Today, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is rightfully considered one of the most common diseases developing in people who have reached old age. In addition, the pathology is also one of the most dangerous due to the high probability of various complications that can lead not only to a deterioration in the patient’s quality of life, but also to the risk of death.
As you know, preventing any disease is much easier than treating it, so “you need to know the enemy by sight.” To prevent atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis and be able to recognize the early stages of the pathology, you should know in detail about the mechanism of its occurrence, predisposing factors, clinical manifestations and other aspects of the course of the disease.
Causes of cardiosclerosis
1. Functional disorders:
- Damage to the heart muscle as a result of inflammatory diseases.
- Hypoxia due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles due to narrowing of large cardiac vessels.
- Stretching of the walls of the heart, which leads to an increase in its volume.
2. Lifestyle and bad habits of the patient:
- Alcohol abuse and smoking.
- No, minimal or excessive physical activity.
- Repetitive stress.
- The habit of overeating and, accordingly, excess body weight.
Hereditary factors play an important role in the occurrence of the disease.
Development mechanism
Atherosclerosis develops as a result of disruption of two mechanisms that ensure the functionality of tissue blood supply.
1st mechanism
The first mechanism is a metabolic disorder that directly affects lipid (fat) metabolism. This leads to an increase in the concentration of cholesterol, non-esterified (free) fatty acids and triglycerides. At the same time, the content of phospholipids in the blood decreases, and cholesterol is converted into a finely dispersed state:
- alpha lipoproteins - strong compounds with proteins and triglycerides;
- beta lipoproteins are fragile molecules – prebeta lipoproteins.
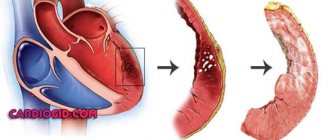
Once in the walls of blood vessels, lipoproteins quickly break down, releasing triglycerides and cholesterol, and have an atherogenic effect on the arteries, that is, they damage them. In atherosclerosis, due to a decrease in the level of alpha proteins, the concentration of fragile lipoproteins increases. Depending on the nature and characteristics of lipid metabolism, the predominance of certain groups of lipoproteins, there are 5 types of hyperlipidemia (increased fat content in the blood).
The most pronounced pathogenic effect is observed when hyperlipidemia of types 2 and 3 occurs, which develop due to the predominance of beta and prebeta lipoproteins, respectively. In addition, an important factor is the increase in free fatty acids necessary for the production of triglycerides and cholesterol.
Their effect also helps to reduce the sensitivity of body cells to insulin, which reduces the speed and quality of transformation of glucose into glycogen, leading to hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar) and other local disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In parallel, pathologies of protein metabolism are also observed, which is due to the direct interaction of proteins and lipids.
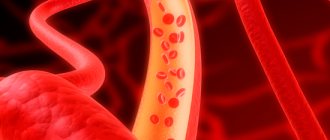
Cholesterol plaque in the lumen of the artery
2nd mechanism
The second mechanism, interruptions in which occur during atherosclerosis, is a morphological change in the vascular walls, that is, a violation of their permeability. As a rule, the ability to pass certain substances through the walls of blood vessels increases, which is caused by a decrease in the quality of microcirculation and an increase in the level of acidic mucopolysaccharides.
At the same time, the number of pores increases, resulting in increased permeability of the vascular walls. Often the cause of such disorders is a high level of concentration of local hormones, for example, bradykinin, which, in turn, causes an increased formation of catecholamines.
In the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, a significant role belongs to the growth of enzyme activity directly in the vascular wall itself, and specifically elastase, which causes changes in the vascular framework. An additional aspect of the development of this pathology can also be an increase in blood pressure (blood pressure), which is a mechanical factor in the appearance of damage.
Classification of cardiosclerosis
According to the morphological principle, focal (most often occurs as a complication after myocardial infarction and myocarditis) and diffuse cardiosclerosis, in which the connective tissue spreads to the entire myocardium, are distinguished.
For etiological reasons, the following types are distinguished:
- Post-infarction. As a result of myocardial infarction, scars form at the site of necrotic damage, which reduces the contractility of the heart muscle. The more cases of myocardial infarction a patient has suffered, the more scar tissue is formed. The threat of chronic aneurysm increases due to protrusion of the walls of the heart muscle, which is stretched and weakened by connective tissue. Aneurysm rupture is associated with high mortality.
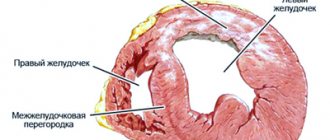
- Myocardial. Myocardial inflammation develops mainly in young patients with chronic allergic and infectious diseases. With this form, the right ventricle of the heart increases in volume and is insufficiently supplied with blood.
