Left bundle branch block is a disruption of the normal signal conduction from the sinus node to the ventricle. Hence the decrease in contractility, hemodynamic problems, hypoxia, ischemia and deviations in the functioning of all internal organs.
Since this is not an independent disease, you need to look for the root cause. It is possible to restore vital activity and functional activity with sufficient efficiency only with long-term therapy. In extreme cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
The mechanism of pathology development
The essence of the deviation lies in the disruption of the conduction of an electrical impulse through special fibers.
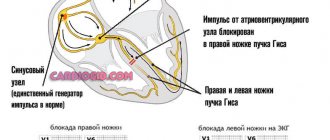
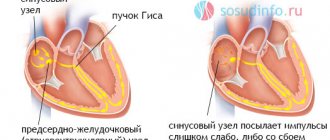
In the normal state of affairs, the heart is capable of working independently, autonomously, for an indefinitely long period of time. This is ensured by the generation of an electrical impulse in the sinus node (natural pacemaker).
Next, the signal moves along special fibers, which are collectively called the His bundle. This structure has a branched, tree-like character. The left leg includes several fibers.
Depending on the degree of blockade, it is divided into partial or complete varieties. Without the normal movement of the electrical impulse, there can be no contraction.
General forms are characterized by the development of secondary, adaptive mechanisms.
Since the left ventricle does not receive sufficient stimulation from the sinus node, it begins to produce signals on its own.
This does not lead to restoration of functions. Moreover, these are not full cuts. More often it ends with extrasystoles or fibrillation. A fatal outcome in such a scenario is the most likely and obvious.
Pacemakers
Currently, there are many options for permanent pacing. They have one thing in common: under the skin of the anterior chest wall (usually near the collarbone) an electric pacemaker is implanted - a small metal box, the wires from which (electrodes) go through the veins to the right side of the heart. These wires sense the heart's own electrical activity (to synchronize their work with it) and transmit impulses to the heart. Modern pacemakers almost always stimulate both the atria and the ventricles. In addition, they are tuned so that the heart rate increases during exercise and decreases at rest. There are essentially no contraindications for cardiac pacing: pacemaker implantation is a simple and harmless procedure that can be performed at any age.
A separate type of cardiac pacing is the so-called biventricular stimulation. It is performed not for conduction disorders themselves, but to achieve synchronous contraction of all the walls of the left ventricle. Therefore, the installation of a biventricular stimulator is also called resynchronization therapy. Electrodes from the stimulator go to the right ventricle and to the coronary sinus (which is directly adjacent to the left ventricle). This type of treatment greatly helps some heart failure patients.
Some pacemakers also have a defibrillator function: they detect life-threatening arrhythmias and automatically deliver a shock to stop them.
Patients with pacemakers lead normal lives. They just need to avoid the influence of a strong magnetic field. Thus, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated in patients with implanted pacemakers.
From time to time, patients with implanted pacemakers need to be seen by specialists: to check the serviceability of the stimulator (in particular, its battery capacity), and to adjust the stimulation parameters.
Share:
Classification
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process:
- One conductive bundle is affected. In most cases, this is exactly the condition that occurs. The general prevalence of blockade of the left leg of His is determined by 1% of the entire population under 40 years of age, after which it is already 3%. The number of situations with minimal fiber involvement is 60%. Symptoms of the condition are completely absent or are so insignificant that they do not attract the patient’s attention. Recovery is likely; fatal complications are rare and take decades to develop at best. Many patients can live until the end of their lives and have no idea that they are suffering from anything.
- Two bundles of the left bundle branch of His are affected. A more dangerous option. Accompanied at first by a mild and then severe clinical picture. Usually we are talking about organic disorders. Recovery is possible, but it is better to start treatment in the early stages, since there are no gross defects yet.
- Three-bundle block. Relatively rare. Causes fatal complications in most cases. The prospect for the development of such is 1-3 years, in some situations we are talking about months. Treatment is urgent, in a hospital.
According to the degree of disturbance and the nature of the course:
- Intermittent. Registration of pathological abnormalities on the ECG is possible. However, the picture is not constant. At one moment a blockade is recorded, at another everything is normal. It is better to determine such “elusive” conditions in a hospital, when there is the possibility of repeated studies, or with the help of a 24-hour Holter monitor.
- Alternating. In this case, there are deviations, but they are also inconsistent. There is a difference. They are always registered, but at each moment of time there are different changes: blockade of one or another bundle. Unstable forms are more difficult to treat and require a special approach. This is why diagnosis is so important.
- Permanent variety. It is characterized by stability of symptoms and clinical, including objective, picture. The relative ease of diagnosis does not make treatment easy.
