Introduction
How often, having a preschooler child, we get tired of the seemingly endless runny nose, daily noticing small changes in the amount, thickness and color of “snot”: sometimes liquid and colorless, sometimes thick, green and plentiful. It is not for nothing that popular rumor, with its inherent irony and worldly wisdom, assigned its caustic stamp to preschool age, long before the emergence of the institution of preschool education: the capacious and simple-minded “brat.” And it becomes completely alarming when, despite careful treatment, an obsessive dry cough at night, snoring during sleep, and significant difficulty in nasal breathing do not go away. Rare and such short “bright” intervals of health, and again a runny nose, cough, and sometimes congestion and pain in the ears. And the natural question arises: “Who is to blame? So what should I do? And of course, a trip to the doctor, and maybe more than one, to make a diagnosis: chronic adenoiditis, adenoid hypertrophy . And again persistent treatment and the thought: “Can I remove them already and forget about the problem?” What choice to make: Delete or save? So is it worth fighting and how to do it in modern conditions of medical development? And what is the effectiveness of this fight? We will talk about all this in this article. But let's start with the very basics:
Chronic adenoiditis is a chronic inflammation of adenoid vegetations (accumulations of lymphoid tissue) located in the nasopharynx, accompanied by their mucus (which is manifested by a runny nose, cough, mucus flowing down the back wall of the pharynx), swelling and/or hypertrophy (enlargement) (which is manifested by difficulty in nasal breathing up to to complete absence of breathing through the nose, sometimes snoring during sleep). All or some of these manifestations can occur periodically up to 4-6 times a year or more, or be present constantly for several months.
Prevention of cervical hypertrophy
Prevention of cervical hypertrophy is based on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Proper and rational nutrition, exercise, timely treatment of inflammatory processes and diseases of the female genital organs, avoidance of casual sexual intercourse - all this is prevention for the development of cervical hypertrophy. In addition, careful management of childbirth, avoidance of birth injuries, prevention of damage in the early postpartum period, as well as in the postoperative period when performing surgical interventions on the internal genital organs - all of this, in general, is also a preventive measure to avoid the development of cervical hypertrophy.
Take care of yourself, take care of your health, regularly (once every 6 months) consult a gynecologist for a consultation and preventive examination.
Remember, preventing any disease is always better than treating it! Make an appointment
What are adenoids?
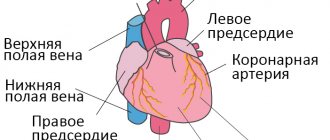
Adenoids are three of the six lymphoid formations (tonsils) of the so-called lymphoid “Pirogov’s ring”: two tubal tonsils (located around the mouths of the auditory tubes) and the nasopharyngeal tonsil (located in the center of the nasopharynx vault. In addition to these three tonsils, the “Pirogov’s ring” includes two palatine tonsils tonsils (tonsillar) and one lingual (located at the root of the tongue in front of the epiglottis). The function of the “Pirogov ring” is very important. This is the main “guard” of the body at the “entrance gate” from possible infection. Everything that enters our body from the outside: air for breathing, food and water, everything undergoes careful control by the lymphatic formations of the nasopharynx and oropharynx (“Pirogov’s rings”). And inflammation is nothing more than the body’s response to an infectious agent (virus, bacteria or fungi), with the aim block the infection, prevent it from entering the body, destroy and remove it.
