Hemoglobin in vegetarians
Increased interest in vegetarianism needs to be supplemented with competent information. Those who want to change their lifestyle, daily menu, or give up meat should choose their diet wisely. Only a balanced diet will not cause a deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood.
Hemoglobin is a transformed protein in the circulatory system based on iron. Its main function is to transport oxygen molecules from the pulmonary vessels to all cells of the body. The protein element has a complex formation process, which involves, in addition to iron, copper, folic acid and B vitamins.
Important! Medical indicators of normal hemoglobin content are the same for vegetarians and for people who eat food of animal origin. It is important to get tested regularly to adjust your diet.
These micronutrients are found both in food of animal origin and in vegetables, herbs, nuts, and fruits. A full menu containing the listed components will provide the body with everything necessary for a normal life.
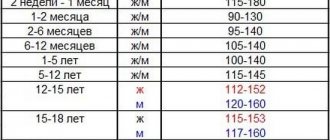
| Category | Hemoglobin norm, g/l | |
| Male | Female | |
| Children under 1 year | 90-140 | 90-140 |
| Children from 1 year to 5 years | 100-140 | 100-140 |
| Children from 5 to 15 years old | 115-145 | 115-145 |
| Teenagers | 120-160 | 112-152 |
| Adults from 18 to 64 years old | 130-160 | 120-155 |
| Adults over 65 years of age | 125-165 | 120-157 |
The presence of meat products in the diet does not guarantee normal hemoglobin content, and vice versa. The indicator is individual for everyone. The region of residence, the presence of bad habits, chronic diseases, hormonal or physiological changes should be taken into account.
ROLE OF IRON IN THE HUMAN BODY
Iron is an essential component of many proteins and enzymes; its most important function is participation in respiration processes. The element is part of hemoglobin and ensures the transport of oxygen to tissues. On the way back, the red blood cells “carry” carbon dioxide to the lungs. If the body lacks iron, then over time the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood decreases, which leads to insufficient oxygen supply to the body’s tissues, and consequently, malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
Why do vegetarians have low hemoglobin and why is it dangerous?
The reason why it is necessary to regularly donate blood to check the level of iron and hemoglobin in the blood of vegetarians is the difference in the absorption of protein components by the body. Animal protein contains divalent iron, while vegetable protein contains trivalent iron. The first form is easier to transform by humans and does not require supplements.
Vegetarians who exclude meat, fish, and eggs from their daily menu must saturate their body with plant-based foods rich in protein. Experts from US research institutes claim that for a person who eats exclusively plant foods, the amount of iron consumed should be increased by 1.8 times. Only in this case will the body's needs be covered.
An unsystematic approach to vegetarianism and lack of monitoring of health can lead to negative consequences in the form of deterioration of well-being, decreased vital activity, and the development of chronic diseases. The absence and deficiency of protein foods in a vegetarian’s diet will cause great harm to the body.
What is vegetarianism
Vegetarianism has existed for several thousand years. From a nutritional point of view, it implies a complete or partial refusal to eat products of animal origin: meat, meat and sausage products, poultry and poultry products, milk, dairy products, eggs, fish and seafood. The term "vegetarianism" was introduced by the British.
Some scientists believe that this word is derived from the Latin vegetus, which means “vigorous”, “strong”, “full of strength”. Vegetarianism, which implies not just a certain set of nutritional rules, but rather a life position, is adhered to by Buddhists. Priests in Ancient Egypt did not eat animal meat, which they believed would interfere with their magical abilities, and the ancient Greeks considered vegetarianism one of the conditions for achieving the cult of a healthy body. The Sacred Books of many nations contain indications of a preference in nutrition for foods of plant origin.
According to statistics, the most vegetarian country is India. This is quite logical, because 80% of the population professes Hinduism, which prohibits the consumption of animal products.
The survey revealed that in Russia only 4% of our citizens accepted vegetarianism as a food system. More than half (55%) have a positive attitude towards vegetarianism, although they themselves eat meat. 29% have a negative opinion on this matter and are sure that vegetarianism is harmful to health. 12% found it difficult to answer.
Vegetarianism presupposes not only the observance of certain food prohibitions, but, first of all, verified ethical, ideological, medical and hygienic beliefs, embodied in nutritional rules. Many vegetarians refuse to use products made from fur, silk, wool, or products that have been tested on animals.
Vegetarians and pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, a pregnant woman is a source of building material for the embryo's body. A lack of any elements is fraught with the development of congenital pathologies and a high risk of miscarriage. Animal foods, fermented milk products, eggs supply the protein necessary for the formation of fetal cells and iron, required for the circulatory system and oxygen transfer.