Based on the nature of the deviation:
- Incomplete blockade of the left bundle branch. Accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture. Despite the severity of the condition, full ventricular contractions are still present because, although to a lesser extent, the signal passes through. There are several clinical variants of the condition. Here the role is played by how many fibers are not involved in the work.
- Complete block of the left bundle branch. The impulse is not transported at all.
These classifications play an important role in practical activities.
Severity
Staging of the pathological process has not been developed with sufficient accuracy. Based on the national recommendations of individual communities, we can talk about four degrees of severity of the blockade:
| Degree | Description |
| First or easy. | There is a conduction disturbance in one leg. There are no symptoms at all, a minimal nonspecific clinical picture is possible. Typically, this stage corresponds to the initial forms of cardiac diseases. |
| Second, moderate. | The block affects one or two bundles of the left bundle branch. The severity of the symptoms is sufficient to consult a doctor. Usually, disorders are diagnosed at this stage, but not always. The prospects for a cure are still good. |
| Third, heavy. | Complete blockades are noted. The symptoms are painful for the patient, and the quality of life decreases significantly. High risk of death. Organic deviations from remote systems are observed. Recovery is carried out urgently, in a hospital setting. |
| Fourth or terminal. | It is provoked by a long course of both the underlying disease and the blockade. The treatment is ineffective and there are no prospects. Palliative care is possible. |
In order not to miss the moment, it is recommended that at the first suspicion you go to a cardiologist or at least a therapist.
Causes
Factors in the development of the pathological process are primary diseases that directly cause the blockade, complete or partial.
Among them:
- Calcinosis. Its essence lies in the disruption of the exchange of salts of the corresponding element. They leave the bones and are deposited in soft tissues and nerve fibers, leading to generalized disorders of the patient’s condition. Damage to cardiac structures is possible and even likely. Calcium blocks the signal. The sources of the problem lie in genetic pathologies, prolonged immobilization, and endocrine diseases.
- Cardiomyopathy. Disruption of the normal formation of muscle structures of the organ. There is a proliferation of myocyte cells, an increase in the size of the heart itself. But this does not add functional activity. It falls in proportion to the changes. There are a group of types of condition, depending on the origin: congenital, alcoholic, toxic and others. Many development factors are potentially controllable and can be influenced as part of prevention.
- Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Leads to disruption of the nutrition of the heart muscle. The result is constant ischemia with the prospect of developing coronary artery disease, and a possible heart attack. Even against the background of incomplete malnutrition, cardiac structures gradually become necrotic. Functionally active tissues are replaced by scar and connective tissues. Hence acquired cardiosclerosis, myopathy. Blockade is a relatively late complication.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the heart and surrounding structures. Usually infectious in nature. Diseases like myocarditis are aggressive and require urgent hospital treatment with antibiotics. The consequence in 30% of cases is blockade of the anterior branch of the left bundle branch. Other fibers are less commonly affected.
- Heart attack. Advanced variant of coronary insufficiency. It differs from IHD in the avalanche-like nature of its flow. Myocardial tissue becomes necrotic in a matter of hours, and the volume of replacement with scar structures is much more significant. Therefore, the options for the blockade afterward may be different. Usually this is a violation of the conductivity of several bundles, less often the deviation affects the entire leg.
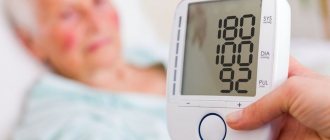
- Hypertension stage 2-3. Usually of the decompensated type, when the blood pressure level is close to 190 to 110-120 mmHg and higher. Leads to constant stress on cardiac structures. Deviations are characteristic, usually talking about left ventricular hypertrophy. Tissue proliferation leads to partial blockade (complete blockade is rare). Recovery is very difficult. Supportive therapy.
- Mitral valve stenosis, up to complete fusion. Leads to disturbances of local hemodynamics (in the heart). Prompt correction is required before it is too late.
- Congenital and acquired malformations of cardiac structures. Various in type and course. They rarely manifest themselves in a pronounced clinical manner, which complicates the early diagnosis of pathologies.
- Pulmonary heart. Proliferation of cardiac structures in response to increased pressure in the artery of the same name. Potentially fatal condition.
There are other diseases that would, however, take a long time to list completely.
These include other cardiac and endocrine conditions. And bad habits like consuming tobacco and alcohol.
All factors, one way or another, are similar in one thing: blockage of the posterior branch of the left leg of His occurs more often. Slightly less common are other options.
