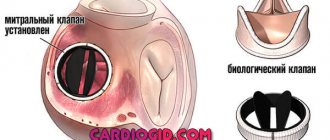
The foramen ovale is the communication between the two upper chambers of the heart, the atria.
Every unborn baby has an oval window; it performs an important function - while the fetus’s lungs are not breathing, thanks to the presence of a special opening (oval window), most of the blood “bypasses” them. At the same time, oxygenated blood flows directly from the right atrium to the left and then to the actively developing organism.
While the baby is in the womb, the task of the “lungs” – to saturate the blood with oxygen – is taken over by the mother’s body, and specifically the blood vessels of the placenta. This type of blood circulation is called fetal.
Why does the fetus need an oval window?
In the womb of the mother, the child does not breathe in the literal sense of the word, since the lungs cannot function, they resemble a deflated balloon. A patent foramen ovale in newborns is a small opening between the atria. Through the oval window, blood from the veins flows into the single large circulation of the fetus.
After birth, the baby takes his first breath, the lungs begin their work. Under the influence of the pressure difference, the open oval window is closed by a valve. But such a valve may be too small to completely tighten the hole.
A functioning foramen ovale is an anomaly of the heart, and in no way a defect.
Army
Examination of conscripts with an open foramen ovale is carried out according to Article 42 of the Schedule of Diseases. The presence of an open foramen ovale, even without bleeding, according to government decree, allows a conscript to be classified in category B4, when military service is possible but in military units where there is no serious physical activity and, accordingly, high health requirements are not required. If there is a discharge of blood with an open oval window, then the young man is assigned category B, and he is exempt from military service.
Sources:
- Preetham Kumar. The Connection Between Patent Foramen Ovale and Migraine, - data from the US National Library of Medicine PubMed, 2019.
- Sharykin A.S. Clinical observation of an increase in the diameter of the patent foramen ovale in adolescence, Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2013.
- Brian H West. Relation of Patent Foramen Ovale to Acute Mountain Sickness, - US National Library of Medicine PubMed, 2021.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 4, 2013 N 565 (as amended on June 1, 2020) “On approval of the Regulations on military medical examination”
Causes of patent oval window
There is no exact cause for this pathology.
There are several most common factors.
- In almost all premature and immature newborns, the window remains open.
- Smoking, maternal substance abuse.
- Intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
- Prolonged labor, asphyxia of the baby during childbirth.
- Adverse environmental factors.
- Mother's stress.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Occupational exposure to toxic substances in the mother.
Causes of congenital heart disease in newborns
Scientists still cannot name the exact causes of congenital heart disease.
However, the good news is that most of them can be corrected surgically. Surgery on a congenital heart defect gives the child the opportunity for normal development and growth.
Thanks to a series of studies, scientists were able to identify a number of factors that increase the risk of congenital heart disease in newborns:
- Viral (if the child was conceived or carried for the first three months of pregnancy during a viral epidemic; influenza and rubella viruses are especially dangerous).
- Ecological (parents living in environmentally disadvantaged areas).
- Exposure of the fetus to ionizing radiation.
- Genetic (hereditary predisposition).
- Bad habits of parents (alcoholism and drug addiction of mothers are especially terrible).
- Autoimmune or severe chronic diseases in parents (the most common negative effect is systemic lupus erythematosus or diabetes in the expectant mother).
- Taking certain medications during pregnancy (containing ethanol, thalidomide, amphetamines, anticonvulsants, trimethadione, lithium, progestogens).
- The mother's age is over 35-37 years.
Open oval window in children and its symptoms
In most cases, such children do not complain.
Therefore, it is very important for mothers to be attentive and monitor the slightest deviations in the behavior of their babies.
What can you notice?
- The appearance of blueness around the mouth of a newborn. This cyanosis appears after crying, screaming, sucking, or bathing.
- In older children, tolerance (resistance) to physical activity decreases. The child rests and sits down after regular outdoor games.
- The appearance of shortness of breath. In general, a child should normally be able to easily climb to the 4th floor without any signs of shortness of breath.