A pregnant vegetarian needs to approach her diet wisely and decide whether it is worth putting her body and the health of her future offspring at risk. If you decide to maintain your lifestyle, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- At your appointment with the supervising doctor, be sure to inform him about your diet and your non-acceptance of meat, dairy foods, and eggs;
- Be monitored regularly at a medical facility. Take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- Competently plan your diet for every day. A vegetarian diet high in sweet foods, grains, and oriental spices will help raise hemoglobin;
- enrich your daily menu with spices and herbs such as ginger, cardamom, cumin, fennel, turmeric, legumes, buckwheat;
- eliminate pistachios, peanuts, spicy, sour, bitter foods;
- limit canned products, packaged drinks;
- sleep at least 8 hours a day, rest regularly;
- Spend at least 2 hours outdoors every day;
- after consulting a doctor, do exercises for pregnant women, visit the pool or do yoga (with the exception of some asanas);
- change your place of residence. It has been established that the climate of Russian regions is not suitable for people who prefer vegetarianism. Lack of sunlight, low-quality products, and low temperatures negatively affect the pregnant woman’s body and the full formation of the embryo. For the safe bearing of a child, women who do not consume food of animal origin are suitable for East Asian countries.
Reduced hemoglobin in the blood is often observed during pregnancy and in meat eaters. Vegetarians are even more vulnerable at this time. You need to reconsider your lifestyle or create a balanced diet that saturates the pregnant woman’s body with all the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Iron deficiency in a pregnant woman's body causes oxygen starvation of the body, which is expressed by general weakness, constant drowsiness, fainting, weakness, and pale skin. There is a high risk of miscarriage and the development of congenital abnormalities of the fetus. A vegetarian woman should be monitored by a hematologist throughout her pregnancy.
DIET: WHAT'S IN THEORY
To maintain normal hemoglobin levels, iron-rich foods are included in the diet. The element concentration in them can be:
- high (more than 4 mg per 100 g): meat, fish, seafood, quail eggs, spinach, peaches, nuts, legumes, grains, etc.;
- moderate (1–2 mg): pomegranate, quince, persimmon, apples, pears;
- low (less than 1 mg): apricots, plums, kiwi.
- But often foods rich in iron do not provide the body with this microelement. What is the reason?
Depending on the digestibility of the element, products are distinguished:
- heme (of animal origin and constituting about 10% of the total diet). Iron is best absorbed from beef (17–20%), followed by liver and offal (10–20%), followed by fish (9–11%);
- non-heme (vegetable, the content of which in the daily menu is close to 90%). From beans, beans, soybeans, rice, corn, apples, lemons, oranges, spinach, parsley, etc., the element is absorbed by only 1–7%.
In addition, in order to increase the value of hemoglobin, during the diet you need to monitor the intake of substances that can improve or worsen the absorption of iron.
A vegetarian child and the problem of low hemoglobin
A child’s growing body needs a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. It is important to maintain caloric intake, the ratio of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Official medicine recommends that minors refrain from vegetarianism.
A growing person needs protein to form muscles, nerve cells, and the hormonal system. Excluding meat, eggs, dairy products, and fish from food leads to a deficiency of iron in the body.
Low hemoglobin entails:
- failure in metabolic reactions;
- formation of a weak muscular skeleton;
- low immunity;
- susceptibility to infectious diseases;
- mental retardation;
- decreased tone;
- early manifestation of genetic diseases.
Hemoglobin deficiency over a long period causes iron deficiency anemia, which is accompanied by a significant developmental lag of the child from his meat-eating peers in physical and intellectual terms.
Healthy! Allow your child to choose food from an early age, do not force your taste habits on him. Let a growing person of conscious age decide for himself what kind of life he should lead.
A vegetarian child must be regularly seen by a doctor, periodically undergo examinations, take a biochemical blood test, and prepare a balanced diet with additives that help absorb the ferric form of iron from plant foods.
Vegetarianism in children and pregnancy
In order for a child’s body to develop normally, adequate nutrition is necessary. Therefore, many doctors have a negative attitude towards vegetarianism in children and adolescents. With an inadequate diet, the health status of minors worsens. Vegetarianism permanently reduces the level of hemoglobin in a child’s body. Therefore, metabolic processes occur with numerous disturbances. Vegetarian children often get sick and grow up physically weaker than meat-eaters. Even regular school assignments are difficult for them to complete. With constantly low iron levels, a disturbance occurs in the psychological, intellectual and emotional state of children. Therefore, it is not recommended to switch minors to a vegetarian diet.
For pregnant women, normal iron levels in the body are of fundamental importance. With a low level of hemoglobin, the supply of oxygen to organs deteriorates. This negatively affects the development of the fetus. Therefore, expectant mothers are advised to give up vegetarianism at least during pregnancy. If a woman is not going to give up her eating habits, she needs to take measures to increase hemoglobin. Otherwise, problems in the development of the fetus and even miscarriage are possible.
Symptoms of reduced hemoglobin
A person is able to receive a full complex of minerals, vitamins, and macronutrients from both animal and exclusively plant foods. It is important to create a balanced menu of vegetables, fruits, nuts and spices to compensate for the deficiency of substances in the body.
The following symptoms indicate low hemoglobin:
- frequent dizziness;
- chilliness;
- pallor and cyanosis of the skin;
- dry dermis;
- lamination and brittleness of nails;
- frequent fatigue;
- fainting;
- muscle weakness;
- mood swings;
- malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (formation of gases, rare bowel movements, belching);
- hair loss;
- irritability;
- disturbance of breathing rhythm after minor physical exertion;
- blurred vision, appearance of spots before the eyes;
- drowsiness;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- frequent colds.
