What is cavernous angioma?
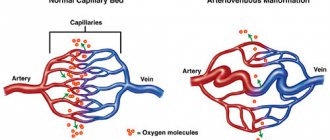
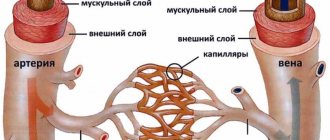
Cavernous angioma is a collection of abnormal vessels that is located in the brain or spinal cord and, in some cases, subcutaneously.
In various literature sources, this disease is also called “cavernous hemangioma”, “cerebral cavernous malformation”, “cavernoma”. Its dimensions vary from microscopic to several centimeters in diameter. It consists of many cavities (cavities) filled with blood and lined with a special type of cells called endothelial cells. Depending on the location in the brain, it can cause epilepsy, be a source of hemorrhages and cause severe headaches. Angioma of the left parietal lobe.
Morbidity
Cavernous angiomas occur in approximately 1 in 100-200 people. In most cases, the first symptoms appear after 30 years of age. In 20% of cases it is a genetically inherited disease, and several tumors are often detected at once.
Causes of angioma and risk factors
The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, with a probability of 50%. According to recent studies, at least three genes are associated with the hereditary form of the disease. A single formation can be detected at the birth of a child or develop during his later life. If parents and relatives did not suffer from this disease, then the angioma is called sporadic. The risk of developing such a tumor is the same for all people.
Angioma of the left parietal lobe during surgical treatment. Image: neurosurgery.wustl.edu
Symptoms of angioma
In most cases, cerebral angiomas are characterized by an asymptomatic course, but sometimes they lead to epileptic (convulsive) seizures. The type of seizure depends on the location of the tumor. Also, the presence of a mass in the brain can lead to neurological deficits, such as weakness of the upper or lower extremities, problems with vision, balance, attention and memory. Symptoms can wax and wane in waves, which is associated with repeated hemorrhages and an increase in the size of the angioma and reabsorption (absorption) of blood.
Angiomas are characterized by various types of hemorrhages:
- Slow, without changing size, since the rate of bleeding is approximately equal to the rate of blood reabsorption by the body.
- Profuse, with an increase in size and compression of the surrounding tissue of the brain or spinal cord.
- A leak in which blood enters the tissue of the brain or spinal cord through a defect in the wall of the angioma, ultimately destroying it.
What is angioma
Venous angiomas are localized in organs and tissues and can be multiple or single.
They are located in most cases on the upper half of the body. Their morphological basis is highly dilated lymphatic/blood vessels. The shape and size of pathological areas can vary, color - from colorless to red-blue. The lesions tend to progress rapidly. There are angiomas of the brain, liver, external genitalia, and bones. Angiomas are classified according to their structure:
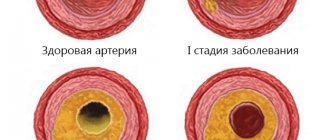
- Simple (hypertrophic, capillary). Small venous and arterial vessels grow. If you study a photo of such an angioma, it will become clear that it is a bright red or bluish-purple spot. Its sizes can be different, even gigantic. If you press on the lesion, it will immediately turn pale due to the outflow of blood. Capillary angiomas of the skin extremely rarely transform into malignant formations.
- Branched (racellose). They are represented by plexuses of tortuous dilated vascular trunks. They are characterized by the presence of constant pulsation. The limbs and face are most often affected. Traumatization of venous branched angiomas is fraught with severe bleeding, which cannot always be stopped on its own.
- Cavernous (cavernous). They are formed by wide spongy cavities that are filled with blood. Cavernous angioma looks like a purple-bluish bumpy spot. Most often located under the skin. It feels hotter than the surrounding tissue. When stressed, it increases in size. A complex form is cavernous angioma of the brain, the treatment of which is very long and involves restoration of impaired blood flow.
- Combined. Combine subcutaneous and superficial location. Formed by overgrown vessels and other tissues (depending on location on the body).
The shape of angiomas is:
- stellate (point angiomatous formations, from which dilated small blood vessels extend in all directions);
- flat (vascular spots of pink-blue color located in the upper layers of the skin);
- nodular (seals protruding above the surface of the skin);
- serpiginous (rashes on the skin in the form of small burgundy nodules).
Surgery for brain hemangioblastoma
During a conventional operation, which is the “gold standard” for this diagnosis, the tactics of craniotomy are used to create a retrosigmoid approach. Trephination is performed in the area of the foramen magnum; the diameter of the trepanation window is 2-4 cm. The surgical process occurs under the control of an ultra-powerful intraoperative microscope. The operation to completely remove the GBM lasts from 2.5 to 5 hours. Let's consider the main stages of surgical intervention.