Age-related features of adenoids (age of adenoid hypertrophy)
It is noteworthy that adenoid lymphoid formations reach their maximum development in preschool age from 1.5-2 to 5-6 years, when the child begins to actively contact the outside world, attend preschool institutions, clubs, sections, and visit places large crowds of people: shops, public transport, cinema, theater, circus, etc. In this case, an exchange of microflora inevitably occurs with surrounding people, including pathogenic ones; in response to this, the adenoids react with inflammation, and as a result, their enlargement. Thus, there is a tireless “training” of the immune response to the action of the infectious agent. That is why in preschool age the adenoids in their physiological norm will be of the 2nd degree of hypertrophy (they occupy ½ of the lumen of the nasopharynx). As a rule, up to 1.5-2 years of age, adenoids are less than grade 1, they are still underdeveloped and do not cause any problems. But at this age a child has much less contacts, and they are limited to family members. If the family does not have many children, then before the child starts attending kindergarten, he either does not get sick at all, or no more than 1-2 times a year. After 8-10 years, adenoids undergo involution (reduction in size); by 12-14 years, most children will not have adenoids when examined. But the lymphoid cells will move to the back wall of the pharynx and will retain their protective role all their lives. This is why it is so important to preserve the immune organ and avoid removal during the “adenoid” (preschool) age.
Adenoid hypertrophy
Adenoid hypertrophy (adenoid vegetations/growths, hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal/pharyngeal tonsil) is a persistent enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. It can occur either alone or in combination with hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils.
The nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) is a collection of lymphoepithelial tissue in the upper part of the nasopharynx. The result of its increase is called adenoid hypertrophy, and with inflammation the process is called adenoiditis. In combination with the palatine, tubal and lingual tonsils, they form the Pirogov-Waldeyer ring, located at the entrance to the upper respiratory tract and digestive tract and acting as a local immune barrier.
Adenoid hypertrophy is most often observed between the ages of 2 and 6 years, but can also occur at a later age.
There are several classifications of adenoids according to the degree of enlargement. The most popular division is based on the doctor’s subjective assessment of the size of the tonsil during examination:
- I degree – the lumen of the choanae is blocked by 1/3
- II degree – the lumen of the choanae is blocked by 1/3–2/3
- III degree – the choanae are completely closed by adenoids.
However, just assessing the size of the tonsil is not enough; a careful history taking is an important criterion.
Causes
Hypertrophy of grade I-II adenoids at the age of 2 to 6 years is often a physiological process that is associated with the fact that the child begins to actively contact the outside world and the amygdala is subjected to constant antigenic stimulation.
Severe (or pathological) hypertrophy, which leads to the symptoms described below, can occur due to an infectious or non-infectious cause. The infectious diseases include the following:
- viral (adenovirus, Coxsackie virus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, herpes simplex virus, parainfluenza virus, rhinovirus, etc.)
- bacterial (Streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Neisseria, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Fusobacterium, Peptostreptococcus, Prevotella, etc.)
Non-infectious causes include gastroesophageal reflux, allergies, and prolonged exposure to cigarette smoke.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hypertrophy occur due to an increase in the size of the tonsil and/or the presence of chronic inflammatory changes in it (chronic adenoiditis). Although these processes are often related (prolonged inflammation leads to hypertrophy), it must be borne in mind that this does not always happen. For example, with adenoid vegetations of the 1st degree, there may be pronounced signs of chronic inflammation, and with vegetations of the 3rd degree there may be no clinical manifestations at all. With physiological hypertrophy, the process occurs without any symptoms or with minor manifestations.
With severe hypertrophy, the child has difficulty breathing through his nose, and therefore he breathes through his mouth, snores during sleep, sometimes with pauses in breathing (obstructive sleep apnea syndrome). Impaired ventilation of the nasal cavity leads to mucous discharge and frequent rhinosinusitis. Characterized by sneezing and bad breath. Large adenoids put pressure on the soft palate, phonation and articulation are impaired in children, children have a nasal sound. If the adenoids block the auditory tubes, this can manifest as recurrent acute otitis media, hearing loss associated with the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear (exudative otitis media). Over time, due to oxygen starvation, the child becomes lethargic, apathetic, and irritable. Memory deterioration, decreased attention, and learning difficulties occur. Sleeping with your mouth open for a long time leads to disruption of the development of the facial skeleton. The hard palate becomes high and narrow, the lower jaw becomes narrow and elongated, the bite is disturbed, which may require orthodontic treatment in the future. An experienced otolaryngologist will immediately recognize the typical “adenoid” appearance of a child.
