Cerebral ischemia is characterized by partial blockage and narrowing of blood vessels in the head, most often due to atherosclerotic deposits. Damaged vessels are not able to pass a normal volume of blood, so the brain tissue does not receive the required amount of oxygen and nutrients. Over time, a person notices memory loss, deterioration in performance, sleep problems against the background of chronic fatigue. These alarming symptoms should be a reason to visit a qualified physician. Otherwise, the patient may risk stroke, memory loss and disability.
How does cerebral ischemia occur?
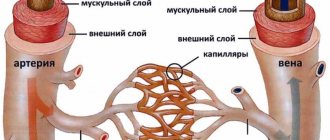
Cerebral vascular ischemia is mainly an age-related phenomenon. The normal functioning of blood vessels ensures that all organs are supplied with a sufficient volume of blood. With age, the elasticity of the vascular walls deteriorates; they become overgrown with accumulations of cholesterol plaques. The greatest danger is caused by damage to large arteries.
The vessels of the head are especially sensitive to these deteriorations, because a fifth of all blood in the body passes through them. The human brain cannot function properly without a constant flow of oxygen and nutrients that the blood contains. A decrease in their volume invariably leads to the degradation of brain tissue, the death of neurons and the loss of some functions, often vital.
Ischemic processes in the brain can also be provoked by changes in the properties and composition of the blood (in particular, increased clotting) due to kidney disease, thyroid dysfunction, and metabolic disorders. Problems with the heart and toxic poisoning can also reduce the activity of blood flow in the vessels of the head. Now you can undergo a consultation and a set of preparatory examinations when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart absolutely free of charge!
Promotion
Just until the end of autumn, undergo a free consultation and a set of preparatory examinations* when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart.**
Send a request
* Check the details of the Promotion by phone. **Has contraindications; consultation with a doctor is required.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) Cardiac shock wave therapy (SWTS)
Hurry up to apply, the promotion period is limited.
Mechanism of formation and pathogenesis
The basis of the disease is the weakening of normal nutrition of cerebral structures.
There are several options, but in all known cases there is a slowdown in the movement of liquid connective tissue through the vessels as a result of a mechanical obstruction.
And what was its cause: stenosis (narrowing) of the lumen, blockage with a cholesterol plaque, thrombus, malformation, aneurysm, other anomalies of anatomical development - needs to be clarified.
Without receiving nutrients and oxygen, tissues begin to die. Death or necrosis, however, does not reach a certain critical mass, at which the process becomes an avalanche-like, uncontrollable character - such an emergency condition is called a stroke.
Discirculatory encephalopathy, another name for chronic ischemia (abbreviated as CICI), is considered a precursor to acute necrosis of cerebral tissue.
Recovery is very difficult, but it is necessary to achieve lasting correction. The patient's life is at stake. Requires hospitalization in a neurological hospital.
Causes of the disease
Atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension are two causes that account for the vast majority of cases of cerebral vascular ischemia. Cholesterol is especially actively deposited on the walls of blood vessels in people over 40 years of age. It is at this age that the risk of ischemic events increases. If the patient does not adjust his lifestyle, the growth of cholesterol deposits only progresses and leads to a deterioration in brain function.
The second most common cause is chronic heart failure. If the heart does not produce enough blood, this automatically disrupts the nutrition of the brain. Also, symptoms of ischemia often appear in patients with various types of arrhythmia, since disruption of blood flow dynamics negatively affects the blood supply to the brain.
Other reasons include:
- hereditary angiopathy;
- kidney disease;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine diseases;
- systemic vasculitis.
Deformations and abnormalities of the blood vessels of the neck, aorta and other large arteries can cause deterioration in blood flow to the brain. These can be either purely vascular diseases (for example, aneurysms), or damage, compression of blood vessels by neighboring tissues and structures (vertebrae with osteochondrosis, tumors).
