Rapid pulse, dizziness, a feeling of fear and nervous tension - these signs directly indicate tachycardia. On average, the heart rate can range from 60 to 90 beats per minute - such indicators are considered normal. However, in some cases, the heart rate increases, including after exercise, when adrenaline is released (due to stress or positive emotions) and in hot weather. If the heart begins to beat quickly for no reason, this symptom must be quickly eliminated, since the increased load on it can be dangerous. There are several simple and proven ways to calm your heartbeat at home, even if you don’t have a first aid kit at hand.
What factors affect heart rate?
The most common non-infectious pathology in all countries of the world is diseases of the circulatory system. Based on the results of epidemiological studies dating back to the late 90s of the 20th century, WHO experts came to the conclusion that an increase in heart rate (HR) at rest is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases in healthy people.
According to the national recommendations of the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiology, the resting heart rate of a healthy adult should be no more than 80-85 beats per minute and correspond to the pulse rate. The optimal heart rate for an adult at rest is from 60 to 80 beats per minute, while the specific heart rate is individual for each person and depends on a number of factors.
The first is gender. Women have higher normal heart rates than men. This is explained by the specific characteristics of hormonal and emotional backgrounds.
The second is age. In adults, the normal heart rate increases with age: at the age of up to 50 years, the average normal value is 70 beats per minute, at the age of 50-60 years - 74 beats per minute and 79 beats per minute in people over 60 years of age.
In addition, heart rate depends on lifestyle, including physical activity: trained people have a lower heart rate than those leading a sedentary lifestyle. Bad habits also have an impact - smoking, alcohol abuse.
And finally, this indicator correlates with external factors: heart rate increases with lack of sleep, nervous tension, after a heavy meal, increased ambient temperature, etc.
Disease prevention
In order for not only the heart, but also the entire body to be strong and healthy, you must first normalize your diet. It is necessary to exclude all caffeine-containing drinks, as well as chocolate, fried foods and reduce the amount of sugar. The best diet is plant-based and dairy. Fruit juices and fresh vegetables are beneficial. Vitamin complexes will help reinforce the effect of the diet. The child must take magnesium and potassium, which normalize the heart rate. Consult your doctor first. And be sure to include moderate physical activity in your child’s daily routine, such as morning exercises. It stimulates the heart and increases its resistance to the release of excess adrenaline. As a result, irritability decreases and the emotional background normalizes. At the same time, you should not overexert yourself; any activity should be moderate. Swimming, for example, is very useful.
Sources:
- E.L. Boqueria. Ectopic atrial tachycardia in children: clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment // Annals of Arrhythmology, 2006, No. 3, pp. 16-19.
- A.I. Safina, I.Ya. Lutfullin, Z.A. Gainullina. Heart rhythm disturbances in newborns // Practical Medicine, November 2010, No. 6(45), pp. 75-79.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6595346/ Ranjit I. Kylat and Ricardo A. Samson. Permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia in infants and children // J Arrhythm. 2021 Jun; 35(3): 494–498.
- L.A. Balykova, I.S. Nazarova, A.N. Silence. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children // Practical Medicine, September 2011, No. (53), pp. 30-37.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How to correctly calculate your pulse?
For self-counting, the most common method is palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage. The accuracy of the result depends on the correct counting technique.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals; then count the pulse on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
Therapy methods
To treat pulse deficiency in the absence of complications, drug therapy is prescribed; it is selected under the control of ECG and blood pressure. During an attack, Cordarone or Novocainamide is administered intravenously, then switched to tablets. With a permanent form of atrial fibrillation, Propanorm (Ritmonorm) for oral administration may be recommended.
If a pulse deficiency occurs against the background of sinus or paroxysmal tachycardia, extrasystole, then Verapamil, Concor, Norvasc helps. For heart failure, Digoxin and Strophanthin are used. They are usually combined with anticoagulants (Warfarin, Aspirin).