There are acute and chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharyngeal tonsil:
- Acute adenoiditis is an acute inflammation caused by a viral or bacterial infection. It manifests itself as a cold: fever, difficulty in nasal breathing, serous or purulent discharge from the nose. The duration of the disease varies and does not exceed one month. In the presence of adenoid hypertrophy, phenomena characteristic of hypertrophy are added to the listed manifestations.
- Chronic adenoiditis is a chronic polyetiological disease, which is based on the disruption of local immune processes and the formation of stable microbial biofilms. It manifests itself as difficulty in nasal breathing, serous or purulent discharge from the nose, mucus running down the throat and coughing. The causes of the disease are the same as those of hypertrophy. There is no consensus on the duration of adenoiditis at which it can be considered chronic. According to various sources, at least 12 weeks must pass from the onset of the disease. This condition can occur independently and over time lead to adenoid hypertrophy.
Diagnostics
The gold standard for diagnosis in global practice and the standard of our hospital is an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity. We carry out this study with a thin flexible fiberscope under local anesthesia.
Lateral x-rays are a common way to assess hypertrophy but can be misleading. For example, an X-ray may show a picture of grade III adenoids due to enlargement of the tubal tonsils (they are located on the sides of the nasopharyngeal tonsil), due to swelling of the mucous membrane or accumulation of thick mucus. This method is used only if endoscopy of the nasopharynx is impossible.
It is important to carry out differential diagnosis with diseases that may have similar clinical manifestations (juvenile angiofibroma, choanal atresia, polyposis, enlargement of the posterior ends of the inferior turbinates, hypertrophy of the tubal tonsils).
Treatment
Physiological hypertrophy without any manifestations or with minimal symptoms does not require treatment, but endoscopic examination is necessary for differential diagnosis.
Treatment may be conservative. It includes eliminating factors that can cause hypertrophy: allergies, gastroesophageal reflux, passive smoking. Accordingly, in some cases a multidisciplinary approach of an otolaryngologist, allergist, gastroenterologist and pediatrician is necessary. A positive effect can be had by changing the climate to a more favorable one, for example, sea climate. Topical corticosteroids have been used as an adjunctive treatment in children over the age of three, with some studies showing some benefit, but overall evidence on the effectiveness of these drugs is mixed. In acute and exacerbation of chronic adenoiditis in the case of a bacterial infection, treatment is carried out with antibiotics. Irrigation of the nasopharynx with saline solution is also used in treatment. The use of various oils, mucolytics, local antibacterial drugs, silver solutions, herbal remedies, and physiotherapy currently do not have a high-quality evidence base.
In some cases, surgical treatment cannot be avoided. Not every child needs surgery and it requires specific indications. When determining them, doctors at Ilyinskaya Hospital follow the principles of evidence-based medicine, relying on global experience. Indications include failure of conservative treatment, recurrent infections, acute otitis media and sinusitis, and an “adenoid” face. Parents should understand that long-term refusal to undergo surgery if indicated, or an attempt to “wait out” or “outgrow” adenoid hypertrophy can lead to complications, the treatment of which in the future will require a lot of time and can negatively affect the development of the child. According to the recommendations of the American Academy of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, adenotomy should be performed in the following cases:
- In children under 4 years of age with symptoms of difficulty in nasal breathing, signs of chronic adenoiditis, as well as exudative otitis media
- In children 4 years of age and older with exudative otitis media
- If you have confirmed obstructive sleep apnea (periodic sudden decrease or cessation of breathing during sleep)
In the presence of pathology of the palatine tonsils, surgery for their resection/removal is often performed simultaneously (adenotonsillotomy/adenotonsillectomy), and in case of exudative otitis media, shunting is performed at the same time.
Adenotomy has undergone significant changes over time. Previously, this operation was performed under local anesthesia using a special knife (adenotome) under the control of a small mirror, and sometimes blindly. During the operation, the child experienced stress, and the surgeon may not have fully performed the operation. Nowadays, this approach is practically not used, but it is preserved in some clinics.