Methods for diagnosing the condition
An important role in establishing the cause of cerebrovascular accidents belongs to the identification of underlying diseases - arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction in the past, angina pectoris, vascular lesions of the lower extremities. Patients' complaints are usually nonspecific or do not reflect the actual picture of the disease.
During a medical examination, attention is paid to the pulsation of the vessels of the neck and limbs, pressure on both arms and legs, and listening to the heart.
To confirm the diagnosis of cerebrovascular insufficiency, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are prescribed:
- blood test - general, coagulogram, glucose, lipid spectrum;
- immunological and acute phase indicators for suspected autoimmune diseases;
- ECG, EchoCG to identify heart disease, the source of thrombosis;
- ophthalmoscopy reflects the condition of blood vessels in angiopathy of diabetic, atherosclerotic or hypertensive origin;
- X-rays of the cervical spine, ultrasound in duplex or triplex mode help to establish the cause of reduced blood flow to the brain (compression due to osteochondrosis, blood clot, cholesterol plaque);
- MRI, CT (alone or in combination with contrast) helps to examine the structure of blood vessels, determine developmental anomalies, aneurysms, and the presence of a bypass pathway for feeding brain cells.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
The disease is quite insidious and in the early stages it can manifest itself with symptoms that a person barely pays attention to or does not associate them with brain activity. For example, loss of attention, sudden mood swings, sleep disturbances (insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness). Most often, these signs are attributed to work fatigue.
However, later the symptoms become obvious and disrupt the usual rhythm of a person’s life.
- Dizziness, nausea.
- Headaches of varying severity.
- Forgetfulness.
- Feeling of coldness in the feet and palms.
- Numbness of the limbs.
If action is not taken at this stage to eliminate the symptoms using medicine, the disease will progress rapidly. Further signs can no longer be ignored.
- Temporary loss of vision (partial or complete).
- Problems with speech (incoherence, slurring).
- Headaches to the point of vomiting.
- Insomnia.
- Memory losses.
- Movement disorders when walking.
- Disorientation in time and space.
The situation becomes extremely dangerous, since with these symptoms the patient is only one step away from a stroke.
Diagnosis of cerebral vascular ischemia
The most important examination method for these symptoms is ultrasound of cerebral vessels. The “gold standard” is duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries, which effectively detects disturbances in the functionality and structure of blood vessels.
An objective picture of the disease is also presented by ultrasound transcranial Dopplerography of cerebral vessels. The study shows the speed of blood flow, the degree of damage to the vascular walls, etc.
These examinations are carried out by the Center for Pathology of the Circulatory Organs of the CBCP. For this purpose, the latest expert-class equipment is used.
Degrees of cerebral vascular ischemia
In medicine, it is customary to classify this pathology into three degrees. The most difficult is cerebral ischemia of the 3rd degree.
1st degree . Characterized by mild disorders of attention and intellectual activity. Most often, patients cope with complex tasks, but it takes them longer. There are no obvious limitations in life activity or coordination disorders yet, but minor signs of the disorder are already noticeable:
- shuffling gait;
- pain and numbness in the hands after physical activity;
- irritability;
- frequent weakness.
2nd degree . In some cases, the patient has little control over his actions. When performing work tasks, he often needs help and hints, which negatively affects his professional activities. The person may also lose some life skills. Increasingly, he is tormented by general ailments with the characteristic symptoms described above.
3rd degree . Pronounced neurological disorders appear in the form of Parkinson's disease, urinary incontinence, and problems with coordination. The patient may lose the ability to move independently, as he has poor control of his legs and loses the ability to navigate in space. There are disturbances in thinking, memory, and speech. In the absence of medical care, a patient with grade 3 ischemia will face complete personality collapse, ischemic stroke, and cerebral hemorrhage.
Chronic cerebral ischemia
Symptoms of chronic cerebral ischemia develop gradually, but with noticeable manifestations. They are often associated with cardiac dysfunction, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries, and other diseases.
Most often, cerebral ischemia becomes chronic in cases of 2nd degree disease. This type of disease is characterized by long-term development without any complications. However, this does not mean that the disease does not progress. Usually, deterioration in health occurs unexpectedly. And any nervous or physical stress can provoke it.
