In practice, the New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification is often used to assess the severity of heart failure:
I class
— Physical activity is not limited
Class II
— Mild limitation of activity.
The appearance of shortness of breath and weakness after moderate physical activity. Class III
- Marked limitation of activity.
Shortness of breath after minimal physical activity Class IV
- Severe limitation of activity. Symptoms of heart failure at rest
What is heart failure?
Our heart is like a pump that pumps blood and supplies oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. Impaired ability of the heart to pump blood leads to stagnation and leads to the development of heart failure .
Poor blood supply puts other organs and tissues at risk. In terms of prevalence, heart failure rivals the most well-known infectious diseases.
According to statistics, around 28 million people suffer from heart failure throughout Europe. In our country, the number of patients with this disease exceeds 9 million (more than 25% of them are under 60 years of age)! At the same time, Russians die from it 10 times more often than from myocardial infarction.
1 Tests for heart failure
2 Tests for heart failure
3 Tests for heart failure
Drug therapy
Treatment of left ventricular failure should be immediate. Especially when it comes to an attack of acute manifestations of the disease. After appropriate diagnostics (ECG recording is required), in accordance with the recommendations of specialists, the following means are used:
- First of all, it is necessary to slow down the metabolic processes in the body. This will help cells better tolerate the lack of oxygen. Morphine is used for these purposes. It has the property of depressing respiration and lowering blood pressure. Droperidol has a sedative effect. If the patient suffers from low blood pressure, then use “sodium oxybutyrate”.
- The next stage of treatment involves reducing venous return. For these purposes, drugs are used that dilate the coronary arteries. If severe swelling is observed, then sodium nitroprusside is used. This is a strong vasodilator, that is, a drug that dilates blood vessels.
- Fast-acting diuretics will help reduce swelling. They are administered intravenously.
- Oxygen inhalation is performed using a catheter or a special mask.
- To increase the contractility of the heart muscle, drugs such as Dopmin or Dobutrex are used.
After the attack of left ventricular failure is stopped, they proceed to long-term therapy. It is also used if the disease has acquired a chronic form (CHF). In this case, the main directions of treatment are:
- Restoring normal heart rhythm. This is especially true if the cause of the disease is arrhythmia. Beta-blockers are used for these purposes. The drug improves the filling of the heart with blood, which results in increased output. The drug has a side effect, namely: it can lead to a narrowing of the bronchi and an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood. Therefore, the use of such medications is not recommended for diabetes and bronchial asthma.
- Removing tachycardia. For this purpose, cardiac glycosides are prescribed.
- Elimination of thrombosis and blockage of blood vessels. For this purpose, anticoagulants that have a blood-thinning effect are used. They suppress the activity of the blood clotting system. The use of such funds requires constant monitoring. In case of overdose, bleeding is possible: uterine, nasal and others.
- The use of diuretics to remove excess fluid from the body. Modern drugs begin to act quickly. In a short time it is possible to get rid of several liters of excess liquid. For this purpose, diuretics are administered intravenously. A side effect of such medications is the removal of potassium from the body, which can cause seizures, weakness and changes in the functioning of the heart.
- Restoring normal blood circulation.
- Bringing the patient into a stable emotional state. For this purpose, the use of sedatives is indicated.
In addition to basic treatment, it is necessary to adhere to a certain lifestyle. If you are overweight, you should try to get rid of it. Give up bad habits. Follow a diet that includes low-calorie foods without salt and animal fats. Walk outdoors more often. Moderate physical activity is beneficial. Constant monitoring of blood pressure is necessary. Traditional medicine methods can be used as additional therapeutic measures after consultation with a doctor.
In some cases, the disease can cause complications. Then the treatment program includes the fight against complications. Patients will have to be constantly under the supervision of a doctor and undergo regular medical examinations.
Sometimes drug treatment is ineffective. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated.
Types of heart failure
There are several classifications of this disease.
Classification by flow type:
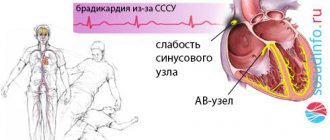
Acute heart failure (AHF) . It develops rapidly (the process can take hours or minutes) against the background of myocardial infarction, myocarditis, severe arrhythmias and other acute conditions.
The disease manifests itself as cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema, and cardiac asthma. Any manifestation of acute heart failure is life-threatening and can be fatal.
