Patients often turn to cardiologists with complaints of chest pain. Such unpleasant sensations are easily distinguished by various manifestations; they cannot be relieved with the help of drug therapy. Instrumental research methods do not allow us to identify pathologies associated with the functioning of the heart. When additional studies are ordered, osteochondrosis is diagnosed. The founder of the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients,” the chief physician of the “Doctor Shishonin Clinic,” Alexander Yuryevich Shishonin, talks about the effect of cervical osteochondrosis on the heart.
Reasons for appearance
In cases of disorders associated with atrophy and destruction of the tissues of the spinal column, there is a flattening and protrusion of the cartilaginous discs that hold the vertebral bodies together and ensure their normal mobility and shock absorption.
Violation of these structures leads to infringement of the nerve fibers responsible for sensitivity and autonomic functions. In this case, irritation is transmitted to nearby organs, and the myocardium is no exception. Pain in the heart and various rhythm disturbances occur, including extrasystole. At the initial stage of the pathology, deviations can be short-term and occur against the background of a sharp turn or tilt, and in advanced forms of osteochondrosis - frequent or constant. In the latter case, the heart will experience continuous overload and hypoxia against its background.
Excitation of different parts of the conduction system occurs in two ways - direct impact on the fibers of the sympathetic nerves and reflex.
Extrasystole: symptoms and treatment
Image from lori.ru
Extrasystoles are untimely contractions of the heart or its individual chambers; ventricular extrasystole is one of the most frequently recorded types of arrhythmias. This disease can be found in 60-70% of people on earth. It is neurogenic in nature, and this disease can be triggered by severe stress, smoking, drinking alcohol, strong coffee and tea. Also, symptoms of extrasystole can be organic. In this case, extrasystoles are caused by myocardial damage - inflammation, dystrophy, coronary heart disease or cardiosclerosis.
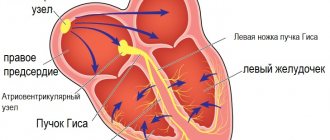
A new untimely impulse can originate from the ventricles of the heart, its atria, as well as from the atrioventricular junction. The occurrence of a disease such as ventricular extrasystole is explained by the presence of a focus of so-called trigger activity. The coupling interval characterizes the relationship in time between the normal and extraordinary impulses.
Etiology of the disease
The causes of extrasystole (including ventricular extrasystole) are: coronary heart disease, acute or chronic heart failure, obstructive chronic pulmonary diseases, as well as acute pulmonary failure. In addition, symptoms of extrasystole can occur due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic and cervical spine, diseases of the abdominal organs. Too frequent intake of cardiac glycosides, aminophylline and B-adrenomimetics can cause extrasystoles, as a result of which it is necessary to begin urgent treatment of extrasystoles. As mentioned above, severe physical and psychological stress, smoking and caffeine can trigger the symptoms of extrasystole.
Symptoms and treatment of extrasystole
When extrasystoles occur, there may be complaints of too strong heart beats and tremors, as well as a feeling that the heart has frozen or stopped. Symptoms of functional extrasystole include pallor, sweating, anxiety, fear, and lack of air. If frequent extrasystoles are observed, this can lead to a decrease in blood flow in the liver and brain by 8-25%, as well as a decrease in cardiac output. Attacks of angina and cerebral circulation disorders can occur with atherosclerosis of the coronary and cerebral vessels.
Treatment of extrasystole includes the elimination of factors that provoke the disease, as well as direct medical intervention. Timely treatment of extrasystole of a neurogenic nature includes recommendations from a nutritionist, adherence to rest and work schedules, exercise, psychotherapy, taking sedatives or tranquilizers (tincture of valerian, diazepam).
Taking specific drugs for the treatment of extrasystoles may be due to the following indications: a feeling of cardiac arrest, extrasystolic allorhythmia, sleep disturbances, early and frequent ventricular extrasystoles. Patients with post-infarction cardiosclerosis must also take special medications to treat extrasystole.
Extrasystole of the ventricles of the heart can be of different gradations. Grade 1-2 disease does not require treatment. The disease of the third gradation can be left without medical intervention if there is no organic damage to the myocardium. With grades 4 and 5 of extrasystole, installation of a special defibrillator is required due to the increased risk of tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation.