- The hair from the scalp in the appropriate area is first shaved.
- In most cases, combined general anesthesia with tracheal intubation and artificial ventilation is chosen for pain relief.
- The patient's position is on his side or stomach, with his head turned to the side. The head is fixed using a special bracket with spikes.
- A longitudinal skin incision is made within the surgical field or a skin flap is cut out and then folded over the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
- Next, a bone hole is formed in the trephinated part of the occipital bone (downward and medial to the sigmoid sinus).
- At the next stage, the neurosurgeon performs a correct opening of the dura mater. After opening the dura mater, access to the surfaces of the cerebellum and other structures of the PCF is freed.
- The specialist begins the process of eliminating the tumor focus with complete preservation of functionally significant brain structures.
- The hemangioblastoma node is removed completely as a single block. All vascular formations feeding the neoplasm are coagulated and intersected as close as possible to its surface.
- If the tumor is a cyst, its contents are carefully aspirated. The walls of the cysts are not removed.
- At the end of the surgical session, the dura mater is sutured, bone fragments are returned to their place and strengthened, and the skin wound defect is closed.
Click on the link to watch a video of the operation to remove hemangioblastoma
The goal of an open operation is to remove the solid component completely, without any residue. It can be completely removed in most cases, in 85-90% of patients. In this situation, we can expect favorable forecasts with a high degree of confidence. But! If partial or subtotal resection is performed, the tumor will continue to grow. It is noted that incomplete removal often leads to the development of hydrocephalus, hemorrhages and hematomas, and death in the very early period.
Causes of angioma formation
Angioma in newborns is a standard clinical picture, since this disease in most cases is congenital. The source of the development of neoplasms in adulthood are persistent fetal anastomoses located between the veins and arteries. The proliferation of blood vessels in a benign tumor leads to the growth of the tumor itself.
The causes of angioma are as follows:
- hereditary predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of lipid metabolism;
- skin pigmentation disorders.
In rare cases, venous angiomas of the skin occur after trauma to the skin area (bruises, cuts). They can also accompany malignant neoplasms of internal organs and cirrhosis of the liver.
How to make a diagnosis
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by neurosurgeons, phlebologists, dermatologists, oncologists and other highly specialized specialists. They prescribe studies that will determine the cause of the problem and the location of the tumor. The presence of a problem can be confirmed using instrumental studies:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- angiography;
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination;
- spinal puncture.
To exclude anomalies similar to venous angioma, differential diagnosis is prescribed.
- Venous discirculation: what is it, brain damage
Symptoms of angioma
Symptoms of angioma depend on the type of vascular tumor, its size and location. In newborns, it is diagnosed immediately or several months after birth, and can grow very quickly, covering large areas of the skin.
Vascular angiomas can affect:
- Integumentary tissues - skin, mucous membranes of the genitals, subcutaneous tissue. Angiomas are also found in the mouth.
- Musculoskeletal system - muscles, bones. A severe form of the disease includes hemangioma of the vertebral body.
- Internal organs.
If integumentary hemangiomas cause cosmetic defects, then hemangiomas of internal organs provoke the occurrence of disturbances of important functions - urination, breathing, vision, defecation.
Angiomas of muscles and bones are accompanied by:
- skeletal deformation;
- severe pain in the joints;
- frequent fractures;
- radicular syndrome (compression of the spinal nerves).
Venous angiomas of the brain (cerebellum, left/right frontal lobe, etc.) are very dangerous. They lead to subarachnoid hemorrhage and epilepsy. Also, due to compression of the brain vessels by the tumor, the following symptoms may occur:
- convulsions;
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- noise in the head;
- taste disturbances;
- speech problems.
During the growth process, angiomas can become inflamed, causing phlebitis and thrombosis. A common complication is bleeding due to trauma.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
General symptoms of the disease
Newly formed cells exert pressure on neighboring ones.
The initial symptom of the disease is mild headaches and slight dizziness. The characteristic pathology begins to manifest itself as follows:
- Headaches of various types;
- Frequent dizziness accompanied by nausea;
- Epilepsy attacks;
- Paralysis of individual areas;
- Fainting;
- The vestibular apparatus malfunctions;
- Speech disruptions;
- Convulsive twitching;
- Distortion of information reading by taste buds;
- Changes in visual perception;
- Decreased mental activity;
- Noise hallucinations in the head;
- Disease of the venous system.
