What influences the indicator level?
To answer this question, let's once again return to the definition: the ratio of the proportion of formed elements of blood to its total volume. So there are several possible mechanisms for increasing hematocrit:
- Increased content of red blood cells in the blood.
- Reduced plasma content.
- Violations of sampling or measurement technology.
For example, when determining hematocrit, it matters whether the person is sitting or lying down at the time of blood sampling. In the second case it will be slightly higher .
Peculiarity. If blood is taken from a vein for measurement, the hematocrit may be elevated if the arm is held with a tourniquet for longer than necessary.
Another technical reason for a false answer is the human factor . Centrifugation time, the correctness of readings, conditions in the laboratory - all this can affect the final result.
So if only the hematocrit is elevated in a child, and the rest of the test results are normal, then there is no need to panic.
Increased hematocrit
Many people are interested in the question of when the hematocrit is increased, what does it mean. First of all, the indicator increases with the accelerated production of red blood cells by the bone marrow. An increase in the size of red blood cells can also lead to deviations above normal. This occurs in various pathological conditions, namely:
- Primary erythrocytosis, which occurs against the background of overactive production of red blood cells, most often indicates tumor processes in the bone marrow.
- Secondary erythrocytosis is associated with pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, in particular, it develops with respiratory failure or heart disease.
A decrease in plasma volume, and, consequently, an increase in hematocrit may indicate the development of peritonitis, leukemia or kidney pathologies. This also happens with extensive burns. The cause of dehydration is often uncompensated diabetes mellitus.
Erythrocytosis at the initial stage, when the hematocrit is slightly increased, is asymptomatic. In most cases, abnormalities are discovered accidentally during a routine medical examination. But with a significant increase, it is discovered by chance, when taking a blood test for other reasons. Only with a significant increase in hematocrit do warning signs arise:
- Pain in joints and muscles.
- Shortness of breath, weakness and increased sweating.
- Dizziness.
- Increased pressure.
Since symptoms are not specific, if they appear, you should undergo a full examination in order to make a correct diagnosis. Treatment can only be successful if the cause of the increase in the number of red blood cells in the total blood volume is established.
Symptoms
The clinical picture is fully dictated by the etiological factor. However, each variant of the pathology described has several specific external manifestations.
If the hematocrit in the blood of children is increased, the following symptoms may appear:
- severe or mild dizziness;
- breathing problems – parents note that the child has difficulty breathing;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- constant nausea that does not end with vomiting;
- weakness that persists on a permanent basis;
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased physical activity;
- partial loss of orientation in space.
A low level of hematocrit in the blood is represented by:
- general malaise;
- shortness of breath, appearing even at rest;
- rapid fatigue;
- increased heart rate;
- constant headaches;
- increased tearfulness;
- pale skin;
- deterioration of hair condition.
It is these signs that should arouse suspicion among parents and become an impetus for seeking help from a pediatrician.
- High hematocrit in a blood test in adults and children - what diseases is it a symptom of, and their treatment
Deviations from the norm
Deviation, both upward and downward, may indicate pathology, but may also have physiological reasons.
If Ht is increased in children, then the blood becomes thicker and more viscous due to an increase in the number of formed elements relative to the volume of the liquid part. This condition is dangerous because there is a risk of blood clots. If the norm is exceeded by 10-12% in a child under one year old, as a rule, this is due to physiology and should not cause concern. It’s another matter if a high level is observed in a child older than one year.
With a low hematocrit in children, the volume of red blood cells that supply oxygen and nutrients to the organs does not reach normal. In this regard, the acid-base balance in the child’s body is disturbed, and the cells experience oxygen starvation. As a result, your health worsens, namely weakness, rapid fatigue, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and pale skin.
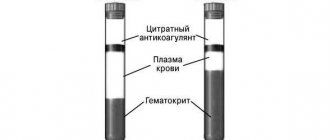
This is how blood hematocrit is determined
Hematocrit norm
A blood viscosity test is prescribed for people who have severe symptoms of dehydration, severe vomiting due to poisoning, or diarrhea. Biological indicators are affected by the age and gender of a person. Doctors have a special formula used to establish the hematocrit number. It is calculated as follows:
- The content of red blood cells is determined as a percentage or as a fractional component.
- The result obtained is multiplied by 0.001.
A high hematocrit in newborns is considered normal. The value of this indicator is 20-30% higher than in adults. Then the number of red blood cells decreases sharply. It is considered normal when the hematocrit value in the blood is 40-45%. In pregnant women, the number of red blood cells begins to decrease from the 20th week, and then returns to normal after childbirth. Sometimes the hematocrit number refers to the number of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells. The number of the latter elements predominates in the blood.
How is the analysis carried out?
The hematocrit number is calculated during a general blood test. To do this, the blood is placed in a special tube called a hematocrit and centrifuged for one and a half hours. As a result, heavier formed elements, most of which are red blood cells, settle to the bottom of the tube, and plasma remains at the top.
Using the applied divisions, you can determine what volume the red cells occupy in relation to the plasma. In modern laboratories, the hematocrit number is calculated using hematological analyzers, which provide more accurate results. Despite the fact that the Ht indicator gives a quantitative, but not qualitative assessment of red blood cells, this analysis is considered quite informative. It is most often expressed as a percentage, sometimes it is written as a fraction - liter/liter.