If at least 3 of the listed signals occur, contact a medical facility for a blood test. Long-term iron deficiency in the body should not be allowed.
Vegetarianism and hemoglobin: myths
A little history
Vegetarianism (refusal of animal slaughter products for food) has been a part of human culture since approximately the 5th-3rd centuries. BC. Pythagoras, Aristotle, Zarathustra and Plato did not eat meat.
The fashion for vegetarianism came to Europe in the mid-19th century. Today, vegetarianism is widespread almost throughout the globe.
People choose a vegetarian lifestyle for various reasons :
- strengthening the immune system;
- cure for chronic diseases;
- ethical considerations or philosophical beliefs.
What about now?
The World Health Organization, as well as the Dietetic Association of the USA and Canada, note that there are many advantages to vegetarianism . Nutritionally balanced, properly calculated vegetarian food is good for health.
Vegetarianism allows you to relieve chronic illnesses, and sometimes get rid of them completely, helps strengthen the immune system, restore the functioning of the digestive system, and much more. Plant-based foods suit everyone.
The risk of cancer, cardiovascular, kidney and other diseases for a vegetarian 40% lower
Living a meat-free life reduces the risk of diabetes, joint and hormonal problems. Estrogen and cholesterol levels are reduced due to the abundance of plant fiber in the diet. Depression goes away, mental problems are alleviated. As medical statistics show, increased consumption of animal fats can cause problems with the cardiovascular system. Eating meat – with the gastrointestinal tract, because. Long-digesting food leads to the accumulation of toxins. By replacing heavy meat proteins with plant fibers and polyunsaturated lipids, cholesterol levels decrease and liver function improves.
Reference!
The benefits of switching to a vegetarian diet do not appear immediately. After one to two weeks, you will feel a surge of energy and improved functioning of the digestive system.
widely known myth is that vegetarians are at risk of developing anemia because... They do not get the required amount of protein, vitamin B12, iron and other microelements found in meat with food.
This often discourages those who want to change their lifestyle in favor of vegetarianism.
Often, beginning vegetarians , faced with a decrease in hemoglobin values, come to the conclusion that such a diet is harmful to their health. Many return to their usual diet, with the presence of meat in it. But a common reason lies not in the lack of meat as such, but in a nutritional imbalance.
Why is low hemoglobin dangerous?
A decrease in iron levels in the blood is accompanied by disturbances in the transport of oxygen throughout the body. The main function of hemoglobin is to transport oxygen molecules. As a result of the failure, oxygen starvation of all organs and systems occurs, which leads to irreversible changes and the emergence of pathologies.
With prolonged iron deficiency anemia, the following diseases may occur:
- unstoppable bleeding (external and internal);
- diseases of the stomach and duodenum;
- cholelithiasis;
- cancer tumors of various locations;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- development of heart failure;
- hormonal disorders;
- enlarged spleen and liver;
- diseases of the circulatory system.
Oxygen starvation as a result of a lack of iron in the blood forces the circulatory organs to work more actively, which increases their wear and tear. The body needs oxygen cells, so it will direct its resources to fill the deficit.
In the initial stages of detecting reduced hemoglobin, iron deficiency can be restored by adjusting the diet and taking medications. With prolonged oxygen starvation and the appearance of diseases, medical intervention and hospital treatment are required. Advanced chronic forms and acute hemoglobin deficiency can lead to death.
Possible harms of vegetarianism
An analysis of research has shown that a properly planned vegetarian diet is beneficial to health, meets the body's nutritional needs and can be effective in preventing and treating certain diseases. However, restrictions on the consumption of certain foods can lead to consequences:
- A decrease in the concentration of iron in the blood serum, which indicates the possible development of iron deficiency anemia.
- Zinc deficiency. Vegetarians are often considered at risk for zinc deficiency. Grains, seeds and legumes contain phytates (a substance that reduces the availability of nutrients in the diet). They “bind” zinc and thereby reduce its bioavailability.
| Clinical manifestations and symptoms of hypovitaminosis | |
| Vitamin deficiency | Clinical manifestations and symptoms |
| B1 (thiamine) |
|
| B2 (riboflavin) |
|
| B6 (pyridoxine) |
|
| B12 (cyanocobalamin) |
|
- Vitamin D deficiency: According to the EPIC study
- Oxford, vegans and vegetarians had the lowest average vitamin D intake (0.88 mcg/day compared to the adult norm of 15 mcg/day). Vitamin D affects the renewal of bone tissue. When calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium from food and supplements are not absorbed to maintain proper levels in the blood, the body begins to release calcium from the bones into the blood. Simply put, the body begins to sacrifice bones (read more in the article “Vitamin D deficiency: norms and symptoms”).
- Calcium deficiency. Due to a lack of vitamin D, vegetarians may experience calcium deficiency and impaired calcium-phosphorus metabolism. People who have been on a vegetarian diet for a long time may also have reduced levels of protein metabolism.
