Iron deficiency anemia is a pathological condition characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells in the blood. Anemia poses a danger to the brain and can cause hypoxia, which causes the death of nerve cells, which leads to mental degradation. The following symptoms are characteristic of anemia:
- constant weakness
- fast fatiguability,
- decreased performance,
- brittle nails,
- dryness and thinning hair,
- pale skin,
- muscle weakness.
The reason for this condition is a deficiency of iron, which is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin, the carrier of oxygen to organs and tissues. Diet for iron deficiency anemia is of great importance. In addition, anemia may be a symptom of another disease.
Heme and non-heme iron
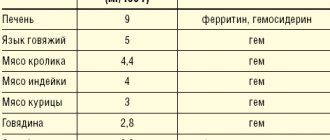
With anemia, the body may experience a lack of heme and non-heme iron. The first is found in hemoglobin in red blood cells. Its function is the formation of a special substance - heme, which binds oxygen in the lungs for its further delivery to cells. For the formation of heme, divalent iron is necessary, which is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Sources of heme iron:
- hemoglobin,
- myoglobin,
- meat (liver especially),
- fish.
Non-heme iron is absorbed much worse. This process depends on how saturated the human body is with iron. If there is a deficiency, then it is absorbed better; if the body is saturated, absorption is lower. In addition, the absorption of non-heme iron depends on how it is dissolved in the intestines, and this is influenced by the composition of the food taken. Non-heme iron is found in most foods.
Iron deficiency
Unfortunately, insufficient intake of minerals is a common phenomenon in the modern world among both adults and children. Iron deficiency disrupts the functioning of all cells in the body, especially if their functioning requires intense metabolism and oxygen supply. Changes affect the main organs and systems, manifested by a decrease in the activity of all processes and the ability to withstand the negative effects of external factors. A late and already pronounced manifestation of iron deficiency is the development of anemia, in common people - anemia. In this condition, the amount of hemoglobin decreases, and the formation of altered erythrocytes (red blood cells) occurs - they become pale and reduced in size. In humans, the total iron content in the blood serum decreases.
Principles of nutrition
Proper nutrition for iron deficiency anemia is one of the important components of treatment, but without iron supplements it is impossible to cope with the pathology.
Products should provide not only the supply of iron, but also trace elements and vitamins. The basis of nutrition is meat and products made from it. The body should receive more protein, at least 135 grams. Protein promotes the formation of quickly absorbed iron. Vegetarianism in this case is unacceptable.
For anemia, food should be steamed, boiled, baked, fried, or stewed. The diet for children should be high in calories and varied. Food should stimulate the appetite and be tasty. If you have severe anemia, you should limit your fat intake.
In case of secretory insufficiency of gastric juice, it is recommended to include various sauces in the menu: mushroom, vegetable, meat, fish.
Causes of deficiency
In young children and pregnant women, the main factor of iron deficiency in the body is its low intake from food. Indeed, due to intensive growth and development, first intrauterine and then independent, the need for this microelement is very high. That is, in these groups, iron deficiency is always associated with its negative balance - insufficient intake compared to the need for daily expenditure. This leads first to consumption from the depot, and then to depletion of mineral reserves in the body. Why is this happening? In the modern life of an urban person, refined foods are often used in the diet, and food is depleted in vitamins and minerals.
IMPORTANT! Iron deficiency during pregnancy and then during breastfeeding is transmitted to the baby from the mother and can have an adverse and even sometimes irreversible effect on his health. Therefore, it is extremely important that the nutrition of a pregnant and lactating woman is complete, containing in sufficient quantities all the necessary nutrients and enriched with useful substances.
Recommendations for taking vitamin-mineral complexes during pregnancy and lactation should not be neglected, since very often it is not possible to make a woman’s diet sufficient and balanced. On the contrary, babies in the first year of life get everything they need from food, without the use of special drugs to prevent deficiency conditions. In the first half of the year, the main role in the child’s nutrition belongs to breast milk, the main source of essential substances, vitamins and minerals, including iron. However, by the sixth month of life, exclusive breastfeeding can satisfy the child’s iron needs by only 6-7%. At the same time, the mother’s nutrition at this age no longer significantly affects the supply of this microelement to the baby. The main task is not to delay and start introducing complementary foods on time to meet the high need for this element in the second half of life.
Grocery list
You need to include foods with iron in your food. The following are recommended:
- pork and beef liver;
- egg whites;
- rabbit, chicken, turkey, veal, beef, lamb, pork;
- kidneys, lungs, heart;
- beef tongue;
- fresh fish (pink salmon, cod);
- mussels, oysters;
- fermented milk products, homemade cottage cheese;
- cheese;
- buckwheat;
- boiled sausage;
- porcini mushrooms, chanterelles.
The best source of heme iron is organ meats, especially liver.
In addition to iron, the above products contain manganese, copper, cobalt, zinc, which are necessary for anemia. It is allowed to eat natural oil: butter, as well as vegetable oils - sunflower and olive.
Every body needs carbohydrates; limiting them is not recommended. The table includes the following:
- cereals,
- vegetables,
- fruits and berries,
- flour,
- honey,
- jam.
In addition to foods with iron, anemia requires vitamins such as riboflavin, folacin, vitamin C, and pyridoxine.
Fully or partially limited products
Excludes:
- Fatty meat and poultry.
- Refractory fats.
- Sausages, smoked meats, canned food.
Limit consumption or consume following certain recommendations:
- Tea as a tannin-containing drink and coffee containing polyphenols. You should not drink them during meals or immediately after them - take a break of 1.5-2 hours.
- Don't go overboard with nuts and legumes due to their polyphenol .