Diagnostics
When a patient with extrasystolic arrhythmia appears at my appointment, I usually conduct an examination, identify the history of the development of the symptom, the nature of the sensations, and accompanying signs:
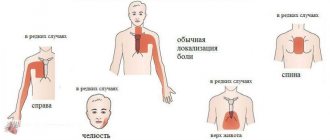
- Single extrasystoles may not manifest themselves clinically. Or described by the patient as sudden jolts, cardiac arrest, or “moving” behind the sternum on the left. Appear when there is a load on the spine after a sharp turn or lifting heavy objects. When the problem is in the myocardium, deterioration is observed after stress, physical activity, and fast walking. There is no dependence on body position.
- On palpation in the affected area of the spine, pain is noted in the paravertebral (located next to the spine) points and muscle spasm. During auscultation, heart sounds do not change, there are no noises, only extrasystole is heard.
- Identifying a history of heart disease indicates the presence of signs of myocardial ischemia (angina attacks), circulatory failure (peripheral edema, shortness of breath, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle).
- A patient with osteochondrosis talks about long-standing problems associated with pain in the area of spinal lesions, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs provide help in this case.
The phenomenon of extrasystole in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is often accompanied by pain in the heart and rhythm disturbances, which are reflected in nature. And when the cervical segment is affected, dizziness and other symptoms of circulatory failure in the brain often occur.
Additional examinations
To exclude cardiac pathology, I immediately refer the patient for an ECG. It cannot always detect angina or extrasystole. For this purpose, Holter monitoring is used, which allows you to record the electrical activity of the human heart throughout the day. During this time, he leads a normal life or performs tests to identify hidden forms of deviations (medicinal or stress).
In the attached figure you can see what extrasystole looks like on an ECG from different parts of the conduction system.
In addition, the following help to finally determine the cause:
- EchoCG and MRI of the heart - these studies allow you to find all organic changes and dysfunction of the myocardium.
- X-ray of spinal segments helps to identify the presence of osteochondrosis; for a more accurate picture, magnetic resonance imaging is sometimes done.
The cause of local excitation of the myocardium can also be VSD, intoxication, fever, overdose of cardiac glycosides, excessive consumption of coffee and other tonic drinks.
If you want to have a healthy heart, treat your spine
- home
- Articles
- My spine is my health
- If you want to have a healthy heart, treat your spine
20.11.2017
It has been proven that problems with the spine provoke the development of heart and vascular diseases. Cardiologists know this, but everyone needs to know about it in order to preserve the heart and blood vessels from a young age.
Back pain is a fairly common occurrence in the lives of each of us. But the statistics of visits to the doctor regarding osteochondrosis are small - only up to 20 percent of potential patients. As a rule, they come when it becomes completely unbearable, although 85 percent of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis translated from Greek osteon means “bone”, hondros – “cartilage”, and the ending “oz” indicates the dystrophic nature of the changes in these structures. The result is a disease of the bone and cartilage. The scientific definition of spinal osteochondrosis is as follows: spinal osteochondrosis is degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc and adjacent vertebral bodies. In other words, osteochondrosis is changes caused by disruption of metabolic processes in the disc, that is, nutrition and dehydration. Osteochondrosis is not a disease, but a sign of aging - the same as wrinkles, baldness and gray hair. With osteochondrosis, intervertebral discs - special cartilaginous structures that provide our spine with flexibility and mobility - become defective. This is where it all begins.
There are many theories for the development of osteochondrosis, in each of which the main factor is one or another reason, such as hereditary predisposition, mechanical trauma, metabolic disorders, etc. It is especially difficult to determine the cause of osteochondrosis due to the fact that this disease occurs in both elderly and young people, and at the same time in well-built people, and vice versa.
What are the prerequisites for the development of osteochondrosis?
- Disruption of normal relationships in the musculoskeletal system (congenital and acquired postural disorders, spinal curvatures such as scoliosis and kyphosis, flat feet, pelvic obliquity, different lengths of limbs, craniovertebral anomalies, etc.).
- Violation of water-electrolyte balance and mineral metabolism in the body, which negatively affects the elasticity of cartilage tissue and the strength of bone tissue, reduces their resistance to static and dynamic loads.
- The development of osteochondrosis in obesity, when excess weight puts additional pressure on the spine. Against the background of excess weight, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine most often occurs, and then pathology occurs in those internal organs that are innervated from this section.
- A very important reason why osteochondrosis occurs is a general disorder of metabolic processes in the body.