- Depression. Australian researchers have found that vegetarians are less optimistic about the future than meat eaters. Moreover, they were 18% more likely to report depression, and 28% were more likely to suffer from panic attacks and anxiety. A separate study in Germany found that vegetarians were 15% more likely to experience depression and twice as likely to suffer from anxiety disorders.
Superfoods and spices
If iron deficiency is detected in the blood, a vegetarian can increase hemoglobin by adjusting their diet. Some types of plant foods are rich in iron in a form that is easily absorbed by the body.
Using available products it is possible to normalize iron levels:
- buckwheat grain;
- legumes;
- millet;
- cabbage;
- carrot;
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- rose hip;
- potato;
- nuts.
The listed ingredients for cooking refer to the source of non-heme ferric iron, which is absorbed by the body only 5%. With the help of natural superfood supplements, you can improve the absorption of complex forms.
Important! Keep a food diary and a kitchen scale. Weigh yourself daily and write down all the foods and foods you eat. This will help you prevent iron deficiency and keep your body healthy.
Natural protagonists (spices, herbs, nuts, berries, etc.), due to their high content of zinc, copper, molybdenum, B vitamins, and sulfur, cause reactions to accelerate the transformation of ferric iron from plant foods. By consuming natural superfood supplements daily, you will ensure a balance of essential elements in your body and increase hemoglobin.
Turmeric
The oriental spice is one of the ten most popular seasonings in the world. For vegetarians, this supplement is especially useful due to its high content of vitamins and minerals. Dishes with the addition of turmeric acquire an appetizing color and bright aroma.
Turmeric contains:
- B vitamins;
- ascorbic acid;
- iron;
- manganese;
- fiber.
Using turmeric in vegetarian recipes raises hemoglobin naturally. Add the spice when preparing vegetable stews, salads, or baking vegetables. Make spicy drinks and smoothies.
Spirulina
Algae contains an abundance of cyanobacteria, which are identical in composition to protein of animal origin.
Spirulina contains:
- easily digestible vegetable protein;
- natural protein;
- amino acids.
Adding spirulina powder to food helps replenish iron and protein deficiency in the body, improve metabolic processes, and increase hemoglobin. Use the additive in any form - in salads, stews, baked vegetables. Depending on the type of processing, spirulina contains from 50 to 73% protein.
You can take spirulina in tablets or powder. In the morning, take up to 5 g of the substance on an empty stomach and wash it down with 1-2 glasses of filtered water. Start breakfast no earlier than 30 minutes later.
Chlorella
The superfood is a vibrant green algae that has a high cell division rate and high DNA and RNA content. Chlorella contains up to 65% natural protein, which can replace the properties of protein nutrients of animal origin.
Chlorella contains:
- amino acids;
- vitamin B12;
- chlorophyll.
Vegetarians should consume at least 5 g of the substance per day to normalize iron deficiency. The superfood supplement will also strengthen the immune system and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Hemp seeds
The superfood hemp seed is a great natural supplement, rich in up to 25% protein in an easily digestible form.
In addition to natural vegetable protein, hemp seeds are rich in acids:
- omega-6;
- omega-3;
- gamma-linolenic.
The superfood also contains phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, magnesium, and sodium. Daily consumption of hemp seeds will help replenish iron deficiency, saturate the body with beneficial acids, improve skin condition, and increase mental activity.
Sesame
Sesame seeds are a universal addition to all vegetarian dishes. Sesame is used as an additional component for recipes without meat; sesame milk, dressings, sweets, honey, and butter are made.
Superfood contains:
- healthy fats;
- fiber;
- calcium;
- magnesium, iron, phosphorus, zinc;
- vitamins A and F;
- antioxidants;
- protein in an easily digestible form.
Prepare vegetarian meals with added superfood or take 1 teaspoon of sesame seeds morning and evening.
Chia seeds
When ripe, Spanish sage produces small seeds that are rich in plant protein. No plants have yet been found that are capable of providing such a form of protein nutrient accessible to the body. The substance is rich in fast carbohydrates, vitamins, fiber
Ways to use chia seeds:
- soaking with water for 2 hours;
- soaking in fruit juice for 1 hour;
- preparing yoghurt-based mousses.
Eating Spanish sage will help compensate for the deficiency of protein and iron, which causes an increase in hemoglobin. A vegetarian should take at least 2 teaspoons of seeds per day.
Goji berries
The Asian berry contains 500 times more ascorbic acid than citrus fruits. Adding superfood to food causes the transformation of ferric iron, which is poorly absorbed by the body.
Goji supplement is rich in:
- antioxidants;
- flavonoids;
- useful acids;
- keratinoids;
- vitamins C, E, groups A and B.
In its pure form, goji berries have a bitter taste. It is possible to consume the superfood in the form of powder or capsules prepared from the supplement.
Cocoa beans
The superfood contains more than 14 g of vegetable protein for every 100 of the substance. Eating cocoa beans by vegetarians helps normalize hemoglobin levels in the blood, strengthen the immune system, and increase emotional tone.
