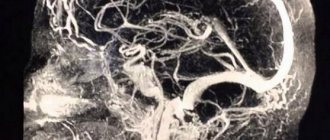
Magnetic resonance imaging has high tissue and fluid contrast. The procedure allows visualization of loose structures of the body without significant invasive manipulations. MRI is actively used in neurology and neurosurgery to diagnose diseases of the nervous system. Magnetic resonance scanning is considered the most informative method of studying the brain. According to the results of tomography, inflammatory, degenerative, dystrophic changes, and tumors are detected.
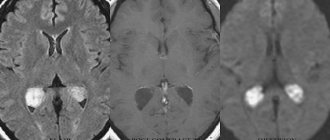
Colloid cyst on MRI
A brain cyst is a benign neoplasm inside the skull. It is a closed pathological formation with predominantly liquid contents. Congenital cysts appear when intrauterine development is disrupted; acquired ones can be the result of head trauma, infectious disease, cerebrovascular accidents and other conditions. The formations are not prone to malignant degeneration, but when they reach an impressive size they can compress surrounding structures. It is important to diagnose a cyst as early as possible and determine treatment tactics. MRI scanning allows you to identify and differentiate formations and track the dynamics of the process.
Read also
Spinal tumors
Spinal tumors are divided into benign and malignant, and the insidiousness of benign forms is that they may not produce any symptoms for many years.
Let's look at how... Read more
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is an accumulation of fluid in the brain. On MRI it looks like ventricular dilatation. Accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. There are two types of hydrocephalus. Obstructive (non-communicating)…
More details
Tumors of the brain and spinal cord
Brain tumors account for about 10% of all cases of neoplasms, while spinal cord tumors are diagnosed in approximately 4.2% of all diseases of the nervous system. Respectively,…
More details
Cluster headache
One of the types of primary cephalgia is cluster headache ("cluster" - "bundle"). This type of cephalalgia is characterized by very intense, short attacks concentrated around the eye...
More details
Neoplasms of the genital organs
The most common neoplasms of the genital organs in urological practice are penile cancer and testicular cancer. Men are at risk for genital cancer if they: Are older...
More details
Brain cyst (Cerebral cyst)
Arachnoid cyst
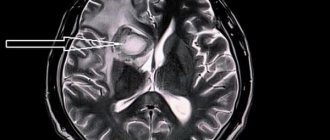
more often it is congenital or post-traumatic in nature. Located in the meninges on the surface of the brain. Filled with cerebrospinal fluid. According to some reports, up to 4% of the population have arachnoid cysts of the brain. However, clinical manifestations are observed only in the case of a large accumulation of fluid in the cyst, which may be due to the production of cerebrospinal fluid by the cells lining the cyst cavity. A sharp increase in the size of the cyst threatens its rupture, leading to death.
Pineal cyst
(pineal cyst) is a cystic formation of the epiphysis. Anecdotal evidence suggests that up to 10% of people have small, asymptomatic pineal cysts. Cysts with a diameter of more than 1 cm are observed much less frequently and can cause clinical symptoms. When it reaches a significant size, a pineal gland cyst can block the entrance to the cerebral aqueduct and block cerebrospinal fluid circulation, causing occlusive hydrocephalus.
Colloid cyst
makes up about 15-20% of intraventricular formations. In most cases, it is located in the anterior region of the third ventricle, above the foramen of Monroe; in some cases - in the IV ventricle and in the area of the transparent septum. The filling of a colloid cyst is highly viscous. The basis of the clinical manifestations are the symptoms of hydrocephalus with a paroxysmal increase in cephalgia in certain positions of the head. Behavioral disorders and memory loss are possible. Cases of weakness in the limbs have been described.
Choroid plexus cyst
is formed when cerebrospinal fluid fills the space between the individual vessels of the plexus. Diagnosed at different ages. Clinically manifested rarely, in some cases it can give symptoms of intracranial hypertension or epilepsy. Often, choroid plexus cysts are detected by obstetric ultrasound at the 20th week of pregnancy, then they resolve on their own and by approximately the 28th week of intrauterine development they are no longer detected on ultrasound.
