The focus of ischemic necrosis of the heart muscle, which develops due to severe circulatory disorders, is called myocardial infarction. The person feels a burning pain in the chest area, which can radiate to the forearm and even the arm. In addition, an obvious symptom is an excessive feeling of fear and cold sweat that appears as a result of heart disease. As soon as a person is diagnosed with a heart attack, he must be hospitalized immediately. Emergency resuscitation greatly increases the chances of saving life.
Statistical data
Alas, the statistics are disappointing. As before, people in our country and in the world often die from this heart disease. Even an ambulance arriving at the scene cannot always help a person whose illness has rapidly developed.
In men after 40 years of age, myocardial infarction occurs much more often than in women at the same age (up to 60 years). This is due to the fact that atherosclerosis in representatives of the stronger half of humanity begins to develop earlier. But after 60 years there is no fundamental difference - both men and women are equally susceptible to this dangerous disease. According to statistics, approximately every third person dies due to a heart attack.
When the blood supply is disrupted for at least 10-20 minutes, this is quite enough for irreversible changes in the heart muscle to occur. A post-infarction scar is formed, which in the future can have a negative impact on a person’s well-being. The risk of another heart attack or stroke increases. It is necessary to be constantly monitored by your doctor!
Life after a heart attack
Mortality from myocardial infarction has been reduced thanks to:
- raising public awareness;
- new diagnostic methods;
- availability of high-tech medical care;
- improvement of outpatient preventive measures.
With proper recovery after myocardial infarction, the quality of life can be improved, and patients can live to a ripe old age. Necessary measures:
- compliance with the medication regimen prescribed by the doctor;
- dosed physical activity;
- weight control;
- proper nutrition;
- positive psychological attitude.
The quality of rehabilitation after a heart attack at home depends on the patient and his family. You should not violate the recommendations, as this may provoke a second heart attack with possible death.
Five periods of illness
Each period has its own characteristics and characteristics:
- Pre-infarction. This period can last for several days or even weeks. The main symptom is an increase in angina attacks.
- The sharpest. It has a short duration - maximum 2 hours. In other words, little time passes from the development of ischemia to the occurrence of necrosis. This period can last only 20 minutes, so urgent hospitalization is necessary.
- Spicy. As a rule, several days pass from the onset of necrosis to myomalacia. Maximum duration – 2 weeks.
- Subacute. Scars are already beginning to form. The maximum duration of this period is 2 months.
- Post-infarction. The scar matures, and the myocardium has to adapt to new working conditions. It is very important here how the heart behaves during fundamental changes. If there is no adaptation, there is a high probability of a second attack.
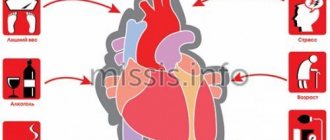
Reasons for the development of the disease
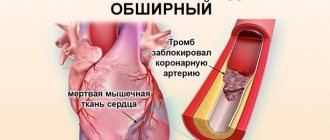
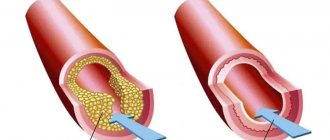
Heart attack is an acute form of IHD (coronary artery disease). In the vast majority of cases (more than 95 percent), the cause of the disease is atherosclerotic damage to the arteries. This, in turn, provokes a narrowing of the lumen. Quite often, doctors record cases where atherosclerosis is combined with acute thrombosis of a part of the heart that has already been affected. All this leads to a complete (or partial) cessation of blood supply to the heart.
A heart attack can also develop due to the following diseases and factors:
- Diabetes.
- High pressure.
- Obesity and poor nutrition.
- Constant stress, depression and other nervous and mental illnesses.
- Constant use of cigarettes and alcoholic beverages. They also provoke symptoms of myocardial infarction.
Factors provoking myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
There are various reasons for the development of the pathological condition:
- Diabetes. The formation and increase in atherosclerotic plaques occurs more intensely in people suffering from diabetes. This disease is characterized by vascular fragility and metabolic disorders. Atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots more often occur on vulnerable vessel walls.
- Hypertonic disease. High blood pressure causes the walls of blood vessels to thicken. They become dense and lose elasticity. During exercise, altered blood vessels cannot meet the heart's increased need for oxygen.