- Atherosclerotic. As a rule, it is the result of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels and coronary heart disease. This form of the disease develops over a long period of time, because due to damage to blood vessels, heart cells do not receive enough oxygen, hypoxia develops, the course of coronary heart disease is complicated, and cholesterol levels increase. This leads to diffuse cardiosclerosis, which is accompanied by arrhythmia.
Treatment
Conservative treatment of atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of ischemia, correcting blood composition, improving blood circulation, increasing the density and elasticity of arterial vessels.
In advanced stages of the disease, drug therapy is inappropriate. To restore hemodynamics, the patient undergoes surgery to correct the arteries. Regardless of the chosen treatment tactics, the medical diet “Table No. 10” is prescribed, intended to eliminate hypercholesterolemia.
Groups of medications
Prescribed drugs are divided into several pharmacological groups:
How to lower blood cholesterol levels?
- Statins. Slow down the production of endogenous cholesterol. As a result, the level of LDL decreases and the content of HDL in the blood compensatory increases.
- Fibrates (fibric acid derivatives). Normalize lipid metabolism and the balance of lipoproteins of different densities.
- Calcium channel blockers and angioprotectors. They tone the walls of the arteries, strengthen the endothelium, and enhance the contractility of blood vessels.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. Reduce high blood clotting rates characteristic of coronary artery disease and its manifestations.
- Bile acid sequitrants. Stimulate hepatocytes to use excess low-density lipoproteins for bile synthesis.
- Cardiac glycosides are plant stabilizers of rhythmic myocardial contractions.
- Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) is an active participant in lipid metabolism.
- Nitroglycerin preparations for the relief of angina attacks.
At the same time, hypertension, metabolic disorders and other chronic diseases are treated.
Diet therapy
Diagnosed atherosclerosis, as a trigger for cardiovascular pathologies, is poor eating behavior, nicotine addiction, and addiction to alcoholic beverages. First of all, cardiologist patients are advised to review their diet, quit smoking, and give up alcohol.
The diet for atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis excludes the consumption of foods rich in animal fats, baked goods, smoked products, sausages, fast food, and pickles. It is prohibited to eat foods prepared by frying (including over charcoal).
Dietary nutrition is organized on the basis of slow carbohydrates (dishes from legumes, grains and cereals), fiber and vitamins (vegetables, herbs, berries, fruits), foods rich in Omega acids (linseed oil, fish, seafood, nuts). The rules of the diet indicate adherence to the eating regimen (every 3-4 hours in small portions).
A short list of products for atherosclerotic disease
Beverage classification
| Refuse | Introduce into your diet on a regular basis |
| coffee | freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices |
| alcohol (any strength) | berry compotes and jelly |
| energy | decoctions of rosehip, linden |
| sweet cocktails and juices |
When compiling a daily menu, special attention should be paid to compliance with the daily calorie intake and the ratio of nutrients.
Surgical intervention
With intense negative dynamics of the disease, surgical methods are used in treatment. Depending on the progressive changes, one of the following types of surgery may be prescribed:
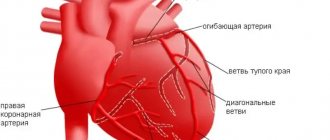
- coronary bypass surgery - creation of an artificial channel for blood flow bypassing the atherosclerotic section of the coronary artery;
- aneurysm resection – excision of the damaged area of the aorta of the heart followed by prosthetics;
- RFA (radiofrequency ablation) – endoscopic cauterization of a section of the myocardium that blocks cardiac impulses;
- angioplasty of coronary vessels with stenting - dilation of arteries by installing a wall.
In difficult cases, an electrical pacemaker (ECS) is implanted.
Symptoms of cardiosclerosis
Very often the initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic. In the clinic of the onset of sclerosis, the first symptom may be arrhythmia. Typical manifestations of the diffuse form should be considered heart failure and disturbances in the rhythm of the heartbeat.
Symptoms regardless of the form (post-infarction or atherosclerotic):
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of fluid in the abdominal and pleural cavities;
- pain in the heart area;
- increased heart rate;
- pulmonary edema;
- increase in liver size.
As the area of affected heart tissue increases, the severity of symptoms increases.
Very often the course of cardiosclerosis is accompanied by arterial hypertension. In this case, high blood pressure alternates with long periods of normal blood pressure.
How to make a diagnosis?