This process provokes the development of heart and vascular diseases and has a very simple physical nature. In diseases of the spine accompanied by degenerative changes, the vertebral (vertebral) artery running along the spinal column is pinched. The vessel is compressed by bone osteophytes (growths of bone tissue) or spasmodic muscles, which provokes an increase in intravascular pressure.
Due to pinching of the vertebral artery and compression of the nerve roots going to the heart, it begins to hurt. This is not yet a heart disease, the pain is of a so-called radicular nature, but the innervation is disrupted, which contributes to the development of heart disease itself.
Against the background of a pathological condition of the spine, tachycardia (palpitations) develops. “Pumping” blood through a compressed vessel requires more effort from the body. For this reason, the heart rate increases. Palpitations are an external manifestation of increased load on the heart with osteochondrosis.
With osteochondrosis, tachycardia has some features:
- it is observed constantly, including in a state of complete rest;
- becomes more pronounced when changing a position to a more uncomfortable one or increasing the load on the spine;
- the correct heart rhythm is maintained: there are no interruptions in the work of the heart, beats follow at equal intervals between them;
- tachycardia is reduced as a result of measures aimed at treating the underlying disease - osteochondrosis.
In cases where the heart muscle cannot cope with a significant load, arrhythmia (heart rhythm disturbances) and extrasystole (so-called interruptions in heart function) develop. In case of prolonged manifestation of the symptom, the risk of developing chronic hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the myocardium increases.
With osteochondrosis, extrasystole initially appears only after physical exertion. In this case, the heart muscle does not have enough oxygen to push blood, and there is a need for additional contractions. With heavy physical activity, sudden movements, bending, turning, the nerve root is pinched. When a nerve in the thoracic spine is compressed, the functioning of the heart can be impaired.
Manifestations of cardiac dysfunction in osteochondrosis are:
- heartbeat;
- increased tension in the interscapular area;
- feeling of lack of air;
- frequent development of pre-fainting states;
- fever, increased sweating;
- feeling of internal discomfort;
- increased pulse with periodically occurring strong waves.
Osteochondrosis is often accompanied by increased blood pressure. The reason for this phenomenon is still the same - compression of the vertebral (vertebral) artery running along the spinal column. It is often compressed as a result of muscle spasm, swelling of soft tissues or displacement of the intervertebral disc. And since the vertebral vessel is responsible for blood circulation in the brain, the narrowing of its lumen leads to insufficient nutrition of the brain (30% of the brain is supplied precisely by the vertebral artery). The natural reaction to this event is an increase in blood pressure. Due to high blood pressure, the body tries to increase blood flow to the brain. At the same time, the heart rate increases, which also leads to increased blood pressure.
These factors explain pressure surges during cervical osteochondrosis and its exacerbation. In such extreme conditions, the body takes measures to eliminate disturbances and normal nutrition of brain cells. Thus, with a significant narrowing of the lumen of the artery, in order for a sufficient volume of blood to pass through, it is necessary to increase the speed of blood flow. For this reason, the body begins to release substances that increase blood pressure. This is the only way to restore normal nutrition to brain tissue. In the chronic form of the disease, high blood pressure is always observed.
As a result of scientific research, it has also been proven that if a person has previously had high blood pressure, then osteochondrosis in the cervical and thoracic region aggravates the course of hypertension, since it increases the resistance (immunity) of the body to the ongoing antihypertensive therapy. With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, pain in the heart often occurs, which patients sometimes mistake for angina. This is explained by the fact that the heart and spine are connected through nerve cells through the spinal cord. Find connections between the seventh cervical and fifth thoracic vertebrae.
Thus, cervicothoracic osteochondrosis contributes to the appearance of heart rhythm disturbances, increased blood pressure and, indirectly, the development of myocardial ischemia.
How can you avoid the development of osteochondrosis and related diseases of the vascular system? And if they are present, how to reduce symptoms and prevent complications?
Unfortunately, neither powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, nor physical therapy, nor other external influences cure osteochondrosis, they only relieve or reduce its exacerbation, and after a while the disease will make itself felt again.
What's the solution? It exists and has been known for a long time .
Osteochondrosis is a disease that is “afraid” of preventive procedures. If you reconsider your lifestyle and change it as much as possible, then with a high degree of probability you will be able to prevent the development of the disease or stop its progression. There are simple rules for this:
- Drink at least two liters of water a day (the spine is afraid of dehydration!).
- Provide your body with maximum mobility.
- Play sports. The most ideal option is swimming.