Forms of the disease
The classification of pathology has several forms. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- disruption of the conductivity of one of the bundles - here the blockade extends to the right or one of the legs of the left bundle;
- blockade of two bundles - the pathology spreads to the right side and one of the branches of the left leg;
- damage to all parts of the His bundle.
Damage to all legs is a direct indication for urgent hospitalization of the patient with the necessary drug therapy or surgical treatment.
Symptoms of complete LBBB
Characterized by the maximum possible clinical picture. It is considered the most severe type of pathological process.
- Constant arrhythmias. As myocardial contractility decreases, the likely scenario is bradycardia with a beat rate of about 40-50 beats per minute, possibly less. In addition to heart rate disturbances, other abnormalities also occur. Group-type extrasystole often occurs, when the left ventricle begins to produce a signal and contract chaotically on its own.
- Chest pain. Non-specific sign. Characterized by mild discomfort. There are no attacks as such, except for cases of coronary insufficiency.
- Shortness of breath during prolonged physical activity or at rest. Depends on the degree of development of the underlying pathological condition. Severe disability is possible with the inability to even serve oneself at home, not to mention professional activities.
- Weakness, feeling of body weakness, periods of apathy. Included in the picture. They represent general manifestations.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Sweating, especially at night.
- Mental disorders. Like aggressiveness, irritability, long periods of depression or low emotional levels.
- Fainting. May be repeated over the course of one day.
- Headache.
- Vertigo.
- Impossibility of orientation in space.
- Blood pressure surges.
The clinical picture may vary, depending on the underlying diagnosis and the degree of blockage.
How does pathology manifest itself?
Signs of blockade depend on the form of pathology and concomitant diseases in the patient. Right unilateral blockade often occurs without visible symptoms and is discovered accidentally during a routine ECG. Sometimes the patient experiences a pain syndrome that spreads to the area of the heart, shoulder blades, collarbones, rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, loss of performance, which is explained by the underlying pathology that provoked the blockade.
When the left bundle (anterior or left branch) is blocked, the patient notices dizziness, periodic heart pain, the pain syndrome is often temporary and intensifies with physical activity. Patients experience rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath. Symptoms of the pathology include fatigue, loss of performance, and depression.
The most common sign of cardiac conduction disorders is pain in the sternum.
Three-bundle blocks are divided into complete and incomplete. The first option is accompanied by a complete block of the passage of cardiac impulses. Due to the impossibility of conducting impulses through this section, separation of contractions of the atria and ventricles occurs. The rhythm of contractions is from 20 to 40 beats/min. The result of this is the risk of blood escaping into the aorta. Symptoms of the pathology are pronounced:
- frequent dizziness;
- fainting;
- interruptions in heart rhythm;
- chronic fatigue, depression;
- chest pain;
- headache.
Sometimes, against the background of severe disturbances, sudden cardiac arrest is diagnosed.
Partial blockade is diagnosed in patients whose electrical impulses travel through intact heart fibers. Here the signs are mild, complications are less common.
How dangerous is the condition?
Possible complications of the process:
- Heart failure. The probability with a complete blockade is 70%. In other situations - proportionally lower. Occurs without preliminary symptoms and requires urgent resuscitation.
- Cardiogenic shock. Generalized hemodynamic disturbances. Mortality is maximum, close to 100%.
- Respiratory failure. Up to asphyxia and death in the later stages. It is developing rapidly.
- Heart attack. As a result of insufficient nutrition of cardiac structures.
- Dangerous forms of arrhythmia. Atrial fibrillation or extrasystole. Involves cardiac arrest without the possibility of effective recovery.
- Stroke. Acute malnutrition of cerebral tissues with the formation of a severe neurological defect. Death occurs a little less often.
- Multiple organ failure. As a result of general hemodynamic disorders. The liver and kidneys suffer. The brain is not the least important.
With a significant amount of impairment, the risk of vascular dementia increases—a sharp, severe weakening of mnestic and cognitive functions.
Additional Research
In addition to electrocardiography, the following instrumental diagnostic methods are used to detect heart disease during blockade:
- Holter monitoring of ECG and blood pressure - the method helps to identify the frequency and intensity of arrhythmia;
- ultrasound examination of the heart - allows you to assess the condition of the organ tissues, determine the size of the ventricles, features of contractile function and other indicators;
- Intraesophageal electrocardiography - examination of the heart is performed through the patient's esophagus. This method is indicated when the regular ECG is insufficiently informative;
- multispiral computed and magnetic resonance imaging.
Important! To clarify the diagnosis, the patient may be sent for consultation to a specialist.
To obtain detailed information about the condition of the heart, several diagnostic methods are used at once.
Diagnostics
It is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist. In inpatient or outpatient settings, depending on the patient’s condition.