- Heredity. The tendency to develop hypertension, atherosclerosis and thrombosis can be inherited.
- Floor. Heart attacks occur 4 times more often in men than in women.
- Age. Young people are less likely to develop atherosclerosis and extensive myocardial infarction.
- Tobacco smoking. After inhaling tobacco smoke, a sharp narrowing of blood vessels occurs.
- Lack of movement. In people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, the walls of blood vessels lose their elasticity.
- Obesity. Excess weight creates additional stress on the cardiovascular system
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol causes dysfunction of the liver, which is responsible for breaking down fats. As a result, fat accumulates in the blood and is deposited on the walls of blood vessels.
- Kidney disorders. In renal failure, the exchange of phosphorus and calcium is disrupted. As a result, calcium is deposited on the walls of blood vessels and thrombosis develops. Many of those suffering from kidney disease have experienced a massive heart attack.
- Stress. Severe psycho-emotional shock or frequently occurring stressful situations can cause a critical narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels.
- Hyperlipidemia. Abnormally elevated levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood are a provoking factor for the development of extensive myocardial infarction.
- Excessive physical activity. High myocardial oxygen demand, insufficient elasticity of blood vessels and their spasms can lead to the development of a heart attack during intense sports.
- Trauma or surgery. Pathological narrowing of the lumen of the coronary vessels can occur as a result of injury or surgery.
Classification of the disease
There is no one specific classification at the moment. Therefore, experts use different concepts, it all depends on different factors. Here are the main classifications used by cardiologists:
- According to the size of the lesion. Here, large-focal and small-focal infarction are distinguished. The first is much more common - in about 80 percent of all people suffering from the disease.
- Depending on the depth of necrosis. For example, transmural or intramural myocardium. There are four varieties in total.
- According to the changes shown by the electrocardiogram. There are two types: heart disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of a Q wave, and an illness in which this wave is absent.
- According to topography. It all depends on which branch of the coronary artery is affected as a result of a heart attack.
- By the brevity of occurrence. There are only three types: primary, recurrent and repeated. A recurrent heart attack occurs less than 2 months after the appearance of the primary one, but a repeat one occurs after 8 or more weeks.
- By complication. Some ailments may be complicated by some concomitant diseases, while others may not.
- According to the presence and type of pain. In most cases, the first sign and symptom of a heart attack is severe chest pain. This is called the typical form. There are also atypical pain manifestations. For example, a person may complain of severe pain in the jaw, shoulder blade, or arm. The appearance of edema, arrhythmia and other unpleasant factors is also possible.
- According to the dynamics. Covers four periods (discussed above): from the acute to the post-infarction period, when scars form.
Main symptoms
Signs of the disease appear depending on the stage of the disease. That is, each of the five periods is characterized by its own symptoms:
- Pre-infarction period. Almost half of all patients report a very rapid, sudden progression of the disease. The rest experience varying (in duration and intensity) periods of progressive angina. Symptoms may vary.
- The most acute period. The person feels severe pain and compression in the chest. It can radiate to the shoulder, ear, neck and other places, causing the patient to feel discomfort. In this case, the nature of the pain can be completely different. Some patients feel bursting or burning pain, others feel pressing, squeezing or sharp pain. An attack of pain can last for several hours (some people even experienced attacks for 2 days). It can either subside or intensify again, accompanied by excessive fear, excitement and constant shortness of breath. Here are some other signs of a heart attack: blanching of the skin, cold sweat, tachycardia, a sharp drop in blood pressure, interruptions in heart function.
- Acute period. In most cases, the person does not feel pain. This period is characterized by the development of a febrile state (from three to ten days). The elevated temperature may persist throughout this period of time, and hypotension usually increases, as do symptoms of heart failure.
- Subacute period. Painful sensations no longer occur. The general condition of the person is normalized, body temperature gradually decreases. The tachycardia that tormented the patient disappears.
- Post-infarction period. In the vast majority of cases, there are no obvious symptoms.
Professional cardiologists classify atypical forms of the disease as a separate group. They are characterized by the occurrence of pain in completely unexpected places - for example, in the throat, epigastrium or area of the left shoulder blade. There are also painless forms, and a person experiences symptoms of a heart attack such as suffocation, collapse, interruptions in heart function, severe dizziness and weakness.