- Review your diet, bringing it closer to “alkaline” (you can read about alkalizing foods on many pages on social networks).
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Every morning, perform exercises from the physical therapy complex (or others - as you wish, but with mandatory stretching elements!)
- Don't overexert your muscles.
- Get a simple relaxing massage to relieve stress after a hard day at work.
- Walk and move more.
But we need to talk specifically about the features of the diet in the twenty-first century. One of the main commandments of Hippocrates: “Eliminate the cause - the disease will go away!” forgotten by modern medicine.
We forget that not only movement is important for the health of our spine. It, like other parts of our body, needs water, oxygen and proper nutrition. It’s no secret that athletes who move and train a lot often develop severe, disabling forms of osteochondrosis. Hippocrates said: “Food must be your medicine, otherwise medicine will be your food.”
Complete natural food has always been and will be the basis for the formation of health, treatment of diseases and their prevention, and there is nothing else left to do but to look for a way to transform modern half-empty food into complete food.
The only question is how to do this in modern conditions, when the condition of the soil, the technology of growing vegetables and grains, the technology of industrial food preparation, and the technology of keeping animals do not contribute to obtaining nutritious food. Not only does it lack protein and vitamins, it does not contain the set of minerals necessary for normal metabolism in the body, without which neither vitamins nor proteins, other things being equal, will be absorbed.
Even scientists who for many years “held a perimeter defense” against the use of biologically active additives (dietary supplements) now agree that in the current conditions it is impossible to ensure a healthy diet without them.
What nutrition does our spine need to keep it healthy?
First of all, a large complex of minerals that are needed for the construction and normal functioning of bones, ligaments, cartilage, synovium and synovial fluid and intervertebral discs. This, of course, is calcium, phosphorus, silicon, magnesium, zinc, selenium and many other equally important ones. How to provide the body with exactly those substances (minerals) that are lacking today, right now? How not to “overdo it” with the dosage and course of administration? How to ensure the absorption of these important elements in the body?
This requires a natural, harmless, easily digestible and multi-component source. And we have been using it in our wellness practice for more than twenty years. This is lithovit, created on the basis of the natural mineral zeolite, which contains about eighty minerals in an easily digestible form. “Litovit-M” (pure zeolite) never causes allergic reactions (and, moreover, is successfully used for all types of allergies, including psoriasis and bronchial asthma), is harmless when used correctly and can be used from the first years of life.
The regimen for taking Litovit-M is very simple: adults take it 2.5-3 grams twice a day with a glass of clean water, or even better, Sabelnik drink concentrate, which contains components that improve the nutrition of the tissues of the spinal joints and relieve them inflammation. The course of treatment is a month, after which it is recommended to “feed” our elastic structures of the spine with a source of organic silicon in the form of the Optisorb dietary supplement, two sachets (2.5 g) twice a day. The course of admission is one month.
If the treatment is preventive, it can be done twice a year, preferably in autumn and spring. If osteochondrosis is already manifesting, then these products should be taken regularly for at least three weeks a month. It is worth recalling that since both dietary supplements are sorbents, they should be taken an hour to an hour and a half before taking medications.
Equally important is a balanced diet of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and phospholipids (lecithin). And such an opportunity also exists; NPF “Nov” has developed and produced, in accordance with GOST requirements, the protein mixture “NovoProtein”. By drinking one glass of cocktail (1-2 tablespoons per 150-200 ml of warm water) per day, you can be sure that the minimum necessary nutrition for cell growth and division will be provided.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, so for a lasting effect you need to be patient and persistently repeat courses of taking Litovit-M, Optisorb, the drink Sabelnik, NovoProtein, and follow all the above recommendations. But if you consider how many problems of the heart and blood vessels (and many other organs too) can be avoided, “the game is worth the candle”!
And when starting to take care of the health of your spine, you should always remember the wise saying - the one who walks can master the road!
Drug treatment
Treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs for extrasystole is carried out only if the cause is heart pathology (read about the drugs used here). In cases of osteochondrosis, proper rehabilitation can improve the condition and eliminate rhythm disturbances.
To stop an exacerbation, the following drugs are taken:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac). They relieve pain and swelling in the affected area.
- Muscle relaxants (“Sirdalud”, “Mydocalm”). Relieves muscle spasm.
- In case of severe infringement, corticosteroids are used or a novocaine blockade is performed.
To prolong remission, massage and physical therapy are used. In very advanced cases, surgery is recommended to eliminate pinched nerves and restore blood flow and nerve conduction.