Approximate list of events:
- Listening to patient complaints about health. Recording for further analysis
- Anamnesis collection. The presence of current or previously suffered pathologies of the cardiac type plays a huge role.
- Blood pressure measurement. Against the background of the blockade, it is consistently high, this is a compensatory mechanism. Also heart rate. Bradycardia with an irregular rhythm is characteristic.
- Listening to heart sounds (auscultation).
- Electrocardiography. Basic technique. Left bundle branch block has specific symptoms.
- Daily monitoring using an automatic tonometer. Used to clarify the process. Especially against the background of an alternating type of deviation. Also if the blockade alternates with periods of spontaneous normalization.
- Echocardiography. To assess the degree of organic disorders.
- MRI. To obtain detailed images of cardiac structures. Required in controversial cases to identify the origin of the process.
- General blood test.
Since there are dozens of reasons, the number of diagnostic methods is also large. Those presented are considered basic.
Controversial cases require extensive examination under the supervision of several specialists.
How common are intraventricular blocks?
Impaired conduction within the ventricles can be found in both children and adults. Among the pathologies detected using electrocardiography, the proportion of intraventricular blockades is up to 2.4%. There has been an increase in the frequency of detection in elderly patients.
By prevalence among the population:
- in the first place is a block in the left leg (anterosuperior branch);
- on the second - the right leg.
Impaired conduction in the posteroinferior bundle is rare.
Signs of left bundle branch block on ECG
Full:
- Widening of the QRS complex (> 0.11 sec), splitting, notching.
- R peak deformation.
- ST depression.
- Negative T wave.
- S is missing.
- Slow down the rhythm to 40-60 beats per minute.
There are other typical features. These are the most typical. Without special training, it will not be possible to decipher a cardiogram.
Incomplete:
- QRS deformation.
- R, S vertex splitting.
- Absence of Q in leads V5-6.
Signs of left bundle branch block on an ECG are determined relatively easily by a cardiologist.
Treatment
{banner_banstat9}
Therapy is carried out in two ways:
- Elimination of the main cause of the pathological condition. The etiotropic technique is aimed at preventing further development and aggravation.
- Relief of symptoms. To normalize the quality of life, reduce the risks of complications in the short term.
In the first direction, the underlying disease is eliminated. Depending on the diagnosis, we may be talking about the use of medications or surgery.
Surgery is required in a limited number of cases: heart defects, including abnormalities in the development of the mitral valve, the need to install a pacemaker, or prosthetics.
Symptomatic therapy consists of the use of medications; surgical removal of the blockade as such will not work.
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Cardiac glycosides. Lily of the valley tincture, Digoxin and others. In minimal dosages to maintain the contractility of the muscle layer.
- Organic nitrates for the relief of acute attacks of arrhythmia or pain.
- Diuretics to normalize fluid removal and prevent congestive heart failure.
- Antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors mainly).
As necessary, thrombolytics, statins, and antiarrhythmics are prescribed in small quantities.
Lifestyle changes can only play a role if the underlying pathological process is determined by addictions.
It is recommended to give up smoking and alcohol, normalize physical activity and adjust the diet under the supervision of a cardiologist.
The use of traditional recipes will not have any effect. It is not recommended to waste time on dubious grandma’s methods. Every day counts.
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- daily routine, full and restful sleep;
- refusal of fried, canned and spicy foods;
- taking medications only prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision;
- consumption of foods with a significant fiber content: fresh fruits and vegetables, herbs;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of all organs, not just the heart;
- mandatory consultation with a doctor if symptoms of the disease appear.
If an operation has been performed to install a pacemaker, a person should exclude the influence of electrical devices and a mobile phone on him. If you become ill, it is important to visit your doctor in a timely manner to assess the condition of the heart and the general well-being of the patient.
Forecast
{banner_banstat10}
With a complete blockade - serious. Complications occur several months or years after diagnosis. Death is the most likely outcome. It is determined in 70% of cases against the background of cardiac arrest.
With incomplete everything is somewhat better. The median survival rate is 5-7 years, with a competent course of therapy the period is indefinitely long.
In any case, treatment improves prognosis. It is difficult to say in advance what awaits the patient; you need to observe for some time before drawing conclusions.
Three-bundle blockades
Mechanism of conduction disturbance: when incomplete, the electrical impulse follows from the atria to the ventricles along one of the branches (less affected). In this case, signs of atrioventricular block are detected. Complete block is characterized by third degree atrioventricular obstruction and an altered source of ventricular rhythm.
The causes are severe organic damage to the myocardium, already listed above.
The shape of the teeth indicates the type of intraventricular block