Find out more about diseases starting with the letter “K”: Causalgia, Brain cyst, Cluster headache, Tick-borne encephalitis, Kozhevnikov epilepsy, Colloid cyst of the third ventricle, Coma, Compressive myelopathy, Balo concentric sclerosis, Radicular syndrome, Corticobasal degeneration, Craniovertebral anomalies, Craniospinal tumor, Craniopharyngioma, Myasthenia gravis crises, Hemorrhage into the ventricles of the brain.
Depending on the location of the formation, focal symptoms may be present. The diagnosis is made based on data from computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the head or neurosonography (in children). Therapy consists of aspiration and surgical removal of the formation if complications develop or its growth progresses.
General information about pathology
A cyst is a fluid-filled cavity located in the substance of the brain or its membranes. When the pathology is small in size, it has a subclinical course and is diagnosed accidentally during a neuroimaging examination of the head. Since the intracranial space has limited dimensions, with a significant increase in the volume of the formation, intracranial hypertension develops.
The size of the cavity with liquid is largely determined by the compensatory capabilities of the formation and its localization. Due to the pliability of the skull bones in children at an early age, the cyst may not manifest itself for a long time.
The formation can be found in people of different ages, both in infants and in elderly patients. Even if the fluid cavity is congenital, it can make itself felt only by the age of 30-50.
According to generally accepted practice, treatment is prescribed only in the case of a pronounced clinical picture and when complications develop. If the cavity with fluid is frozen or slowly progressing and its volumes are insignificant, a wait-and-see approach is chosen, which involves regular monitoring of the patient.
By what signs can you identify a cyst in a child?
Vascular compactions are diagnosed during special diagnostic methods, so ultrasound and neurosonography can provide a complete description of the cyst. According to accepted WHO recommendations, these studies must be carried out on all children under one year of age to exclude possible neurological disorders.
In infants, cystic formation is practically asymptomatic
Mandatory indications for neurosonography are:
- trauma during childbirth;
- high risk of intrauterine infection;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- severe pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the mother;
- intense physical activity during pregnancy;
- deviations in the physical development of the newborn (underweight, insufficient growth);
- severe deformation of the anatomical parts of the skull.
According to statistical data, cystic formations are recorded both in children without deviations in physiological development and in those with developmental delays.
Classification
Classification by location:
- Cerebral (intracerebral). It is formed in areas of dead brain tissue in the internal structures of the brain.
- Arachnoid. It is formed as a result of the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in places of adhesions formed as a result of inflammatory processes and in places of their congenital duplication. The advantage is localized in the meninges.
The following types of brain cysts are distinguished separately:
- dermoid;
- colloidal;
- choroid plexus;
- pineal gland.
According to its genesis, a cavity with fluid can be congenital or acquired. In turn, congenital is divided into colloid and dermoid, and due to its formation into post-infectious, post-traumatic, post-stroke and echinococcal.
Difference from other types of cysts
This pathology should be distinguished from a cyst that forms in the medulla. The appearance of these formations is often caused by infections suffered by the fetus. To identify a cyst and eliminate it, PCR diagnostics are prescribed. This is done to determine the causative agent of the infection. After the examination, treatment is prescribed, and after its completion, the examination is repeated.
Cystic formations of the brain are divided into subependymal and arachnoid. Formations of the first type appear when there is insufficient nutrition of the brain in the area of the ventricles. This entails tissue death and the appearance of empty cavities.
Arachnoid cysts develop inside the meninges. This cavity occurs as a result of infection. This pathology requires medical treatment, and sometimes surgical intervention. If the subcutaneous cyst is not removed, it will lead to disruption of the motor system and damage the visual and other areas of the brain.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The causes of a congenital cyst are unfavorable factors that occur during the development of the fetus. These are:
- fetal hypoxia during delivery;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- taking a specific group of medications by a pregnant woman;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- intrauterine infections.
Factors that provoke the development of a congenital cavity with fluid are drug, alcohol or nicotine addiction of the mother. In this case, the child’s development takes place under conditions of intrauterine intoxication, which negatively affects the brain structures. The causes of the cavity can also be chronic decompensated diseases of the expectant mother.
An acquired cavity with fluid in the head develops as a result of:
- inflammatory diseases (encephalitis, brain abscess, arachnoiditis, meningitis);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- injuries of newborns received during childbirth;
- cerebrovascular accidents (subarachnoid hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke).