A situation may arise when there is simultaneously a violation of the structure of the spine and pathology of the heart. In this case, treatment is carried out jointly by a cardiologist and a vertebrologist. But the priority is the treatment of problems with the myocardium, as they can lead to serious consequences and even death.
Diagnostic complex of measures
As the disease develops, osteochondrosis also manifests itself in extrasystole. For rare pathological processes, treatment is minimal; if the number of systoles per day is more than 700, a mandatory set of therapy is prescribed. When a patient approaches, the doctor’s duty is to listen to the heart, measure the pressure parameter, and assess the general condition of the fiber and skin. This is required to create a complete picture of the disease. In addition to the above list of activities, you need:
- Determine the type of pathology;
- study individual characteristics;
- find out the frequency of contractions;
- conduct instrumental and laboratory tests;
- do a long-term ECG study;
- take samples for arrhythmia;
- undergo MRI and ultrasound.
After determining the type and complexity of osteochondrosis and accompanying extrasystole, the treating specialist prescribes comprehensive treatment.
Case from practice
A patient came to see me at the clinic with complaints of sensations of paroxysmal interruptions in the heart that occur periodically during hard work. Palpation revealed pain in the thoracic spine. Single extrasystoles from the atrioventricular junction were recorded on the ECG. No ischemia or other signs of cardiac pathology were detected. After a week of taking Naklofen and Sirdalud, as well as topical use of Diclofenac ointment, the condition improved and the patient stopped feeling interruptions.
Types of pathological process in osteochondrosis
Noticeable heartbeats can be detected during diagnostic measures through a cardiogram. But only after conducting a full diagnostic complex can the treating specialist present the overall picture and make recommendations. In medical practice, there are several types of such heart contractions.
- Rare extrasystoles - appear several times up to several dozen repetitions;
- Average manifestations - their number per day reaches 100-200 times.
- Frequent pathological reactions - extraordinary tremors are repeated up to 1,000 times.
Strong blows in some groups of diseases may not be single, but paired.
What happens if you start this disease?
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/YDqgQ3L_YfQ
Many believe that arrhythmia in osteochondrosis is not dangerous. Often patients do not pay attention to the treatment of the underlying pathology. All efforts are aimed at eliminating the symptoms, but the underlying disease is not treated. As a result, the condition worsens, and heart problems are accompanied by other diseases.
Heart problems cause the following complications:
- The appearance of blood clots, aggravating the condition.
- Problems with blood circulation in the head increases the likelihood of developing strokes.
- The heart suddenly stops, signs of clinical death appear.
Arrhythmia and pain in the heart are considered grounds for contacting a cardiologist for an ECG. Monitoring using the Holter technique allows you to get the best results. Such diagnostics allows you to accurately determine the nature of cardiac dysfunction and the necessary therapeutic techniques.
If pain in the heart appears due to osteochondrosis, it is important to recognize the symptoms in time and begin treatment immediately. A sedentary, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, easy access to transport, and lack of time for sports have led to the fact that osteochondrosis has become a scourge not only for older people, but also for the younger generation.
Probably, this osteochondrosis gives off pain in the heart. How to distinguish pain in the heart from osteochondrosis, and true heart disease, what can cause a symptom and how to get rid of it?
Osteochondrosis is a disease of the spine when there is displacement and deformation of the intervertebral discs, thinning of cartilage tissue, pinched or irritated nerves, muscle strain, poor circulation and, as a result, pain in a particularly vulnerable place. This is a common situation when patients come to doctors complaining of heart pain, but cardiac diagnostic methods indicate normal cardiac parameters.
Many people believe that the arrhythmia that occurs with osteochondrosis is not dangerous. But not everything is so simple: often the patient ignores treatment of the underlying disease, directing all his efforts to suppressing various kinds of symptoms. As a result, the disease worsens, and a whole bunch of new problems are added to the disruption of the heart.
When a cardiac nerve is pinched, arrhythmia develops
If ventricular extrasystole or tachycardia is not eliminated in time, they can cause the following complications:
- The formation of blood clots, the rupture of which can have the most serious consequences for the patient’s life.
- Insufficient blood circulation to the brain, which increases the risk of strokes.
- The risk of sudden cardiac arrest with symptoms of clinical death increases.
Untreated osteochondrosis can be dangerous due to the following conditions:
- Cochleo-vestibular disorders, visual disorders.