If drugs fail to normalize the rhythm, then the method of electrical cardioversion is used. It involves applying a pulsed electric discharge to the heart area. This gives results in 90% of cases.
To radically eliminate arrhythmia, cauterization of the focus is carried out using radio waves, in which frequent pulses are formed using radiofrequency ablation. The second method is to create a complete blockade of impulse transmission, then the atrioventricular node is destroyed with an electrode. Then the conduction of impulses completely stops, and a permanent pacemaker is installed to stimulate contractions.
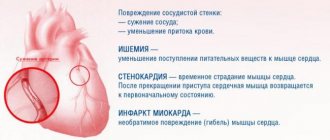
Pulse deficiency is a symptom typical of the heart contracting ineffectively and not pumping out enough blood. In most patients, it occurs against the background of atrial fibrillation, which complicates the course of coronary heart disease. With a small difference between heart contractions and pulse, there may be no symptoms, but a pronounced deficiency in pulse leads to cardiac weakness and poor circulation.
Physiological and pathological tachycardia
Depending on the causes of occurrence, physiological and pathological tachycardia are distinguished.
Physiological tachycardia occurs during emotional, physical stress, high temperature and humidity, being in hot and stuffy rooms, abuse of tonic drinks - strong tea, coffee, energy drinks, taking certain medications, smoking or drinking alcohol.
In healthy people, physiological tachycardia is an adaptive mechanism and, when the external stimulus is removed, the heart rate returns to normal within 5 minutes.
Pathological tachycardia occurs in cardiovascular, endocrine, acute infectious, oncological and other diseases and accompanying conditions - dehydration, large blood loss, shock conditions, pain syndrome, etc. - or when the functioning of the autonomic nervous system is disrupted.
Thus, tachycardia at rest is most often a symptom of some disease and requires medical examination.
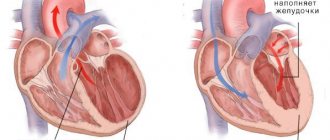
With tachycardia, the heart works under increased load and does not have time to fill with blood in the required volume, the blood supply to all organs deteriorates, and oxygen starvation develops.
The kidneys, organs of vision and gastrointestinal tract, central and peripheral nervous systems suffer, and the course of existing diseases is complicated.
The heart muscle gradually wears out, which can result in heart failure. In addition, there is a life-threatening type of tachycardia, so a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed.
Drug treatment
The sinus variety is treated in the system. Medicines that can be used if the pulse is 100 or more:
- Sedatives. Calms the central nervous system and reduces heart rate. Diazepam, Motherwort, Valerian, Phenobarbital in various preparations.
- Calcium channel blockers. They do not allow Ca+ ions to penetrate into the structures of blood vessels and cause their stenosis. Hence the impossibility of rapidly increasing heart rate.
- Magnesium-based products (Magnelis, Magne B6). Helps normalize cardiac activity.
- Beta blockers. Used to relieve irritation of the third reflex zone of the organ. Can be used as emergency aid.
Supraventricular tachycardia:
- Additionally, cardiac glycosides are prescribed.
- Antiarrhythmic drugs.
Ventricular arrhythmia is treated much more seriously, since it is the most dangerous and lethal type. The same groups of media are used, but strictly in combination.
When should you see a doctor?
Alarming symptoms include constant heartbeat at rest with a heart rate of more than 80 beats per minute, different time intervals between pulse beats when counting the pulse, different pulse values on the left and right arms.
You should also consult a doctor in case of fainting, episodes of loss of consciousness, chest pain, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart, tachycardia after blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, when tachycardia is combined with shortness of breath, dizziness, insomnia, frequent headaches, increased blood pressure. pressure, increased sweating, trembling hands.
In addition, it is important to inform your doctor if tachycardia occurs even with minor physical activity and does not go away within 5 minutes, as well as if an attack of tachycardia begins suddenly or there are repeated attacks.
An attack of tachycardia is manifested by the following symptoms: within a few minutes, the heart rate increases sharply and can reach 150-200 beats per minute, accompanied by sweating, weakness, and a feeling of fear.
