What does an electrocardiogram show?
An electrocardiogram during a heart attack is common. But you should not wait for such an extreme condition to undergo the procedure.
It is advisable to do it when:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Rheumatism
- Arterial hypertension
- Pain in the heart area
- Fainting
- Interruptions in heart function
The results of the electrocardiogram show at what frequency the heart beats and in what rhythm. It can be used to determine the position of the electrical axis of the heart muscle.
Heart sinking
Atherosclerosis
Menopause
40983 20 October
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Fading of the heart: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Description
Fading of the heart is a subjective feeling of the absence or skipping of another heartbeat in a certain period of time, accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the heart area, in some cases, dizziness and darkening of the eyes. Heart stopping is a symptom of a wide range of diseases: from the most harmless ones that do not require treatment to serious pathologies that require medical intervention.
Types of heart palpitations
Normally, the heart contracts rhythmically, at approximately equal intervals. The contraction frequency ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
There are several types of heart failure:
- Fading of the heart due to a compensatory pause during extrasystole. There is a sensation of a strong or double heartbeat against the background of a normal rhythm, followed by a short pause felt by the patient.
- Varying intervals between contractions can also cause the heart to feel as if it is stopping (common with atrial fibrillation).
- Pauses of the heart due to blockade of impulses.
- Feeling of freezing with reduced pumping function of the heart (with severe heart failure).
Possible causes of heart failure
First, we list the most common risk factors for cardiac problems:
- Smoking
is one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease. This also includes alcohol, caffeine and drugs. - High levels of “bad” cholesterol
- intermediate, low and very low density lipoproteins (IDL, LDL, VLDL). - High blood pressure
.
The feeling of interruptions and pauses in the work of the heart in most cases is caused by extrasystoles, or premature contractions of the heart.
Extrasystoles are often observed in completely healthy people, while there are no signs of myocardial dysfunction, and correction is not required.
However, if attacks of extrasystole exceed the permissible norms per day (diagnosis is carried out using daily ECG monitoring), additional examination and treatment are required.
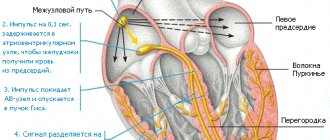
Less commonly, the cause of heart failure is atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) or blockade of the conduction system of the heart. Atrial fibrillation occurs when the electrical activity of the atria is disrupted with the occurrence of a large number of impulses and chaotic contraction of the atria.
Only a portion of the impulses pass to the ventricles of the heart in an irregular rhythm - hence the fading of the heart, as well as other unpleasant sensations.
Atrial fibrillation can occur in the form of attacks (paroxysms), or it can be permanent. The diagnosis is made based on the results of the ECG.
Blockades of the conduction system of the heart, depending on the severity, manifest themselves in different ways: from asymptomatic to loss of consciousness. Feelings of heart stopping most often occur with 2nd degree atrioventricular block.
There is a gradual depletion of the atrioventricular (AV, AV) node, a decrease in the ability to conduct impulses, and a kind of pause occurs, which the patient clearly feels.
Causes of disturbances in the structure of the conduction system of the heart:
- myocardial infarction with subsequent replacement by connective tissue of destroyed heart structures, including important bundles that conduct electrical impulses from the sinus node;
- coronary heart disease, when due to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, adequate blood supply to the myocardial areas in the area of the conduction bundles is disrupted and sclerodegenerative fibrosis (replacement with connective tissue) of the affected tissue areas develops;
- myocarditis (inflammatory damage to the heart muscle);
- dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the conduction system of the heart.
Sick sinus node syndrome (SSNS) is a rare condition caused by a decrease in the functional ability of the sinus node to act as the main pacemaker and ensure regular conduction of impulses to the atria, which predetermines the appearance of cardiac slowdown and accompanying arrhythmias.
Patients often complain of dizziness, poor exercise tolerance, shortness of breath on exertion, fatigue and episodes of weakness.
Many cardiac problems, which at first glance are not related to rhythm disturbances, can ultimately lead to the appearance of various arrhythmias, accompanied by a feeling of cardiac arrest. For example, with hypertension, the myocardial wall thickens and the nutrition of heart cells is disrupted, which leads to the appearance of ectopic (irregular) impulses. With various defects of the valve apparatus, without treatment, a gradual change in the structure of the heart muscle occurs with the appearance of connective tissue and disruption of the normal conduction pathways of the heart.