The atypical form develops to a greater extent in people whose age has exceeded 60 years. Such patients have obvious symptoms of cardiosclerosis. A distinctive feature of the course of the disease is a severe circulatory disorder that arose as a result of a repeated heart attack.
At the same time, only one period has an atypical form - the most acute one.
What does death from a heart attack look like?
Any cause of death due to myocardial infarction is associated with a malfunction of the circulatory system. A pathological process in the heart muscle leads to irreversible processes, fatal sensations and, as a rule, death.
Processes in the body
Violation of the blood supply to the heart muscle of any etiology, which is the cause of death from a heart attack, is manifested by the following symptoms:
| Cause | Consequence |
| Violation of the rhythm and sequence of the stage of excitation and contraction of the heart muscle | Blood is pumped in insufficient volume, and coronary shock occurs (a sharp decrease in the ability of the myocardium to contract). In this case, clinical death occurs. |
| Stopping venous blood flow | Pulmonary edema occurs and death occurs due to a heart attack. |
| Inconsistency of the heart ventricles | Disorganized series of impulses arise in the ventricles of the heart, their source is in the lower chambers of the heart. Blood pumping stops, which causes death in myocardial infarction. |
| Rupture of the walls of the heart | The heart fills with blood, a rupture occurs and the heartbeat stops immediately. |
External signs of death from a heart attack
By some signs you can understand that a person is no longer a tenant.
They show what death that occurs from a heart attack looks like. In these cases, the following symptoms of impending death are noted:
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- decrease in blood pressure: pulse becomes very rare;
- the skin acquires a bluish tint, the lips turn blue especially quickly;
- fluid stagnation and swelling occur in the lungs;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- dilated pupils - reaction to light is almost completely lost;
- breathing is initially noisy and frequent, then becomes rarer, until it stops completely (apnea is recorded).
- absence of a curve on the electrocardiogram.
Important! Irreversible processes in the body develop 3-5 minutes after clinical death is declared. Only about 3-4% of patients emerge from clinical death without consequences. Other patients do not restore all body functions after resuscitation.
External signs of death from a heart attack are not reflected in any way on the dead body of the patient. Rigor mortis and discoloration of the skin occur at the same time as in patients who die for other reasons.
Possible complications
In the first hours and days after the development of the disease, complications may appear. They significantly worsen the course of the disease and reduce the chances of successful treatment.
Most patients complain of interruptions in the heart (arrhythmia can be different). They can persist for several days. Particularly dangerous during this period is ventricular fibrillation, which then turns into fibrillation. A person's risk of death increases significantly.
Left ventricular failure has the following symptoms: congestive wheeze, pulmonary edema and some manifestations of asthma. Cardiogenic shock, which rapidly develops with a large infarction, poses a huge danger. Often doctors simply do not have a chance to save a dying patient. The main signs of such shock are: a sharp drop in blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, cyanosis, and impaired consciousness.
Often, patients experience rupture of muscle fibers, which can subsequently provoke cardiac tamponade. In less than 4 percent of cases, a person experiences a severe disruption of blood flow in the lungs. This complication is also characterized by increased mortality.
Another complication is acute cardiac aneurysm, which gradually turns into a chronic stage. As a result, heart failure occurs.
Fibrin deposition that occurs on the endocardial walls is a direct threat to various internal organs, including the kidneys, brain and lungs. Because of this complication, signs of a heart attack are especially severe in men and women.
The later period of the disease is accompanied by complications such as pericarditis and eosinophilia. There are also other serious illnesses.
Expert advice
I recommend to all my patients who have suffered a major heart attack to reconsider their diet, give up spicy and salty foods, fried and fatty foods. During the rehabilitation period, you need to perform physical exercises, which are shown by a physical therapy specialist. It is also necessary to monitor your weight and stop drinking alcohol and smoking. Hypertensive patients and diabetics who have had a heart attack should be under constant medical supervision and do everything to normalize blood sugar and pressure.
Diagnosis of the disease
The peculiarity of diagnostic procedures is that they can be prescribed not only during the examination period, but also during the treatment of the disease. The doctor should systematically study data on the activity of serum enzymes, as well as electrocardiogram indicators. This allows you to avoid various complications in the future, which in turn increases the patient’s chances of successful treatment.