- Eggs because they contain albumin and phosphoprotein .
- Whole grain cereals, rice, soy flour, legumes, baked goods, bran, walnuts due to the content of dietary fiber and phytic acid . Dietary fiber in the intestines is almost not digested, and iron is fixed on them and excreted in feces. Phytic acid reduces the absorption of many microelements, including this one. Based on this, meat and fish should be eaten separately from bread, cereals and pasta.
- Products with a high content of oxalic acid , which interferes with the complete absorption of the microelement, are spinach, sorrel, beets, asparagus, rhubarb, nuts, chocolate, corn.
- Products high in calcium: sesame, milk, cottage cheese, cheeses, dried fruits; calcium can reduce the absorption of heme and non-heme iron.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Food restrictions
It should be remembered that fatty foods interfere with hematopoiesis, so some of the menu will have to be removed. Among them:
- fat meat;
- fatty fish;
- lamb and beef fat;
- salo;
- fatty sausages;
- margarine.
It is recommended to exclude or limit foods containing oxalates and phytic acid from the diet, which prevent iron from being absorbed. These are chocolate, bran, beans, beans, whole grains, nuts, rhubarb, spinach, parsley, basil. In this case, it is better to soak legumes, this way you can reduce their negative impact.
Calcium is one of the elements that impairs the absorption of iron. It is impossible to give up calcium completely, but you should limit foods with it and not eat them at the same time as foods rich in iron.
You should know that such popular and beloved drinks as coffee, cocoa and tea contain polyphenols, which interfere with the absorption of iron, and this can lead to the development of anemia. If you already have it, then it is advisable to refuse these drinks or not drink them immediately after consuming foods containing iron, that is, it is recommended to wait until it is absorbed.
Iron and health: what role does the microelement play in our body?
Iron is part of hemoglobin. In turn, the protein hemoglobin is a building material for erythrocytes - red blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the organs, and on the way back rid them of carbon dioxide.
Actually, this process is called cellular respiration. Without iron it is impossible. And since every cell in our body needs oxygen, iron can be called one of the most important elements.
The synthesis of hemoglobin takes 60–70% of all iron entering the body. The remaining 30–40% is deposited in tissues and spent on solving other problems - metabolic processes, regulation of the thyroid gland, maintaining the body's defense system and connective tissue synthesis.
As you can see, the functions of iron are varied and numerous, but oxygen transport is the most important of them.
Iron is poorly absorbed even with ideal health and proper diet - the human body is able to absorb up to 10% of the iron supplied with food.
Daily iron requirement in healthy people
Iron requirements vary depending on age and health status.
Infants under six months of age have little need for iron, since they are born with a fair supply of this element.
- Newborns only need 0.27 mg of iron per day.
- Children from six months to one year require 11 mg,
- children from 1–3 years old - 7 mg,
- children aged 4–8 years - 10 mg,
- 9–13 years - 8 mg.
- Adolescents 14–18 years old should receive 11–15 mg daily, with girls having a higher need for iron due to monthly blood loss during menstruation.
- Men require about 10 mg of iron per day,
- women - 15–18 mg.
- During pregnancy, the norm increases to 25–35 mg, and during breastfeeding - to 25 mg.
After about 50 years, the iron requirement for men and women becomes the same - about 10 mg per day.
These are average figures, but in some cases the need for iron may be slightly higher than the statistical average. Athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor require more iron. The need for iron also increases during recovery from operations and injuries (especially if they were accompanied by blood loss), infectious diseases, as well as for those who suffer from constant bleeding (hemorrhoids, stomach ulcers, nosebleeds, heavy menstruation, etc.).
Microelements to enhance hematopoiesis
The following microelements stimulate the formation of red cells and hemoglobin:
- zinc: offal, beef, mushrooms, eggs, beans, cereals, yeast, Dutch cheese;
- copper: cereals, black currants, watermelon, cranberries, strawberries, beans, liver, beef, horseradish;
- cobalt: beans, cereals, nuts, fish, offal, milk, gooseberries, parsley, apricots, cherries, pears, raspberries;
- manganese: beans, greens, cereals, pumpkin, raspberries, beets, black currants, cranberries.
Microelements are very important in the treatment and prevention of anemia
How to create a menu?
Breakfast options
- any porridge;
- steamed or fried cutlet;
- soft-boiled egg;
- stewed meat;
- pudding;
- boiled fish;
- vegetable puree;
- fried liver;
- hard cheese;
- tea with milk.
Lunch options
- first course: cabbage soup, borscht, fish soup, milk soup, meatball soup (beef or chicken), vegetable soup;
- second course: liver or kidneys (fried, stewed), meat (steamed, fried, boiled, baked, stewed), vegetable cutlets.
- dessert: jelly, fruit salad or fresh fruit, cottage cheese.
- drink: compote, jelly, tea.
Afternoon snack
- coffee or tea with milk;
- biscuits;
- fruits.
Dinner
- cottage cheese dish;
- pudding;
- cheese;
- meat dish;
- a fish dish;
- caviar;
- vegetable stew;
- scrambled eggs;
- milk, rose hip decoction, tea.
For the night
- kefir;
- bifidocus;
- curdled milk;
- Ryazhenka
A sample menu for the day might look like this:
- In the morning you can eat fried liver with stewed vegetables and drink herbal tea.
- Snack on an apple or egg.
- In the afternoon, prepare vegetable soup, cabbage salad, boiled chicken breast, eat an orange.
- During the afternoon snack, drink a rosehip decoction and eat a hematogen (bar).
- For the evening, oatmeal, cottage cheese or cottage cheese casserole are suitable.
- You can drink kefir at night.