Chronic heart failure (CHF) . The development of the disease occurs gradually - weeks and months, sometimes years. The cause of CHF can be coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias and heart block, arterial hypertension, heart defects, anemia, etc.
Chronic heart failure, in turn, is divided into 4 subtypes:
1. The general condition is almost normal, however, with significant physical effort, shortness of breath and increased heart rate appear (which the person did not have before).
2. Physical activity is partially reduced. With moderate exertion (such as fast walking, climbing stairs), shortness of breath, discomfort in the chest, and other initial signs of CHF appear.
3. Shortness of breath and fatigue appear even with weak physical efforts (walking, tying shoelaces), but the condition stabilizes at rest.
4. Signs of heart failure appear clearly even at rest.
Classification by localization of the pathological condition:
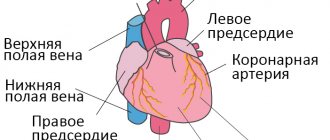
left ventricular heart failure - blood stagnates in the pulmonary circulation (in the lungs); right ventricular heart failure - stagnation of blood in the systemic circulation (swelling of the legs, hydrothorax, ascites); mixed (total) heart failure is a one-time stagnation process in both circulation circles.
Classification of heart failure by origin:
myocardial heart failure (occurs with pathological changes in the myocardium); overload HF (develops when the heart is overloaded, for example with heart defects); combined heart failure .
Systolic (impaired contractile function of the heart) and diastolic (impaired relaxation of the myocardium) heart failure are also distinguished
1 Radiography for heart failure
2 Radiography for heart failure
3 Radiography for heart failure
Classification
This is done for a number of reasons.
Based on the nature of the pathological process:
- Acute left ventricular failure. Develops in minutes. Accompanied by a critical drop in myocardial contractility and impaired circulation of all organs.
Associated with intense symptoms: chest pain, arrhythmia, fainting and others. Considered an emergency. Leads to cardiogenic shock, which is fatal in almost 100% of cases.
If you're lucky, the attack will be a signal, but not the cause of death. The acute process is stopped in the hospital, then long-term observation by a cardiologist is indicated.
- Chronic type. Develops in 80% of cases without a prior emergency condition. Determined by the minimal clinical picture.
For a long time, sometimes until death from cardiac shock and cardiac arrest, the patient is unaware of his own condition.
The prognosis is determined by the moment of detection and the root cause. It often turns out to be too late. Therefore, any discomfort should be grounds for urgent treatment at the hospital.
Left ventricular failure is almost always secondary in origin. That is, it is caused by other diseases. Usually cardiac.
Symptoms of heart failure
Common signs of heart failure of any type:
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, suffocation;
- increased fatigue, decreased physical activity;
- swelling in heart failure (including internal organs);
- weight gain due to fluid retention.
As for other symptoms of heart failure, manifestations may vary depending on which ventricle of the heart the pathology develops in.
For left ventricular acute heart failure (due to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation) the following are typical:
- Cardiac asthma - an attack of suffocation occurs at night or after physical effort. There is a feeling of acute lack of air, shortness of breath quickly increases to suffocation. The patient breathes through the mouth to ensure greater air flow.
- Orthopnea - the patient is forced to take a sitting position, which improves the outflow of blood from the vessels of the lungs.
- The cough is dry at first, then with the release of pinkish sputum and foam.
- Pulmonary edema - moist wheezing, bubbling difficulty breathing, foam at the mouth.
Characteristic signs of right ventricular acute heart failure are caused by stagnation of blood in the veins of the systemic circulation:
- Swelling of the neck veins (associated with difficulty in blood flow to the heart, worsens with inhalation);
- rapid heartbeat (accompanied by shortness of breath);
- swelling (due to slow blood circulation, fluid retention occurs);
- lowering blood pressure.
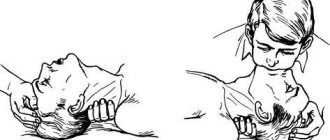
First aid for heart failure (HF)
It is necessary to call an ambulance, sit the patient down, making sure to lower his legs. Provide fresh air flow. If the person is conscious, talk to him and try to calm him down. If possible, immerse the patient's limbs in warm water to reduce blood flow to the heart. Measure blood pressure: if the numbers are elevated, give a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue.