Hematocrit test information
The hematocrit value shows the ratio of blood cells to plasma, expressed as a percentage. The research methodology is quite simple. It is necessary to collect venous blood from a small patient and place it in a tube with divisions. After which the tube with the test material is placed in a centrifuge and centrifuged at sufficient speed. As a result, the blood in the tube is stratified: formed elements (cells) settle at the bottom, and plasma accumulates on top of them.
Previously, when assessing the hematocrit value, the laboratory assistant independently assessed the height of the column of formed elements in the tube. The plasma-to-cell percentage was calculated manually. This could lead to some errors and inaccurate analysis results.
Currently, modern centrifuges are connected to computers that automatically read data and display it on a monitor screen. This eliminates the possibility of inaccurate data and makes the error minimal. However, instrument error, which varies among different measuring devices, should not be excluded. Therefore, if repeated tests are necessary, you should contact one laboratory department.
Main article: What is hematocrit in a blood test and its norms
When should I get tested?
The study is relevant for children with a routine visit to the clinic for examination. Hematocrit values are determined as part of a clinical blood test, which is prescribed to the child at each visit. Despite the low specificity of the study, it helps to make a preliminary diagnosis and get an overall picture of the state of health.
Hematocrit in the blood of children is measured after prolonged dehydration, as well as during bleeding in order to assess its severity. A final decision on the need for donor blood transfusion is impossible without the laboratory analysis in question. Analysis plays an important role in establishing the effectiveness of the methods that were chosen for the treatment of blood diseases.
Invalid analysis results
Having received a result that deviates from the norm, the pediatrician will prescribe a repeat test for the child. This is necessary to exclude false results that were obtained due to improper preparation of the child for the study or violation of the rules for collecting biomaterial.
Biomaterial for analysis is submitted on an empty stomach. It is permissible for children aged 1-2 years not to feed for 2-3 hours before taking biomaterial; for children 3-5 years old it is allowed to take a break after the last meal for 3-4 hours. Older children will have to refuse food for 8 hours. Therefore, it is advisable to take the test in the morning. You should give your child plenty of clean and unsweetened water. This will greatly facilitate the venipuncture process for a young patient and will avoid the need for repeated blood draws.
Venipuncture is an unpleasant and painful process for children. Many children get scared and cry a lot. In this condition, it is quite difficult to detect a vein for blood sampling. Incorrect application of a tourniquet for a long time leads to distortion of the obtained laboratory analysis results.
It should be emphasized that a deviation from the norm of one indicator is not enough to establish the exact cause of the disease. If a child's hematocrit is found to be elevated in duplicate tests, they will not be treated immediately. The pediatrician will select additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. Only after collecting anamnesis and collecting data from a comprehensive study, a final diagnosis is established and the necessary treatment is selected.
What does it mean and what does it mean if the hematocrit is elevated in a child?
The main reasons why a child’s hematocrit increases:
- an increase in the total number of red blood cells in the blood (erythrocytosis);
- decrease in blood plasma volume;
- dehydration;
- leukemia
Let's take a closer look at each of the reasons - what causes them and how to treat them correctly.
Erythrocytosis
An increase in the level of red blood cells is observed in polycythemia vera in children. This is a benign pathology, which is characterized by an overly active process of red blood cell formation. Along with red blood cells, but to a lesser extent, the level of leukocytes and platelets increases. The resulting red blood cells have the correct morphological structure and are able to fully exhibit functional activity.
In patients, blood viscosity increases significantly, which disrupts the normal blood supply to organs and tissues. The supply of oxygen slows down, which over a long period of time can lead to organ hypoxia.
Polycythemia vera is a disease of adults, the average age is 55 years. However, the pathology can also affect children. The peculiarity of the course of the disease in them is a more severe condition and severity of clinical symptoms. Main symptoms:
- change in skin color to red or cherry, tongue and lips - to bluish-red;
- feeling of severe itching after hygiene procedures in warm water;
- short-term severe pain at the ends of the fingers or toes;
- frequent fatigue and headaches;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased blood pressure.
When diagnosing pathology, the doctor pays special attention to blood tests, external signs of the disease and an increased tendency to form blood clots in the vessels.
For treatment, methods are used that are aimed at reducing the degree of blood viscosity. The leading method of therapy is bloodletting. It allows you to reduce the total volume of blood (red blood cells) and return the hematocrit to normal values. A well-known technique is erythrocytepheresis, when certain blood cells, in particular red blood cells, are removed from the patient.
Decrease in blood plasma volume
A similar condition is observed in burn disease and peritonitis.
Burn disease develops in people whose skin lesion area exceeds 10%. In children, the percentage of affected area for the development of the disease may be reduced. A favorable outcome is expected with timely and competent provision of medical care. After restoration of functional activity, the patient may require transplantation of the affected areas of the skin.
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the peritoneum, which is normally sterile. The condition poses a serious threat to life and is accompanied by an extremely serious condition.
In children, the pathology develops rapidly and is much more aggressive than in adult patients. In 75% of cases in newborn babies, peritonitis leads to death. Therefore, the provision of medical care must be urgent.
A particular difficulty for timely diagnosis is that the child cannot specifically identify the area that hurts. Babies with peritonitis cry non-stop and do not latch on to the breast. They have blood clots in their stool and a constantly elevated temperature. The cause of the disease in newborns is intestinal volvulus or ischemic infarction.