Dermoid cyst
(epidermoid) is an abnormality of embryonic development in which the cells that give rise to the skin and its appendages (hair, nails) remain inside the brain. The contents of the cyst, along with the liquid, are represented by elements of the ectoderm (hair follicles, sebaceous glands, etc.). It is characterized by a rapid increase in size after birth, and therefore must be removed.
2. Symptoms of a tumor cyst
Clinically, these neoplasms begin to manifest themselves when pressure comes on the surrounding brain tissue due to the increased size of the cyst. These symptoms are characteristic not only of cysts, but also of other types of benign tumors:
- auditory, visual and olfactory disorders;
- movement coordination disorders;
- inability to concentrate;
- difficulties with memory and speech;
- dizziness, nausea, vomiting;
- partial or complete paresis of the facial muscles;
- loss of sensation in the limbs, convulsions.
Visit our Neurosurgery page
MRI with contrast
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed with contrast, especially if any neoplasm is suspected. This makes it possible to examine the tumor in detail and distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
The contrast agent clearly highlights the vessels, which allows you to see any tissue pathologies. Don't worry, contrast agents are safe for the human body. Most patients tolerate this procedure well. You must first consult a doctor and exclude all possible contraindications.
MRI diagnostics for arachnoid cyst
Despite the fact that CT allows you to accurately determine the size and location of the cyst, MRI provides the most accurate and complete information about the formation. Typically, to diagnose an arachnoid cyst, an MRI scan is performed with the injection of contrast into the patient's bloodstream. At the same time, brain tumors tend to accumulate contrast, and cysts do not absorb it from the blood vessels, which is very clearly visible on MRI.
Also, MRI scanning allows you to distinguish a cyst from hemorrhages, hematomas, hygromas, abscesses and other diseases with similar symptoms. In addition, MRI makes it possible to identify a cyst even in cases where the patient does not yet have any symptoms, and the cyst itself measures only a few millimeters.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
Treatment with folk remedies
Any folk remedies can only be used as additional treatment. In particular, it is recommended to prepare decoctions of plants - both collections and individual herbs. It is recommended to prepare decoctions of elecampane, hemlock, wormwood, chamomile, yarrow, calendula, chamomile, etc. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 1 tbsp. l. selected plant or mixture thereof, pour boiling water (200 ml) and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes. Drink 150 ml three times a day before meals.
Alcohol infusions can be prepared from the listed plants. For this purpose, 100 g of the plant is poured with 300 ml of alcohol and infused in a dark place for two months, shaking occasionally. Take 1 tsp. a day before meals.
Consequences and complications
As the formation progresses, the following complications may develop:
- Encephalitis.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Developmental delay of the child.
- Epilepsy.
- Brain hernia.
- Cyst rupture is a serious complication that can be fatal.
Preparation rules
During a routine examination, doctors recommend following a few simple recommendations:
- If it is necessary to administer contrast, you must come to the clinic on an empty stomach, that is, do not eat food for 7-8 hours.
- If you are afraid of research or confined spaces, be sure to consult with a specialist. Your doctor may prescribe you sedatives to make the examination process more comfortable.
- Do not bring any metal products inside the tomograph. For this reason, doctors recommend removing metal accessories in advance.
- Prepare a change of clothes that do not have metal or metal-containing accessories.
- The duration of the diagnostic test is about 40 minutes. Empty your bladder in advance to avoid discomfort during the procedure.
4.Basic treatment methods
As a rule, cysts that do not show a tendency to grow do not require treatment at all. Otherwise, treatment of neoplasms is carried out surgically. It could be:
- transcranial surgery, which provides high efficiency of cystectomy, but is traumatic for the patient;
- shunting the cyst to evacuate the liquid contents, after which its walls collapse;
- gentle endoscopic surgery using special equipment.
Diet
Diet number 12
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2-3 weeks
- Terms: 21 days or more
- Cost of food: 1590-1680 rubles per week
If you have a brain cyst, your diet should be complete, varied, and enriched with vitamins and minerals. It is useful to introduce the following products into your diet:
- Fruits and vegetables.