Among the non-cardiological reasons for the feeling of heart failure, it is worth noting the menopause, which is accompanied by changes in hormonal levels and various unpleasant sensations and discomfort not associated with disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
Hypothyroidism may cause a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) and a feeling of pauses in the heart. This is due to insufficient levels of thyroid hormones.
During intoxication (during infectious diseases, with severe sweating, vomiting and diarrhea), a loss of electrolytes (potassium, sodium and magnesium ions) occurs, which leads to disruption of the water-salt balance in the body and the occurrence of various rhythm disturbances.
Taking certain medications may be accompanied by a slower heart rate, slower impulse conduction, and a feeling of heart stopping. These drugs include cardiac glycosides, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, sympatholytic agents, antidepressants, and narcotic analgesics.
In persons with a labile psyche and frequent emotional experiences, a subjective feeling of discomfort in the chest area and cardiac arrest without visible organic pathology is possible.
Which doctors should I contact?
If various disturbances in the functioning of the heart occur, you should consult a cardiologist. To exclude non-cardiological causes of the feeling of heart failure, the cardiologist can refer you to a general practitioner and endocrinologist.
If the cause of heart rhythm disturbances is the use of medications, you must contact your doctor to adjust the dose or replace the drug.
Diagnosis and examination of cardiac arrest
First of all, to detect cardiac arrhythmias, counting the pulse and heart rate is used. When examining a patient, the doctor uses auscultation to listen to the heart rhythm and detect other accompanying symptoms in order to diagnose the disease that has caused the change in heart rate.
If a pathological change in heart rhythm is detected, a therapist or cardiologist will prescribe an electrocardiographic study (ECG).
Detectable diseases
This is what an electrocardiogram determines:
- Arrhythmia
- Myocardial infarction
- Myocardial dystrophy
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Angina pectoris
- Tachycardia
- Bradycardia
- Cardiac aneurysm
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
It is mandatory to do an ECG for patients over 40 years of age.
What is not visible on the cardiogram
No matter how perfect the diagnosis may seem, it does not show some pathological changes in the functioning of the heart muscle.
These include:
- Congenital heart defect
- Neoplasms
An ECG cannot diagnose cerebrovascular accidents (stroke). This pathology disrupts blood circulation in the brain, which can disrupt the functioning of other important organs. Carrying out a cardiogram in this situation will only determine the state of the heart muscle.
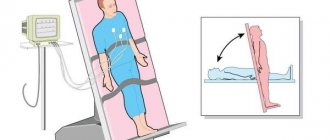
How to undergo an ECG without problems, so that there are no difficulties in making a diagnosis?
POSITION
about the processing of personal data
This Regulation defines the policy, procedure and conditions of the Operator regarding the processing of personal data, establishes procedures aimed at preventing and identifying violations of the legislation of the Russian Federation, eliminating the consequences of such violations related to the processing of personal data. All issues related to the processing of personal data that are not regulated by these Regulations are resolved in accordance with current legislation
Russian Federation in the field of personal data.
1) directly personal data.
regarding the processing of personal data, with this Regulation and amendments to it. Training of these employees is organized by the structural unit for advanced training in accordance with schedules approved by the Operator.
subject to the prior consent of the subject of personal data. Consent may be oral or written.
The specified processing of personal data is considered to be carried out without the prior consent of the subject of personal data, unless the Operator proves that such consent has been obtained.
ensuring the protection of personal data processed by the Operator from unauthorized or accidental access to it, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, provision, distribution of personal data, as well as from other unlawful actions in relation to personal data;
exercise internal control over compliance by his subordinates with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of personal data, including requirements for the protection of personal data;
bring to the attention of the Operator’s employees the provisions of the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of personal data, local acts on the processing of personal data, requirements for the protection of personal data;
organize the reception and processing of requests and requests from personal data subjects or their representatives, as well as monitor the receipt and processing of such requests and requests;
in case of violation of the requirements for the protection of personal data, take the necessary measures to restore the violated rights of personal data subjects.
have access to information regarding the processing of personal data entrusted to him and including:
purposes of processing personal data;
categories of personal data processed;
categories of subjects whose personal data is processed; legal grounds for processing personal data;
a list of actions with personal data, a general description of the methods used by the Operator for processing personal data;
description of the measures provided for in Art. Art. 18.1 and 19 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 N 152-FZ “Personal Data”, including information on the availability of encryption (cryptographic) means and the names of these means;
date of commencement of processing of personal data;
term or conditions for termination of processing of personal data;
information about the presence or absence of cross-border transfer of personal data during their processing;
information on ensuring the security of personal data in accordance with the requirements for the protection of personal data established by the Government of the Russian Federation;
involve other employees of the Operator in the implementation of measures aimed at ensuring the security of personal data, assigning them the corresponding duties and assigning responsibility.
executive power, internal documents of the Operator, as well as the reasons and conditions that contributed to the commission of the violation.