- Bulging of the intervertebral disc.
- Protrusions and intervertebral hernias.
- Lumbago or sciatica.
- Prolapse of discs between the vertebrae.
- Spinosis of the spinal canal.
How to help patients
Often, heart medications are not used unless the extrasystole is too severe. In this situation, the cause of the relationship between arrhythmia and osteochondrosis is not determined. Prevention of bone tissue diseases is carried out. Such measures are often enough, if you manage to get rid of the underlying pathology, the arrhythmia goes away.
Complex bone tissue therapy involves the use of the following techniques:
- A diet in which you need to maintain the ratio of magnesium and calcium in food.
- Exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage, osteopathy to improve muscle function.
- Ointments with bee or snake venom, turpentine, tea tree oil. The use of warming ointments that relieve pain and eliminate harmful symptoms.
- Medicines to eliminate edema.
- Products that correct microcirculation in capillaries and relieve muscle spasms.
Treatment with medication is acceptable if heartbeat problems are moderate or severe. In this situation, simultaneously with the indicated therapeutic methods, the specialist prescribes the use of Pentoxifylline to improve the circulatory system of the head and block calcium channels affecting the heart.
If ventricular extrasystole or tachycardia is mild, heart medications are usually not prescribed. In this case, it is determined why the connection between arrhythmia and osteochondrosis arose, and preventive measures are prescribed to combat bone pathology. This is often enough: as soon as osteochondrosis is eliminated, the arrhythmia will go away on its own.
Thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis can cause cardiac pathology
Complex treatment of the skeletal system may include the following procedures:
- A balanced diet that involves consuming foods high in magnesium and calcium.
- Therapeutic exercise, physiotherapy, manual therapy, osteopathy, used to eliminate reflex muscle complications.
- Ointments containing bee or snake venom, turpentine, tea tree oil. The use of warming external agents with an analgesic effect for cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis is exclusively anti-symptomatic (temporarily improves the condition, but does not eliminate the cause).
- Medicines to relieve tissue swelling (diuretic, sedative, anti-inflammatory).
- Drugs for correcting blood microcirculation and eliminating muscle spasms (for example, muscle relaxants).
In this case, in parallel with the measures described above for the treatment of the musculoskeletal system, the doctor may prescribe Pentoxifylline to restore normal blood supply to the brain, calcium channel blockers that affect the heart, and class 3 antirhythmics (Amiadoron, Amiacordin, Cardarone, Sotalex and others medications containing sotalol or amiadorone).
In extremely severe cases, temporary or permanent cardiac pacing (installation of an artificial pacemaker) may be indicated. Eliminating only one arrhythmia without measures to treat osteochondrosis is useless - the cause of the heart rhythm disturbance will remain, and no medications will be able to help the patient. Only complex therapy is effective in the case of complicated arrhythmia caused by pathologies of the osseous-ligamentous apparatus.
Features of the therapeutic process
Therapy to eliminate extrasystole, like osteochondrosis, is aimed at strengthening the body as a whole and providing a comprehensive approach.
- Most often, potassium salts are used in treatment in case of ventricular pathology. If there are reflex and functional forms of the disease, this method is inappropriate due to lack of effectiveness. In such situations, potassium chloride has the greatest effect.
- If the disease has a pronounced manifestation, the specialist prescribes from 6 to 14 g of the drug at a time on the first day of treatment. Next, the dosage is reduced to 2 g per day, applied 3-4 times. If there is a malabsorption in the gastrointestinal tract, the drug is injected into a vein together with a polarizing mixture.
- The drug PANANGIN is another drug often prescribed by doctors. It is used 2 tablets orally or by injecting 10 ml into a vein. After receiving the first results, consisting of less frequent contractions or their disappearance, you can reduce the dosage. Due to potassium, myocardial excitability decreases, so the general condition of the heart muscle should be monitored using an ECG.
- Another effective drug is NOVOCAINAMIDE, which helps fight ventricular problems. In particularly severe situations, this composition is injected into a vein or muscle, followed by constant monitoring of blood pressure. If the latter indicator decreases, MEZATONE should be administered.
This is not the entire range of drugs used in the presence and progression of this disease. However, before using any of them, you should consult a specialist. Measures to prevent exacerbation of the disease play an important role. It is worth monitoring your eating style, giving up bad habits and taking moderate physical activity daily. Following the recommendations of specialists will allow you to achieve good results in eliminating the disease and improve your overall well-being.