Signs of chronic heart failure:
Shortness of breath - with physical effort, and with a long course of the disease - even at rest. Inability to exercise - the heart cannot provide the blood flow necessary for active activities. Shortness of breath and weakness appear. Cyanosis - due to a lack of oxygen in the blood, the skin turns blue. The most common cyanosis is on the lips, fingertips, and the rim of the ears (acrocyanosis). Edema - the first thing to occur in CHF is swelling of the extremities. Then excess fluid begins to accumulate in the cavities: pleural, abdominal. Over time, edema due to heart failure and other congestion lead to pathological changes in the lungs, liver, and kidneys.
1 Ultrasound for heart failure
2 Ultrasound for heart failure
3 Diagnosis of heart failure
Treatment
{banner_banstat9}
Urgent. The directions of influence are as follows: elimination of the root cause of the condition, removal of threatening symptoms, prevention of complications. All three problems are solved simultaneously, but in different ways.
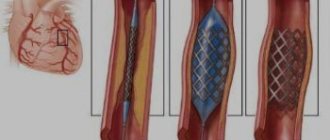
Etiotropic therapy requires surgical intervention in most cases. Mitral and aortic valve replacement, stenting or ballooning (dilation of the affected vessel).
For myocarditis, immunosuppressants (autoimmune type) or antibiotics, antivirals, fungicides under the guise of cardioprotectors are indicated.
Symptomatic effects require the use of antiarrhythmic, organic nitrates, and sedatives.
Additionally, glycosides (Digoxin, tincture of lily of the valley), beta blockers (Anaprilin, Carvedilol), and diuretics to evacuate excess fluid (Veroshpiron) are prescribed. It is also possible to prescribe ACE inhibitors (Perindopril in different variations).
Prevention is carried out using the same pharmaceutical agents in small dosages.
Additionally, lifestyle changes are indicated. Refusal of smoking, alcohol, drugs, fatty foods, salt intake in the amount of 7 grams per day. Fortification of the diet, refusal of significant physical activity. The recommendations are strict, you cannot deviate from them if you want to be cured.
LVAD is such a complex and complex process that there is no and cannot be an unambiguous answer about the treatment regimen.
Causes of heart failure
A variety of diseases can lead to this disease, but more often its development is facilitated by:
- cardiac ischemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- heart defects;
- myocardial infarction;
- myocarditis;
- cardiomyopathy (including alcoholic);
- arrhythmias;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes.
Risk factors for developing heart failure include smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs, taking certain medications, and being overweight.
1 ECG for heart failure
2 Ultrasound for heart failure
3 ECHO-CG for heart failure
Forecast
{banner_banstat10}
Left ventricular failure causes death in 70% of cases. The outcome directly depends on many factors:
- General health.
- Presence of somatic pathologies.
- Working blood pressure level.
- Family history.
- Time course of pulmonary hypertension and other diseases.
- The quality of the treatment provided.
- Age.
- Floor.
- Body type, weight, overweight and obesity.
- Nature of nutrition.
- Bad habits, lifestyle.
- Emotional condition.
- Hormonal background.
- Type of professional activity.
In combination, these factors give a unique, unique picture. Accordingly, the forecast depends on the mass of moments.
To roughly formalize the numbers: the probability of survival at the first stage is 95% with proper treatment. The process is stopped completely.
Starting from the second, the values decrease proportionally:
| Stage | Survival percentage |
| 2A | 75% |
| 2B | 30% |
| 3 | 5% |
Diagnosis of heart failure
When diagnosing a disease, it is extremely important to identify the true cause of its development - only then can treatment be as successful as possible.
After collecting an anamnesis and physical examination, a cardiologist may prescribe:
- general clinical, biochemical blood and urine tests;
- electrocardiography (at rest);
- Ultrasound of the heart (Echocardiography);
- chest x-ray;
- coronary angiography;
- Holter ECG monitoring and other studies.
Surgical operations
Often, normal functioning of the heart muscle can only be restored through surgery. In this case, the following types of operations apply:
- Stenting. It involves installing a special spring inside a clogged vessel. The operation is carried out under the control of coronography - an X-ray examination of the vascular system.
- Valve replacement. This operation is performed if it is not possible to restore normal heart function in any other way. An artificial metal valve or a donor organ is used. Porcine heart valve may be used.
- If cardiomyopathy develops, the only treatment option is a complete heart transplant. Then a search for a suitable donor is necessary.
Before surgery, a complete medical examination of the patient is performed to identify possible contraindications. Since operations are performed under full anesthesia, the anesthetist must first find out a drug that will not cause a negative reaction in the patient and calculate its dosage.
