What kind of disease is this and what are its causes?
The main etiological cause of the development of acute myocardial infarction is atherosclerotic damage to the intima (inner lining) of the coronary arteries.
As a result of the formation of deposits, the lumen of the vessel narrows, and blood begins to flow in limited quantities. This is how IHD begins with angina attacks. When exposed to provoking factors (physical or emotional stress), the artery is completely blocked and permanent ischemia develops with the formation of an area of necrosis. Other (very rare) causes of heart attack are conditions in which blood flow is disrupted:
- rheumatism;
- vasculitis;
- tumors;
- allergy;
During my practice, I often encountered the fact that many patients do not eliminate bad habits and poor nutrition from their lifestyle. But these risk factors for myocardial infarction often lead to fatal consequences.
Deterioration of the blood supply to the heart occurs more often in the elderly: men after 45 years of age and women after 55 years of age should beware of the disease. Psycho-emotional shocks can provoke an attack - many patients come to our department after the death of loved ones, dismissal from work, divorce.
“It will hurt and it will go away”
“In case of a heart attack, you need to act quickly: if you do not open the lumen of the vessel within 6-12 hours to restore blood flow, necrosis of the myocardium will begin,” says Professor of the Department of Preventive and Emergency Cardiology of the First State Medical University.
Sechenova, chief cardiologist of the Moscow region Maria Glezer. Now there are very strict standards for ambulances: the team must arrive 20 minutes after the call. A network of vascular centers has been created where the patient is helped quickly and efficiently. Fortunately, both the emergence of effective drugs and the development of minimally invasive methods (angioplasty, stenting) make it possible to treat a heart attack much more productively. In most cases, after placement of the stent, the patient is discharged within 2-3 days. And he feels quite healthy.
But for this system to work, the patient must get to the clinic according to the principle “the sooner the better.” At the same time, cardiologists warn: every third heart attack passes without symptoms - pain, nausea, vomiting, dizziness. Or with mild symptoms. Even an ECG does not always show changes. But the patient is often in no hurry to see a cardiologist.
“I ask my patients: why sit at home? - says Maria Glezer. “And they are like children to me: “I thought it would pass, it would resolve.” As a result of such carelessness, every second death from a heart attack happens at home, even before the doctors arrive. At the same time, if the patient is taken to a vascular center, the mortality rate from acute heart attack is reduced by 60%.
Classification
Classification of myocardial infarction is carried out according to several principles.
Based on the time of occurrence, they are distinguished:
- first appeared (primary);
- recurrent (repeated within 1.5 months after the first);
- repeated (occurring later than 6 weeks after the primary).
The following types of myocardial infarction are determined by location:
- left ventricle (anterior, posterior, lateral and septal walls);
- extensive, affecting several departments at once;
- right ventricle (occurs extremely rarely, often accompanied by damage to other areas of the heart muscle).
According to the degree of prevalence of ischemia and necrosis, there are the following types of acute myocardial infarction:
- intramural (located deep in the wall of the organ);
- subendocardial (develops in the inner layer);
- transmural (passes through all three layers of the heart);
- subepicardial (disorder in the outer part of the organ).
Diagnosis of heart attack
Ultrasound examination of the heart
Extensive myocardial infarction is diagnosed based on the following points:
- Patient complaints
- ECG study in dynamics
- Ultrasound examination of the heart
- Laboratory detection of elevated levels of myocardial enzymes, monitoring them over time
- Coronary angiography according to indications
- Myocardial infarction in diabetes mellitus
How many heart attacks can a person have?
Almost all patients who have had a heart attack once ask me about the risk of another at their appointment. Understanding their concerns very well, I will still say that no specialist will give a definite answer in this case. It is necessary to take into account the location of the scar, the depth and width of the lesion, and the presence of complications. The degree of restoration of cardiac function depends on the development of collateral circulation (additional vascular pathways). I have seen cases where the patient remained alive after the fifth episode, although death can also occur as a result of a primary heart attack.
Stages of disease development
The clinical course of a heart attack goes through five main periods:
- Subromal or pre-infarction. It can be short (up to several hours or days) or quite long (1-2 weeks or a month). At this time, pain attacks become more frequent and prolonged. The same option includes a heart attack, which manifests itself against the background of sudden and rapidly progressing angina.
- The sharpest. Consists of persistent ischemia followed by the development of necrosis. Lasts from 20-30 minutes to 2 hours (but no more). Anginal pain by this time becomes weaker or completely disappears. Blood pressure drops, signs of heart failure appear or increase.
- Spicy. Necrosis smoothly progresses into melting of the heart tissue (can last from two days to two weeks).