ECG signs
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis is established on the basis of anamnesis (previous infarction), laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
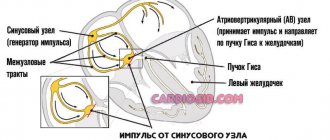
- ECG - signs of a heart attack: a Q or QR wave may be observed, the T wave may be negative, or smoothed, weakly positive. The ECG may also show various rhythm disturbances, conduction disturbances, and signs of an aneurysm;
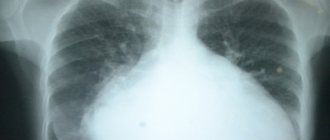
- X-ray - expansion of the heart shadow mainly on the left (enlargement of the left chambers);
- Echocardiography - zones of akinesia are observed - areas of non-contractile tissue, other contractility disorders, a chronic aneurysm, valve defects, an increase in the size of the heart chambers can be visualized;
- Cardiac positron emission tomography. Areas of reduced blood supply are diagnosed—myocardial hypoperfusion;
- Coronary angiography - conflicting information: the arteries may not be changed at all, or their blockage may be observed;
- Ventriculography - provides information about the functioning of the left ventricle: it allows you to determine the ejection fraction and the percentage of scar changes. Ejection fraction is an important indicator of heart function; if this figure decreases below 25%, the prognosis for life is extremely unfavorable: the quality of life of patients significantly deteriorates; without a heart transplant, survival is no more than five years.
At-risk groups
The risk of cardiosclerosis is highest in patients with pathologies in the development of the heart and cardiovascular diseases, as well as in people with various types of allergies.
Pregnant women can be identified as a separate group. Pregnancy causes hormonal, autonomic, metabolic and hemodynamic changes in the body of women and can act as a proarrhythmogenic factor. Complex heart rhythm disturbances are diagnosed both in pregnant women with cardiovascular pathology and in patients without changes in metabolism and the condition of internal organs.
Cardiosclerosis in children is possible against the background of myocardial pathologies, for example, inflammatory and dystrophic processes, in particular diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells. These biochemical disorders significantly weaken the contractile, conductive, excitatory and automatic functions of the myocardium.
Cardiosclerosis medications
The European Society of Cardiology recommends the following medications for the treatment of cardiosclerosis, eliminating the symptoms of the disease, as well as its root cause:
- Antihypertensive drugs. To maintain vascular tone and normalize blood pressure, ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Ramipril) are prescribed; calcium antagonists (Amlodipine, Semlopin, Phenigidine), beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol), antiplatelet drugs (Aspirin), lipid-lowering drugs (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Allesta).
- Cardioprotectors (antianginal agents). Their task is to maintain the functional activity of the heart and counteract the influence of negative exo- and endogenous factors on it. These include organic nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide Mono- and Dinitrate); sydnonimines (Mosikor, Sidocard); metabolic agents (Trimetazidine).
- To normalize heart rate and conduction: amiodarone (Amiodarone), dronedarone (Multak).
- To normalize metabolic processes - potassium and magnesium preparations: Panangin, Asparkam, Magnerot.
- Antibiotics and corticosteroids: for myocarditis and other inflammatory processes.
List of used literature
- Stryuk R.I., Shoikiemova D.U., Borisov I.V.; State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after. A.I. Evdokimov" Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow, Russia / Pregnancy as a risk factor for heart rhythm disturbances
- POKROVSKAYA E.M., 2, Ph.D., N.A. VOLOV 2, Ph.D., I.S. VASILYEVA 2, GORDEEV I.G. 1, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, PAVLIKOVA E.P., 2, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor 1 State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Russian National Research Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Department of Hospital Therapy No. 1, Faculty of Medicine 2, State Budgetary Institution "City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatova "DZ Moscow / NEW OPPORTUNITIES FOR TREATING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE DUE TO POST-INFARCTION CARDIOSCLEROSIS
- Berezin A. E., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Internal Medicine No. 2 of the 1st Medical Faculty of Zaporozhye State Medical University / Combined potassium and magnesium preparations in the treatment of patients with high cardiovascular risk.
Prevention
Cardiosclerosis and all its types do not require primary prevention.
Secondary measures include:
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations and lifelong use of medications;
- organization of work and rest schedule (no overload);
- regular low-intensity physical activity;
- diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- prompt referral to specialists if clinical symptoms progress.
As sad as this may sound, in reality only 20-30% of cardiology patients comply with all recommendations. Why is that? Experience as a doctor has shown that their life expectancy is noticeably reduced compared to patients who consider compliance with the doctor's instructions to be a waste of time.
Frequently asked questions about cardiosclerosis
Which doctor treats cardiosclerosis?
If you suspect cardiosclerosis, you should contact a cardiologist.
What signs should you see a doctor for?
High blood pressure; arrhythmia; increased fatigue and swelling of the limbs.
Can cardiosclerosis develop in children?
Cardiosclerosis in children can develop against the background of inflammatory and dystrophic processes in the myocardium - in particular, diseases of the heart muscle caused by metabolic disorders in heart cells.