The additive is useful due to the presence in it:
- folic acid;
- vitamins of groups B and A;
- minerals zinc, magnesium, iron, calcium.
Interesting! By drinking just 1 cup of a drink made from high-quality cocoa per day, you will replenish half of your daily requirement of vitamin B12.
Cocoa consumption should be limited to children under 3 years of age, persons with kidney disease and allergic reactions.
Chyawanprash
Superfood in the form of Indian jam made from amalaki has a complex effect on the vegetarian body. The main components of the supplement improve the production of blood cells and the functioning of the circulatory system.
Regular consumption of chyawanprash:
- strengthens the immune system;
- replenishes iron deficiency in the blood;
- normalizes hemoglobin levels;
- improves digestion;
- promotes reproductive functions.
The superfood comes in 6 different flavors. A vegetarian should take 2 teaspoons 2 times a day to compensate for the deficiency of substances necessary for the body.
Types of vegetarianism
Classical vegetarianism is divided into 4 types: veganism, lacto-vegetarianism, ovo-vegetarianism and lacto-ovo-vegetarianism.
- Lactovegetarians, in addition to plant foods, consume milk and dairy products.
- In addition to plant foods, lacto-ovo vegetarians consume milk, dairy products and bird eggs.
- Ovo-vegetarians do not consume meat, fish, or milk, but do eat eggs.
- Vegans eat exclusively plant foods and do not consume not only meat and fish, but also eggs and dairy products.
Not all vegans are the same: there are fruitarians - they eat only plant foods, for which there is no need to destroy plants (fruits, berries, fruits, nuts, grains, seeds) and raw foodists - they do not eat foods that have been subjected to heat (frying, stewing, boiling).
In addition to the listed types and subtypes of vegetarianism, there are movements that are similar, but are not vegetarianism. They involve the killing of living beings. So, flexitarians eat meat and seafood, but only occasionally. Pescetarians allow themselves to eat fish, and pollotarians eat bird meat.
| Nutrition | Power types | Meat | Poultry meat | Fish | Eggs | Honey | Dairy | Fruits, berries, vegetables, nuts | Cereal sprouts, raw foods |
| Vegetarianism | Sproutarianism | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | + |
| Fruitarianism | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | + | |
| Veganism | – | – | – | – | – | – | + | + | |
| Lactovegetarianism | – | – | – | – | + | + | + | + | |
| Ovo-lacto vegetarianism | – | – | — | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Other diets | Pollo-vegetarianism | – | + | – | + | + | + | + | + |
| Pesco-vegetarianism | – | – | + | – | + | + | + | + | |
| Young vegetarianism | — | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Flexitarians | (English flexible “flexible”) - moderate or extremely rare consumption of meat, poultry, fish and seafood. | ||||||||
Recipes and techniques
To increase the amount of iron in the blood without consuming meat, dairy products, fish, eggs, you need to enrich your diet with a variety of vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
Make sure that you often have on your table:
- apricots;
- apples,
- pomegranate;
- plums;
- watermelon;
- raspberries;
- pears;
- black currant;
- persimmon.
Instead of tea or coffee drinks, use compotes, herbal infusions, and juices. Avoid heat treatment of vegetables and fruits. As a result of heating, the iron in plant foods is destroyed. For sweets, eat honey, dried apricots, and dark chocolate with a high cocoa content. Regular intake of drinking yeast and hematogen will help a vegetarian increase hemoglobin naturally.
Create a daily food menu for the week ahead. Choose vegetarian recipes, shop for groceries, vegetables, and herbs in advance. Planning and keeping records will help you create a balanced diet.
How to switch to a vegetarian diet
A person must decide for himself whether he should switch to a vegetarian diet. Strict vegetarianism (veganism) is indicated for adults who are practically healthy. Vegetarians additionally need to take balanced vitamin and mineral complexes. Veganism may be contraindicated for children, pregnant women and those with chronic diseases. For these categories, a type of vegetarianism that is lighter in terms of nutrition is recommended (lacto-vegetarianism, lacto-ovo-vegetarianism, flexitarianism or pescetarianism) subject to the recommendations of a nutritionist, taking balanced vitamin-mineral complexes and constant laboratory monitoring.