- Whole grain porridge, bran.
- Seafood, fish, seaweed.
- Nuts.
You should not consume fatty and fried foods, smoked foods, preservatives, and alcohol.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the body only if all contraindications are excluded.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended in the following cases:
Very often, to obtain more informative images, doctors prescribe additional contrast. In this case, you must ensure that there are no following contraindications:
- Pregnancy of any stage.
- Breastfeeding period.
- Kidney failure.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Allergic reaction to components included in contrast agents.
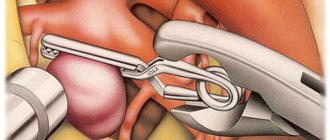
4. Stereotactic aspiration of tumor cysts
The essence of this gentle technique is to insert a small-diameter probe into the cyst through a small hole in the skull in order to pump out excess liquid contents from its cavity. This procedure occurs either using the neuronavigation
, or using a special
navigation frame
. In both cases, the operating neurosurgeon has the opportunity to extremely accurately hit the desired area with the instrument. When using neuronavigation, a three-dimensional image of the surgical field is displayed on the monitor, which increases the efficiency of the surgeon’s actions. The manipulation is carried out with high precision, taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the patient and does not cause damage to surrounding tissues. A disadvantage of stereotactic aspiration can be considered the lack of opportunity for the surgeon to conduct a thorough inspection of the operating area and control the risk of possible bleeding. But this does not at all detract from the advantages of minimally invasive surgery compared to traditional surgery.
Symptoms of an arachnoid cyst
Depending on the location and size of the cyst, one or more symptoms may appear:
- Headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Lethargy, including excessive fatigue or lack of energy;
- Seizures;
- Developmental delays;
- Hydrocephalus caused by disruption of the natural circulation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Problems with the endocrine system, for example, early onset of puberty;
- Involuntary shaking of the head;
- Vision problems.
The larger the cyst, the more symptoms will appear, their frequency and severity will increase. With prolonged and strong compression, it can lead to irreversible changes in brain tissue. If excessive compression and rupture of the cyst membranes occurs, the patient may die.
Treatment
In neurology departments, when treating colloid cysts of the third ventricle, doctors adhere to the following tactics: small formations without symptoms of the disease are not treated, the patient is sent for an annual MRI or CT scan, which evaluates the size of the formation and its tendency to grow.
For large tumors with clinical manifestations or with progressive enlargement of the cyst, consultation with a neurosurgeon is indicated to decide on surgical treatment. During surgery, the cyst is completely removed, the cerebrospinal fluid ducts are cleared, and thereby the syndrome of increased intracranial pressure is eliminated. The following surgical techniques are used: craniotomy and endoscopic removal. Craniotomy is an opening of the skull and open brain surgery; it allows you to completely remove the tumor, examine the cavity of the third ventricle, and restore the cerebrospinal fluid tract. Its disadvantages are greater trauma and cosmetic defects after surgery. Endoscopic removal of a colloid cyst is carried out through a small hole in the bones of the skull using a special apparatus, which allows both to examine the cavity of the third ventricle and to remove the tumor. After surgery to remove the cystic formation and restore the flow of cerebrospinal fluid using modern methods, an almost complete recovery of patients is noted. In rare cases, the pathological process recurs, and then a repeat operation becomes necessary. To prevent the onset of colloid cyst growth in adults, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Causes
The formation of congenital brain cysts occurs at the stage of intrauterine development under the influence of a number of factors, which may include:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- Rhesus conflict;
- infectious diseases;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- fetal hypoxia during childbirth;
- use of certain medications;
- taking drugs, alcohol, smoking during pregnancy .
Acquired formations may appear under the influence of the following factors:
- injury to the baby's head during childbirth;
- inflammatory diseases of the brain;
- TBI;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- complications after surgery;
- degenerative and dystrophic processes;
- parasitic infections.
Vascular disorders, head injuries, neuroinfections, inflammatory processes, etc. can provoke an increase in existing cysts.