Degrees of hypertrophy (enlargement) of adenoids
I degree - when adenoid vegetations during endoscopic examination cover less than 1/3 of the lumen of the choana (the outlet from each half of the nose into the nasopharynx)
II degree - when adenoid vegetations during endoscopic examination cover 1/2 of the lumen of the choana (the outlet from each half of the nose into the nasopharynx)
III degree - when adenoid vegetations during endoscopic examination cover the entire lumen of the choana (the outlet from each half of the nose into the nasopharynx)
Often, ENT doctors assign grade II-III - in the case when more than ½ of the lumen of the choanae is closed, but the lumen for breathing still remains, and is not completely closed.
Symptoms of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy
- Frequent lingering runny nose
- Nasal congestion, up to complete absence of nasal breathing
- As a result of the previous symptom, the child often breathes with his mouth open during the day or during sleep
- Cough, including dry cough at night (due to mucus draining down the back of the throat)
- Snoring while sleeping
- Decreased attention and fatigue due to lack of oxygen through nasal breathing
Is it possible to “give up” on these symptoms?
Even the uncomplicated form of chronic adenoiditis cannot be ignored; oxygen starvation, which develops against the background of difficulty in nasal breathing or breathing through the mouth, is manifested by a decrease in memory, perseverance, attention, and learning ability. The child becomes irritable, capricious, and gets tired quickly. The immune system is under constant stress of chronic inflammation, as a result of which a symptom of natural immunodeficiency appears, due to the depletion of the cellular elements of the immune system, and the child becomes weakened and often ill. With a large degree of hypertrophy, the facial skeleton may change, the so-called “adenoid” type of face is formed with an elongated lower part of the skeleton, a change in the bite, and a slightly open mouth.
In addition, we are afraid of the formation of complications
Complications of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy:
- Acute otitis media
- Exudative otitis (so-called “silent” otitis, when in the absence of pain hearing loss occurs due to the accumulation of fluid behind the eardrum)
- Persistent conductive hearing loss
- Frequent sore throats
- Tracheitis, bronchitis
- Sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sinusitis
Traditional diagnostic methods (examination by an ENT doctor or pediatrician)
In a regular clinic, to diagnose chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy, an examination of the nose, throat and ears is used using metal instruments for examining ENT organs: nasal and ear mirrors and a spatula illuminated with reflected light, using a conventional head reflector (head mirror) or a head lamp in the form flashlight. In this case, the ENT doctor (or pediatrician) only sees the area of the nasal vestibule and the surrounding parts of the nose. The nasopharynx, the anatomical location of the adenoids, is not visible. The examination is contact (when examining the nose, the wings of the nose in the vestibule area are expanded with a nasal speculum; when examining the ear, an ear speculum is inserted into the ear canal)
In addition, it will be possible to perform a digital examination of the nasopharynx for a subjective assessment of the size of the adenoids (the doctor feels the nasopharynx and the surface of the adenoids through the mouth, trying to determine their size). This method is not reliable, is unpleasant for a small patient and is traumatic for adenoid vegetations.
About cervical hypertrophy
Cervical hypertrophy is nothing more than an increase in the volume of the vaginal part of the cervix, which is associated with excessive development of connective tissue stroma.
As a result, the walls of the cervix thicken and lengthen. Cervical hypertrophy is usually accompanied by certain symptoms that make it possible to suspect this particular disease. In addition to the usual gynecological symptoms, infertility often occurs with cervical hypertrophy. Sometimes it is with this problem that women turn to a gynecologist, and after an examination and a series of diagnostic manipulations, cervical hypertrophy is revealed.
Cervical hypertrophy requires certain specialized gynecological treatment. Only qualified specialists can correctly and effectively eliminate this disease, while being as painless and safe as possible for the patient. Our modern DeVita clinic employs highly qualified gynecologists who eliminate cervical hypertrophy using effective and safe methods and means. By contacting us, you can rest assured that your health is in good hands!