A person can come to a specialist with various complaints. They directly depend on the degree of development of the disease, its form and duration. A heart attack is detected when severe pain in the chest area persists for 30 minutes (the attack lasts up to one hour). In this case, the patient feels acute heart failure. Other heart attack symptoms may also appear in women and men.
An electrocardiogram, among other things, allows you to record various changes in the activity of the heart. For example, the doctor has the opportunity to detect a negative T wave, a pathological QRS complex and other negative phenomena. After this, the doctor needs to conduct a number of other diagnostic examinations, or prescribe an urgent operation.
In the first few hours after the onset of severe pain, there is a sharp increase in myoglobin in the blood. This is a special protein whose main task is to supply oxygen inside the cells.
8 hours after the onset of a heart attack, a noticeable increase in creatine phosphokinase activity may be observed. Gradually the indicators are normalizing. The stabilization process takes about two days, sometimes less. The level of creatine phosphokinase in the blood should be measured several times a day. This should also be classified as diagnostic procedures that are of particular importance to the patient.
In the later stages of the disease, doctors also use different diagnostic methods, despite the fact that the risk of death increases. In particular, a specialist needs to determine the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase. The indicator returns to normal only after one week. It often takes two weeks for lactate dehydrogenase enzyme levels to normalize and stabilize.
Unstable angina can provoke an increase in troponin protein isoforms. Doctors detect these changes through tests. Symptoms of a heart attack in a man or woman may also subside.
The blood test that the patient gives allows the doctor to see an increase in the level of ESR, leukocytes and other elements. The clinical picture looks more complete, which contributes to successful treatment in the future.
Many cardiologists prescribe echocardiography, the main task of which is to identify various disorders of ventricular contractility, as well as thinning of its wall.
In more prestigious clinics, a modern diagnostic procedure is performed - coronary angiography. It allows the specialist to identify thrombotic occlusion of the artery. In addition, this diagnostic method allows the doctor to determine whether it is advisable to perform surgery on the patient’s heart or not. In other words, the likelihood of bypass surgery or angioplasty is assessed. Such radical treatment methods are often the only path to salvation when serious heart diseases are detected.
HELP OF THE SAMAZDRAV RESPIRATORY SIMULATOR IN REHABILITATION
To quickly return to a normal lifestyle, you can use the Samozdrav breathing simulator. Regular exercises on this device will improve blood supply to the heart. It can be especially useful for that group of patients who undergo rehabilitation at home.
You can start training on the simulator within 3 months after a heart attack. The Samozdrav simulator is useful both for the rehabilitation of the patient and for the prevention of a recurrent heart attack. After all, with the help of a hypercapnic mixture, vascular spasm is relieved and the functioning of the entire cardiovascular system is improved.
Due to constant training, a system of collaterals is formed - small blood vessels around the heart. They provide alternative blood supply and more complete nutrition of the heart muscle.
By exercising on the Samozdrav simulator, the patient will recover faster after a heart attack, because blood flow is normalized and the load is removed from the coronary vessels. Classes on the Samozdrav simulator will give tangible results within 3-4 months, and for such a serious illness as a heart attack this period is quite short.
Disability after a heart attack
A heart attack requires a long period of treatment and rehabilitation. At the same time, a person’s full working capacity is not always restored. For these reasons, permanent or temporary disability is given to patients with a heart attack quite often.
All patients who have suffered a major heart attack have the right to four months of paid rehabilitation based on the compulsory medical insurance policy. Usually this period of rehabilitation is enough to understand whether a person needs a disability or whether he is able to fully begin his usual work. If there is reason to think about partial loss of ability to work, the patient, on the recommendation of the attending physician, can undergo an examination by a medical and social expert commission.
To assess the level of disability, the commission will assess:
- patient self-care options,
- his education,
- possibility of returning to normal work,
- general health.
As a result, disability may be assigned to those whose work involves frequent stress, increased attention, and physical activity; pensioners and patients who have undergone vascular surgery; people with heart failure or unstable angina, as well as those who have lost their ability to work by 50 percent or more.
The commission evaluates each case individually and makes a decision based on a combination of factors both on the fact of establishing disability and on its group.