Depending on the etiology, the following types of liquid cavities are distinguished:
- A cyst of iatrogenic origin forms as a complication after brain surgery.
- Parasitic - develops with paragonimiasis, cerebral form of taeniasis and echinococcosis.
A cavity with fluid can also replace cerebral tissue during degenerative and dystrophic processes in the head.
If a cyst is present, there are a number of factors that can trigger its growth. These include obstruction of venous outflow from the skull, strokes and other vascular disorders, as well as head injuries, hydrocephalus, and neuroinfections.
Relationship with other abnormalities
Some sources sometimes contain information about the existence of some connection between the presence of a cyst and congenital pathologies that are caused by mutations in genes. In this case, the localization of the site of formation does not matter, because this cystic cavity is not capable of causing an abnormality in the development of the child. Everything is just the opposite: it is anomalies or infections that can lead to the development of pathology.
The genetic abnormalities in which the presence of a cyst is most often detected include trisomy 18, known as Edwards syndrome. Even trisomy 21, called Down's disease, does not have such a strong effect on the incidence of cystic cavities in the blood vessels of the brain.
If other fetal diseases are detected, the main role here is played not by the cyst, but by the abnormalities that accompany it. Women expecting babies should know this. And you should not be afraid of such a diagnosis.
Brain cyst
The growth of the formation at the initial stage is in most cases accompanied by symptoms of intracranial hypertension. Patients constantly complain of nausea, which has nothing to do with food, deterioration in general health and decreased performance, constant cephalalgia and pressure on the eyeballs.
In some cases, the main symptoms include a constant feeling of pulsation in the head, sleep disturbance, mild hearing loss, dizziness, motor dysfunction, fainting and tremors of the limbs. Possible visual impairment, namely double vision, visual hallucinations, deterioration of visual acuity. With high intracranial hypertension, the patient is worried about constant vomiting.
There are cases when the first signs indicating a cavity with fluid are the first occurrence of epileptic paroxysm. Subsequently, epileptic seizures recur. Paroxysms can take the form of focal Jacksonian epilepsy or absence seizures and be of a primary generalized nature.
Compared to general cerebral manifestations, focal symptoms are observed in fewer cases. These may be sensory disorders, monoparesis and hemiparesis, brainstem symptoms. The latter include dysarthria, eye movement disorders, and swallowing disorders.
One of the complications of formation is cyst rupture. In this case, hemorrhage due to rupture of the vessel, compression of the brain, the formation of an epileptogenic focus and occlusive hydrocephalus are possible.
In the congenital form of the cyst, episyndromes and intracranial hypertension are recorded at an early age. Education in the brain can cause the child to develop mental retardation and mental development disorders.
Clinical picture
Subependymal cystic formations affect both the left and right hemispheres of the gray matter. Most often, the ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid are affected.
Clinical manifestations depend on the location, size and rate of growth of the cyst. Different parts of the brain perform specific functions, so compression of them leads to specific symptoms.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Damage to the occipital zone leads to deterioration of visual acuity, up to complete blindness. When the temporal region is affected, hearing is impaired. A tumor of the cerebellum causes deterioration in motor coordination.
When the pituitary gland is damaged, developmental delays occur, and sometimes the child suffers from dwarfism. If the pathogenic process affects the frontal part, then speech formation is disrupted.
In addition to the signs described above, the baby may experience general symptoms such as worsening sleep, anxiety, weight loss, pathological muscle tone, and frequent crying for no reason.
A newborn child with a subependymal cyst often refuses to drink breast milk, spits up heavily, moves excessively, periodically loses consciousness, and suffers from attacks of epilepsy and tremors in the limbs.
Types of brain cysts and their symptoms
Arachnoid - occurs in almost 4% of the population. A cavity with fluid can be congenital or acquired. In the latter case, it develops in response to traumatic brain injury. The formation is localized on the surface of the brain in its membranes. The cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
In most cases, an arachnoid cyst does not make itself felt for quite a long time and is discovered by chance. Severe symptoms appear only if a large amount of fluid accumulates in the cavity. In this case, cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the cells lining the cavity.
With a sharp increase in the volume of the cavity with liquid, it can rupture and, as a result, die.
Colloid cysts are recorded in 15-20% of all cases of formations inside the ventricles of the brain. Most often it is localized above the foramen of Monroe in the anterior region of the 3rd ventricle. Less common in the area of the transparent cerebral septum in the 4th ventricle.