Modern diagnostic methods (endoscopic examination of the ear, nose and throat by an ENT doctor)
The gold standard for diagnosis (and the only correct one) is an endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx by an ENT doctor with good skills and experience working with children from birth. An endoscopic examination is an examination using a video camera, with additional powerful lighting and magnification and display on a television screen, on which both the doctor and the child’s parents will clearly see not only all the structures of the nose, but also the nasopharynx with the mouths of the auditory tubes and adenoid vegetations. In this case, the doctor will evaluate the degree of their increase, inflammation of the mucous membrane, the nature of the discharge, the presence and size of the respiratory lumen. The examination is carried out with a special children's nozzle - a tube less than 3 millimeters in diameter, the examination is non-contact, absolutely painless, does not require special preparation (the ENT doctor only drips vasoconstrictor drops in an age-appropriate dosage before the examination) and has no contraindications and is used in children from birth.
Of course, with such a diagnosis, digital examination is not required.
It is very important that during an endoscopic examination of the ears, such a significant complication as exudative otitis (accumulation of fluid behind a healthy, non-inflamed eardrum) will not be missed. Thanks to good lighting and magnification, the eardrum is transparent during endoscopic examination, so the liquid and air bubbles behind it are clearly visible. Whereas when examined in the usual way, the eardrum, if it is not inflamed, reflects the light of a flashlight and looks gray and opaque, the liquid behind it cannot be seen.
Comparative characteristics of traditional examination of ENT organs and endoscopic examination of ENT organs
| Criteria | Traditional ENT examination | Endoscopic examination of ENT organs |
| Price | Low inspection costs due to the use of tools and a reflector | High cost due to the use of expensive equipment |
| Painless | The contact method can be unpleasant due to the instrumental expansion of the entrance to the nose for examination; the use of an ear mirror is also contact. Digital examination is traumatic and can be painful | The method is non-contact, painless, as nozzles of less than 3 mm are used. in diameter |
| Diagnostic reliability | The examination is superficial, the structures of the nose are examined only in the anterior sections, the nasopharynx is inaccessible for inspection, the adenoids and the mouths of the auditory tubes are not visible, it is impossible to assess the condition of the middle ear behind a healthy eardrum | The reliability of diagnosis of adenoiditis, adenoid hypertrophy, and complications in ENT organs is 100%. All structures of the nose, nasopharynx, ear and throat are examined on a screen with additional magnification and lighting. A diagnostic error has been ruled out. |
| Accuracy of the diagnosis | The diagnosis is presumptive | Reliable diagnosis with assessment of possible risks and complications |
| Purpose of treatment | Overdiagnosis, high probability of prescribing antibacterial therapy “just in case” | Prescribing adequate therapy |
| Assessment of dynamics during treatment | Assessment of only external signs and symptoms (presence of runny nose, cough, etc.) | Assessment of both the dynamics of symptoms and mucus and size of the adenoids, development or relief of complications. |
| Recommendations for adenoid removal | It is possible to prescribe removal of adenoids if they can be preserved and monitored. | Appointment of adenoid removal only if there are indications for removal and an objective assessment of the lack of effect of treatment. |
| Who can carry out diagnostics | Pediatrician, ENT doctor with any experience and qualifications | ENT doctor with practical skills and experience in endoscopic examination of ENT organs in children from birth. |
Laboratory diagnostic methods (the goal is to clarify the cause of chronic adenoiditis and/or adenoid hypertrophy)
To establish the cause of enlarged adenoids, as a rule, a detailed blood test is prescribed, a nasal smear for cytology (cellular composition of nasal discharge), blood for total immunoglobulin E (to exclude an allergic nature or allergic background), feces for worm eggs and scraping for enterobiasis ( adenoids often enlarge due to helminthic lesions), a PCR test for the Epstein bar virus is possible (if mononucleosis is suspected)
Treatment of chronic adenoiditis and/or adenoid hypertrophy
Conservative methods:
- Drug treatment (includes the prescription of vasoconstrictor drops in a short course, local anti-inflammatory treatment, general anti-inflammatory or antiallergic treatment, expectorants, antibacterial drugs for bacterial infections, as well as treatment of complications if they occur) IMPORTANT: Treatment methods, as well as drug therapy only prescribed by a specialist doctor. Ideally, an ENT doctor under the supervision of an endoscopic examination of the adenoids and laboratory parameters
- Hardware, manipulation and physiotherapy (includes both mechanical sanitation of adenoid vegetations, for example, washing the adenoids using an electric suction, and numerous options for physiotherapy, both in the form of monotherapy and combining different methods: USOL therapy of the nasopharynx; laser therapy with red, violet, infrared laser; magnetic therapy; treatment with the Intralor device; photochromotherapy with orange color, etc.) The method of exposure is selected by the ENT doctor depending on the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the patient. These methods allow, in most cases, to avoid the unnecessary prescription of antibiotic therapy, significantly reduce the prognosis of the course of the disease, avoid the development of complications, speed up recovery or significantly prolong the remission of the disease, and avoid long-term residual effects.