Left ventricular failure is a serious life-threatening disease. Even with timely, competent treatment, it is impossible to get rid of it forever. But if you strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions, you can significantly improve your quality of life and make it full.
Preventive measures
You can reduce the likelihood of developing left ventricular failure. To do this, you will need to adhere to preventive measures:
- existing cardiac pathologies must be monitored and undergo timely examination to identify negative changes;
- proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and microelements, will support the heart, making it resilient;
- physical activity must be rationed, it should not exceed the body’s capabilities;
- a passive lifestyle and sedentary work are wrong and dangerous for the cardiovascular system;
- bad habits saturate the body with toxic substances that poison it and reduce the ability to resist illnesses;
- A large amount of stress and nervous shock greatly wears out the heart.
By making such adjustments to your life, you can reduce the likelihood of developing not only left ventricular, but also any other heart failure.
Only you yourself can save yourself from dangerous heart pathologies that pose a threat to life. Any symptoms require contacting a doctor and finding out the cause of its occurrence.
Cardiac diagnostics
Heart failure of all types is a disease that has the ability to progress rapidly. In order to slow down the progress in myocardial destruction, it is necessary to make a timely diagnosis and begin complex therapy.
One examination of the patient is not enough for the doctor to establish the correct diagnosis of left ventricular failure.
The anamnesis indicates visible obvious signs of deficiency, but in order to determine its type, you need to undergo an instrumental study of the pathology:
- ECG (electrocardiography) - displays signs of hypertrophy of the left ventricle and left atrium, identifies signs of ischemia in the myocardium. Electrocardiography alone is not enough to diagnose insufficiency;
- Ultrasound of the heart organ (ultrasound examination) - this technique reveals defects in the heart muscle and its functional ability to contract. Data from the results of a diagnostic study show how much progress there is towards a cure during therapy;
- X-ray of the thoracic region - using the shadow of the X-ray image, the doctor determines the boundaries of the cardiac organ, the convexity of the left-sided ventricle, as well as the left-sided atrium. X-rays show disturbances in the small (cardiac) circle of blood flow;
- Radioisotope ventriculography is a technique that assesses the ability of the myocardium to contract, and also reveals the performance of the two ventricles during systole, the volume of blood absorbed in them during diastole, and the functioning of the valves during the release of biological fluid into the aorta (blood flow system). Based on this method, it is possible to outline a therapeutic drug treatment regimen;
- The PET (positron emission tomography) diagnostic technique is the latest cardiological technique that allows you to determine areas of viable heart muscle in case of cardiac failure of all types. This is an important indicator for the possible prescription of intensive care treatment.
X-ray showing changes in left ventricular failure
Based on all instrumental studies, the doctor prescribes therapeutic drug therapy.
Emergency care for cardiogenic shock
Treatment of cardiogenic shock should be started as early as possible and carried out as efficiently as possible. The patient’s life depends on these two components.
Emergency care algorithm for cardiogenic shock:
- Place the patient on a flat horizontal surface and, if possible, raise the foot end.
- Provide maximum access to oxygen: open the window, unfasten clothing that restricts breathing.
- Give oxygen (the algorithm assumes supply through a nasal catheter or a special mask).
- Anesthetize the patient. For reflex shock and myocardial infarction, narcotic medications can be used, for example, Morphine , which is administered slowly intravenously, after dissolving in saline.
- Emergency care involves restoring circulating blood volume and blood flow through the administration of Reopoliglucin . If there is no positive dynamics, then blood pressure is increased by introducing a 0.1% Atropine in a dose of 0.5-1 ml.
Actions should also be aimed at eliminating the causes that provoked the development of shock. For ventricular arrhythmias, the antiarrhythmic drug Lidocaine . If ineffective, defibrillation is organized. In case of myocardial infarction, antiplatelet and thrombolytic therapy is carried out with the drugs Aspirin , Clopidogrel , Alteplase .
Prevention
Preventive measures for left ventricular failure are:
- Weight control - prevent obesity;
- Diet to prevent an increase in cholesterol in the blood - limiting the amount of salt, fatty foods and large amounts of liquid;
- Do not overload the body physically;
- Quit nicotine addiction;
- Don't drink alcohol.
Heart failure can lead to sudden death. Therefore, left ventricular failure should be treated in the cardiology intensive care unit in order to relieve pulmonary edema as quickly as possible and prevent a state of cardiogenic shock.