- Subacute (from 1 to 45 days from the onset of the episode). At this stage, the formation of connective tissue in the affected area begins, and the remaining myocardiocytes adapt to continue further work.
- Post-infarction. The scar is completely organized, granulations appear at the site of necrosis. It takes from the beginning of the acute stage from 1.5 months to six months.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that the provision of qualified assistance during the deterioration of angina pectoris or during the acute period of myocardial infarction helps prevent the development of necrosis. In this case, the process is reversible and the prognosis is favorable.
Read more about what happens and how to act correctly at each of the above stages of a heart attack here.
Consequences of a heart attack
After a severe heart attack, complications are often recorded. The main consequences of a major heart attack in men and women are as follows:
- heart block;
- pulmonary edema (acute heart failure);
- blood clot formation;
- recurrence of heart attack;
- pericarditis;
- there is a danger of mental disorders;
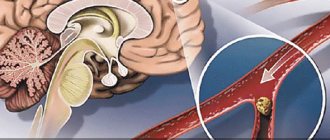
- disorders of blood circulation in the brain;
- malfunctions of the digestive system;
- heartbreak;
- failure of internal organs;
- Paralysis of the limbs may occur.
How long do they live after a heart attack?
Many people who have suffered a heart attack and their relatives are always interested in how long they live after a major myocardial infarction. Life expectancy depends on the quality and quantity of the consequences of the blow, the size of the lesion of the heart muscle, and the age of the patient. To prolong your life as fully as possible after a heart attack, you need to take prescribed medications, lead a healthy lifestyle, and follow all medical recommendations. According to statistics, about 20% of patients live up to 5 years after a major attack.
Early signs of a heart attack
Most of the patients (approximately 60 to 80%) who were observed by me with this diagnosis indicate that the disease did not begin suddenly in them. It was preceded by precursors of a heart attack, or a prodromal period. The most favorable outcome was observed in those patients who sought help or were brought by the team in the first hours of the attack.
I would like to make a small disclaimer - early signs of myocardial infarction do not always occur, it all depends on the pain threshold and the state of the patient’s nervous system.
But in most cases I have seen the following symptoms:
- Pain along the anterior surface of the chest radiating to the left arm, part of the lower jaw, and scapula.
- The unpleasant sensation is not relieved by taking nitro-containing drugs and goes away only after the administration of narcotic analgesics.
- It has a constant, increasing or wave-like character with periods of subsidence and resumption.
- Lasts more than 20-30 minutes.
- The patient begins to sweat and tries to sit down or lie down as high as possible. This position makes the attack a little easier.
- Shortness of breath develops, the skin becomes pale, and the nasolabial triangle turns blue.
- When it comes to the first signs of myocardial infarction, rhythm disturbances cannot be ignored. According to my observations, they are observed in 90% of cases at the stage of ischemia development and before scar formation.
Any suspicion of a heart attack requires an immediate ECG, which will reveal all signs of ischemia, and at a later stage, necrosis and scar formation. Read more about what changes will be visible on film here.
Myocardial infarction. What it is?
The myocardium is the heart muscle. Blood flows to it through arteries called coronary arteries. If any of these arteries is blocked by a blood clot, then the area of the heart that it supplies is left without blood supply, and therefore without oxygen. “On a starvation diet,” myocardial cells can survive for 20-30 minutes at best. Then they die - this is a heart attack, an area of necrosis in the tissue of the heart. A scar remains on the affected area.
Why does this happen?
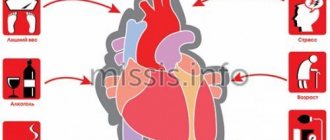
The main cause of the disease is atherosclerosis, which almost all of us have. In addition, we will name the circumstances of life (both those that depend on us and those that do not) in which the likelihood of getting sick is highest: male gender; for women, the dangerous age comes after 50 years; heredity (IHD) heart attack, cerebral stroke, in at least one of the direct relatives: parents, grandparents, brother, sister, especially if the disease began before the age of 55); elevated blood cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/l or more than 200 mg/dl); smoking (one of the most significant risk factors!); excess body weight and sedentary lifestyle; increased blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg at any age); diabetes mellitus.
The presence of at least one of these factors actually increases the risk of “acquaintance” with myocardial infarction. Moreover, the addition of each new risk factor increases the likelihood of getting sick exponentially. They also say that baldness in men is a kind of harbinger of a heart attack, since one of the factors in the appearance of baldness is an increased level of androgens, and in the case of hormonal fluctuations, the body reacts to changes in hormone levels by raising blood pressure pressure and increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
What happens?