Surgical treatment of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy:
This treatment method is used only if there are absolute indications for adenoid removal (including the threat of developing persistent hearing loss), and if there is no effect from conservative therapy (including hardware and physical therapy). As practice shows, conservative treatment is effective in more than 99% of children with chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy. Any surgical intervention is an “act of desperation” when everything possible has been done, but the effect is not obtained and the threat of serious complications remains.
If there is no effect from conservative therapy and there are absolute indications for adenotomy, we recommend choosing a modern endoscopic method of adenotomy, which is performed endoscopically under visual control, which means it is less traumatic and more effective. The traditional method of removal with an adenotomy is a blind method, does not always achieve full effect and is more traumatic.
“Disadvantages” of adenotomy:
- The operation is performed under general injection anesthesia, therefore it carries the risks of using narcotic drugs like any surgical intervention;
- If there are unforeseen anatomical features of the skeleton of the nasopharyngeal vault (absence, underdevelopment or thinning of bone in the nasopharyngeal vault), there may be a risk of damage to the brain stem;
- the process of scar-adhesive changes in the nasopharynx cannot be excluded, which, in the presence of these changes in the area of the mouths of the auditory tubes, can disrupt the anatomy and cause a deterioration in the patency of the auditory tubes;
- But probably the most important thing is the removal of the immune organ (three lymph nodes: two tubar and one nasopharyngeal), which plays a protective role as an independent organ, and disrupts the functioning of the entire immune system during a very crucial period of its formation. For example, the formation of the most persistent prostaglandin form of bronchial asthma has been proven during adenotomy in children with a certain allergic background. It is impossible to even predict all the consequences of such interference in the immune system.
Of course, all these complications are very rare, but adenotomy should be treated as an operation that carries all possible operational risks.
Causes of cervical hypertrophy
The causes of cervical hypertrophy are as follows::
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Frequent inflammatory diseases in the cervix and vagina that have not been cured, or their therapy has been unsuccessful and ineffective;
- Myoma located in the cervical area;
- Nabothian cysts;
- Damage to the cervix as a result of abortion, childbirth;
- Changes in a woman's hormonal background.
These and other reasons may become the basis for the development of cervical hypertrophy . Therefore, in order to avoid this disease, it is worth paying due attention to its prevention.
Modern diagnostic and treatment methods offered at ENT Clinic No. 1
Diagnostics:
ENT clinic number 1, Moscow, is a specialized otolaryngology clinic. The clinic’s ENT doctors are fluent in the method of endoscopic diagnosis of ENT organs and have sufficient experience in working with children from birth. An endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx, ears and throat will make it possible to assess the degree of enlargement of the adenoids and the presence of inflammation, as well as to determine the presence or absence of complications.
To clarify the cause of adenoid hypertrophy in the clinic, on the first day of admission, it is possible to take the necessary laboratory tests.
If complications are suspected, on the day of admission tympanometry (diagnosis of middle ear pathology) or ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses if sinusitis or sinusitis is suspected.