Features of the procedure
An ECG shows ischemia, angina, arrhythmia and other pathologies of the heart muscle in both adults and children. The study is carried out at rest, although studying changes in some indicators requires a small load. An ECG will also show heart failure. When carrying out the procedure in children, it should be taken into account that their normal values will differ from the established limits for adults.
To obtain accurate data from the results of an electrocardiogram, you should trust your heart to be checked by qualified specialists and have it done in specialized institutions. They are in every city. In the city of Bronnitsy, the Immunity MC conducts similar cardiological studies.
Cost and appointment
Ultrasound of the heart
Ultrasound examination of the heart or echocardiography is a method of studying the anatomy of the heart muscle. During the procedure, the diagnostician directs a special device to the heart. The device passes ultrasonic waves through the body. Our organs reflect and partially absorb waves. The ability of different human tissues to reflect/absorb ultrasound differs. The ultrasound machine receives the reflected waves and converts them into an image on the monitor.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
- Valve condition.
- Pathologies, for example, a tumor or a previous microinfarction.
- The speed of blood flow in the heart.
- Vessel diameter.
- Changes in the thickness of the walls of the ventricles and atria.
- Changes in large vessels.
- Blood clots.
- Is there fluid in the pericardial sac?
A professional cardiologist uses ultrasound results to detect many heart diseases. The doctor makes a conclusion based on the results of the study, taking into account age, gender, lifestyle and many other factors. Therefore, during the examination, answer the doctor’s questions in detail and honestly.
Indications for cardiac ultrasound
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the heart according to the following indications:
- weakness and dizziness;
- fainting and recurring headaches;
- nausea due to high blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- swelling on the body in the late afternoon, especially on the legs;
- constant and recurrent pain in the chest or under the shoulder blade;
- rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations;
- pale or bluish skin;
- heart murmurs;
- suspicion of congenital or acquired heart disease;
- vascular pathology, for example, varicose veins or thrombophlebitis;
- suspicion of rheumatism, lupus erythematosus or scleroderma;
- upcoming surgery if there is a history of cardiac problems or if the patient is over 50 years of age.
If after a routine echocardiography the doctor still has doubts, he may prescribe an ultrasound of the heart through the esophagus. Such a study causes some discomfort to the patient, but gives a more accurate result.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination. It is safely prescribed to everyone, including children and pregnant women.
Caution: fainting!
“AiF”: – Your center pays great attention to the so-called syncope, that is, fainting. Why?
L.M.: – First of all, because this is a very common problem. Especially in childhood. By the way, for a long time, many fainting spells in children were considered a purely neurological problem and were primarily associated with epilepsy. But later it turned out that in most cases, fainting is associated not only with neurological problems, but also with a sudden disruption of cardiovascular regulation, with a drop in blood pressure, which may be based on cardiac arrest caused by a disturbance in the heart rhythm. Moreover, 5% of fainting in children are associated with life-threatening arrhythmias. Most often - with a sudden increase in contractions of the ventricles of the heart (ventricular tachycardia) or a sudden slowdown in the rhythm (up to long pauses that can last 10 seconds or more).
This problem cannot be left without attention. If, after running up the stairs or racing with someone, your child gets tired quickly, sit down, if he turns pale or loses consciousness. The same thing with babies. If your baby suddenly turns pale or limp while crying or feeding, or if his nasolabial triangle suddenly turns blue, there is no need to think twice. See a doctor urgently!
Moreover, now there are a lot of technologies with which you can determine what causes fainting in a child, most of which are quite harmless. And often it is enough to simply adjust the child’s lifestyle, remove provoking factors and achieve excellent results without any medications.
“AiF”: – What if the situation is serious?
L.M.: – And in this case there is no need to panic. In the arsenal of arrhythmologists there are many effective means for treating cardiac arrhythmias. The main thing is to correctly assess the situation, which in childhood can range from normal to serious pathology, when the most active therapy or even heart surgery is necessary.
Pharmacological tests
Pharmacological tests are an alternative to stress tests and are recommended for patients who, for various reasons, cannot perform physical activity. The principle of their action is the introduction of special drugs, due to which the myocardial need for oxygen increases, thereby simulating activity. Depending on the drug, this need arises as a result of an increase in heart rate or redistribution of blood in favor of vessels not affected by atherosclerosis.