Based on the foregoing, we can conclude: the decision to switch to vegetarianism (veganism) should be carefully considered, since this food system has negative aspects if the diet is not balanced. It should be varied and supplemented, if necessary, with vitamin and mineral complexes. It is worth carefully studying the information presented in the table, which shows products of plant origin containing essential vitamins, minerals, proteins and essential amino acids necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
Content of vitamins, minerals, protein and essential amino acids in basic plant foods
| Vitamins, minerals, proteins, essential amino acids | Products with the highest content |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | Red carrots, red bell peppers, tomatoes, pumpkin, apricots, peaches, melons, plums, greens (parsley, sorrel, spinach, green onions, wild garlic, green lettuce), rowan berries, blackberries, currants, walnuts, apples and oranges. However, plant foods contain less vitamin A than animal products. |
| Vitamin B1 | Buckwheat, oatmeal, nuts, wholemeal bread, rice bran, sprouted wheat, vegetables (mostly green), legumes, some fruits and berries, garden herbs, wild herbs (burdock, nettle, clover), brewer's yeast, algae |
| Vitamin B2 | Nuts (primarily peanuts and almonds), cereals (rolled oats, rice, buckwheat), vegetables (primarily green), legumes (especially lentils, beans and peas), fruits (the largest amount in apricots), greens (most in parsley, nettles, dandelion leaves and green onions), mushrooms |
| Vitamin B3 | Mushrooms (ceps, champignons), nuts (peanuts, pistachios, hazelnuts, walnuts), legumes (beans), cereals (oatmeal, wheat, barley), vegetables (corn, broccoli, potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, sorrel) , coffee |
| Vitamin B5 | Vegetables, brewer's yeast, legumes, grains, nuts, mushrooms, royal jelly, whole wheat, whole rye flour |
| Vitamin B6 | Sprouted grains, potatoes, peas, cabbage, carrots, tomatoes, beans, lentils, soybeans, leafy green vegetables, many cereals and cereals, yeast, nuts, seeds, berries and fruits (many vitamins in bananas), herbs (alfalfa) |
| Vitamin B12 | Food products are actually only of animal origin. Available to the human body is not found in plant foods |
| Vitamin C | Fruits and berries (all citrus fruits, kiwi, apples, peaches, apricots, strawberries, black currants, melon, persimmons, rowan berries, raspberries, blackberries, rose hips, sea buckthorn), vegetables (cabbage, green leafy vegetables, green peas, bell peppers, tomatoes , beets, carrots, onions, new potatoes), herbs (burdock root, alfalfa, hops, eyebright, fennel seed, peppermint, parsley, nettle, sorrel) |
| Vitamin D | There is practically no vitamin D of plant origin in products. It is found in very small quantities in oatmeal, parsley, potatoes, alfalfa, dandelion greens, and nettles. |
| Vitamin E | Vegetable oils, nuts, whole grains, seeds, spinach, broccoli, carrots, oatmeal, cucumbers, potatoes, radishes, green leafy vegetables, onions, herbs (alfalfa, nettle, dandelion, rose hips) |
| Vitamin K | Green leafy vegetables, green tomatoes, all types of cabbage (especially broccoli), soybean and olive oil, walnuts, herbs (nettle). Vitamin K is found in small quantities in avocados, kiwis, bananas, cereals and bran. |
| Folic acid | Leafy green vegetables (green salad, parsley, cabbage, green tops of many vegetables), legumes (peas, beans), vegetables (beets, cucumbers, carrots, pumpkin), cereals, fruits (bananas, oranges, apricots). |
| Minerals | |
| Potassium | Vegetables (potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes, beets, celery root), fruits (apples, pears, bananas, oranges), grains (rye, wheat, oats, rice), legumes (peas, beans), mushrooms |
| Sodium | Vegetables (potatoes, cabbage, pumpkin, cucumbers, tomatoes, carrots), fruits (watermelons, melons, apricots, plums, grapes, bananas, oranges), grains (rye, wheat, oats, buckwheat), nuts (almonds, walnuts, pine nuts, peanuts, cashews), dried fruits |
| Calcium | Legumes (beans, peas), nuts (almonds, pistachios, hazelnuts, walnuts), cereals (oatmeal, barley), garlic |
| Phosphorus | Legumes (especially green peas), nuts, pumpkin seeds, vegetables and fruits (cucumbers, cabbage, pears, apples), cereals, dried fruits, yeast, bran, garlic |
| Magnesium | Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, pine nuts and walnuts, chocolate, cocoa powder, lentils, beans, sprouted wheat seeds |
| Zinc | Sea kale (kelp), vegetables (beets, tomatoes, garlic, ginger), legumes, wheat germ, wheat bran, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, corn, fruits and berries (raspberries, blueberries, oranges) |
| Iron | Iron can be of several types: heme (in animal products) and non-heme (in plant products). Non-heme iron is less easily absorbed. Large amounts of non-heme iron are found in bread, cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, rye, wheat bran, corn), vegetables (cauliflower, broccoli, beets), greens (spinach, asparagus), legumes (beans, beans, lentils, peas). ), fruits and berries (pomegranate, plum, persimmon, apples, dogwood), nuts (pistachios, cashews, almonds, peanuts, walnuts), pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds |
| Squirrels | |
| Protein | Legumes (soybeans, beans, peas, lentils), nuts (peanuts, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, almonds, walnuts), cereals (buckwheat, millet, rice, oats, semolina), broccoli, spinach, mushrooms |
| Essential amino acids | |
| Phenylalanine | The natural form of the amino acid is found in large quantities in soybeans, nuts, seeds, beans, cereals, mushrooms, parsley, figs, dried apricots, bananas, Jerusalem artichokes |
| Lysine | A sufficient amount is found in soy, nuts, lentils, and cereals. Small amounts - in beets, white cabbage, carrots |
| Threonine | Mushrooms, sesame, lentils, cereals (rye, buckwheat, barley) |
| Methionine | Sesame seeds, nuts, peas, beans, lentils, soybeans, brown rice, corn and wheat flour, wheat sprouts, pasta, cereals (oatmeal, millet, buckwheat, pearl barley, semolina) |
| Valin | Plant foods are not so rich in valine; nuts, sunflower seeds, parsley, and cocoa contain sufficient amounts of it. |
| Leucine | Soybeans, peanuts, wheat germ, almonds, oats, beans, beans, lentils, chickpeas, corn, rice |
| Tryptophan | Cereals, legumes (soybeans, beans, peas), nuts (peanuts, almonds, cashews, pine nuts, pistachios), seeds, cocoa beans |
| Histidine | Large amounts - in wheat, soybeans, rice, peas, walnuts, peanuts |
| Isoleucine | Soybeans, lentils, buckwheat, rye, chickpeas, grain bread, almonds, cashews |
First of all, before switching to a vegetarian diet, it is recommended to conduct a laboratory examination to assess the general state of health, determine the concentration of the most important substances for the body, vitamins and minerals. For convenience, you can use diagnostic complexes available for ordering in the LAB4U online laboratory, such as: “Annual examination” “Mineral metabolism”.