Treatment:
Based on the ENT diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe medication, manipulation and physical treatment. ENT clinic number 1 presents the maximum variety of hardware treatment for adenoiditis:
- rinsing the nose with an electric suction;
- laser therapy with red, infrared and violet lasers;
- USOL therapy of adenoids (nasopharynx);
- photochromotherapy with orange color;
- magnetic therapy;
- nasal rinsing using the Intralor device;
- galacamera (salt cave).
These types of physiotherapeutic effects have a wide evidence base in the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiseptic, anti-edematous effects on adenoid tissue and absolute safety of use in children of any age. Each method can be used as an independent treatment or in combination with another method. At the same time, different methods of physical therapy act as synergists (increasing each other’s effectiveness and facilitating the penetration of topically applied drugs into the mucous membrane.)
As a consequence of all of the above effects, the prescribed combination treatment gives a very good result in relieving inflammation and reducing adenoid vegetations to physiological norms. This allows you to preserve the adenoids and subsequently monitor their condition over time.
This in no way means that one course of therapy will be enough to prevent exacerbations of chronic adenoiditis. A child who is in contact with other people, especially if he attends a kindergarten, if he is re-infected, will go through an exacerbation of adenoiditis again and, of course, it would be right to come for a consultation with an ENT doctor and choose a new course of treatment. But against the background of professional treatment, firstly, the size of the adenoids will return to their normal age, the symptoms will be completely relieved, the child will breathe well through the nose in the intervals between diseases, the auditory tubes will function, and hearing will be preserved. The number and duration of courses of drug therapy will be reduced, including the number of antibiotics taken by the child. Taking into account the immunomodulating and preventive effect of physical therapy, the child will get sick much less often and the intervals of health will increase significantly. This means that complications will not form and surgery will be avoided.
Prevention of exacerbations of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy:
Many of the physiotherapeutic treatment methods (laser therapy with red and infrared lasers; orange photochromotherapy; magnetic therapy; halo-chamber) are used against the background of complete health without exacerbation, for the prevention of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy. They have extensive experience in using it with a proven effect of reducing morbidity in frequently ill children. Wherein:
- adenoid vegetations decrease in size;
- antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal effect allows you to maintain the normal microflora of the nasopharynx, suppressing the growth of pathogenic microflora;
- immunomodulating effect (stimulates the production of interferon, immunoglobulins, antibodies) increases the protective function of the mucous membrane;
- anti-inflammatory effect, relieves the manifestations of chronic inflammation;
- Magnetic therapy also affects the hypothalamus region, regulating and normalizing the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems (balances the production of hormones, which is disturbed in frequently ill children)
A preventive course of therapy is prescribed by an ENT doctor and is carried out during the remission stage or against the background of full health at least 2 times a year. Preventive courses of treatment are recommended not only for children with an established diagnosis of Chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy, but also for children at risk: first of all, these are children of preschool and early school age attending preschool and school educational institutions; sections and circles; crowded places (cinema, theater, circus, shopping and entertainment complexes).
Treatment of cervical hypertrophy
Treatment of cervical hypertrophy in each individual case should be selected individually by a gynecologist. In our DeVita clinic, treatment of cervical hypertrophy is always high-quality and safe , and it is carried out only by the best professionals. Treatment of cervical hypertrophy is often always conservative and includes the use of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating and hormonal drugs.
If significant hypertrophy of the cervix is detected, which does not respond to conservative therapy, then doctors prescribe surgical intervention to eliminate the hypertrophy.
After treatment, the woman should be observed by a gynecologist for some more time to prevent relapses or complications. Treatment in our clinic is always carried out in a comfortable environment for the patient, and is also carried out in a trusting relationship with the gynecologist. It is worth noting that highly qualified specialists, experienced gynecologists work in our DeVita clinic and provide the best medical care to patients with cervical hypertrophy . In their work, they use only accurate diagnostic techniques that allow them to quickly and reliably establish a diagnosis, as well as modern and effective treatment methods that quickly eliminate the causes of the disease and its symptoms.