Diet
In the first week after myocardial infarction, a low-calorie diet with limited fluid, salt, fat, excessive fiber and cholesterol is recommended. The diet should include foods rich in potassium and vitamin C.
In the first week, food is served pureed, in small portions 6-7 times a day. It can be:
- semolina,
- oatmeal,
- buckwheat,
- rice porridge,
- lean veal,
- chicken,
- fish,
- steamed white omelette,
- cottage cheese and kefir,
- carrot and apple salad,
- beets and cabbage,
- fruit purees,
- honey.
You can't eat:
- baked goods and sweets,
- smoked,
- fried,
- fatty,
- spicy,
- salted and pickled dishes;
- pasta,
- beans,
- coffee,
- boiled and fried eggs.
After the acute period, whole foods are introduced into the diet, but dietary restrictions should become the norm for a person.
The basis of the diet should be:
- vegetables,
- fruits,
- nuts,
- lean meats and fish,
- cereals
Smoked, canned, fried and salted foods are not recommended for consumption. It is convenient to control your weight using your body mass index (the result of dividing your weight in kg and height in meters squared).
It should be within 25-27 kg/m. In addition, the waist circumference is assessed: for men this figure should not exceed 94 cm, for women – 80 cm.
Diet for weight loss
First breakfast.
One hundred grams of low-fat cottage cheese, a cup of coffee with milk and without sugar.
Lunch.
Fresh cabbage salad (170 g) with sour cream without salt.
Dinner.
Vegetarian cabbage soup (200 ml), 90 g lean boiled meat, 50 g green peas, 100 g apples.
Afternoon snack.
One hundred grams of cottage cheese and 180 ml of rosehip decoction.
Dinner.
Boiled fish (100 g) and vegetable stew (125 g).
Before going to bed, at night.
Kefir (180 ml) and 150 g of rye bread.
Let us repeat, this is an approximate diet for one day. This diet contains 1800 kcal.
For patients without excess weight problems, the diet is significantly expanded.
They are prescribed a diet with a calorie content of 2500 - 3000 kcal
. The consumption of animal fats and carbohydrates is limited. Also 4-5 meals a day. It is useful to spend fasting days on apples (1.5 kg) or fresh cucumbers (2 kg). For “avid meat eaters”, 600 g of lean meat plus a side dish of vegetables (fresh cabbage, green peas) are even allowed.
Strongly not recommended
Doctors do not allow such patients to drink
alcohol
, even of the highest quality. It causes tachycardia and an undesirable increase in appetite. The consumption of smoked meats, fried foods, fatty sausages and sweets is absolutely unacceptable.
Breathing exercises after a heart attack
A heart attack is an acute condition associated with extreme strain on blood vessels and extreme circulatory impairment. Lack of oxygen in the heart muscle leads to its death. Unfortunately, necrosis of the heart muscle is irreversible, but nevertheless, it is necessary to create conditions for sufficient oxygen in the body for both primary and secondary prevention of the disease.
Acute pain during angina attacks, which are precursors to a heart attack, signals the myocardium about problems with oxygen.
The surest way to provide the heart muscle with enough oxygen is to reduce risk factors and breathe properly. We receive oxygen through the respiratory organs, and they must be trained and tuned to support a full respiratory cycle.
The Samozdrav breathing simulator can become a confident and powerful support in the prevention of heart attack. One of the basic positive effects of breathing training on the body is sufficient oxygen supply to the body and maintenance of normal CO2 levels. Thanks to training with Samozdrav, you can constantly maintain oxygen levels at a level that eliminates oxygen deficiency. This means a high probability of myocardial preservation and significantly reduces the risk of heart attack.
In addition to the “direct supply” of oxygen to the body, breathing training strengthens the functioning of the nervous system and corrects reactions to stress, providing peace and a smooth emotional background even under high loads.
Training with Samozdrav corrects metabolism and is effective in treating obesity. They activate metabolism by normalizing the level of oxygen in cells and tissues, normalize the excretion of metabolic products, and allow for better absorption of nutrients.
Samozdrav is indispensable for patients with hypertension. It was the treatment of this disease that became the primary goal of the creators of the breathing simulator, and today its effectiveness in treating hypertension without medications has been fully proven by research and many years of practice of use by millions of people.