- Frequent colds in infants, namely: bronchitis, pneumonia.
- Doctors listen for a heart murmur.
PERSONAL EXPERIENCE. The child is 10 days old; during bathing, the mother notes the blueness of the nasolabial triangle. The child was born full-term, weighing 3500. The mother admitted that she smoked during pregnancy. On examination, a murmur was noted at the apex of the heart. The baby was sent for an ultrasound. As a result, an open oval window of 3.6 mm was revealed. The child has been registered.
Possible complications of congenital heart disease in newborns
Sometimes there are cases when, when diagnosed with congenital heart disease, a newborn does not show any signs of the disease.
The absence of symptoms may continue until primary school age. At this age, any congenital heart defect in children manifests itself. The child begins to lag behind his peers in physical development, suffocates during exercise, and his skin turns pale or blue. Not only poor physical performance, but also learning problems, emotional disorders - all this can be caused by one disease.
Unfortunately, a child with congenital heart disease subsequently needs lifelong monitoring of his health due to the possible development of complications and concomitant diseases. Even if surgery was performed at an early age, it is not a panacea for life. In addition, strict dosing of physical activity will be necessary throughout your life.
Congenital heart defects in children can be complicated by other diseases.
Among them:
- Heart failure
- Early prolonged pneumonia
- High pulmonary hypertension
- Endocarditis
- Syncope (loss of consciousness)
- Angina pectoris
- Myocardial infarction
- Attacks of shortness of breath and blueness
Diagnostics
Ultrasound of the heart is of primary clinical significance. The doctor clearly sees a small hole in the projection of the left atrium, as well as the direction of blood flow.
When listening to a heart murmur, the pediatrician will definitely refer your baby for this type of examination.
According to new standards, at 1 month all newborns must undergo ultrasound screening, including the heart.
As a rule, there are no pathological changes on the ECG with LLC.
Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in newborns
Naturally, the earlier a congenital heart defect in newborns is detected and timely treatment begins, the more favorable the prognosis. However, due to the absence of clearly defined symptoms and, accordingly, no treatment at all, there are cases of death among children under 1 year of age (occasionally even older).
Usually, during preventive examinations, the doctor must listen to the baby’s heart. If murmurs are heard there, this is a reason for a detailed examination of the heart (although not necessarily a symptom of congenital heart disease).
For this purpose, parents and children are referred to specialists with a narrower profile - a cardiologist and a cardiac surgeon.
If you suspect a heart defect, the baby’s parents do not need to immediately turn to Internet search engines with the request “congenital heart defect surgery.” Not all defects require radical surgical intervention. And the main thing is to first establish the correct diagnosis.
Changes characteristic of congenital heart disease in a newborn are revealed by the following research methods:
- X-ray of the chest (as well as ventriculography - x-ray with contrast injection).
- Echocardiography (using ultrasound to examine the condition of the heart muscle, valves, blood flow in the heart cavities).
- Electrocardiogram – ECG (or methods based on it: stress ECG (treadmill test, bicycle ergometry), ECG Holter monitoring).
If the above examination methods reveal the presence of a serious disease - congenital heart disease, then further diagnostics are carried out in the cardiac surgery department on an inpatient basis. Surgeons, if necessary, conduct examinations using procedures such as angiocardiography and probing of the heart chambers.
Modern high-tech medical equipment allows you to conduct a full comprehensive examination of the heart and blood vessels in order to establish the most accurate diagnosis and choose the necessary treatment tactics.
Treatment
In 50% of children, the oval window functions for up to a year and then closes on its own; in 25%, fusion occurs by the fifth year of life.
In 8% of the adult population, the window remains unlocked. What to do if the window has not closed after 5 years? Basically, nothing. The open foramen ovale in a newborn is too small in size to ensure overload of the atria with the development of heart failure. Therefore, it is necessary to dynamically monitor the baby, undergo an annual heart ultrasound and be examined by a pediatric cardiologist.