Chronic ischemia does not require mandatory hospitalization.
Classification of cerebrovascular pathology
CVD is a brain disease associated with progressive tissue damage due to impaired circulation in the organ. It can arise due to pathologies of cerebral vessels, which cause changes in the blood circulation of brain tissue and hypoxia. It is mainly diagnosed in older people, but in rare cases, the disease can also occur in a child.
Cerebrovascular disease develops gradually. At the very beginning, the brain begins to experience oxygen deficiency due to vascular dysfunction.
With chronic hypoxia, all brain functions begin to suffer. First, transient and then persistent changes in brain tissue occur.
Cerebrovascular disease contributes to the development of grade 2 DEP, which causes brain damage.
Based on the classification, CVD can be divided into transient, acute and chronic.
Acute cerebrovascular insufficiency includes:
- Encephalopathy of the hypertensive type.
- Ischemic attacks.
- Stroke (multilacunar form, ischemic, hemorrhagic, unspecified).
Chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency (CVI) is divided into:
- Embolism, which results in blockage of blood vessels by blood clots. Which arise in the large arteries of the body and can enter small ones with the blood.
- Bleeding resulting from rupture of the vascular walls. This condition provokes the development of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Thrombosis is a pathology when the lumen of blood vessels narrows and becomes clogged with plaques.
Neurologist Mikhail Moiseevich Shperling will tell you more about the ischemic form of stroke:
The transient form of cerebrovascular disease includes:
- Cerebral hypertensive crisis.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
Treatment of cerebral vascular ischemia
The patient is prescribed complex treatment, which includes:
- massage and physiotherapeutic procedures to improve blood circulation;
- hypoxic therapy to saturate tissues with oxygen;
- drug therapy to normalize blood pressure and restore blood circulation;
- surgical intervention to remove atherosclerotic plaques from blood vessels.
Treatment of chronic cerebral ischemia is combined with therapy for other organs and systems.
Treatment
The point is to eliminate the root cause. For atherosclerosis, statins are prescribed. Atoris as the main one. They remove cholesterol and dissolve existing cholesterol plaques.
Antiaggregants allow you to restore blood fluidity and prevent the formation of blood clots and clots that can block blood vessels. Aspirin, Heparin.
Anti-inflammatory, glucocorticoid drugs (Prednisolone, Dexamatezone and others), if necessary, antibiotics to eliminate arteritis and vasculitis. Lesions of the internal lining of blood vessels.
In fact, cerebrovascular agents and protectors are used to correct cerebral blood flow. Piracetam, Actovegin, nootropics like Glycine and others.
Operations are required in extreme cases, for example, if there is malformation, aneurysms, advanced atherosclerosis with plaque hardening. The question of the appropriateness of therapy is decided at the discretion of the specialist.
Lifestyle changes do not play a big role. It is enough to give up smoking and alcohol, minimize the amount of fatty foods and everything will fall into place. Adequate physical activity will not be superfluous.
Treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency of the brain is medicinal, less often surgical, according to indications.
Prognosis and prevention
The consequences of cerebral vascular ischemia can be minimized if you consult a qualified doctor in a timely manner. This should be done when symptoms of the 1st degree of complexity appear. At this stage, preventive actions are sufficient:
- maintaining physical activity;
- nutrition correction;
- abstaining from nervous stress.
Even with symptoms of the 2nd degree of severity, the prognosis is positive, provided the patient follows all the doctor’s prescriptions. Seeking help at the 3rd stage of the disease is in most cases ineffective.
Forecast
Depends on the root cause. At the initial two stages - favorable. It is possible to completely reverse the process, restore cognitive functions and higher nervous activity in general.
When adding deviations of consciousness, gross deficits (behavioral disorders, mental disability), the likelihood of cure is already low. But there is still a chance to take control of the process.
However, it is recommended to consult a doctor at the very first stages when suspicious symptoms arise.