Diagnostics
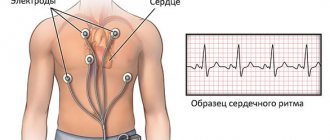
Based on the symptoms and collection of anamnesis (patient complaints), one can suspect the cause of tachycardia. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe special examinations: an electrocardiogram (ECG), ultrasound of the heart (ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY), general blood test, urine test, blood test for hormones.
Currently, it is possible to monitor the work of a patient’s heart in the normal rhythm of life. Using a portable device, which is attached to the belt under clothing, an ECG is continuously recorded throughout the day. This procedure is called 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring. It can be done in the hospital and at home.
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia?
Unbutton your clothing collar, open a window or balcony, inhale deeply and exhale very slowly; breathe like this for 5-10 minutes. Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down;
Take Corvalol or Valocordin: dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature;
Wash your face with cold water, lie down on a high pillow, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead, try to relax;
Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes: press for 10 seconds, break for 10 seconds;
Find the right carotid artery (immediately under the jaw, at this point it connects to the cervical artery) and gently, without pressure, massage it. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If the condition does not improve, the heart rate does not decrease, dizziness appears, a feeling of shortness of breath, darkened vision, call an ambulance.
What does the heart need?
Of all the chemical elements, the heart needs most:
- iodine (products containing it have a beneficial effect on metabolism: these are sea fish, squid, shrimp, seaweed and other gifts of Neptune),
- potassium (it improves the activity of the heart muscle, promotes the removal of excess fluid: most of it is found in potatoes, pumpkin, cabbage, apricots, prunes, dried apricots, figs, rose hips, black and red currants, parsley),
- magnesium (this element has a calming, vasodilating and diuretic effect, maintains the tone of the walls of blood vessels, and therefore do not neglect porridges: oatmeal, millet, barley, buckwheat, as well as walnuts, peas, beets, carrots, salad; wheat bran is rich in magnesium, soy flour, sweet almonds, bananas.American scientists have concluded that those who receive at least half a gram of magnesium daily (that’s how much it is contained in one banana) have a minimal risk of heart attack).
And another gastronomic addiction of your heart is dairy and vegetarian soups: from cereals, vegetables. Do you remember the last time these dishes were on your table?
Possible consequences
A rare pulse (40–45 beats/min) is dangerous for the patient when high blood pressure is recorded, as it leads to the development of hypoxia. Oxygen starvation provokes a disorder of cerebral circulation, resulting in destructive changes in the vascular system of the brain.
Frequent attacks of bradycardia increase the risk of blood clots, since slow blood circulation contributes to its stagnation in the heart chambers. Blood clots that have formed in the heart can migrate to any vessel, causing blockage.
Traditional medicine to normalize heart rate
Along with medications, traditional medicine recipes can also prevent increased heart rate. Most often, medicinal plants are used in the treatment of tachycardia, which contain natural glycosides and herbs with a calming effect.
| Product name | Ingredients and preparation | Mode of application |
| Viburnum and cranberry balm | Viburnum and hawthorn (berries) - 1 kg each. Rose hips, cranberries - 0.5 kg each. Place in layers in a 5-liter container, sprinkle with sugar (you can use honey). Pour vodka to the level of the berries. Leave in a dark place for 21 days | 30 g twice a day - morning and evening. You can use berries from balsam to make compotes |
| Oriental Heart Balm | Lemon (with peel) – 500 grams. Dried apricots, raisins – 500 grams each. Walnuts (kernels) – 500 grams. Grind using a blender, add 1 kg of honey. Store in a cool place | 1 teaspoon per day in the morning |
| Clover tincture | Place fresh clover flowers in a container (liter jar) and fill with vodka. Infusion time: 30 days in a dark place | 1 teaspoon three times a day, after meals |
Take a medium sized head of garlic and make a paste from it. We put everything in a jar, fill it with unrefined sunflower oil and leave it at home inside the refrigerator for the whole next night. In the morning, cut out the top of a ripe lemon with a knife and squeeze fresh juice into a teaspoon. Let's add a little garlic oil.
