rheolytic. A puncture of the vascular areas is performed to remove blood clots with a catheter.
- Aspiration. The clot is removed with a syringe. This treatment method does not prevent relapses of the disease.
The method of surgical treatment of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is determined by a specialist after a thorough examination of the patient.
Aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI
ACC/AHA/SCAI 2015 Summary Update of Guidelines for Primary Percutaneous Coronary Interventions for Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Supplement to Guidelines
| 2013 Recommendations | Brief updated recommendations 2015 | Comments |
| Class IIa: Mechanical aspiration thrombectomy is appropriate as part of primary PCI. (Level of Evidence: B) | Class IIb The benefit of selective and emergency aspiration thrombectomy during primary PCI has not been well studied. (Level of Evidence: C) Class III: no benefit Routine aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI does not provide any benefit. (Level of Evidence: A) | The recommendation has been changed (transition from class “IIa” to class “IIb” for selective and emergency aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI). New recommendation (“Class III: no benefit” for routine aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI). |
The Class IIa recommendation for aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI in the 2011 PCI guidelines and the 2013 ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction guidelines was based on the results of two randomized controlled trials and one meta-analysis and was largely dictated by the results of the TAPAS , which assessed thromboaspiration during primary PCI for acute myocardial infarction. In this single-center, randomized trial, 1071 patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction underwent primary PCI with prior thromboaspiration or primary PCI alone.
Three multicenter studies contributed to the revision of this recommendation, two of which included many more patients than previous studies of aspiration thrombectomy. In the INFUSEAMI evaluating intracoronary abciximab and aspiration thrombectomy in patients with large anterior myocardial infarction, 452 patients with anterior ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction due to occlusion of the anterior interventricular branch in the proximal or middle segment did not observe a decrease in infarct size when performed. aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI.
In the TASTE (n=7244), there were no significant differences between primary PCI with prior aspiration thrombectomy and primary PCI without aspiration thrombectomy at 30 days or 1 year postprocedure in mortality, recurrent infarction, stent thrombosis, or target revascularization. lesions or a difficult endpoint (major adverse cardiac events).
TOTAL study , emergency thrombectomy was performed in 7.1% of cases in the standard PCI group, but the conversion rate from the PCI with aspiration thrombectomy group to the standard primary PCI group was only 4.6%. There were no differences between treatment groups in the composite primary endpoint (CV mortality, recurrent myocardial infarction, cardiogenic shock, NYHA class IV heart failure at 180 days) or in individual components of the primary endpoint, or in stent thrombosis or revascularization. target vessel. Along with this, a small but significant increase in the incidence of stroke was observed in the aspiration thrombectomy group.
Recent results from a meta-analysis of 17 studies (n=20,960), including these 3 studies, showed no significant reduction in mortality, recurrent infarction, or stent thrombosis with routine aspiration thrombectomy. There was a small and nonsignificant increase in the risk of stroke for aspiration thrombectomy. Several previous studies have shown that a large thrombotic load in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is independently associated with an increased risk of distal embolization, no-reflow, transmural myocardial necrosis, major adverse cardiac events, stent thrombosis, and death. However, subgroup analyzes of the TASTE and TOTAL trials showed no significant benefit of aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI in patients with a large thrombotic load, or in patients with a primary TIMI flow score of 0-1, or in patients with anterior interventricular branch infarction.
Based on the results of these studies, the previous class IIa recommendation for aspiration thrombectomy has been modified. Currently, routine aspiration thrombectomy before primary PCI is not recommended (Class III: no benefit, level of evidence A). There are currently insufficient data to evaluate the potential benefit of selective or emergency aspiration thrombectomy (Class IIb, Level of Evidence C).
“Emergency” thrombectomy is referred to in cases where thrombectomy was not initially planned, but the decision to perform it was made during the procedure due to an unsatisfactory result or complications, by analogy with the concept of “emergency” administration of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa. It should be noted that these recommendations and text apply only to aspiration thrombectomy. The clinical benefit of routine rheolytic thrombectomy during primary PCI in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction has not been demonstrated.
Contraindications
For an experienced surgeon, removing a blood clot is not a difficult operation. The manipulation itself does not require intravenous anesthesia, so there are very few contraindications to it.
The main limitations to surgical treatment:
- blood poisoning;
- significant exhaustion of the body;
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa;
- infectious lesion in the pararectal area.
Attention! Thrombectomy of a hemorrhoid during pregnancy and lactation is carried out only in case of strong need.
Indications for thrombectomy
Thrombosed hemorrhoids disrupt the patient’s usual lifestyle and bring excruciating pain. KDS CLINIC offers emergency medical care and two ways to solve the problem:
- medicated
- surgical
The main goal of the medicinal procedure is to relieve the inflammatory process and relieve pain. In especially severe cases, treatment takes a long time and the course lasts up to 4 weeks. When the pain becomes unbearable, proctologists recommend immediately using radical therapy - thrombectomy of hemorrhoids. Often, patients can independently insist on surgical treatment, without waiting for the effect of long-term drug treatment.
Indications for surgical operations are:
- Ineffectiveness of drug therapy.
- Severe pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers.
- Symptoms of acute hemorrhoids, accompanied by the appearance of a thrombosed node.
- The desire to get rid of hemorrhoids quickly and effectively.
- Reluctance or inability to undergo long-term drug treatment.
Preparation for the procedure
On the eve of planned surgical treatment of hemorrhoids, the following studies are required:
- blood and urine tests;
- Wasserman test;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram;
- determination of glucose in blood.
At the same time, before the operation, the dinner should be light; foods that cause flatulence are not allowed. It is also recommended to perform two cleansing enemas a few hours before surgery (interval - about 60 minutes).
Pros and cons of the method
The disadvantage of the method is the impossibility of its use in severe pathological processes. Also, surgery does not guarantee the absence of recurrence of hemorrhoids in the future, but in the area of other hemorrhoidal vessels.
However, these disadvantages cannot be compared with the positive aspects of laser surgery:
- No blood loss;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Fast procedure;
- Possibility of using conduction and, in some cases, local anesthesia;
- No need for a long stay in the clinic;
- Almost instant effect: after a few hours the pain and other manifestations of hemorrhoids go away.
In any case, the surgical option is selected individually for each patient. And if the doctor recommends laser thrombectomy , the operation will bring only positive aspects.
We invite residents of Lobnya to undergo an ultrasound of the joints at the Harmony clinic!
What complications may arise
Most often, the operation and healing are quick and painless. Possible complications:
- wound infection;
- pain syndrome;
- bleeding.
For severe pain in the anus, the doctor prescribes suppositories and ointments with an analgesic effect. After 5-7 days, the need for medications disappears. Infection and bleeding occur if hygiene is not observed. It is worth noting that the cost of hemorrhoidal thrombectomy is quite affordable for patients. The surgical procedure takes no more than 15 minutes. With proper preparation for surgery and following the doctor’s recommendations, complications are practically excluded. The patient recovers quickly and returns to his normal lifestyle.
If any complications occur, contact the proctology center immediately.
To get a consultation
Symptoms of node thrombosis
- Acute pain in the anus. The patient has difficulty moving and cannot sit.
- The prolapsed hemorrhoidal node acquires a dark shade, even black.
- Swelling and redness appear around the anal area.
- A mucous discharge with an unpleasant odor comes from the anal canal.
- When emptying, severe pain occurs.
- Defecation is almost impossible.
- Inflammation causes intoxication of the body (pain, fever, chills).
If you do not start removing the hemorrhoid using thrombectomy in time, there is a risk of getting a purulent complication and tissue necrosis.