Diagnostics
Angiomas located on the surface of the skin are diagnosed during examination and palpation. The characteristic coloring, ability to contract and increase in size when pressed and strained allow the doctor to easily make the correct diagnosis.
If the localization of the lesion is more complex (internal organs, bones, brain), a number of diagnostic measures are required:
Skeletal hemangiomas are identified using x-rays of the spine, ribs, bones, skull and pelvis.
To identify angiomas of internal organs, antiography (contrast x-ray examination of blood vessels) of the kidneys, brain, lungs, etc. is performed.
Pharyngeal angiomas are examined by an otolaryngologist.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the exact depth of growth of the angioma, its structure and location features. If a vascular angioma is suspected, the doctor may additionally prescribe a puncture. The resulting yellowish liquid is examined in the laboratory. This makes it possible to differentiate angioma from lymphadenitis, lipoma, cyst, hernia.
Treatment of angioma
Treatment of angioma is aimed at stopping its growth, eliminating the pathological process and normalizing the functioning of the vascular network. Indications for urgent intervention are:
- extensive tissue damage;
- rapid growth of the tumor;
- localization in the neck, head;
- frequent bleeding;
- dysfunction of the organ in which the angioma is located.
Watchful waiting is justified only if regression of a vascular benign tumor is observed.
Among the most common treatments for angiomas:
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation. Cauterization with electric current is indicated if it is necessary to remove hard-to-reach punctate angiomas and angiofibromas. The method cannot be used if the angioma is deep and occupies a large area.
- Laser treatment. Using a laser, the doctor removes pathological tissue layer by layer. The advantage of laser treatment of angiomas is minimal bleeding.
- Radiation treatment. Allows you to achieve good results when removing angiomas of complex anatomical localization.
- Surgery. It is used if the vascular tumor is deep and it is not possible to remove it without affecting the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Cryotherapy. Makes it possible to remove simple small angiomas of any location. During the procedure, liquid nitrogen is applied to the tumor. The method is painless and does not cause bleeding.
- Sclerosing therapy. Seventy percent alcohol is injected into the tumor. The treatment is painful and is suitable if the angioma is located in the deep layers of the skin.
- Hormonal therapy. Relevant if the lesion is extensive, angiomas grow quickly.
- Excision of angiomatous areas followed by reconstruction of the vessel.
- Ligation of the arteries supplying the angioma. A ligature is applied to the end of the artery, as a result of which the neoplasm gradually dies.
It is possible to treat angioma with folk remedies:
- Apply the kombucha to the tumor site and fix it. After a day, replace the compress. The duration of such treatment is 2-3 weeks.
- Dilute a tablespoon of copper sulfate with 100 ml of clean water. Wipe the neoplasm with the resulting liquid 4-5 times a day for 10 days.
- Apply a compress of onion pulp to the affected area of skin for 10 days. Change the bandage every 12 hours.
- Cover the angioma with fresh grated carrots and tie gauze on top. Change 3 times a day.
- Mix fresh celandine juice in a ratio of 1:4 with petroleum jelly and add a drop of 0.25% carbolic acid. Use the ointment daily in the morning and evening.
- If the angioma has affected the internal organs, you can use the following recipe: pour 3 tablespoons of potato flowers into 300 ml of boiling water. Leave in a thermos. Drink half a glass 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The treatment course is 2 weeks.
It should be remembered that any folk recipe can be used only after consultation with your doctor. Some medicinal plants can provoke the growth of angiomas, so preparing decoctions and infusions from them yourself is not recommended.
Prevention of vascular neoplasms of the kidneys
There is no specific prevention of angiomas.
Recommendations are general in nature only and include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- hardening;
- avoidance of traumatic situations;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases.
Many people, upon hearing the diagnosis of angioma, feel fear. In most cases, this occurs due to ignorance and lack of information about the disease. Angioma does not pose a health hazard, but requires observation. Modern medicine has effective methods for treating angiomas, so even with large tumors, there is no need to panic, but you just need to follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Danger
A small spot formed on the skin can go unnoticed or be ignored by the patient for a long time. Since it can transform into a malignant formation, the lack of necessary treatment can lead to dire consequences.
Particular attention should be paid to angiomas located in places of increased friction with clothing (neck, chest, abdomen, shoulders), on the scalp. Frequent traumatization can lead to inflammation of a benign tumor and its rapid growth and bleeding.
The greatest danger to life is posed by angiomas of the brain and internal organs. As practice shows, if you do not treat a cerebral angioma, the prognosis is unfavorable - the area of accumulation of blood vessels will increase, which will lead to their rupture, hemorrhage in the brain and death.