We make butter this way. Peel 2 garlic heads and cut them into small pieces. Place in a jar made of any glass and fill with vegetable oil (about half a glass). We store the jar in the sun for 11 days, stirring it every day. After 11 days, filter and add 1 drop of purified glycerin (sold at the pharmacy). Let's put everything into a bottle, but now from darkish-colored glass with a good cork. It belongs in the refrigerator. Treatment at least three times in one day. The course is usually allowed for up to 90 days.
Diagnostic measures
In order to diagnose bradycardia, the general clinical picture is studied: a person’s lifestyle, his complaints, and accompanying symptoms. A cardiac examination is required to identify possible heart pathologies. The doctor analyzes information about the medications the person is taking and compares the electrocardiogram data with other indicators obtained as a result of laboratory tests and examinations. The classic Holter method or weekly monitoring of the heart rhythm using a special mobile device can be used.
First aid for bradycardia
The selection of medications for the correction of pathological changes is carried out by the attending physician, taking into account the etiological factor of the condition. If the relationship between pulse and pressure is abnormal, it is contraindicated to take drugs from the group of beta blockers and calcium antagonists, as they cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure and inhibition of the activity of the sinus node. The drugs of choice are drugs from the class of ACE inhibitors, which have a smooth mechanism of action. However, if there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, every hypertensive patient should know what to do at home to stabilize the indicators.
During an attack, the following measures should be taken:
- Take a horizontal position on your back, while your torso should be slightly raised.
- Wrap the lower limbs in a blanket, apply a heating pad or mustard plasters to the feet.
- Take medicine (Losartan, Lasix, Amlodipine, Captopress).
In cases where an increase in blood pressure occurs even with a slight decrease in heart rate, but is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in condition, it is necessary to call an ambulance or transport the patient to a hospital.
Causes of increased heart rate
The etiology of tachycardia may be associated with various endo- and exogenous factors:
- pregnancy;
- failure of the central nervous system;
- intoxication;
- malignant neoplasms;
- excess weight;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- presence of bad habits (drinking alcohol, taking drugs, smoking);
- psycho-emotional stress (joy, fear, stress, etc.);
- excessive physical activity;
- a- and hypovitaminosis;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- menopause;
- uncontrolled use of certain medications;
- systematic overeating;
- anemia;
- heatstroke;
- chronic fatigue.
How dangerous is the condition?
The consequences of the pathological process are varied.
- Heart failure. Asystole is the first thing a patient risks encountering when bradycardia develops. A fatal complication occurs not so much as a result of a decrease in the frequency of contractions, but as the main cause of this condition.
There is a decrease in myocardial contractility, the intensity of blood ejection into the large and small circles weakens. Insufficient nutrition affects the tissues of the heart, the process is aggravated by myocardial ischemia.
Attention:
The likelihood of asystole does not depend on the severity of bradycardia, therefore, equal attention to all patients is necessary.
- Heart attack. If the above process takes a different path and ischemia reaches a critical point, acute necrosis of the heart muscle will develop. Mortality compared to other diseases is almost 70%; even timely first aid and treatment do not guarantee survival.
- Stroke. This time ischemic brain damage. As a result of weakened hemodynamics, cerebral structures receive a small amount of nutrients and oxygen.
The danger of the condition is not only the probable death from damage to vital centers, swelling and other complications.
Even if therapy is started in a timely manner, the risk of neurological deficit is high. How it will manifest itself—impaired speech, hearing, vision, or other means—is not known.
- Pulmonary edema. Weakening of gas exchange leads to the formation of effusion in the tissues between the alveoli. The liquid compresses the structures. The amount of oxygen delivered decreases. In addition to suffocation itself, there is an inferiority of cellular respiration.
Preventing fatal complications is a priority goal of therapy, along with eliminating symptoms and etiological factors.