The liquid filling the cavity of the colloid cyst has high viscosity. Patients experience symptoms of hydrocephalus and, with a certain position of the head, a paroxysmal increase in cephalgia is noted.
In rare cases, memory loss, behavioral disorders and weakness in the limbs occur.
Pineal cyst of the pineal gland - according to statistics, 10% of patients have formations of this type that are small in size and do not make themselves felt. Cystic formations are localized in the epiphysis of the brain, in most cases they are no more than 1 cm in size. Otherwise, symptoms appear. When it grows, it can block the entrance to the “plumbing” of the brain and block the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, causing occlusive hydrocephalus.
Epidermoid or dermoid is a formation that is an anomaly of intrauterine development. In this case, the cells of the baby's future skin and its appendages remain inside the brain. Accordingly, in addition to liquid, elements of the ectoderm are present, namely sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
After the birth of a child, such a cyst quickly increases in size. The only possible treatment is surgical removal of the formation.
Choroid plexus cyst - forms regardless of the person’s age. In this case, the space between the plexus vessels is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Symptoms are rarely present, sometimes accompanied by epileptic seizures and symptoms of intracranial hypertension.
With a congenital choroid plexus cyst, the formation is diagnosed at the 20th week of intrauterine development using ultrasound. By the 28th week, such formations resolve.
What is education?
A choroid plexus cyst is a benign formation with clear contours, filled with fluid. It occurs among normal pregnancies with a frequency of approximately 3%.
Cystic formations of the choroid plexus tend to self-resolve, suggesting that they are pseudocysts. Bilateral choroid plexus cysts of the brain are very often observed, but by the 28th week of pregnancy they resolve, which is associated with the active development of the fetal nervous system. In cases where the cyst continues to be detected during an ultrasound scan until childbirth, then its significance does not particularly increase.
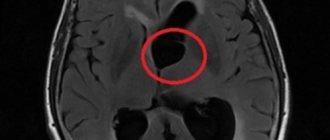
MRI images show cysts in both hemispheres
One of the early signs of the formation of the central nervous system in the embryo is the choroid plexus. They act as structural units in the formation of the right and left hemispheres of the brain. The choroid plexuses do not have nerve endings, but they ensure timely maturation and sufficient blood supply to the brain in the fetus.
A choroid plexus cyst of the brain has the following characteristics:
- minimal harm to health;
- lack of significance for concomitant pathologies;
- not affecting any of the vital systems and functions of the body;
- lack of growth and deformation.
Education does not cause significant harm or danger to either the fetus or the infant; it does not affect the functioning of the brain. However, they can increase the risk of developing other pathologies or cause functional impairment of all body systems.
Diagnostic measures
A neurologist may suspect the presence of an intracranial formation of significant size based on the patient’s neurological status and clinical symptoms. In this case, the patient is sent for examination to an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist to check vision and hearing. Specialists perform ophthalmoscopy, audiometry, perimetry and visometry. With severe hydrocephalus, ophthalmoscopy reveals congested optic discs.
By referring the patient for echo-encephalography, it is possible to diagnose increased intracranial pressure. If the patient experiences epileptic paroxysms, he is additionally sent for electroencephalography.
It is extremely important to differentiate a cavity with fluid from a tumor, abscess and hematoma. It is not possible to do this on the basis of collected clinical data alone. Therefore, to make a clear diagnosis, neurologists use neuroimaging diagnostic methods.
By performing an ultrasound examination, it is possible to diagnose certain types of congenital cysts even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. After birth, until the baby's large fontanelle closes, neurosonography is performed to make the correct diagnosis. In adulthood, to visualize a brain cyst, the patient is sent to a magnetic resonance or computed tomography scan of the head.
MRI and CT are performed with contrast in order to differentiate a cyst from a tumor. A cavity with liquid is not able to accumulate a contrast agent, unlike a tumor.
After diagnosis, constant monitoring of the patient with a cystic formation is important. During regular examinations, the doctor monitors the volume of the cyst over time.
If the cyst is a consequence of a stroke, additional vascular examinations are carried out: ultrasound, MRI and CT of vessels, duplex scanning.
Possible complications
Echo signs of a vascular neoplasm should make a specialist wary. Cysts themselves are not dangerous, but their presence may increase the risk of developing chromosomal pathologies in the future.
Increases in the frequency of cysts are largely influenced by Edwards syndrome
With normal laboratory test results, a vascular cyst does not indicate a pathological process in the body. To exclude genetic abnormalities, the doctor prescribes amniocentesis (sampling of a small amount of amniotic fluid).