Breathing training can cope with any modified risk factor for heart attack. Regular exercise will give the myocardium sufficient oxygen levels and keep the heart healthy.
Professional treatment. Why should you only contact experienced doctors?
As soon as myocardial infarction is suspected, the patient should be immediately admitted to the local cardiac intensive care unit. If an acute period is recorded, then the person first needs to remain in bed. Any psychological stress during this period is excluded! As for nutrition, it is severely limited in volume and calorie content. When the subacute period begins, the person can already be transferred from the intensive care unit to cardiology, where he will continue the recovery course after a severe attack. Treatment of myocardial infarction can take a long time, when the patient will systematically have to be checked by the attending physician, take various tests and undergo a bunch of examinations.
To relieve severe pain, the doctor prescribes narcotic analgesics. In this case, treatment is carried out in combination with antipsychotics, as well as the administration of nitroglycerin through an injection into a vein.
Therapy carried out by experienced specialists in case of a heart attack is necessary in order to prevent and eliminate interruptions in the heart and cardiogenic shock. As a rule, during this period the patient takes antiarrhythmic drugs, including thrombolytics, antispasmodics and nitrates.
It is extremely important that treatment for myocardial infarction is carried out by an experienced doctor. Only a prestigious clinic employs specialists who can correctly assess the patient’s condition. When a person survives an attack, this does not mean that the danger is over. There is a long course of treatment ahead, and the success of the process depends on the selection of medications, the experience of doctors and the technical equipment of the clinic.
Of course, when a person loses consciousness as a result of a heart attack, it is not advisable for family and friends to go to a private clinic. But the recovery period is better spent in a commercial medical institution. When the patient can walk normally, you can make an appointment with a specialist who will help minimize the consequences of a serious illness.
Symptoms of atypical forms of MI
Abdominal type:
- Acute pain in the abdomen, in the epigastric region. Partially relieved by Nitroglycerin, which indicates a cardiac origin.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting without signs of relief. It is a reflex, so the discomfort does not subside as with
- poisoning Heartburn, dyspeptic symptoms.
Cerebrovascular form:
- Strong headache. In the occipital, parietal regions. It may be diffuse and not have a specific localization.
- Vertigo. Up to the impossibility of orientation in space. The vestibular apparatus does not function normally due to damage to the cerebellum and its ischemia.
- Nausea without vomiting.
- Loss of consciousness. May be repeated during one emergency episode. Deep fainting requires urgent help.
Stroke becomes a natural result of cerebral ischemia.
Arrhythmic form:
- Tachycardia or decreased heart rate.
- Feeling of freezing in the chest, turning over, missing blows.
- Asthmatic type:
- Choking, asphyxia. It gets worse at night and when lying down.
- Increase in heart rate.
Pain syndrome is minimal or completely absent.
To limit conditions, the patient is urgently transported to the hospital. The following shows urgent actions.
Features of making a prognosis for a heart attack
The peculiarity is that only after the acute period of the disease has passed, the doctor can give a positive prognosis. If the patient has some complications, then experts usually give a negative prognosis.
A heart attack itself is a very serious and in many cases fatal disease. There is a high probability of various complications occurring. In most cases, death occurs within the first 24 hours after the attack occurs. When more than half of the entire area of the myocardium is damaged, the heart can no longer function normally, resulting in the rapid development of cardiogenic shock and death. Even if the myocardium is damaged by 40 percent or less, the heart may not be able to cope with sudden loads, and severe complications appear, one of which is heart failure.
Help with sudden cardiac arrest
However, upon discovering that a person has suffered cardiac arrest, you must immediately call an ambulance, informing the operator that the person has suffered cardiac arrest. It is advisable to independently perform chest compressions and carry out artificial ventilation using the mouth-to-mouth breathing technique. This will allow the body to hold out until the doctors arrive.
In the clinic, in the intensive care unit, measures to bring the patient back to life will include defibrillation of the heart using electric current pulses, intubation of the lungs, and administration of special medications that nourish the heart muscle. If everything is done correctly, and most importantly, quickly, the patient will have a chance to survive.
Important! In women, the symptoms of a heart attack may be vague. It can be confused with the flu or severe fatigue. Pay attention to the heart rhythm and provide immediate assistance, since death from a heart attack occurs very quickly.