Causes of heart block in adults
The most common cause of heart block is a heart attack.
Other causes include heart disease, problems with the structure of the heart (due to defects) and rheumatism. The blockage can also be caused by damage during open heart surgery, as a side effect of certain medications or exposure to toxins. Heart block can be congenital, but it is a rare pathology. The risk of heart block increases with age and the presence of heart disease.
First-degree heart block is common in well-trained athletes, teenagers, young adults, and people with a highly active vagus nerve.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris at the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs
Today, instrumental diagnostics play a valuable role in monitoring the state of the cardiovascular system. Coronary heart disease cannot be completely cured and requires the patient to pay increased attention to his own body. Monitoring the condition using modern medical equipment allows you to correctly adjust therapy, thereby prolonging the patient’s life.
The Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs conducts a full range of studies of the cardiovascular system . Our experienced cardiologists work with the latest medical equipment, which allows us to detect the disease in the early stages, as well as diagnose asymptomatic forms of angina.
Specializing in non-surgical methods for diagnosing and treating heart disease, our doctors quickly, painlessly and, most importantly, completely safely carry out any procedure, make an accurate diagnosis and return you to a healthy and fulfilling life!
Do not put off health problems; the key to success in the treatment of coronary artery disease is its timely diagnosis!
The best for children
“AiF”: – Is high-tech cardiac care available for children in our country? For example, is it possible to get into your center?
L.M.: – Absolutely. Our center has patients from several environmentally disadvantaged regions of Siberia, the European part of our country, the North and the Far East, for whom we provide comprehensive examination and therapeutic treatment at the expense of budgetary funds. But we can accept Muscovites only according to quotas: our center is under federal subordination.
“AiF”: – Is there anywhere else besides Moscow that they diagnose and treat cardiac arrhythmias in children?
L.M.: – We have several strong arrhythmology schools – in Tomsk, Novosibirsk, St. Petersburg. But this, of course, is very little for such a large country as ours. There are also problems in the provision of diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. It is necessary to more actively implement advanced protocols for the examination and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children, which have been successfully practiced in the world for a long time. But I am an optimist and hope that the situation will change for the better.
Causes of ischemic disease. Warning the heart
If we consider organic lesions of the cardiovascular system, arrhythmias most often occur with ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, cardiomyopathies, heart defects, pathologies of large vessels (pulmonary embolism, aortic aneurysms), hypertension, pericarditis and heart tumors. Arrhythmias can also be observed in endocrinopathies (pheochromocytoma, thyrotoxicosis), drug intoxication (glycosides, catecholamines), acute infectious diseases, anemia, in violation of the body's electrolyte balance (especially potassium, calcium and magnesium) and other pathological conditions.
Sometimes heart rhythm disturbances also occur under the influence of exogenous factors: excessive consumption of coffee, alcohol, tobacco. Some types of arrhythmias can also develop in healthy people in response to physical activity or nervous tension.
The arrhythmic variant of IHD is spoken of only in cases where cardiac arrhythmias are the only symptom of this disease. The diagnosis of coronary artery disease remains presumptive until ECG, Holter monitoring and coronary angiography are performed, which reveal various heart lesions. However, in most patients, arrhythmias are combined with other clinical forms of IHD. Rhythm disturbances are also a common symptom of atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, especially with angina pectoris or heart failure. However, despite the many reasons that can cause rhythm disturbances, all arrhythmias can be divided into three main groups: those associated with impaired impulse formation, those associated with impaired impulse conduction, and combined arrhythmias. Table 1 presents the classification of arrhythmias depending on the mechanism of their occurrence.
Table 1.
Classification of arrhythmias depending on the mechanism of occurrence
| Mechanism of occurrence | Impulse formation disorders | Impulse conduction disorders | Combined disorders |
| Types of rhythm disturbances | Sinus tachy- and bradyarrhythmias, sick sinus syndrome, ectopic rhythms (non-paroxysmal tachycardias), extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardias, fibrillation and flutter of the atria and ventricles | Blockades: sinoatrial, intraatrial, atrioventricular; premature ventricular excitation syndrome | Atrioventricular dissociations, ectopic rhythms with block, parasystoles* |
* Rarely encountered
The diagnosis of “cardiac arrhythmia” is always based on clinical and electrocardiographic data, and treatment includes therapy for the underlying disease and antiarrhythmic measures themselves.