In cases where genetic abnormalities are detected in the fetus, their consequences are the following developmental anomalies:
- Down syndrome.
- Edwards syndrome.
Pseudocysts have no absolute influence on the development of genetic defects, since they also occur in healthy children.
General principles of therapy
Drug therapy for cystic formations has practically no results. The only possible treatment is surgical removal of the fluid cavity. But, most forms are small in size and remain in a “dormant” state for many years. In this case, no methods of therapy are used; a wait-and-see regimen is chosen and the patient is regularly examined.
Formations that are accompanied by symptoms of hydrocephalus, complicated by bleeding and rupture, compressing the brain and rapidly increasing in size must be removed. Only a neurosurgeon decides which method of surgical treatment to use.
If the patient has a disorder of consciousness (coma or stupor), he is urgently referred to external ventricular drainage. This method allows you to reduce compression of the brain by the cyst and intracranial pressure. If the cyst ruptures or hemorrhages, surgery is performed. The patient undergoes craniotomy and the formation is excised.
In the absence of complications and disturbances of consciousness, the operation is performed planned and endoscopically. The advantage is the patient’s quick recovery period and low trauma. With endoscopic access, a milling hole is made in the skull, through which fluid is sucked out from the cavity. In order to avoid subsequent accumulation of fluid, several holes are made in the cavity (connected to the cerebrospinal fluid space) or cystoperiotoneal shunting is performed (a special shunt is installed).
The postoperative period involves rehabilitation therapy, including exercise therapy, reflexology and massage. The patient is prescribed drugs to improve blood supply to the brain, absorbents and decongestants.
Consequences of choroid plexus cysts
Complicated cystic formations cause specific manifestations:
- Hypertonicity of newborns;
- Neurological symptoms due to compression of brain structures;
- Epilepsy (muscle cramps);
- Slight loss of vision and hearing.
Magnetic resonance imaging will need to distinguish a true vascular cyst from a pseudocyst. The latter type is a variant of the physiological development of the brain, but the anatomical structure when examined by ultrasound resembles a cavity. Magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate study (informativeness is about 96%). The three-dimensional modeling mode will allow you to correctly verify the nosology.
Edwards syndrome can be detected by ultrasound by identifying abnormalities of the limbs and changes in internal organs. Additional diagnostic tests:
- Determination of the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin;
- Blood chemistry;
- Analysis of amniotic fluid.
A special risk group is women aged 32 years and older with hormonal disorders.
Forecasts
In most cases, a frozen cavity with liquid of insignificant size does not bother the patient and does not cause any symptoms. In other cases, with adequate and timely treatment, the outcome is favorable.
In rare cases, patients after surgical removal of a cyst experience a residual moderate-to-severe liquor-hypertensive symptom. If a focal neurological deficit develops, it persists after treatment.
With the removal of the cyst, epileptic paroxysms disappear, but often appear later. This is justified by changes in the operated area of the head, in particular the formed adhesions. Secondary epilepsy is practically uncontrollable by anticonvulsant therapy.
Prevention
An acquired cyst most often becomes a consequence of developing inflammatory, vascular, infectious and post-traumatic processes. Therefore, it is absolutely obvious that only correct and timely treatment of any pathologies, including resorption and neuroprotective therapy, can serve as a preventive measure for the development of formations in the brain.
The only measure to prevent congenital cysts is to protect the woman and fetus from exposure to provoking factors. Equally important are correct management of pregnancy and delivery.
Treatment
The basis of therapy is the elimination of the factor that provoked the development of a subependymal cyst in a newborn. Most often it is necessary to treat hypoxia. The treatment process occurs in several stages.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Immediately after birth, in the presence of hypoxia, resuscitation procedures are immediately performed to prevent the development of formation. To do this, the trachea, oropharynx and nasopharynx are cleared of fluid, and artificial respiration is used.
After this, the baby’s condition is monitored by a neurologist for three days, who selects treatment tactics. Special medications are prescribed, courses of therapeutic massage and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to improve the condition and eliminate the lack of oxygen.
If the cyst was diagnosed in childhood, then drugs are used to normalize metabolic processes in the gray matter, and vitamin complexes. In case of rapid increase and large size, surgery is performed.
Using an endoscope, the cavity is cleared of liquid contents. Sometimes open manipulation of the brain is required.