PERSONAL EXPERIENCE. At the reception there was a 13-year-old boy. For 4 years the child has been involved in active sports – rowing. By chance, during a medical examination, an ultrasound of the heart was performed, where an oval window measuring 4 mm was first discovered. At the same time, the child did not show any complaints throughout his 13 years and coped well with physical activity. He even took first place in competitions.
If a child has complaints, drug therapy is prescribed in the form of cardiotrophic drugs and nootropics - Magnelis, Kudesan, Piracetam.
These drugs improve myocardial nutrition and exercise tolerance.
Recently, it has become reliable that the drug levocarnitine (Elkar) promotes rapid closure of the oval window if taken for 2 months in a course 3 times a year. True, it is not entirely clear what this is connected with. From personal experience, I can say that I did not see a clear connection between Elkar’s appointment and the closure of the LLC.
But it still happens that the oval window can lead to poor circulation and heart failure. In pediatric practice, this is rare, in most cases it occurs by the age of 30-40. Then the issue of surgical intervention to close this hole is decided. A small patch is applied endovascularly (that is, using a catheter) through the femoral vein.
As for sports and a functioning oval window, if there are no complaints and good cardiac ultrasound indicators, you can engage in any kind of sport.
It is not recommended for children with limited liability to engage in scuba diving and parachute jumping. This is due to a sharp change in pressure. The foramen ovale may increase in size to the point of an atrial septal defect.
Congenital heart disease in newborns - what is it?
The disease congenital heart disease implies an anatomical pathology or defect (impairment) in the development of the heart and/or large vessels, as well as the valve apparatus, which leads to cardiac overload, myocardial insufficiency of the heart chambers and changes in blood flow.
Congenital heart defects in children are called when pathologies formed before the birth of the child, during the intrauterine period of fetal development.
Most often, congenital heart defects in future newborns develop between the second and eighth weeks of pregnancy.
A disease such as congenital heart disease is relatively rare. Out of every thousand babies born, six to eight children are given a similar diagnosis.
Complications
They are quite rare. Associated with embolism and impaired blood flow. These are heart attacks, strokes and kidney infarctions.
These complications can already occur in adults. And such a patient should always warn the doctor that he has a functioning foramen ovale.
Minor heart anomalies for the most part do not harm the health of children. Some famous athletes have this pathology and become Olympic champions. Many doctors consider LLC normal. But it should be remembered that annual supervision by a specialist is necessary.
Course of therapy
Treatment of an abnormal window in the heart muscle, which does not manifest itself with a characteristic clinical picture and does not contribute to the development of complications, is usually not carried out. The doctor will only give the following recommendations:
- Engage in physical therapy to strengthen the heart muscle and keep the body in good shape.
- Rest more, taking breaks at work every hour (5-10 minutes) and observing a sleep schedule (sleep at least 7-8 hours).
- Avoid conflicts and stressful situations. It is advisable for the patient to devote more time to hobbies and listen to his favorite music in order to relax and not overstrain the heart.
- Competently create a diet, removing fatty foods from it and filling it with vegetables and fruits. It is necessary to cook by steaming or boiling, and eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
If the patient complains of attacks of tachycardia and other disorders of the cardiovascular system, the doctor may advise combining the above measures with drug treatment. It is based on taking pills to stabilize the condition:
- Antiarrhythmic medications (sodium, calcium and adrenaline blockers, cardiac glycosides, diuretics, sedatives) intended to eliminate arrhythmia.
- Vitamin complexes based on magnesium, potassium and B vitamins (Panangin, Magne B6) improve the condition of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Surgical intervention is possible only in the case of a pronounced clinical picture, which significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life. It is no less relevant if there is a high chance of blood clots. The specialist will recommend endovascular treatment. Its essence is to insert a catheter into the femoral artery. Next, it is advanced into the right atrium and a special patch is applied to the hole, which stimulates the area to become overgrown with connective tissue. After 3-4 weeks it will resolve on its own without repeated intervention.
The operation must be combined with the use of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants to reduce the risk of blood clots. During the recovery period, the patient should undergo antibacterial therapy to prevent the development of myocarditis. A successful surgical intervention will allow the patient to live without any restrictions, since the anomaly will be completely eliminated.