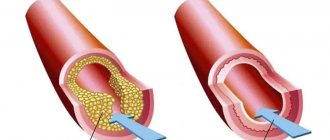
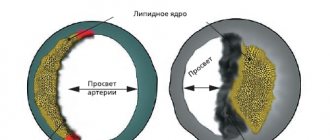
Atherosclerosis is a process in which certain fats (cholesterol and other lipids) are deposited in the walls of large arteries if they are found in excess in the blood. Those places on the vascular wall where there are especially many lipid accumulations are called atherosclerotic plaques.
Plaque is the most vulnerable place in the vascular wall. Especially if it is “young” and calcium has not yet had time to be deposited in it. At the most unexpected moment, the wall of the plaque, and therefore the inner lining of the artery of the heart, can crack and tear. This is an alarm signal for the body. He tries to heal the crack with a blood clot. Therefore, blood immediately begins to clot at the damaged area. The formation of a blood clot resembles a snowball rolling down a mountain. If nothing interferes with it, the thrombus grows very quickly until it closes the entire lumen of the artery. Then the blood flow through it stops, cell death begins and myocardial infarction develops. The larger the artery that the thrombus has closed, the more myocardial cells will die.
The integrity of the atherosclerotic plaque can be disrupted by rapid heartbeat and increased blood pressure. A heart attack can begin during severe physical or emotional stress, but often it develops for no apparent reason, as if out of nowhere. Perhaps even in a dream. But his most “favorite” time is early morning. Depending on the size, infarctions are divided into large-focal, in which necrosis spreads throughout the entire thickness of the heart muscle, and small-focal. Large focal infarctions of the anterior wall of the myocardium are more dangerous. With an infarction of the posterior or lateral walls, especially a small-focal one (not of the full thickness), its consequences are not so traumatic. The scar on the heart muscle remains for life. It cannot resolve, and the heart always “remembers” the heart attack.
Symptoms and diagnosis of heart attack
The first sign to suspect a heart attack is usually severe pain behind the sternum, that is, in the middle of the chest. Usually at rest; presses, burns, squeezes, can radiate to the arm, shoulder, back, jaw, neck. With (angina pectoris, similar pain occurs during exercise, and with a heart attack it is more severe and often begins at rest and does not go away after taking 3 nitroglycerin tablets one after another (1 tablet under the tongue every 5 minutes). If these signs are present, call immediately "Ambulance". The ability to endure in this case is a dangerous enemy. Sometimes the disease manifests itself with vomiting or discomfort in the stomach, interruptions in the heart or difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness or... nothing.
Yes, this also happens: a person suffers a heart attack without even noticing it. The so-called painless form of myocardial infarction is more often observed in people with diabetes. The changes that occur during a heart attack are clearly visible on the electrocardiogram. To clarify the area and extent of the lesion, an ultrasound of the heart, echocardiography, which makes it possible to see structural changes, may be prescribed, the doctor may recommend scintigraphy.
Treatment
To play it safe, at the slightest suspicion of a heart attack, doctors send the person to the intensive care unit of the hospital. And the sooner the better. After all, only during the first few hours, by introducing special drugs, can a “fresh” blood clot be dissolved and blood flow in the coronary artery restored. The formation of new blood clots should then be prevented. For this purpose, medications that slow down blood clotting are used. One of the most reliable remedies is acetylsalicylic acid, that is, regular aspirin. It reduces the number of complications and prolongs the life of people who have had a heart attack. Beta blockers are often used in treatment. These drugs reduce the myocardium's need for oxygen, which means they save heart muscle cells from death and reduce the size of necrosis. At the same time, they make the heart work more economically, which is very important during a heart attack. In recent years, not only medications have been used to treat heart attack. Angioplasty is indicated when drug therapy is ineffective. In another case, a cardiac surgeon may suggest surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting). In the first days, strict bed rest is required. At this time, the damaged heart may not withstand even minimal stress. Previously, a person who had a heart attack did not get out of bed for several weeks. Today, the period of bed rest has been significantly reduced. But all the same, at least three days after a heart attack you need to lie in bed under the supervision of doctors. Then you are allowed to sit, later get up, walk... Recovery begins, adaptation to a new, “post-heart attack” life.
Rehabilitation; after a heart attack
Is it possible to return to normal life after a heart attack? It is difficult to say firmly “yes” or “no”. After all, everyone has their own: one works as a loader, and the other spends his days at a desk. It will not be easy for the first to engage in usual activities, and for the second there will be little to interfere. In addition, complications, and the heart attacks themselves, are different for everyone. Recovery after a heart attack takes several months. After all, the disease is not a joke, it requires you to reconsider your lifestyle and change something in it. Rehabilitation begins in the hospital, where the intensity of physical exercise is gradually increased along with medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. (Particular attention to the word “gradually”). Do not force things under any circumstances. Exercise therapy, walking first on a flat surface, then on stairs... By the way, stairs are a good test of readiness for an active life. If the patient can climb to the fourth floor at an average pace without feeling chest pain or shortness of breath, then recovery is successful. For a more accurate assessment of the condition, a dosed load test is often used. It is usually performed on a special bicycle - a bicycle ergometer or on a treadmill.