It is best to discuss the results obtained with your general practitioner or family doctor. Based on your medical history, examination, and test results, your doctor will determine whether you have medical contraindications to vegetarianism and how strictly you can adhere to a vegetarian diet. This is possible in the presence of certain diseases.
It would be a good idea to consult a nutritionist for advice and develop a nutrition plan, taking into account the results of medical and laboratory examinations. He will also recommend nutritional supplements and vitamin-mineral complexes.
Prohibited Products
A vegetarian needs to create a menu of all dishes in advance. To increase hemoglobin, it is necessary not only to introduce foods rich in iron and protein into the diet, but also to exclude certain products.
In case of iron deficiency, a vegetarian must remove from food:
- Black tea. Tannin interferes with iron absorption;
- natural and instant coffee. Caffeine is a blocker of ferric iron transformation;
- baked goods and baked goods made from yeast dough. Bakery products made with yeast contain phytin, which is an inhibitor in the absorption of iron by the body.
You cannot saturate your body with useful substances if you simultaneously use blockers. Vegetarianism requires a competent approach to nutrition.
RISK FACTORS
Iron deficiency and a decrease in hemoglobin concentration can be observed in cases where an insufficient amount of the element enters the body or its absorption is impaired, when an excessive amount of iron is lost or there is an increased need for it.
Low hemoglobin levels are observed in vegetarians and those whose diet is unbalanced. The need for iron increases in people involved in sports, experiencing increased physical and mental stress, as well as in adolescents due to intensive growth. Increased loss of trace elements and a decrease in hemoglobin can be observed with heavy bleeding, including prolonged and heavy menstruation.
Cleansing
Vegetarianism is considered not only an eating behavior, it is following Eastern practices. Followers of the technique often use various methods of emptying the gastrointestinal tract for cleansing purposes.
Vegetarians carry out cleansing taking into account the following features:
- laxatives should not be used. Taking drugs or foods that cause diarrhea stresses the body;
- it is necessary to adhere to gentle bowel movements;
- cleaning the gastrointestinal tract must be done with water;
- It is necessary to drink warm liquid in slow sips until it feels like the water has reached the throat;
- it is necessary to move the contents by tensing and relaxing individual parts of the gastrointestinal tract;
- when the water concentrates in the abdominal area, remove it;
- For the first time, it is better to practice cleansing with a mentor;
Cleansing the intestinal tract improves overall well-being, removes toxins, and normalizes digestion. A cleansed body better absorbs nutrients from plant foods.
Herbs to raise hemoglobin
In addition to raising the level of iron in the blood by adjusting the daily menu, it is possible to saturate the body by taking medicinal herbs.
A vegetarian with a low hemoglobin level needs to take a course of 7-10 days from the following types of herbs:
- creeping wheatgrass. The plant is rich in B vitamins, iron, ascorbic acid, and manganese. The leaves are brewed with boiling water in a 1:1 ratio, left for 1 hour and drunk 1 glass daily before meals;
- stinging nettle. For every 100 g of leaves there are 6 g of iron in a form easily absorbed by the body. A decoction or squeezed nettle juice strengthens the immune system and increases hemoglobin. Brew 1 glass of raw material with the same amount of boiling water, let it brew for 2 hours, strain and drink before eating;
- sea buckthorn leaves. The green parts of the bush are rich in natural iron and can cure anemia. Brew 100 g of raw material with boiling water, cool naturally, strain and drink 2 times a day on an empty stomach.
Greens from the garden are the leader in the presence of folic acid in the green parts, which normalizes water and electrolyte balance. Daily consumption of dill, green onions, lettuce, and parsley will help the body absorb ferric iron more easily.
How to increase hemoglobin: examples and recipes.