How long should I take the medicine? There is only one answer: all your life! Even if you feel great. That’s why it’s wonderful, because medications taken constantly help the heart.
Is it possible to have sex after a heart attack? Feel free to ask your doctor this question. Everything will depend on how you tolerate physical activity (and sexual intercourse is a load, and a considerable one). But there are also rules that are common to everyone, which must be remembered so that sexual contact ends in pleasure and not in a new heart attack. Firstly, it should take place with a familiar partner, secondly, in a familiar environment, and thirdly, when choosing a position for sexual intercourse, you should prefer one in which the load is minimal, for example, on your side.
Prevention
There is no escape from some risk factors (gender and heredity). But everyone else is quite amenable to our efforts! Maintain normal blood pressure, and also monitor the weather - for example, heat and geomagnetic storms are dangerous for people with high blood pressure. Normalize your blood sugar levels.
Move more! It is not at all necessary to run, it is enough to walk in the fresh air at least 5-6 kilometers a day. It is very important to quit smoking - this is one of the most “aggressive” risk factors. Try to lose excess weight. What should be a normal weight? Let's do the math: divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. The resulting number is called the body mass index. We must strive to ensure that it does not exceed 26. The diet should contain a minimum content of animal fats and cholesterol. More vegetables and fruits. Instead of fatty pork, use white poultry, replace butter with sunflower oil, and lard with fish. This diet allows you to reduce not only your cholesterol levels, but also your costs.
Consequences and complications
In any period from the onset of an acute infarction to its resolution in the form of the formation of a connective tissue scar, the following complications may be observed:
- cardiogenic shock;
- heart failure;
- ventricular fibrillation;
- wall rupture due to myomalacia;
- formation of a parietal thrombus and thromboembolism;
- pericarditis.
The lethal outcome of this disease is recorded in the early stages in approximately 35% of cases. Its cause is rhythm disturbance, cardiogenic shock and acute heart failure. Later death may occur as a result of the formation of an aneurysm with rupture, thromboembolic complications, or acute pericardial tamponade.
After the acute period, the heart muscle adapts to new working conditions, but there remains a high risk of repeated episodes.
Treatment
Treatment of myocardial infarction should be carried out in an intensive care unit with qualified personnel and special equipment. But assistance should begin at the prehospital stage.
This is usually done by the ambulance crew.
After taking an ECG and establishing a presumptive diagnosis, you should:
- put a Nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue;
- give 300 mg of Aspirin to drink;
- administer narcotic analgesics to eliminate pain;
- if necessary, use intravenous antiarrhythmic drugs;
- carry out resuscitation measures in case of cardiac arrest and clinical death.
Read more about how to properly provide emergency care to a patient with a heart attack here.
Drug therapy
After the patient is admitted, my colleagues and I provide care according to the established protocol. All measures are aimed at relieving pain, limiting the area of necrosis, preventing the development of complications, and restoring blood flow through the coronary arteries.
Treatment of myocardial infarction begins with the elimination of pain. Since conventional drugs are ineffective in this case, doctors use intravenous administration of the narcotic analgesics Promedol or Morphine. This helps normalize a person’s emotional state, lower the heart rate and equalize blood pressure. When discomfort is relieved, the likelihood of reflex cardiogenic shock decreases.
Acute myocardial infarction is a coronary thrombosis. Therefore, the patient is administered a direct anticoagulant, thereby performing the procedure of thrombolysis - dissolving the blood clot.
The modern and most effective approach is considered to be a stenting procedure, which allows you to instantly restore blood flow in the affected heart vessel. After this, Clopidogrel with Acetylsalicylic acid is prescribed for 2 years to prevent platelet aggregation and the development of a recurrent attack.
The use of beta blockers can reduce the load on the heart and also prevent the development of arrhythmia. Treatment of myocardial infarction necessarily includes prolonged nitrates (“Kardiket”). They allow, by dilating the coronary vessels, to improve blood flow to the heart and limit the area of necrosis.
An important point is the prescription of high doses of statins (“Rosuvastatin” up to 40 mg, “Atorvastatin” up to 80 mg) - drugs. Their use can reduce the degree of inflammatory reaction.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction and their characteristics are also taken into account during treatment. In case of severe anxiety, the patient is given sedatives; if the pressure remains high, antihypertensive drugs are used.
I would like to note that treatment after a heart attack does not end. The patient will need to take blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) throughout his life. Read about how to properly undergo rehabilitation after an attack here.
Surgical methods
In the absence of treatment effectiveness and in order to prevent the recurrence of a heart attack in the same area, the following operations are used:
- Coronary artery bypass grafting. It consists of restoring the passage of blood through the heart arteries by creating an artificial anastomosis.
- Balloon angioplasty. A tube with a ball at the end is inserted into the lumen of the vessel. Having reached the point of application, it is inflated and the atherosclerotic plaque is pressed against the wall, restoring normal blood flow.
Only in hospital
Acute coronary syndrome is a collective concept that includes unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. The treatment strategy for this condition is to quickly restore blood flow, which saves the myocardium and the life of the patient. And such assistance can only be provided in a hospital or vascular center, provided that the patient is delivered within two hours from the moment the vessel is blocked. Statistics confirm this: mortality in hospitals from myocardial infarction is 13–14%, in vascular centers – even lower.
Correct routing of patients and stenting are a real opportunity to reduce mortality from heart attacks, Maria Glezer emphasized. According to her, the introduction of a system of vascular centers made it possible to reduce hospital mortality from acute heart attack in the Moscow region by 60% - an impressive figure. But the problem is that people don't call an ambulance. 40–50% of patients die at home, Maria Glezer laments: “When I ask why they were sitting at home, they answer: they thought it would go away on its own, it would resolve.” So one of the main tasks is the education of the population.
Repeated myocardial infarction is a real threat. It ranges from 10 to 20%. It is very important for people who have suffered it to be told about secondary prevention measures that can prevent rhythm disturbances and the development of such a serious pathology as heart failure, which often leads to death, says Professor Glezer.
“If the patient is lucky and survives the first time, he will not necessarily survive the second or third time,” warns the deputy director for scientific work of the medical research and educational center of Moscow State University. Lomonosov, member of the Presidium of the Russian Cardiological Society, corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Professor Simon Matskeplishvili . “But, unfortunately, it very often happens that doctors did everything in their power to save the patient’s life: they performed primary coronary intervention, placed a stent and eliminated the cause of acute coronary syndrome or treated it conservatively. And upon discharge, they gave instructions that were designed to preserve the life and health of the patient. But, after being discharged from the hospital, he goes to the clinic, where his treatment is completely changed.”
It often happens that patients take their own medications off, and instead of really effective drugs prescribed in the hospital, they ask the doctor at the clinic to prescribe drugs from a very limited list of subsidized medications. Or worse, they switch to dietary supplements.
Heart attack is inherited. Why the heart stops in young people Read more
Clinical case
A patient was admitted to the hospital with severe chest pain and other typical symptoms of myocardial infarction.
He was sent from the clinic, where a cardiogram was taken, which revealed large-focal necrosis in the acute stage of development along the anterior wall of the left ventricle. He notes that lately there have been warning signs of a heart attack - angina attacks became stronger and were poorly controlled with Nitroglycerin. The patient was referred for percutaneous coronary intervention—stenting. On the second day after the procedure, the patient felt much better, and therefore he was transferred to the general cardiology department. Recommendations were issued: follow a diet with limited fluid and salt, as well as the exclusion of fatty foods and foods high in cholesterol, lifelong use of Aspirin and statins, adequate physical rehabilitation.
“I feel good - pills in the toilet, and a cigarette in my teeth”
“It is important that patients understand that myocardial infarction is an ongoing process. The disease began long before the vascular accident and, unfortunately, continues after it,” explains Alexey Erlikh, Doctor of Medical Sciences, senior researcher at the Laboratory of Cardiology of the Federal Scientific Center for Physical and Chemical Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency. — Heart attack is a disease associated with two serious pathological processes: atherosclerosis and thrombosis, when atherosclerotic plaques grow in the vessels and blood clots form on these plaques. And after a heart attack, this process, unfortunately, continues.”
Experts say: there are two powerful effects on the body - non-drug and medicinal. And neither one nor the other can be neglected.
“Non-drug” recommendations are changes in lifestyle:
quit smoking and alcohol;
ensure uniform physical activity, gradually increasing it;
the “gold standard” for both healthy people and “heart attack patients” is 10,000 steps daily or 30 minutes of aerobic exercise;
eat right: complete proteins, limit animal fats and fast carbohydrates; more different vegetables, fruits, herbs, a minimum of sugar, salt, smoked, fried foods. We must try to reduce weight.