Here are some popular, proven recipes for raising hemoglobin for a vegetarian:
- Mix a tablespoon of sprouted wheat with a tablespoon of dried fruit, preferably raisins. Drink in the morning on an empty stomach *;
- Add the juice of half a lemon and one teaspoon of honey to the rosehip infusion. Take on an empty stomach. The product is also useful for the prevention of colds;
- Drink two parts of carrot juice and one part of apple and beet juice twice a day before meals, freshly prepared.*;
- A mixture of honey, cranberries and walnuts. Take a tablespoon throughout the day *;
- Mix a glass of buckwheat (grind in a coffee grinder) with a glass of walnuts and honey. Take a tablespoon several times a day *;
- Pour a tablespoon of chopped celery leaves into two cups of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain, take half a cup of the decoction before meals.*;
- Salad of cabbage leaves, dandelion, bell pepper and spinach. You can add sesame *;
- Pour two tablespoons of oats into two glasses of water and boil until swelling. Strain, squeeze, add the yolk, one tablespoon of ground almonds, one tablespoon of honey and two tablespoons of ground rose hips. Take one tablespoon before meals;
- Dissolve 50 grams of chopped chocolate in 100 ml of hot milk, cool and add three tablespoons of ice cream;
- Drink rosehip infusion (50 g per liter of water) instead of tea every day.*;
- An excellent remedy for anemia is Hemobin. It is a unique source of natural heme iron. The only iron-containing product in the world that does not have; contraindications and side effects.
- You can also increase hemoglobin with the following drugs: sorbifer durules, ferrogradumet and fenuls. There are contraindications. Should be taken under medical supervision.
with an asterisk ( * ) recipes that are suitable for vegans .
Ayurvedic preparations
Vegetarians are followers of Eastern practices. The Indian system of traditional medicine recommends improving blood composition and increasing hemoglobin by including natural foods in the diet.
Ayurvedic diet for low hemoglobin:
- eat beets every day in any form and drink beet juice;
- regularly for 1 month eat 12 black currants, which were soaked for 12 hours in water;
- include almonds, bananas, dates, pomegranates in the menu;
- cook all dishes with the addition of carrots. Use at least 1 root vegetable for each recipe;
- drink fresh apple juice before meals.
Ayurveda prohibits people suffering from anemia from drinking tea or coffee immediately after eating. Indian medicine recommends replacing drinks with herbal infusions.
HOW TO ADD TASTE TO YOUR DIET
Often there is not enough iron in food, especially for vegetarians. Adjustment of the diet aimed at the synthesis of hemoglobin and red blood cells - the formed elements of blood - is enhanced by taking special medications. Iron-rich hematogen lozenges can be used as a tasty aid, as well as additional prevention. “FERROGEMATOGEN®-PHARMSTANDARD” has been developed for adults, and “FERROGEMATOGEN® CHILDREN” has been developed for children of different ages.
The drugs belong to dietary supplements and serve as additional sources of iron. They contain black food albumin, proteins, iron, copper and vitamins (pyridoxine hydrochloride, ascorbic and folic acid) in optimal proportions.
Adults and children over 11 years of age can take FERROHEMATOGEN®-PHARMSTANDARD 50 g per day. Children 3–7 years old are given 30 g of FERROHEMATOGEN® CHILDREN, and 7–11 year old children – 40 g. Duration of administration is 1–2 months.
Hematogen is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance and diabetes mellitus. Before use, consult a doctor.
Asanas and pranayama
Eastern medicine advises vegetarians to regularly perform their yoga exercises. A number of asanas and breathing manipulations (pranayama) help improve the functioning of the body, cell renewal, and the removal of toxins.
If your hemoglobin is low, do the following exercises daily:
- shoulder blade stand (birch tree). On the floor, lift your legs and pelvis up, rest your hands on your buttocks with your elbows bent;
- raising the legs at a straight angle. From a lying position, lift your closed straight legs and maintain an angle of 90 degrees;
- deep breathing. Sit on the floor, clasp your knees with your hands and press them against your chest. Take deep, long breaths in and out for 1 minute;
- holding your breath. From a sitting position on the floor, take a full lungful of air, rest the tip of your tongue on the roof of your upper jaw, arch your chest forward and arch your back. Hold your breath as long as possible and exhale deeply.
Yoga and breathing exercises help improve blood flow by compressing blood vessels. Static poses and pranayama stabilize the emotional state and improve well-being.
Prevention of anemia in vegetarians
A balanced diet for a vegetarian is the basis of his health. It is required to competently create a menu rich in natural iron and protein in order to maintain normal hemoglobin.
Follow these guidelines to prevent anemia in vegetarians:
- eat apples, cabbage, buckwheat, pomegranate, rose hips, tomatoes every day;
- add superfoods or iron supplements to your meals;
- take Hematogen or brewer's yeast to compensate for the lack of essential substances;
- Limit your intake of black tea and coffee. Replace drinks with a decoction of rose hips, medicinal herbs or cocoa;
- Visit the clinic regularly for tests.
Monitor how you feel. At the first signs of anemia, do not self-medicate, contact a medical facility, and adjust your diet. A balanced diet, daily activity, the introduction of Eastern practices, and the use of natural superfood supplements will help a vegetarian increase hemoglobin quickly and without medications.